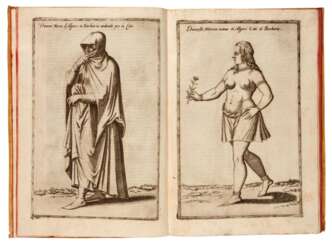
le colas
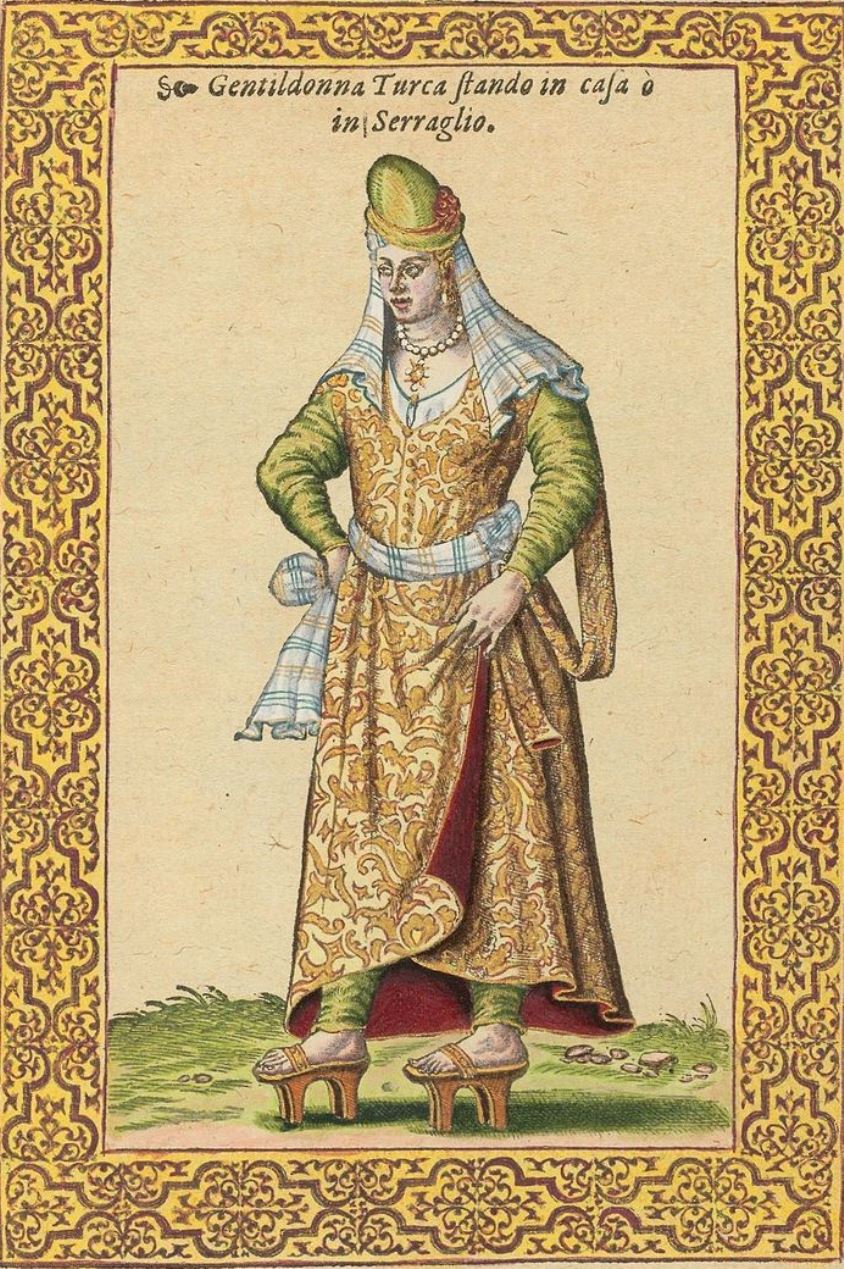

Nicolas de Nicolay, Sieur d'Arfeville & de Belair was a French geographer and artist.
He traveled in Germany, Denmark, England, Sweden, Italy, Spain, Greece and Turkey and served in the armies of most of these countries. Nicholas was the king's geographer, and in 1551 Henry II sent him to Constantinople to work on the d'Aramont embassy. This enabled Nicolas to see a world hitherto virtually unknown in the West. As a result of his work, Nicolas published Travels in Turkey (1567), which depicts the costumes of the peoples of the Middle East, representatives of various nationalities and ethnicities, including Turks, Greeks, Armenians, Jews, and pilgrims to Mecca.
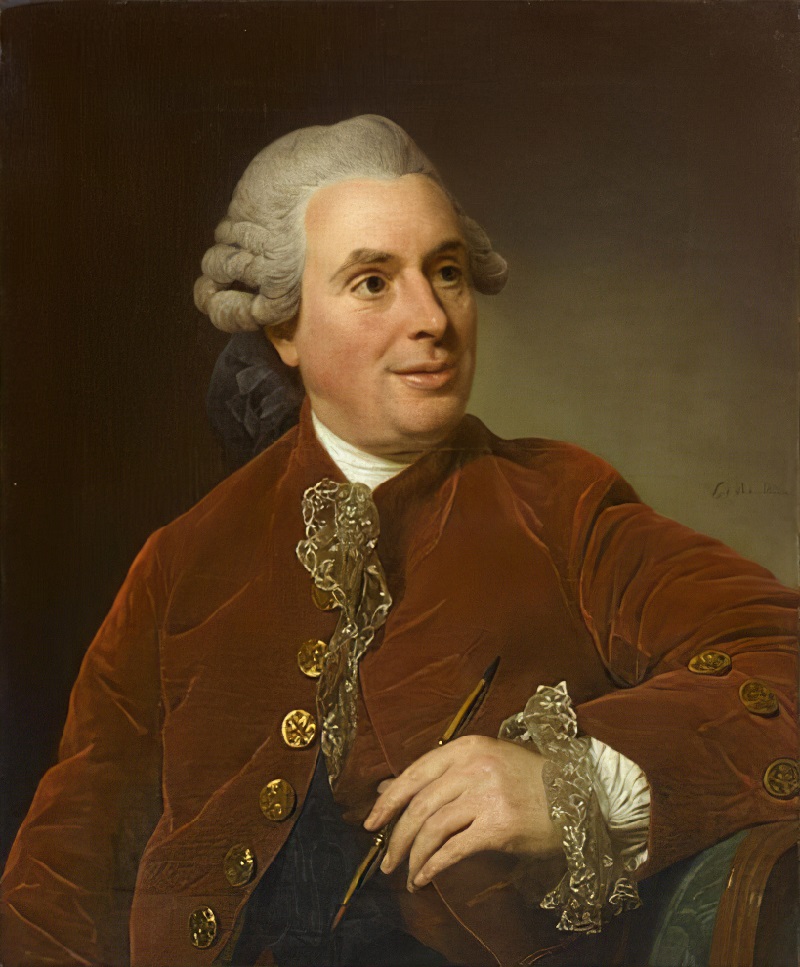


