manuscrit
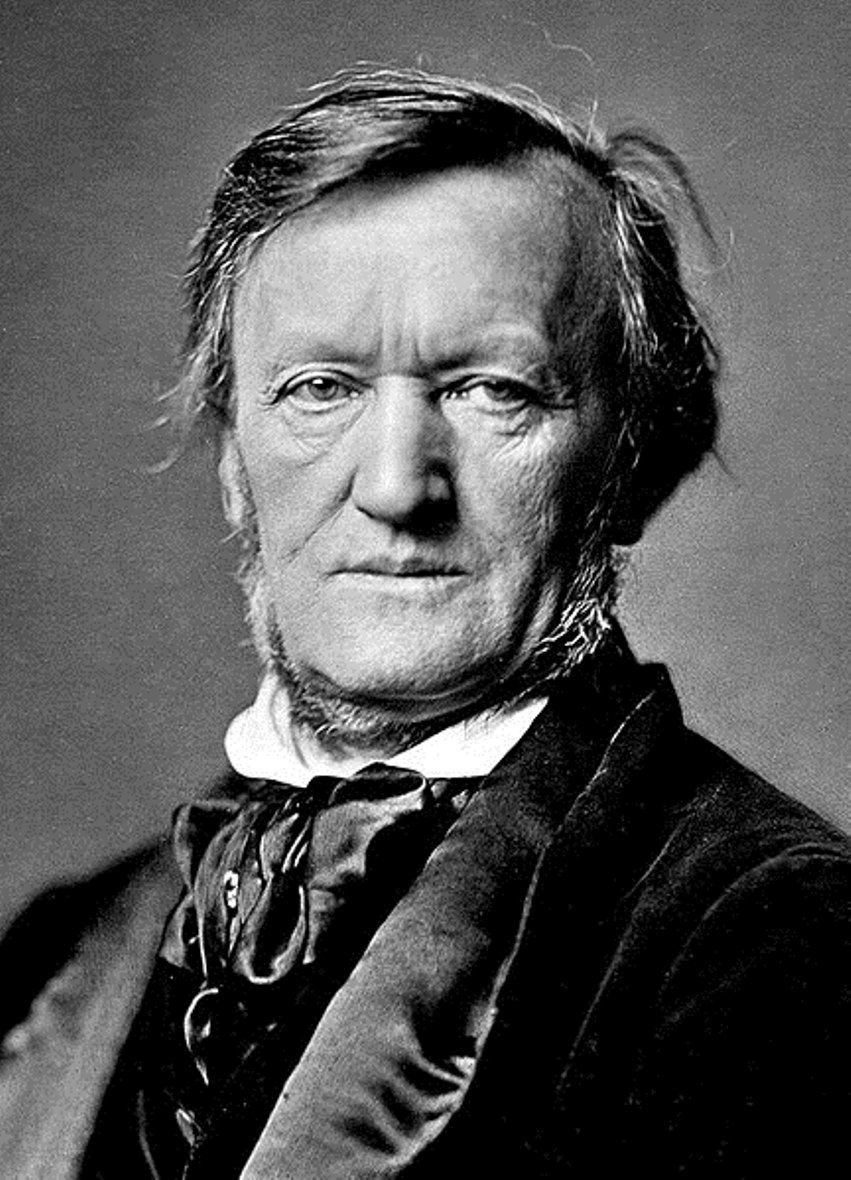
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).
