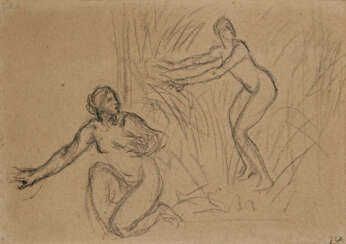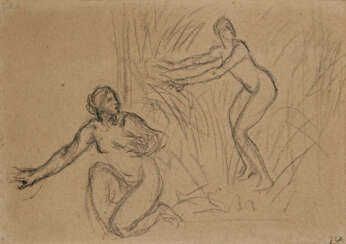милле




.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.


John Everett Millais was an influential British artist and a key figure in the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, celebrated for his detailed and naturalistic paintings. Born in Southampton in 1829, Millais was a child prodigy, gaining admission to the Royal Academy Schools at the remarkable age of eleven. His early work, characterized by meticulous attention to detail and vibrant naturalism, stirred controversy and admiration alike. One of his most renowned pieces, "Ophelia" (1851-52), exemplifies his style during this period, capturing intricate natural scenes with profound emotional depth.
Millais's personal life was as notable as his artistic career, particularly his marriage to Effie Gray, who was previously married to the art critic John Ruskin. This union, following Effie's annulment from Ruskin, produced eight children and intertwined with Millais's evolving artistic journey.
Later in his career, Millais's style transitioned towards a broader approach, a change criticized by some contemporaries but which also garnered him significant acclaim and financial success. His influence extended to various artists, including John Singer Sargent, and his works remain pivotal in the study of Victorian art. His dedication to his craft earned him numerous honors, including a baronetcy, making him the first artist to be bestowed such an honor.
Millais's legacy is preserved in numerous galleries worldwide, with Tate Britain and the Ashmolean Museum housing key works like "The Order of Release" and "The Return of the Dove to the Ark." His contribution to art and culture remains significant, offering a window into the Victorian era's aesthetic and social dynamics.
For enthusiasts and collectors interested in Millais's work, staying updated on exhibitions and sales can provide invaluable insights into his artistry and its enduring appeal. Subscribing to updates on Millais can ensure you remain informed about upcoming events and opportunities related to this seminal artist.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.


John Everett Millais was an influential British artist and a key figure in the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, celebrated for his detailed and naturalistic paintings. Born in Southampton in 1829, Millais was a child prodigy, gaining admission to the Royal Academy Schools at the remarkable age of eleven. His early work, characterized by meticulous attention to detail and vibrant naturalism, stirred controversy and admiration alike. One of his most renowned pieces, "Ophelia" (1851-52), exemplifies his style during this period, capturing intricate natural scenes with profound emotional depth.
Millais's personal life was as notable as his artistic career, particularly his marriage to Effie Gray, who was previously married to the art critic John Ruskin. This union, following Effie's annulment from Ruskin, produced eight children and intertwined with Millais's evolving artistic journey.
Later in his career, Millais's style transitioned towards a broader approach, a change criticized by some contemporaries but which also garnered him significant acclaim and financial success. His influence extended to various artists, including John Singer Sargent, and his works remain pivotal in the study of Victorian art. His dedication to his craft earned him numerous honors, including a baronetcy, making him the first artist to be bestowed such an honor.
Millais's legacy is preserved in numerous galleries worldwide, with Tate Britain and the Ashmolean Museum housing key works like "The Order of Release" and "The Return of the Dove to the Ark." His contribution to art and culture remains significant, offering a window into the Victorian era's aesthetic and social dynamics.
For enthusiasts and collectors interested in Millais's work, staying updated on exhibitions and sales can provide invaluable insights into his artistry and its enduring appeal. Subscribing to updates on Millais can ensure you remain informed about upcoming events and opportunities related to this seminal artist.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.


John Everett Millais was an influential British artist and a key figure in the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, celebrated for his detailed and naturalistic paintings. Born in Southampton in 1829, Millais was a child prodigy, gaining admission to the Royal Academy Schools at the remarkable age of eleven. His early work, characterized by meticulous attention to detail and vibrant naturalism, stirred controversy and admiration alike. One of his most renowned pieces, "Ophelia" (1851-52), exemplifies his style during this period, capturing intricate natural scenes with profound emotional depth.
Millais's personal life was as notable as his artistic career, particularly his marriage to Effie Gray, who was previously married to the art critic John Ruskin. This union, following Effie's annulment from Ruskin, produced eight children and intertwined with Millais's evolving artistic journey.
Later in his career, Millais's style transitioned towards a broader approach, a change criticized by some contemporaries but which also garnered him significant acclaim and financial success. His influence extended to various artists, including John Singer Sargent, and his works remain pivotal in the study of Victorian art. His dedication to his craft earned him numerous honors, including a baronetcy, making him the first artist to be bestowed such an honor.
Millais's legacy is preserved in numerous galleries worldwide, with Tate Britain and the Ashmolean Museum housing key works like "The Order of Release" and "The Return of the Dove to the Ark." His contribution to art and culture remains significant, offering a window into the Victorian era's aesthetic and social dynamics.
For enthusiasts and collectors interested in Millais's work, staying updated on exhibitions and sales can provide invaluable insights into his artistry and its enduring appeal. Subscribing to updates on Millais can ensure you remain informed about upcoming events and opportunities related to this seminal artist.