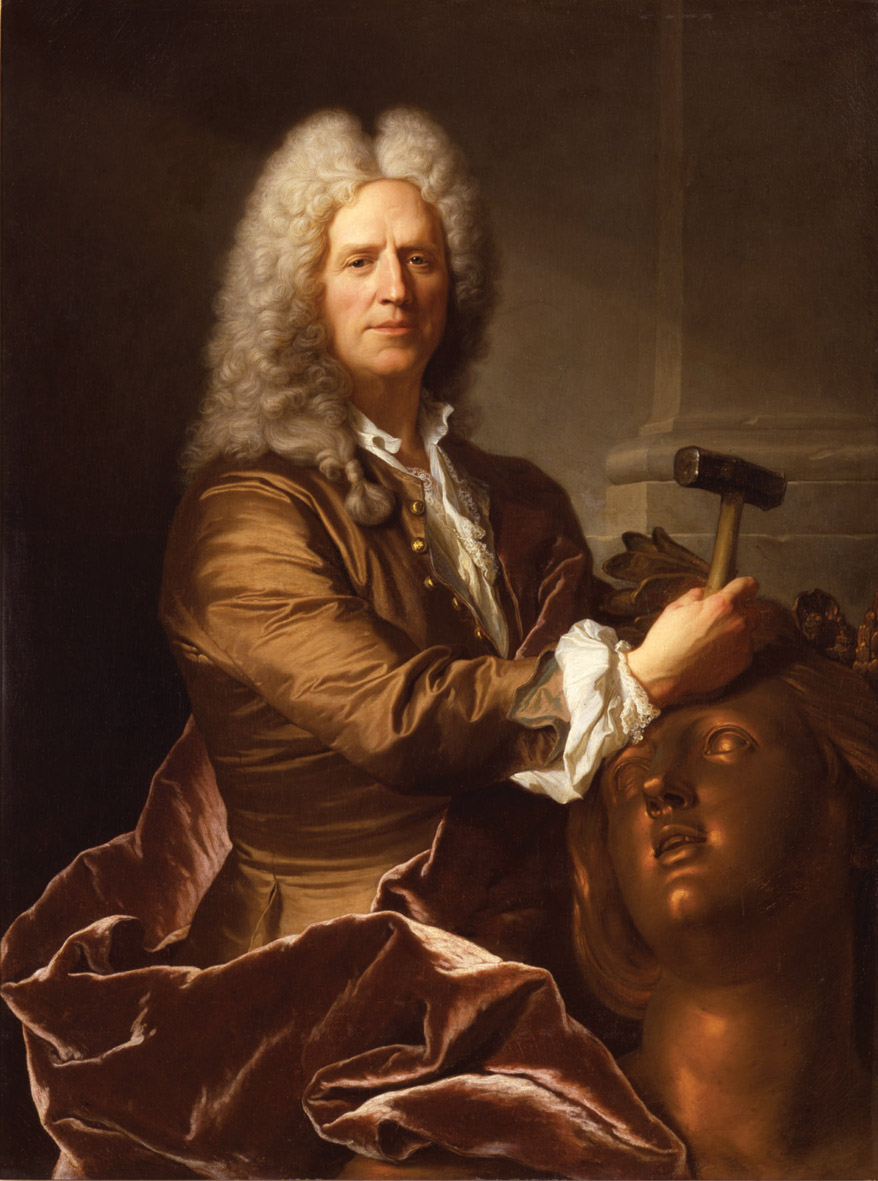
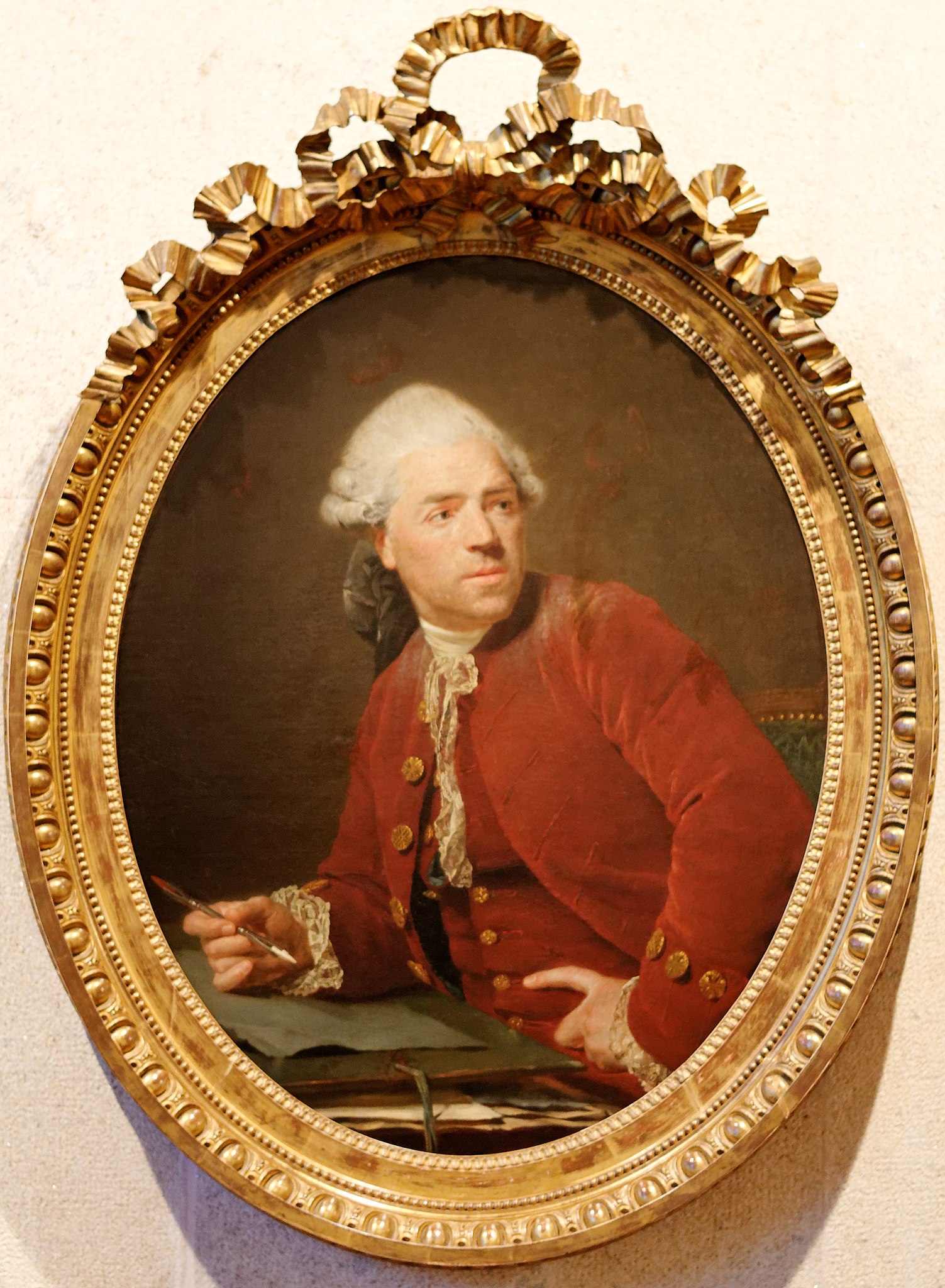
Charles-Nicolas Cochin was a French engraver, designer, writer, and art critic. To distinguish him from his father of the same name, he is variously called Charles-Nicolas Cochin the Younger, Charles-Nicolas Cochin the son, or Charles-Nicolas Cochin II.
More than fifteen hundred works by Cochin can be identified. They include historical subjects, book illustrations, and portraits in pencil and crayon. The richest collection of his engravings, apparently selected by himself, is in the Royal Library, now part of the Bibliothèque nationale.
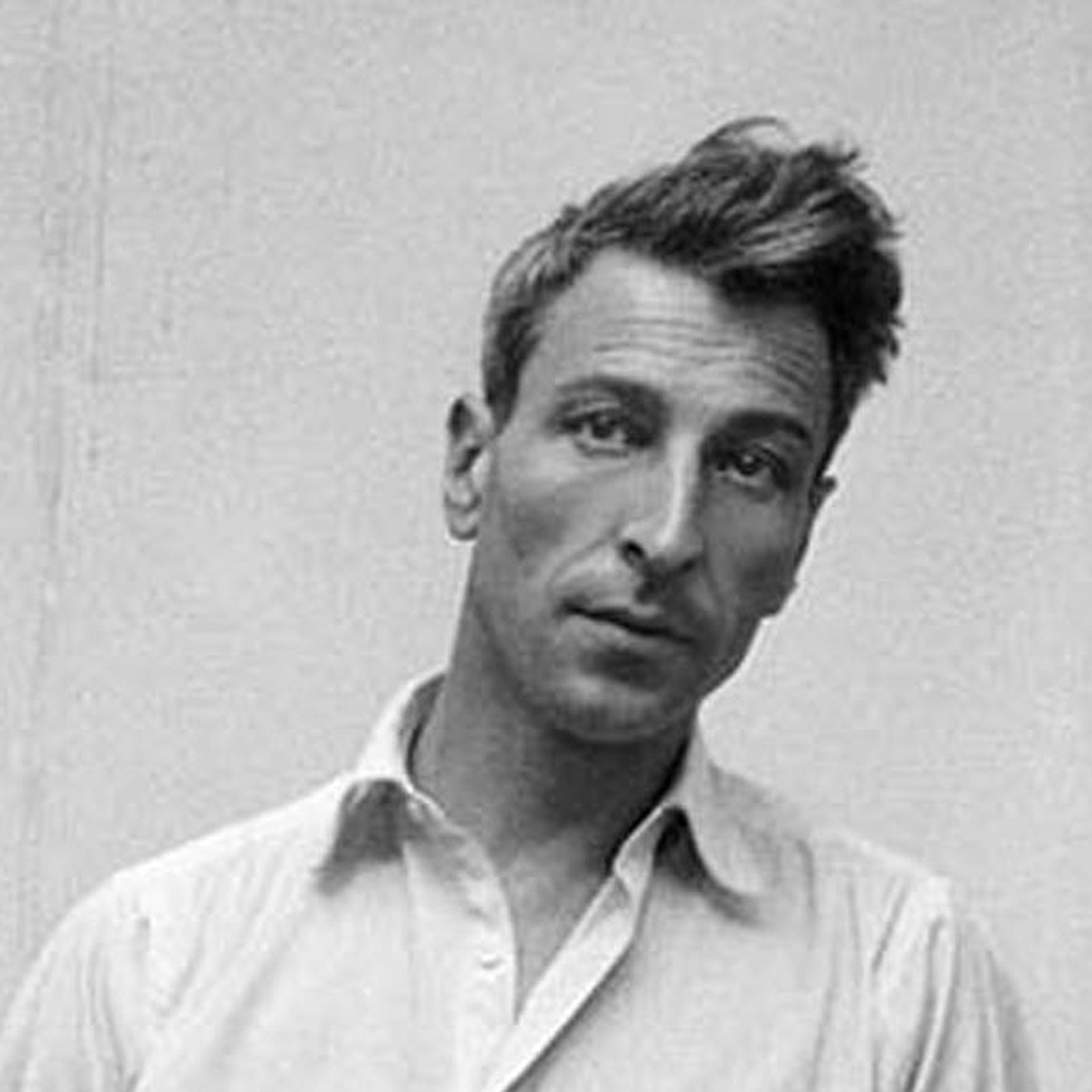