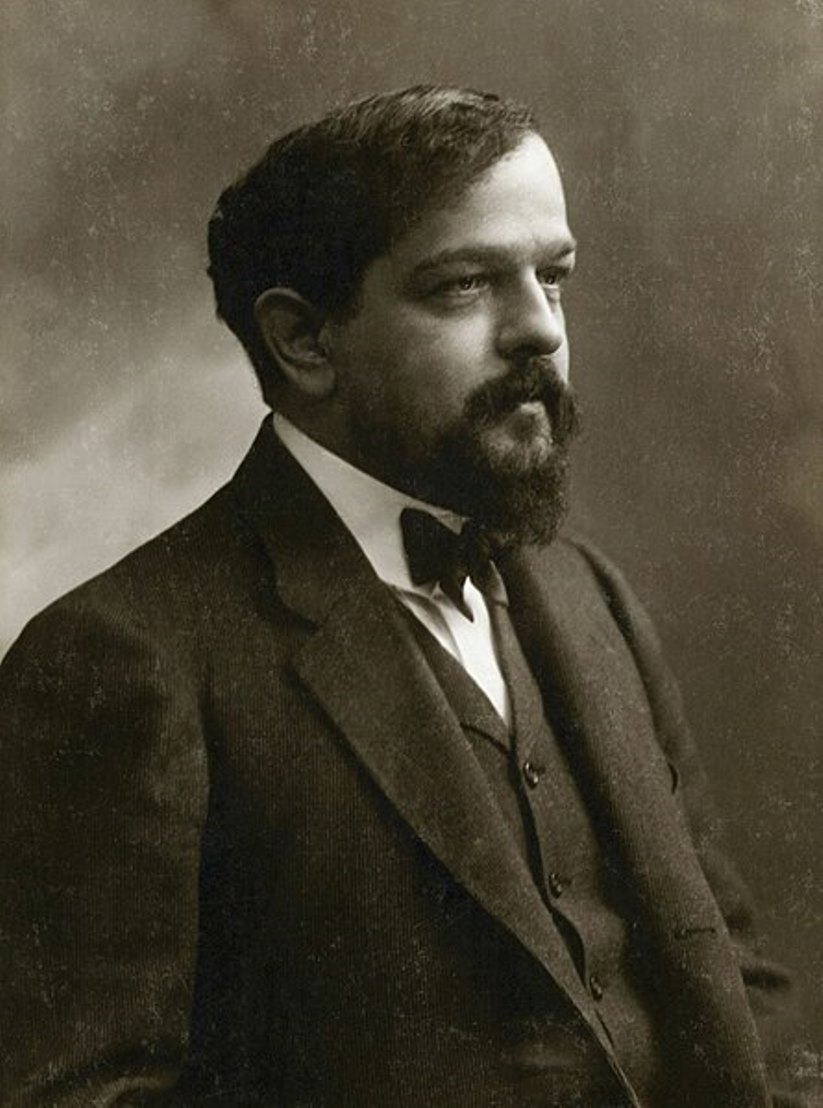


Claude Debussy, full name Achille-Claude Debussy, was a French composer, conductor, pianist and critic, a leading representative of Impressionism in music.
Debussy showed musical talent early and entered the Paris Conservatory. He lived in poverty, but at the same time he learned a luxurious life: the Russian philanthropist and the richest woman, Nadezhda Filaretovna von Meck, took him under her tutelage, he mused with her children and traveled with her around Europe. His sensitive nature could not but respond to all these contrasts. During this period Debussy created one of his masterpieces, Moonlight from the Bergamo Suite.
Debussy spent the summers of 1881 and 1882 near Moscow, at the von Meck estate. In this house Debussy became acquainted with the new Russian music of Tchaikovsky, Borodin, Balakirev and Modest Mussorgsky. His stay in Russia had a beneficial effect on the young musician's development. Debussy was also influenced by the work of Richard Wagner. He developed a highly original system of harmony and musical structure that in many ways expressed the ideals to which the Impressionist and Symbolist artists and writers of his time aspired.
Debussy toured with concerts and conducted his works in England, Italy, Russia and other countries. Claude Debussy's famous works include the Prelude to the Afternoon of a Faun (1894), the operas Pelléas et Mélisande and The Sea (1905), the suite Children's Corner (1906-1908) and the orchestral cycle Images (1912). In 1913 he composed music for the ballet Games, which was performed by Sergei Diaghilev's Russian Seasons company in Paris and London.
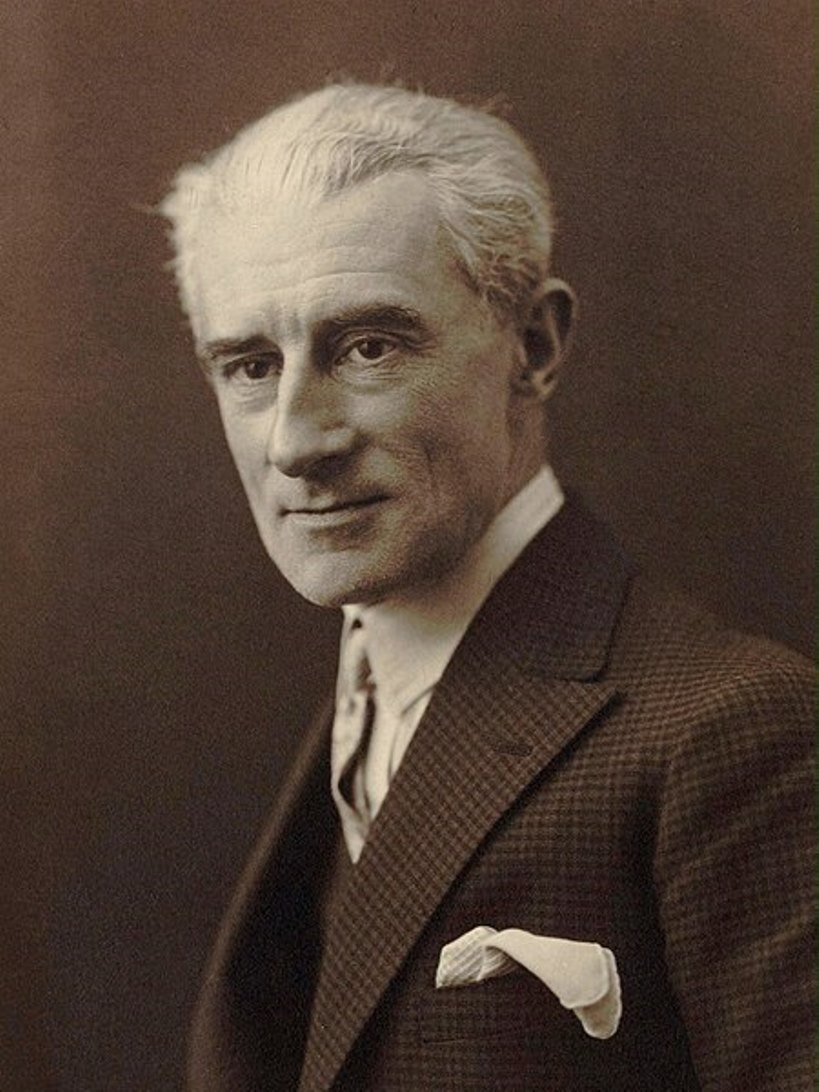


Maurice Ravel, full name Joseph Maurice Ravel, was a French composer, pianist and conductor, a representative of Impressionism in music.