John Everett Millais was an influential British artist and a key figure in the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, celebrated for his detailed and naturalistic paintings. Born in Southampton in 1829, Millais was a child prodigy, gaining admission to the Royal Academy Schools at the remarkable age of eleven. His early work, characterized by meticulous attention to detail and vibrant naturalism, stirred controversy and admiration alike. One of his most renowned pieces, "Ophelia" (1851-52), exemplifies his style during this period, capturing intricate natural scenes with profound emotional depth.
Millais's personal life was as notable as his artistic career, particularly his marriage to Effie Gray, who was previously married to the art critic John Ruskin. This union, following Effie's annulment from Ruskin, produced eight children and intertwined with Millais's evolving artistic journey.
Later in his career, Millais's style transitioned towards a broader approach, a change criticized by some contemporaries but which also garnered him significant acclaim and financial success. His influence extended to various artists, including John Singer Sargent, and his works remain pivotal in the study of Victorian art. His dedication to his craft earned him numerous honors, including a baronetcy, making him the first artist to be bestowed such an honor.
Millais's legacy is preserved in numerous galleries worldwide, with Tate Britain and the Ashmolean Museum housing key works like "The Order of Release" and "The Return of the Dove to the Ark." His contribution to art and culture remains significant, offering a window into the Victorian era's aesthetic and social dynamics.
For enthusiasts and collectors interested in Millais's work, staying updated on exhibitions and sales can provide invaluable insights into his artistry and its enduring appeal. Subscribing to updates on Millais can ensure you remain informed about upcoming events and opportunities related to this seminal artist.


John Everett Millais was an influential British artist and a key figure in the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, celebrated for his detailed and naturalistic paintings. Born in Southampton in 1829, Millais was a child prodigy, gaining admission to the Royal Academy Schools at the remarkable age of eleven. His early work, characterized by meticulous attention to detail and vibrant naturalism, stirred controversy and admiration alike. One of his most renowned pieces, "Ophelia" (1851-52), exemplifies his style during this period, capturing intricate natural scenes with profound emotional depth.
Millais's personal life was as notable as his artistic career, particularly his marriage to Effie Gray, who was previously married to the art critic John Ruskin. This union, following Effie's annulment from Ruskin, produced eight children and intertwined with Millais's evolving artistic journey.
Later in his career, Millais's style transitioned towards a broader approach, a change criticized by some contemporaries but which also garnered him significant acclaim and financial success. His influence extended to various artists, including John Singer Sargent, and his works remain pivotal in the study of Victorian art. His dedication to his craft earned him numerous honors, including a baronetcy, making him the first artist to be bestowed such an honor.
Millais's legacy is preserved in numerous galleries worldwide, with Tate Britain and the Ashmolean Museum housing key works like "The Order of Release" and "The Return of the Dove to the Ark." His contribution to art and culture remains significant, offering a window into the Victorian era's aesthetic and social dynamics.
For enthusiasts and collectors interested in Millais's work, staying updated on exhibitions and sales can provide invaluable insights into his artistry and its enduring appeal. Subscribing to updates on Millais can ensure you remain informed about upcoming events and opportunities related to this seminal artist.


John Everett Millais was an influential British artist and a key figure in the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, celebrated for his detailed and naturalistic paintings. Born in Southampton in 1829, Millais was a child prodigy, gaining admission to the Royal Academy Schools at the remarkable age of eleven. His early work, characterized by meticulous attention to detail and vibrant naturalism, stirred controversy and admiration alike. One of his most renowned pieces, "Ophelia" (1851-52), exemplifies his style during this period, capturing intricate natural scenes with profound emotional depth.
Millais's personal life was as notable as his artistic career, particularly his marriage to Effie Gray, who was previously married to the art critic John Ruskin. This union, following Effie's annulment from Ruskin, produced eight children and intertwined with Millais's evolving artistic journey.
Later in his career, Millais's style transitioned towards a broader approach, a change criticized by some contemporaries but which also garnered him significant acclaim and financial success. His influence extended to various artists, including John Singer Sargent, and his works remain pivotal in the study of Victorian art. His dedication to his craft earned him numerous honors, including a baronetcy, making him the first artist to be bestowed such an honor.
Millais's legacy is preserved in numerous galleries worldwide, with Tate Britain and the Ashmolean Museum housing key works like "The Order of Release" and "The Return of the Dove to the Ark." His contribution to art and culture remains significant, offering a window into the Victorian era's aesthetic and social dynamics.
For enthusiasts and collectors interested in Millais's work, staying updated on exhibitions and sales can provide invaluable insights into his artistry and its enduring appeal. Subscribing to updates on Millais can ensure you remain informed about upcoming events and opportunities related to this seminal artist.

.jpg)
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism art movement. Toward the end of his career, he became increasingly interested in painting pure landscapes. He is known best for his oil paintings but is also noted for his pastels, conte crayon drawings, and etchings.

![Миллер, В. Пушкин как поэт-этнограф: С прилож. неизданных народных песен, записанных А. С. Пушкиным / [Соч.] проф. Всеволода Миллера.](/assets/image/picture_4216366/52030/u4ff4qmbc1wjqjzunds2dgy73nst678mkmqtmyqpowhmelvnjffttt2fpn5qv5jx1727119669jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Миллер, В. Пушкин как поэт-этнограф: С прилож. неизданных народных песен, записанных А. С. Пушкиным / [Соч.] проф. Всеволода Миллера.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4216366/52030/u4ff4qmbc1wjqjzunds2dgy73nst678mkmqtmyqpowhmelvnjffttt2fpn5qv5jx1727119669jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)








![Général Eugène MILLER (Eugen Ludwig Müller, 1867-1939) [signé].](/assets/image/picture_144873/6f6fb/lbkjvxznqe4r5vc4mxm0fi9gcmxyxiwpymrcrreoanemarkkt22qe-4sv7g0nclo1523312654jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Général Eugène MILLER (Eugen Ludwig Müller, 1867-1939) [signé].](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_144873/6f6fb/lbkjvxznqe4r5vc4mxm0fi9gcmxyxiwpymrcrreoanemarkkt22qe-4sv7g0nclo1523312654jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)