Nicolas de Staël was a Russian-born French artist known for his abstract and figurative paintings. He was born in 1914 in St. Petersburg, Russia and grew up in a wealthy family. In 1919, his family fled Russia and settled in Poland before eventually moving to Brussels, Belgium.
De Staël began studying painting at the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts in Brussels in 1932. After several years of studying and traveling, he settled in Paris in 1938, where he became associated with the group of artists known as the School of Paris.
During the 1940s and 1950s, de Staël developed a distinctive style that blended elements of abstraction and figuration. He used a palette knife and bold, thick brushstrokes to create abstract landscapes and seascapes that were often inspired by his travels to the south of France and the Mediterranean.
In the early 1950s, de Staël began to incorporate figurative elements into his work, creating portraits and still lifes that were characterized by their simplified forms and bold colors. He also experimented with different mediums, including lithography and stained glass.
De Staël's work was well-received by critics and collectors during his lifetime, and he participated in numerous exhibitions in France and internationally. However, he struggled with depression and committed suicide. His legacy has continued to inspire artists and art lovers around the world, and his paintings are held in the collections of major museums, including the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris and the Museum of Modern Art in New York.



Louis-Nicolas de Lespinasse was a French illustrator and politician.


Nicolas de Staël was a Russian-born French artist known for his abstract and figurative paintings. He was born in 1914 in St. Petersburg, Russia and grew up in a wealthy family. In 1919, his family fled Russia and settled in Poland before eventually moving to Brussels, Belgium.
De Staël began studying painting at the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts in Brussels in 1932. After several years of studying and traveling, he settled in Paris in 1938, where he became associated with the group of artists known as the School of Paris.
During the 1940s and 1950s, de Staël developed a distinctive style that blended elements of abstraction and figuration. He used a palette knife and bold, thick brushstrokes to create abstract landscapes and seascapes that were often inspired by his travels to the south of France and the Mediterranean.
In the early 1950s, de Staël began to incorporate figurative elements into his work, creating portraits and still lifes that were characterized by their simplified forms and bold colors. He also experimented with different mediums, including lithography and stained glass.
De Staël's work was well-received by critics and collectors during his lifetime, and he participated in numerous exhibitions in France and internationally. However, he struggled with depression and committed suicide. His legacy has continued to inspire artists and art lovers around the world, and his paintings are held in the collections of major museums, including the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris and the Museum of Modern Art in New York.