At the age of 14 Maurice entered the Paris Conservatory and during his studies he composed several works. Already in these early sonatas and compositions he skillfully adapted traditional structures in music to his own personal ones, thus creating his own musical style.
Of Ravel's piano works, the virtuosic "Miroir" and "Gaspard de la Nuit" are popular, while of his orchestral works the most famous are the "Spanish Rhapsody" and Bolero. After 1905, Ravel's name is placed almost on a par with the recognized Impressionist composer Claude Debussy. Ravel met the famous Russian entrepreneur and organizer of the Russian Seasons, Sergei Diaghilev, which was a highlight in his career. He was specially commissioned by him to compose music for Mikhail Fokine's ballet Daphnis and Chloe (1912), starring the great Russian dancer Vatslav Nijinsky.
Ravel toured extensively as a pianist and conductor, performing his own works in Italy, Holland and England. In 1928, he made a successful four-month tour of Canada and the United States, where he impressed with jazz and blues compositions.
Maurice Ravel has gone down in history as one of the leading exponents of musical impressionism.

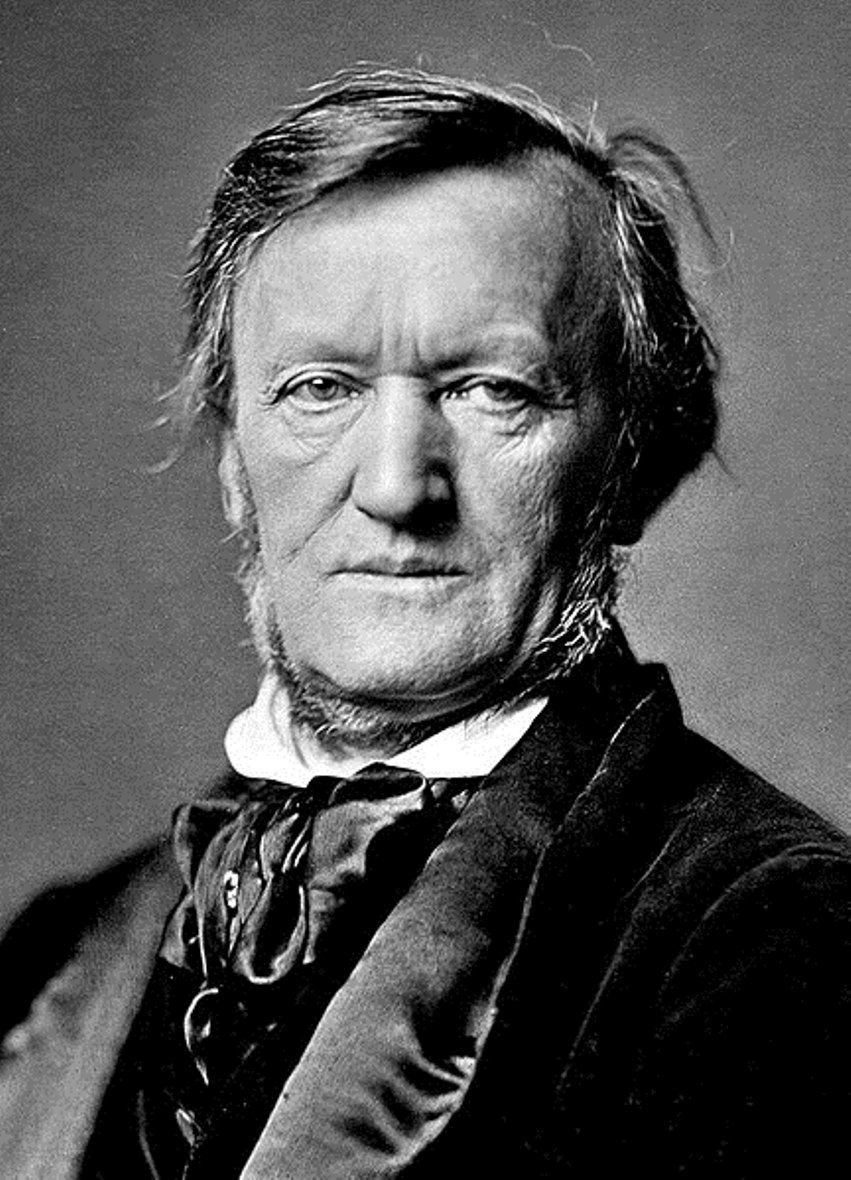
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).
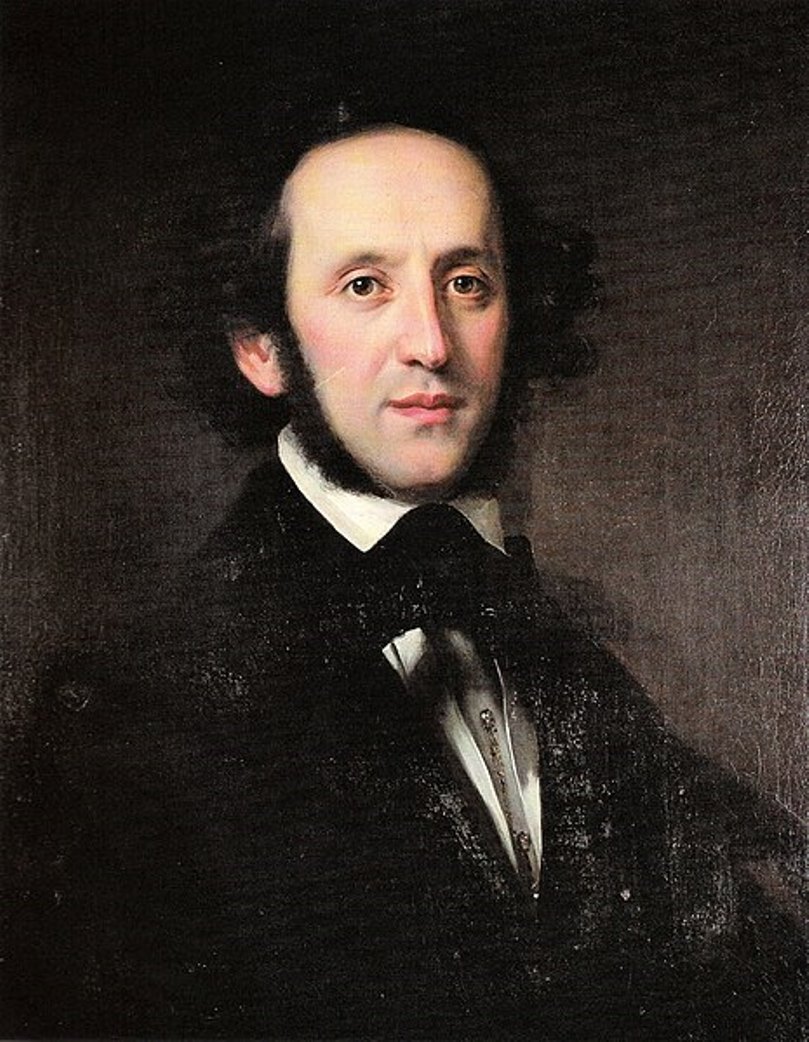


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".