Charles-Nicolas Cochin was a French engraver, designer, writer, and art critic. To distinguish him from his father of the same name, he is variously called Charles-Nicolas Cochin the Younger, Charles-Nicolas Cochin the son, or Charles-Nicolas Cochin II.
More than fifteen hundred works by Cochin can be identified. They include historical subjects, book illustrations, and portraits in pencil and crayon. The richest collection of his engravings, apparently selected by himself, is in the Royal Library, now part of the Bibliothèque nationale.
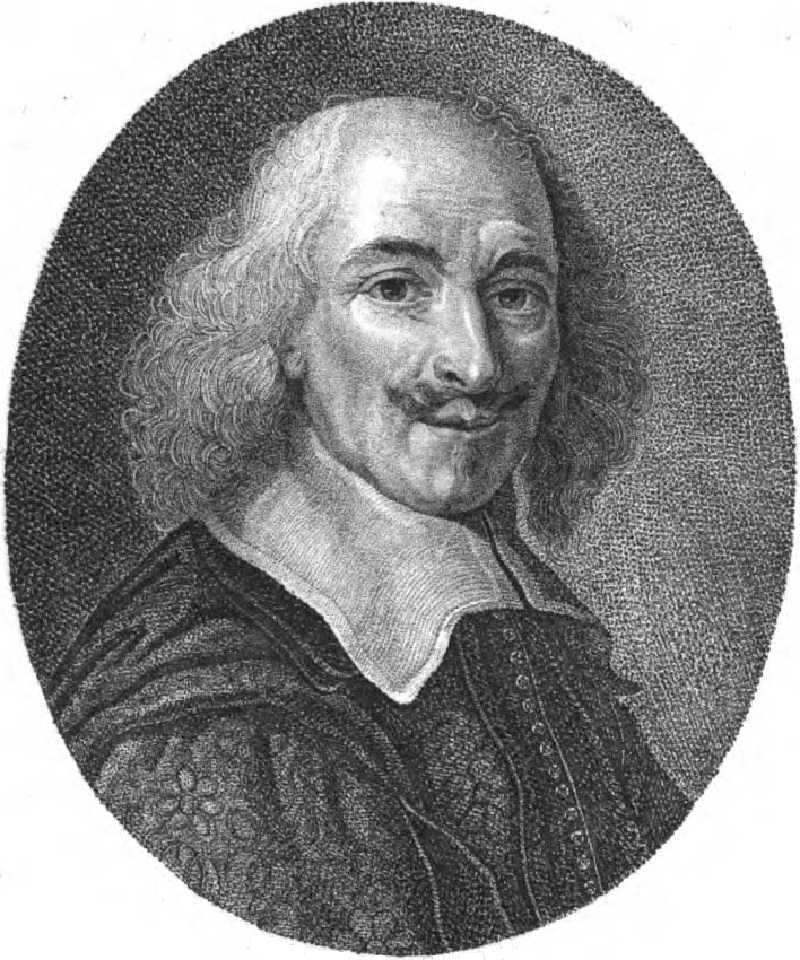


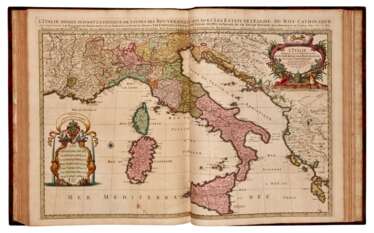
Nicolas Sanson the Elder (Nicolas Sanson d’Abbeville) was a French cartographer who served under two kings in matters of geography. He has been called the "father of French cartography." He gave lessons in geography both to Louis XIII and to Louis XIV. Active from 1627, Sanson issued his first map of importance, the "Postes de France". After publishing several general atlases himself he became the associate of Pierre Mariette, a publisher of prints. He died in Paris on 7 July 1667. Two younger sons succeeded him as geographers to the king. Sanson's maps were used as a model by his son, Guillaume, and, at least initially, by Duval, his nephew, in his 1664 folio map and 1660 atlas minor map. In 1692 Hubert Jaillot collected Sanson's maps in an Atlas nouveau.
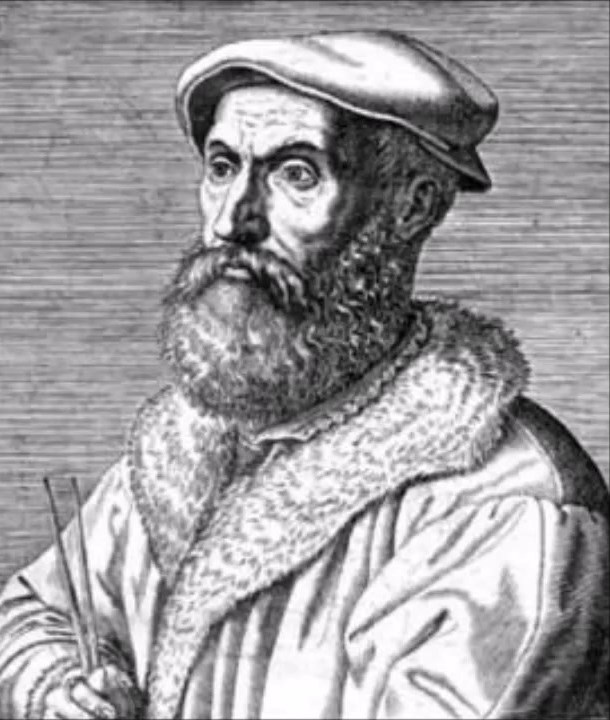


Nicolas Chuquet was a 15th century French mathematician.
The exact dates of birth and death of this scientist are not known, nor are the places of birth. Chuquet received a Bachelor of Medicine degree from the University of Paris, went to Italy in the early 1470s, and around 1480 moved to Lyon, where he worked as a physician, mathematics teacher, and scribe. He is also known to have translated Latin works into French.
In 1484 he wrote his major algebraic work, the treatise Le Triparty en la Science des Nombres (The Science of Numbers in Three Parts), now considered one of the most original mathematical texts of the 15th century. At the time, arithmeticians lacked even the most basic notations for addition subtraction, multiplication, and division. Chuquet was one of the first to propose these symbols; he also introduced the names of large numbers into common use: billion, trillion, etc. In addition to general arithmetic and rules for calculating roots, the treatise contains a doctrine of equations and a collection of problems.
This treatise was published only in 1880, but the works of Nicolas Chuquet had a significant influence on the development of algebra, and they were consistently supplemented and expanded by scientists of the following generations.
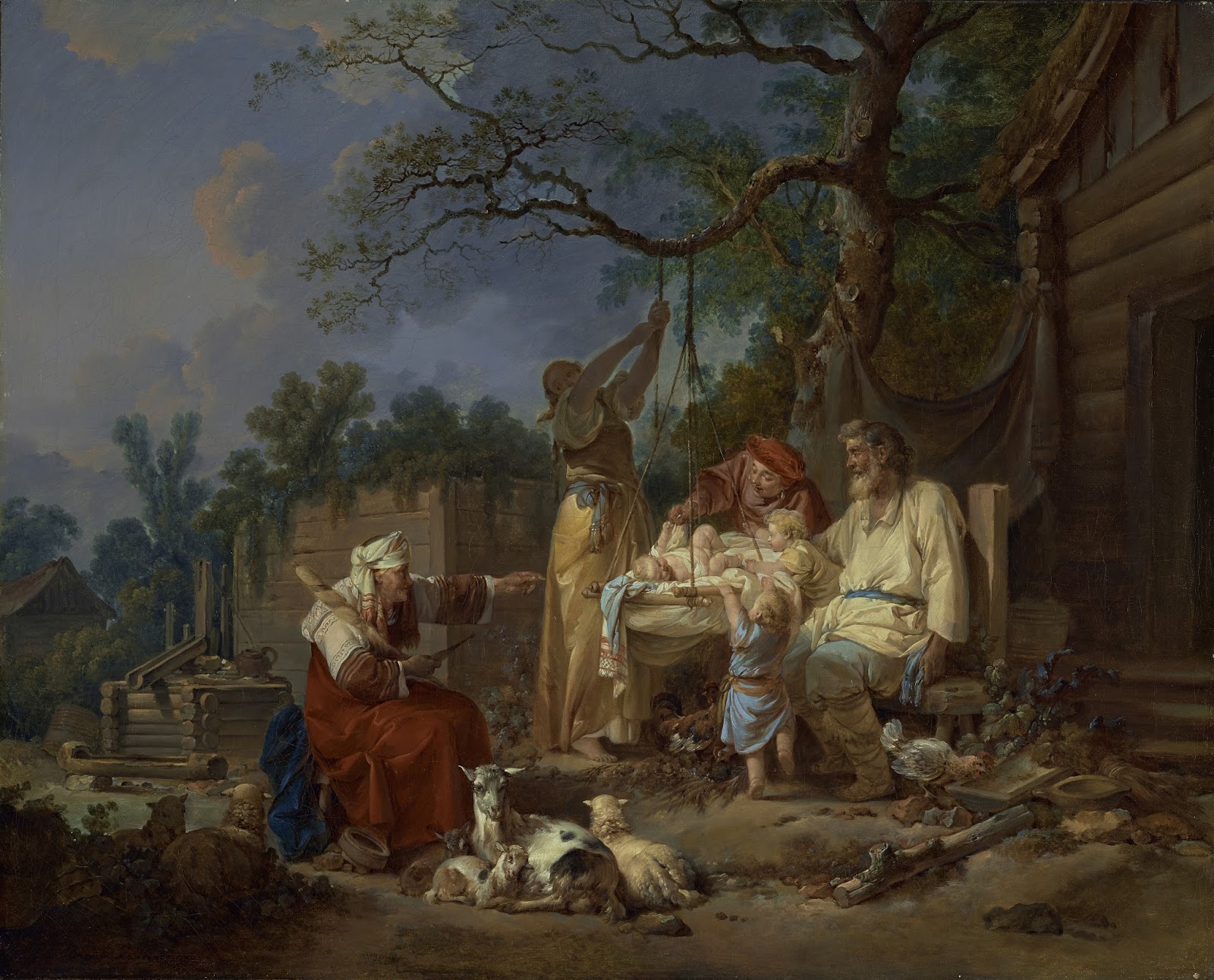