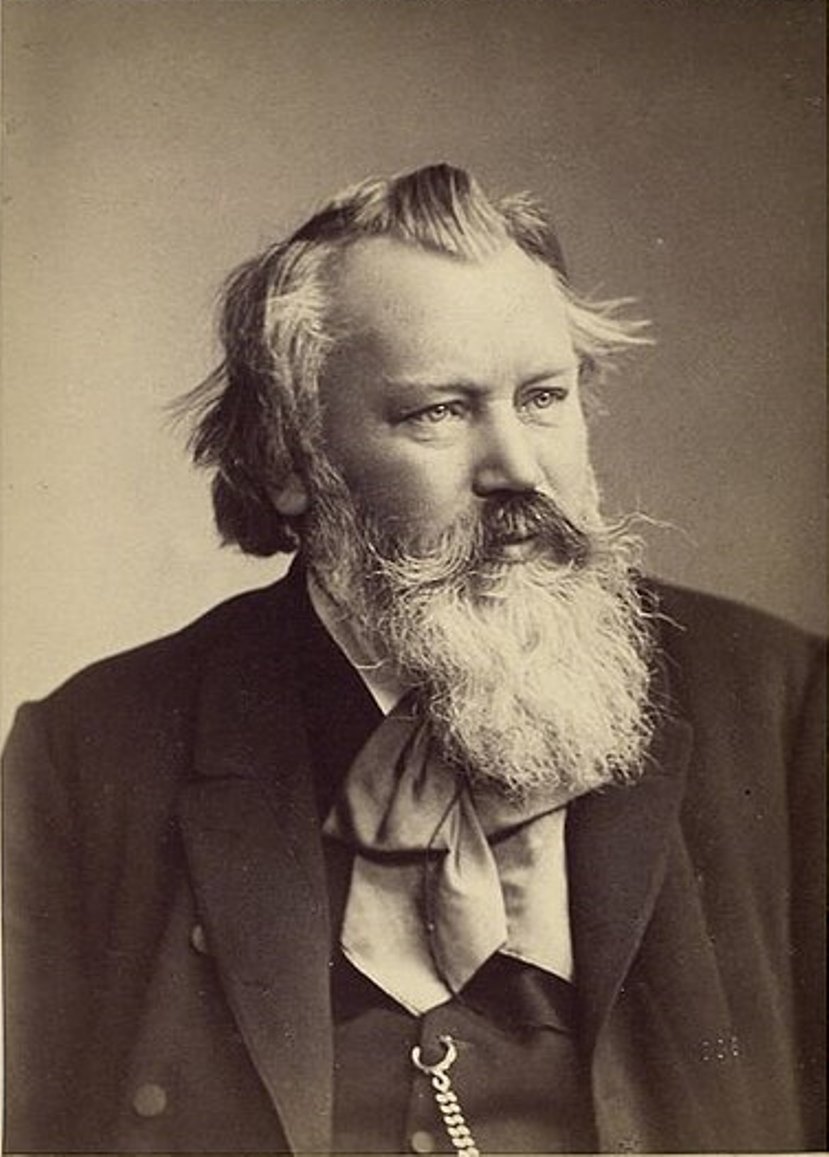


Johannes Brahms was a great German composer, conductor and pianist of the Romantic era.
Johannes showed a talent for music early on, learning to play the piano and earning a living from it; in 1850 he met the Hungarian violinist of Jewish origin Eduard Remenyi - from him he learned gypsy music, which often manifested itself in his later work.
In 1853, Brahms had a fateful encounter with the composer Robert Schumann. Schumann wrote an enthusiastic article about Brahms in a periodical, and from that moment the general public became aware of the young talent. In 1859 Brahms was appointed conductor of the women's choir in Hamburg, which gave him ample time for his own work. During this period he composed two Serenades for orchestra and a String Sextet in B flat major, and completed the Piano Concerto No 1 in D minor. A little later he settled in Vienna and directed the Singakademie choir.
In 1868 Brahms completed his most famous choral work, the German Requiem, which is still considered one of the most important works of 19th century choral music. The following year he composed two volumes of Hungarian Dances for piano duet - these were brilliant arrangements of gypsy melodies, their success was phenomenal, and they were performed all over the world.
For the rest of his life, Brahms never stopped composing works in a wide variety of genres: symphonies, concertos, chamber music, piano works, choral works, waltzes and songs. Brahms was a great master of the symphonic and sonata style of the second half of the nineteenth century, which placed him in the first ranks of German composers. He made his last concert appearance in March 1897, and died of cancer in Vienna in April.

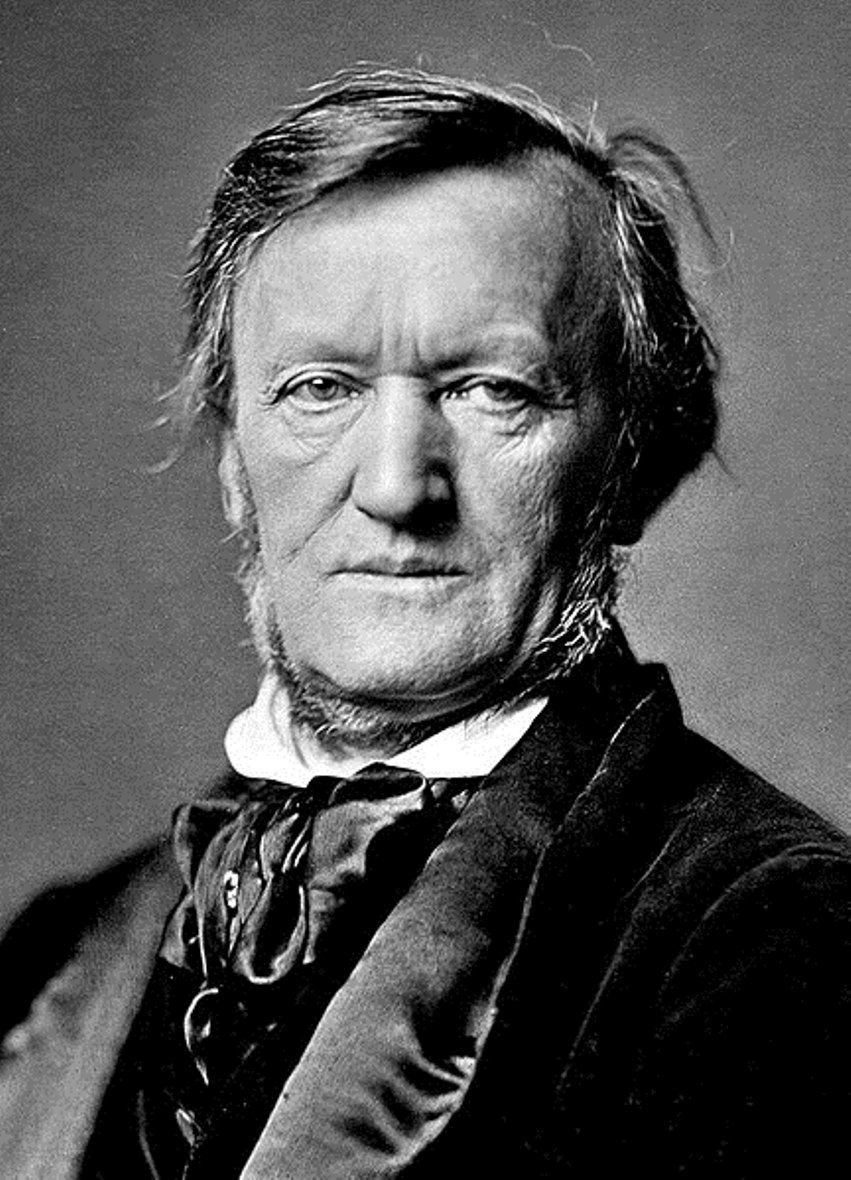
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).

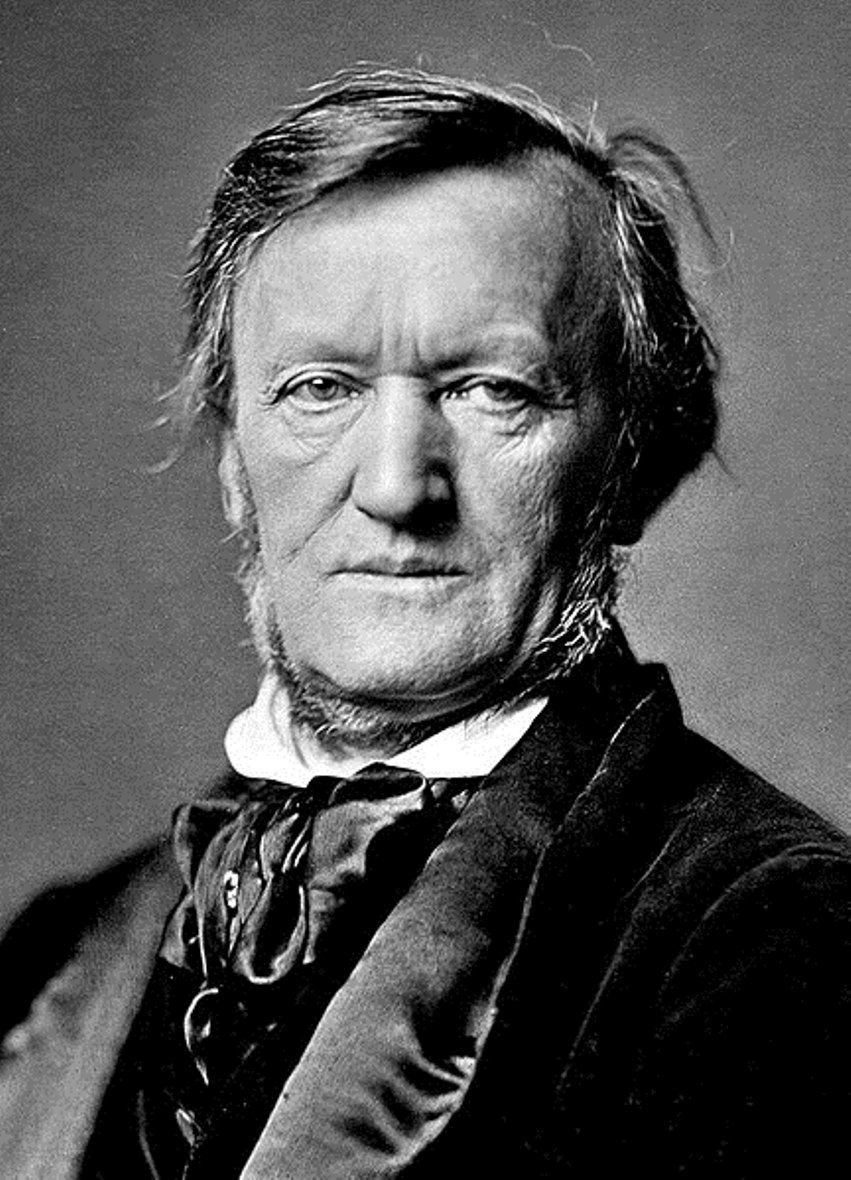
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).