Jean-Baptiste Le Prince was an important French etcher and painter.

.jpeg)
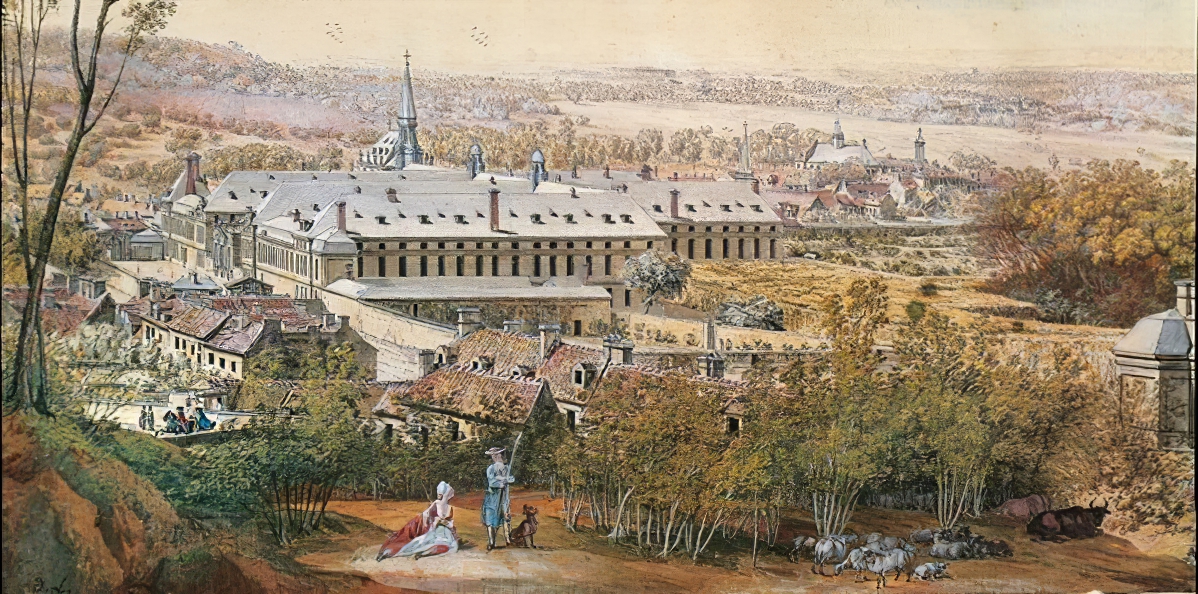
Louis Nicolas van Blarenberghe was a distinguished French painter, born into a dynasty of artists from French Flanders. With a career that spanned the 18th century, he was celebrated for his specialization in detailed miniatures and panoramic battle scenes. His artistic journey began in the Flemish Baroque tradition, evolving into a notable figure within the Rococo movement. Louis Nicolas, alongside his son Henri-Joseph, made significant contributions to the art world, working as miniaturists for the elite at the Palace of Versailles and serving as the official campaign painter for the French court.
His works, particularly those on snuff boxes and his panoramic gouache paintings of military and revolutionary subjects, garnered acclaim. These pieces often featured intricate detail and vivid storytelling, making them highly prized among collectors. The Blarenberghe family's art was so revered that it attracted the attention of the Rothschild family in the 19th century, leading to a substantial collection of their works being displayed publicly at Waddesdon Manor. A significant collection was also part of the Mentmore Towers sale in 1977, underlining the enduring legacy and collector interest in their works.
For art enthusiasts and collectors keen on exploring the rich tapestry of 18th-century French painting, Louis Nicolas van Blarenberghe's oeuvre offers a captivating glimpse into the period's military history and societal elite. His works can be viewed in prestigious institutions and collections, echoing the lasting impact of his and his family's artistic contributions. For updates on sales and auction events featuring Louis Nicolas van Blarenberghe's works, signing up for newsletters from art auction houses and galleries is highly recommended. This ensures enthusiasts stay informed about opportunities to own a piece of this remarkable artist's legacy.

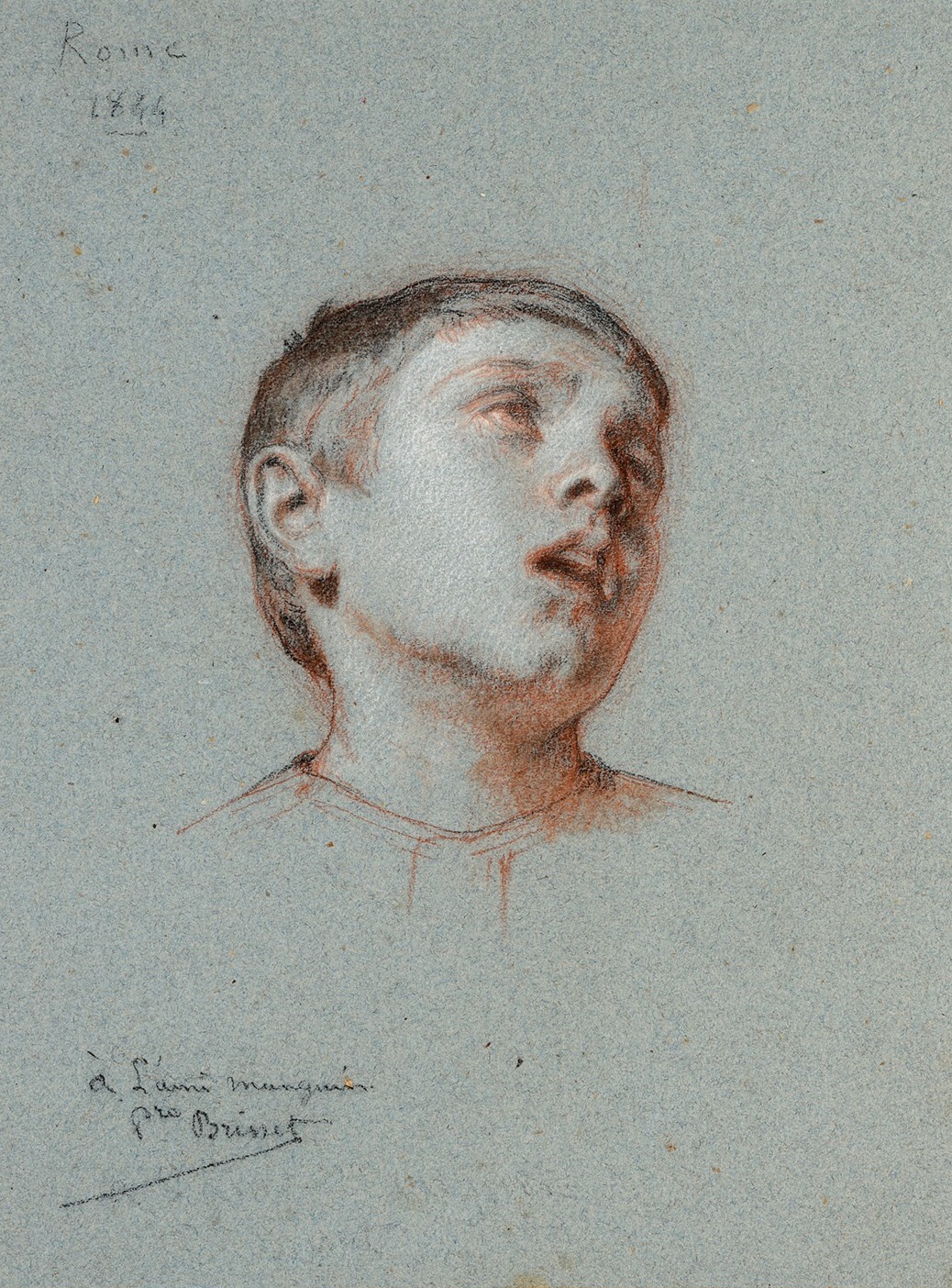
Pierre-Nicolas Brisset was a French painter and muralist in the Academic style. He is best known for his mythological, historical and religious scenes, but also painted landscapes and portraits.


Nicolas de Staël was a Russian-born French artist known for his abstract and figurative paintings. He was born in 1914 in St. Petersburg, Russia and grew up in a wealthy family. In 1919, his family fled Russia and settled in Poland before eventually moving to Brussels, Belgium.
De Staël began studying painting at the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts in Brussels in 1932. After several years of studying and traveling, he settled in Paris in 1938, where he became associated with the group of artists known as the School of Paris.
During the 1940s and 1950s, de Staël developed a distinctive style that blended elements of abstraction and figuration. He used a palette knife and bold, thick brushstrokes to create abstract landscapes and seascapes that were often inspired by his travels to the south of France and the Mediterranean.
In the early 1950s, de Staël began to incorporate figurative elements into his work, creating portraits and still lifes that were characterized by their simplified forms and bold colors. He also experimented with different mediums, including lithography and stained glass.
De Staël's work was well-received by critics and collectors during his lifetime, and he participated in numerous exhibitions in France and internationally. However, he struggled with depression and committed suicide. His legacy has continued to inspire artists and art lovers around the world, and his paintings are held in the collections of major museums, including the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris and the Museum of Modern Art in New York.


Nicolas Poussin, a French painter, is celebrated for establishing the French Classical tradition in art. His life's work was predominantly carried out in Rome, where he specialized in history paintings, drawing from biblical, mythological, and ancient historical narratives. These works are renowned for their narrative clarity and dramatic impact, reflecting Poussin's shift from the sensuous and colorful style of his early years to a more disciplined and rational manner influenced by classical art and the works of Raphael.
Nicolas Poussin's journey into art began in Paris around 1612, where his exposure to royal art collections and the works of Italian Renaissance artists profoundly influenced his style. His move to Rome in 1624 marked the beginning of his most impactful period, where he connected with key figures and patrons, further honing his unique style through commissions that allowed him to explore religious, mythological, and historical themes.
In Rome, Nicolas Poussin's work garnered attention and respect, culminating in his brief return to France in 1640 to become First Painter to the King. However, the challenges of the court and a preference for his life in Rome saw him return to Italy, where he continued to produce significant works like "Orion Blinded Searching for the Sun" and "The Seasons". His late works, characterized by their use of dramatic landscapes to convey human emotions, mark a departure from his earlier, more tranquil compositions.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art and the National Gallery in London house some of Poussin's most important works, offering a glimpse into the evolution of his style and the enduring impact of his art on the classical tradition.
For those interested in delving deeper into Nicolas Poussin's world and staying updated on related artworks and events, subscribing for updates is a practical step. By signing up, you'll receive curated information on new findings, sales, and auction events related to Poussin, ensuring you're well-informed about this pivotal figure in art history.
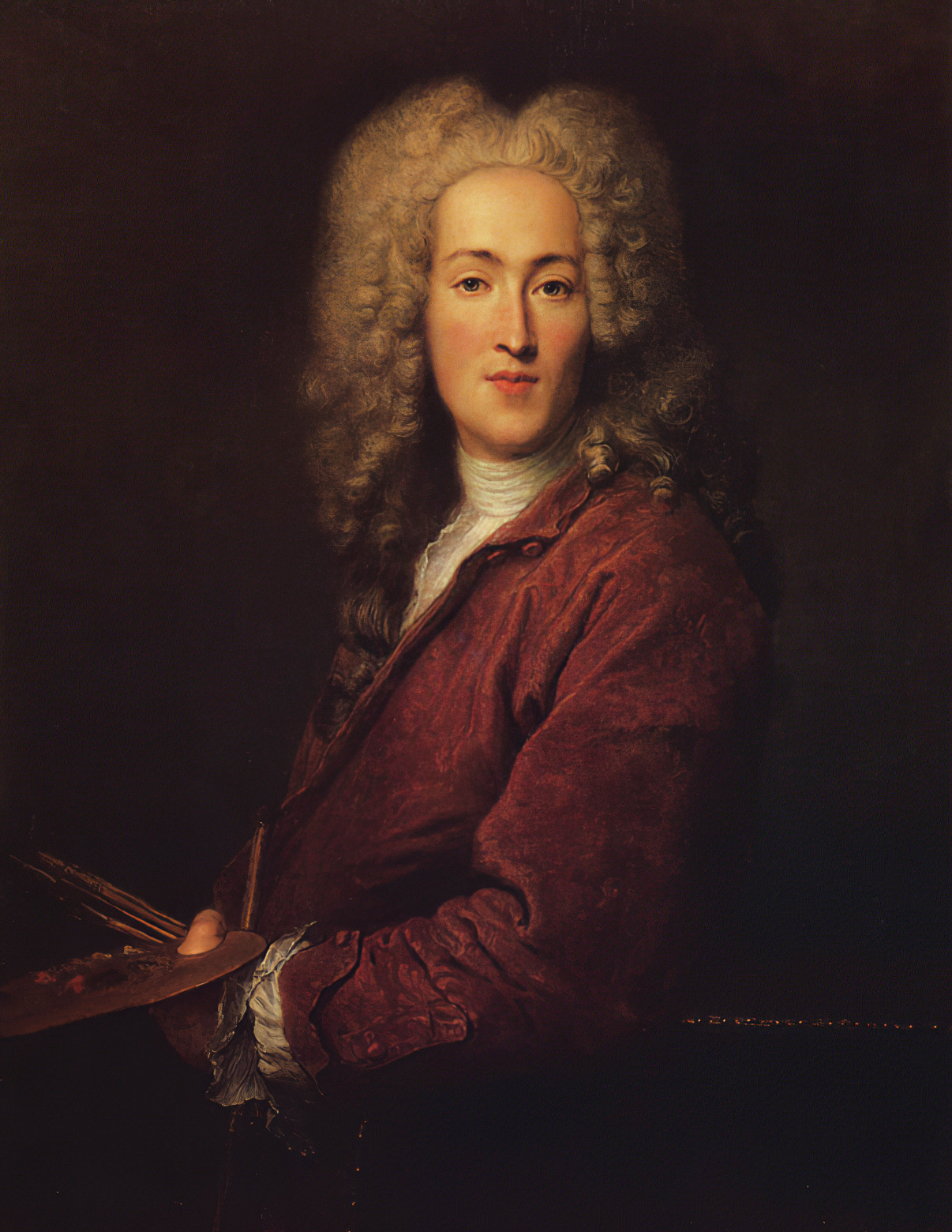