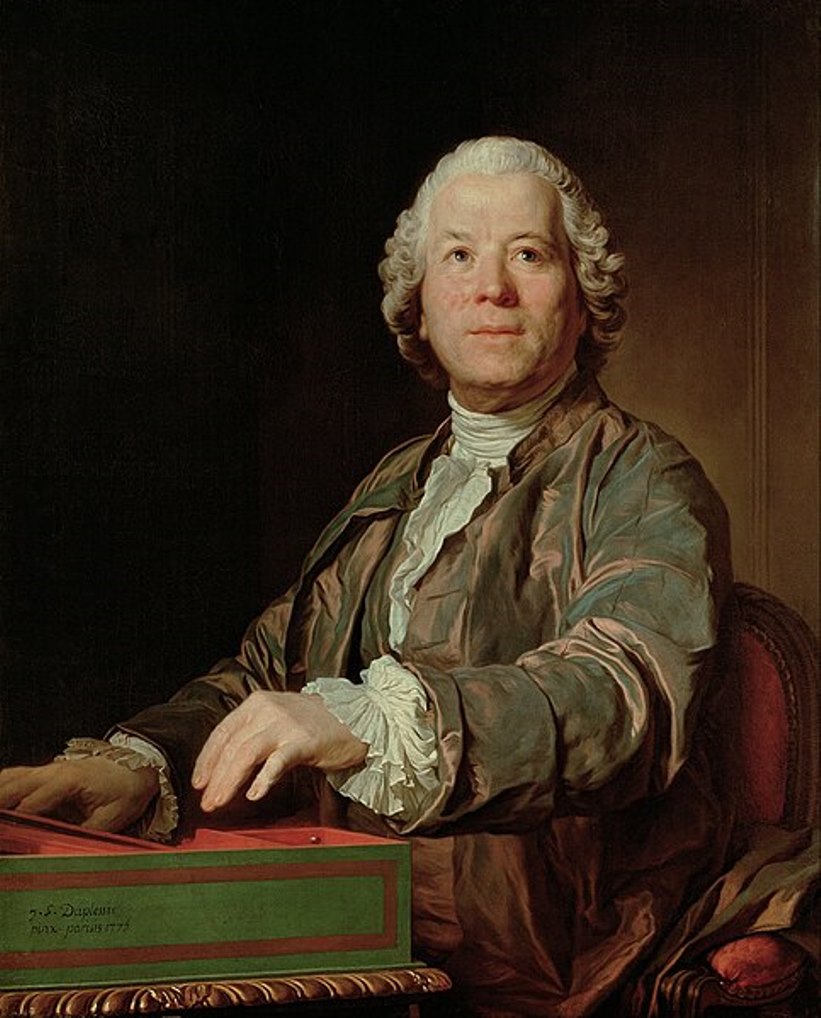


Christoph Willibald Gluck was a German classical composer and reformer of the opera genre.
Christoph showed a talent for music early on, playing violin and cello, leaving home and studying music with various teachers in Prague, Vienna and Milan. In 1741, Gluck had his first significant success with his first opera, Artasers, at the Milan theater. In 1745 Gluck, by then already well known as an opera composer, was invited to England, but in 1750 he settled in Vienna, where he lived for the rest of his life. While in Paris in 1773-79, he won the favor of Louis XVI's wife Marie Antoinette.
Christoph Gluck played a historic role in the formation of a new operatic style, becoming the main reformer in the transition from baroque to classical opera.
During his career, Christoph Gluck composed about 40 operas. Of these, his first "reformist" opera was Orpheus and Eurydice, staged in Vienna in 1762. Next were "Alceste" (1767), "Parida et Helena" (1770), "Iphigenia in Aulida" (1774), a French version of "Orpheus" (1774), and "Iphigenia in Tauris" (1779). He also wrote five ballets, of which Don Giovanni (1761) was one of the first successful action ballets.
Gluck spent the last eight years of his life in Vienna, continuing to work tirelessly. During these years he met several times with Wolfgang Mozart, who by then had already become a bright star.