Nicolas Lancret was a French painter. Born in Paris, he was a brilliant depicter of light comedy which reflected the tastes and manners of French society during the regency of the Duke of Orleans and, later, early reign of King Louis XV.

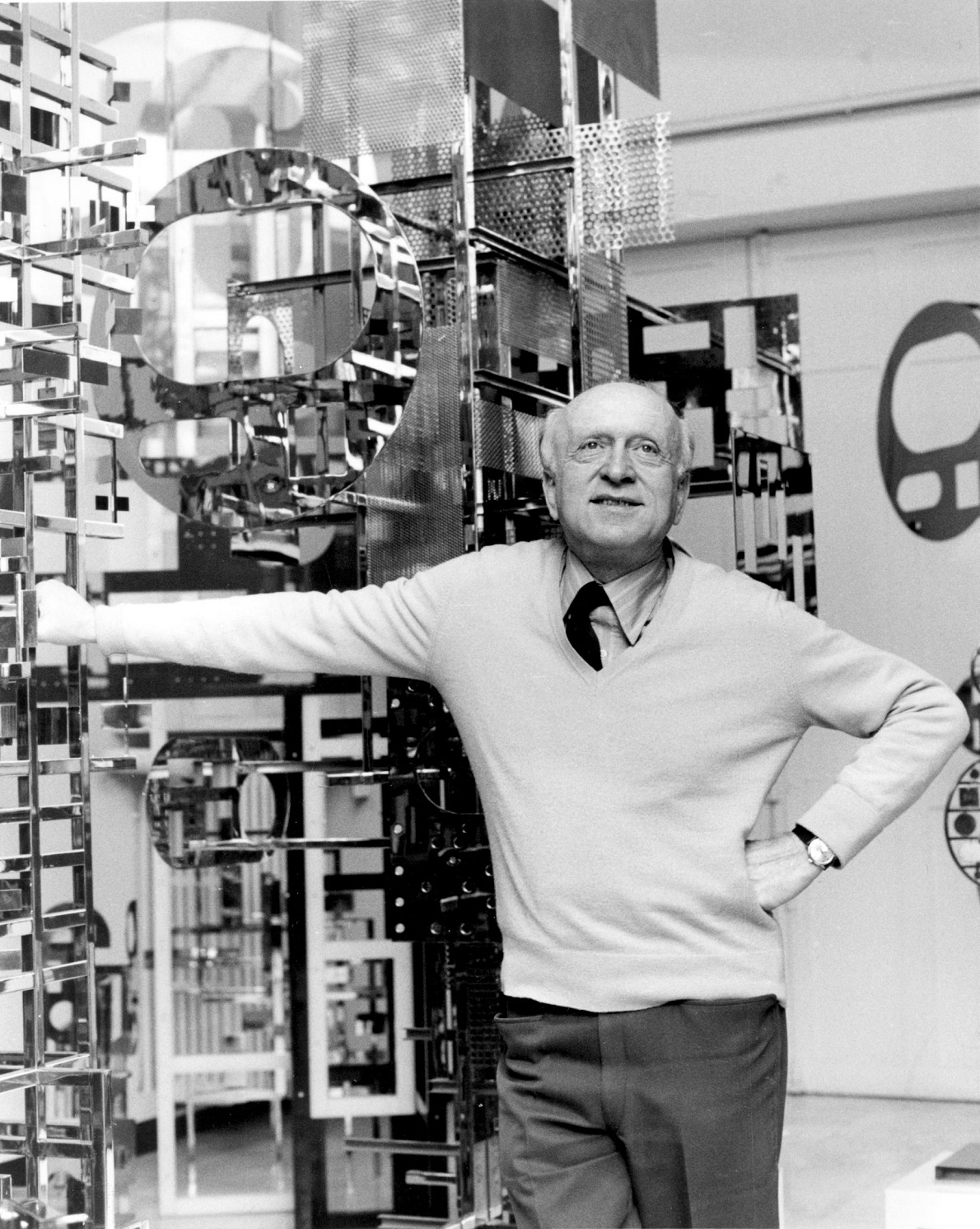
Nicolas Schöffer (Hungarian: Schöffer Miklós) was a Hungarian-born French cybernetic artist.
He built his artworks on cybernetic theories of contol and feedback primarily based on the ideas of Norbert Wiener. Wiener's work suggested to Schöffer an artistic process in terms of the circular causality of feedback loops that he used on a wide range of art genres. His career spans painting, sculpture, architecture, urbanism, film, theatre, television and music. The quest for dematerialisation of the artwork and the pursuit of movement and dynamics became the central themes of his work. He worked with the immaterial media space, time, light, sound and climate that he called the five topologies.


Nicolas Lancret was a French painter. Born in Paris, he was a brilliant depicter of light comedy which reflected the tastes and manners of French society during the regency of the Duke of Orleans and, later, early reign of King Louis XV.


Nicolas Sanson the Elder (Nicolas Sanson d’Abbeville) was a French cartographer who served under two kings in matters of geography. He has been called the "father of French cartography." He gave lessons in geography both to Louis XIII and to Louis XIV. Active from 1627, Sanson issued his first map of importance, the "Postes de France". After publishing several general atlases himself he became the associate of Pierre Mariette, a publisher of prints. He died in Paris on 7 July 1667. Two younger sons succeeded him as geographers to the king. Sanson's maps were used as a model by his son, Guillaume, and, at least initially, by Duval, his nephew, in his 1664 folio map and 1660 atlas minor map. In 1692 Hubert Jaillot collected Sanson's maps in an Atlas nouveau.



Nicolas Lancret was a French painter. Born in Paris, he was a brilliant depicter of light comedy which reflected the tastes and manners of French society during the regency of the Duke of Orleans and, later, early reign of King Louis XV.


Nicolas de Nicolay, Sieur d'Arfeville & de Belair was a French geographer and artist.
He traveled in Germany, Denmark, England, Sweden, Italy, Spain, Greece and Turkey and served in the armies of most of these countries. Nicholas was the king's geographer, and in 1551 Henry II sent him to Constantinople to work on the d'Aramont embassy. This enabled Nicolas to see a world hitherto virtually unknown in the West. As a result of his work, Nicolas published Travels in Turkey (1567), which depicts the costumes of the peoples of the Middle East, representatives of various nationalities and ethnicities, including Turks, Greeks, Armenians, Jews, and pilgrims to Mecca.


Nicolas Poussin, a French painter, is celebrated for establishing the French Classical tradition in art. His life's work was predominantly carried out in Rome, where he specialized in history paintings, drawing from biblical, mythological, and ancient historical narratives. These works are renowned for their narrative clarity and dramatic impact, reflecting Poussin's shift from the sensuous and colorful style of his early years to a more disciplined and rational manner influenced by classical art and the works of Raphael.
Nicolas Poussin's journey into art began in Paris around 1612, where his exposure to royal art collections and the works of Italian Renaissance artists profoundly influenced his style. His move to Rome in 1624 marked the beginning of his most impactful period, where he connected with key figures and patrons, further honing his unique style through commissions that allowed him to explore religious, mythological, and historical themes.
In Rome, Nicolas Poussin's work garnered attention and respect, culminating in his brief return to France in 1640 to become First Painter to the King. However, the challenges of the court and a preference for his life in Rome saw him return to Italy, where he continued to produce significant works like "Orion Blinded Searching for the Sun" and "The Seasons". His late works, characterized by their use of dramatic landscapes to convey human emotions, mark a departure from his earlier, more tranquil compositions.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art and the National Gallery in London house some of Poussin's most important works, offering a glimpse into the evolution of his style and the enduring impact of his art on the classical tradition.
For those interested in delving deeper into Nicolas Poussin's world and staying updated on related artworks and events, subscribing for updates is a practical step. By signing up, you'll receive curated information on new findings, sales, and auction events related to Poussin, ensuring you're well-informed about this pivotal figure in art history.
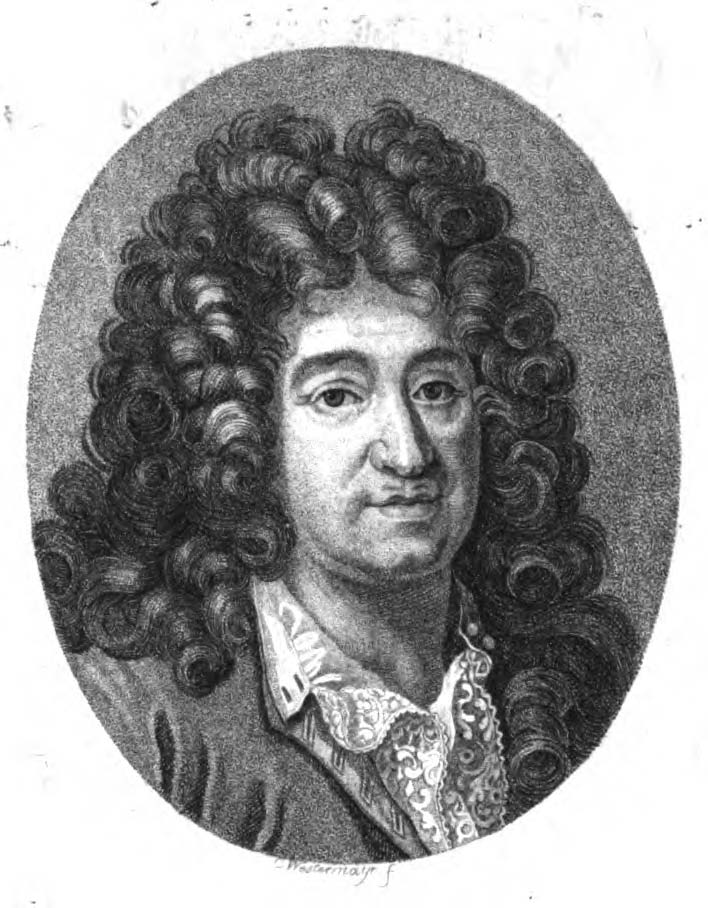



Nicolas Sanson the Elder (Nicolas Sanson d’Abbeville) was a French cartographer who served under two kings in matters of geography. He has been called the "father of French cartography." He gave lessons in geography both to Louis XIII and to Louis XIV. Active from 1627, Sanson issued his first map of importance, the "Postes de France". After publishing several general atlases himself he became the associate of Pierre Mariette, a publisher of prints. He died in Paris on 7 July 1667. Two younger sons succeeded him as geographers to the king. Sanson's maps were used as a model by his son, Guillaume, and, at least initially, by Duval, his nephew, in his 1664 folio map and 1660 atlas minor map. In 1692 Hubert Jaillot collected Sanson's maps in an Atlas nouveau.

.jpeg)
Louis Nicolas van Blarenberghe was a distinguished French painter, born into a dynasty of artists from French Flanders. With a career that spanned the 18th century, he was celebrated for his specialization in detailed miniatures and panoramic battle scenes. His artistic journey began in the Flemish Baroque tradition, evolving into a notable figure within the Rococo movement. Louis Nicolas, alongside his son Henri-Joseph, made significant contributions to the art world, working as miniaturists for the elite at the Palace of Versailles and serving as the official campaign painter for the French court.
His works, particularly those on snuff boxes and his panoramic gouache paintings of military and revolutionary subjects, garnered acclaim. These pieces often featured intricate detail and vivid storytelling, making them highly prized among collectors. The Blarenberghe family's art was so revered that it attracted the attention of the Rothschild family in the 19th century, leading to a substantial collection of their works being displayed publicly at Waddesdon Manor. A significant collection was also part of the Mentmore Towers sale in 1977, underlining the enduring legacy and collector interest in their works.
For art enthusiasts and collectors keen on exploring the rich tapestry of 18th-century French painting, Louis Nicolas van Blarenberghe's oeuvre offers a captivating glimpse into the period's military history and societal elite. His works can be viewed in prestigious institutions and collections, echoing the lasting impact of his and his family's artistic contributions. For updates on sales and auction events featuring Louis Nicolas van Blarenberghe's works, signing up for newsletters from art auction houses and galleries is highly recommended. This ensures enthusiasts stay informed about opportunities to own a piece of this remarkable artist's legacy.














![[QIANLONG, Empereur de Chine (1711-1799) et Charles-Nicolas COCHIN (1715-1790), dir.]](/assets/image/picture_3601309/f9d87/rqfwcmyodhwl6a3u3cnvjqatap9yfxpvbnyt77bbuqb0bh1q4smembav9v5ika1700204263jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[QIANLONG, Empereur de Chine (1711-1799) et Charles-Nicolas COCHIN (1715-1790), dir.]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3601309/f9d87/rqfwcmyodhwl6a3u3cnvjqatap9yfxpvbnyt77bbuqb0bh1q4smembav9v5ika1700204263jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)