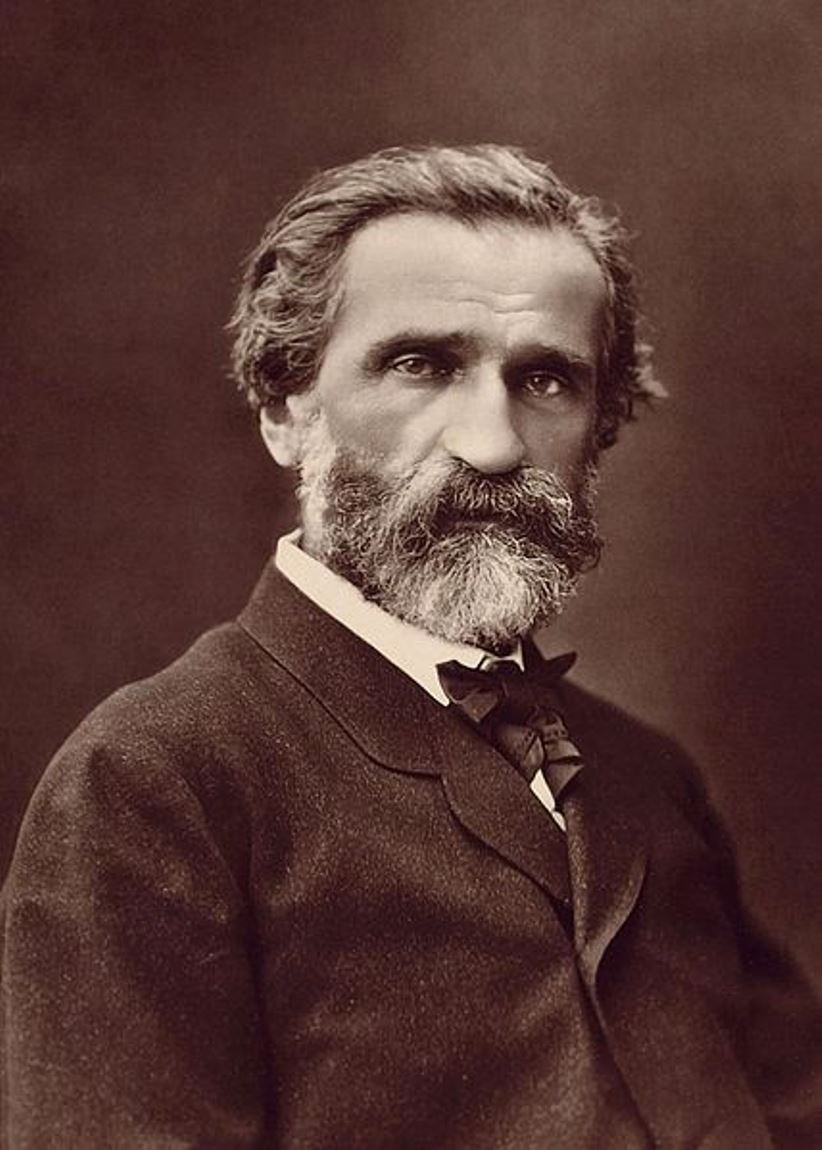


Giuseppe Verdi, full name Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi, was an Italian opera composer.
The son of a village innkeeper, Giuseppe showed musical talent very early, already playing the organ in church by the age of nine. He studied music in Milan, taught, and in March 1839 staged his first opera "Oberto, conte di San Bonifacio" at La Scala. In 1842 Verdi's opera "Nabucco" was a great success, passing through all the major theaters of Europe.
Verdi wrote a total of 26 operas during his career, the most famous of which are Rigoletto (1851), Trovatore (1853), La Traviata (1853), Don Carlos (1867), Aida (1871), Otello (1887) and Falstaff (1893).
In 1873, Giuseppe Verdi decided to retire from the world of opera. He settled in Sant'Agata, where he became a large landowner and a very wealthy man due to his tireless work in agriculture, he also financed large charitable organizations.
Verdi took a break from these activities for his opera Otello, but after a successful tour of Europe with it, he retreated again to Sant'Agata. The work of Giuseppe Verdi is one of the greatest achievements of world opera art. Many generations of opera lovers still enjoy the composer's brilliant works.

































![[Otto F. Ege (1888-1951)]](/assets/image/picture_4361004/50cef/f6fdd7d6cb08b448d829bbf7342315281733871600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Otto F. Ege (1888-1951)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4361004/50cef/f6fdd7d6cb08b448d829bbf7342315281733871600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
























![Francesco Maria Piave (1810-1876) – [Giuseppe Verdi (1813-1901)]](/assets/image/picture_4361092/b52dd/9bf0c3aa8d8cf02c8a808d9e3da16cac1733871600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Francesco Maria Piave (1810-1876) – [Giuseppe Verdi (1813-1901)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4361092/b52dd/9bf0c3aa8d8cf02c8a808d9e3da16cac1733871600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)