manoir
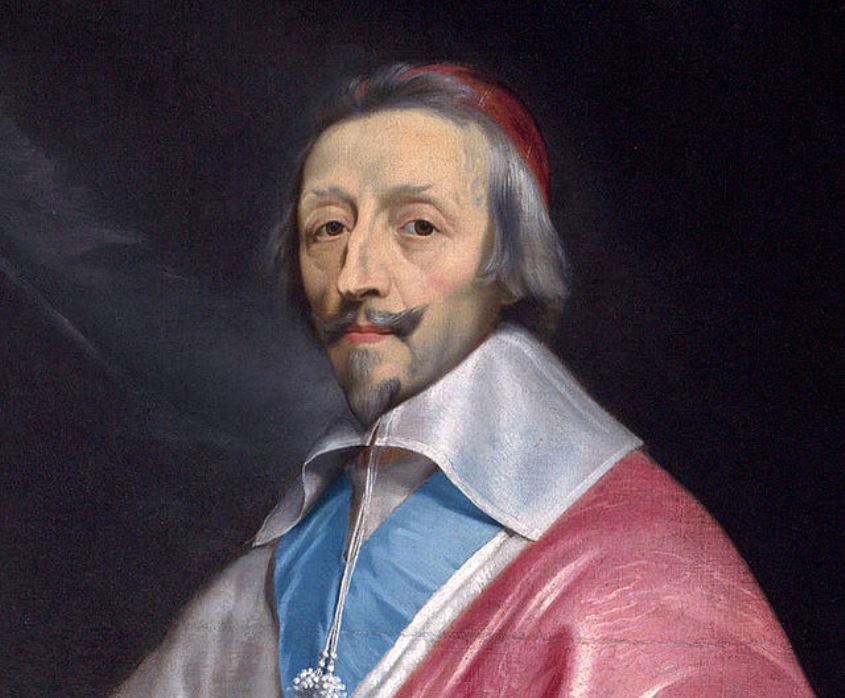

Armand-Jean du Plessis, duc de Richelieu, also known as Cardinal Richelieu or the Red Cardinal (French: l'Éminence rouge) was a Roman Catholic cardinal, aristocrat and statesman of France.
Armand Jean's father, François du Plessis, Signor de Richelieu, was the grand proclaimer (chief magistrate) of Henry III, but left his family devastated at his death. At the age of 22, Armand was ordained a priest and began to build a career. Thanks to his intellectual talents, he was soon appointed chaplain to the new Queen Anne of Austria, and in 1616 he was appointed Secretary of State for War and Foreign Affairs. Further events and a palace coup led to his exile, but he returned to Paris five years later.
The Duc de Richelieu became a cardinal in 1622, and from 1624 until his death in 1642 he was chief minister to King Louis XIII of France. His main goals were to establish royal absolutism in France and to end the Spanish-Habsburg hegemony in Europe. He made significant strides in reforming France, especially in terms of the administrative structure of the government.
The intrigues of his opponents accompanied the Duc de Richelieu throughout his political life. In the last years of his life he found himself involved in religious conflicts, in opposition to the pope in a struggle with the French church over the distribution of revenues intended to finance the war.
Richelieu possessed outstanding intellectual ability, willpower, and industriousness. He directed his own wealth to patronizing the arts and the University of Paris; he established the French Academy. Richelieu was also a talented playwright and musician.
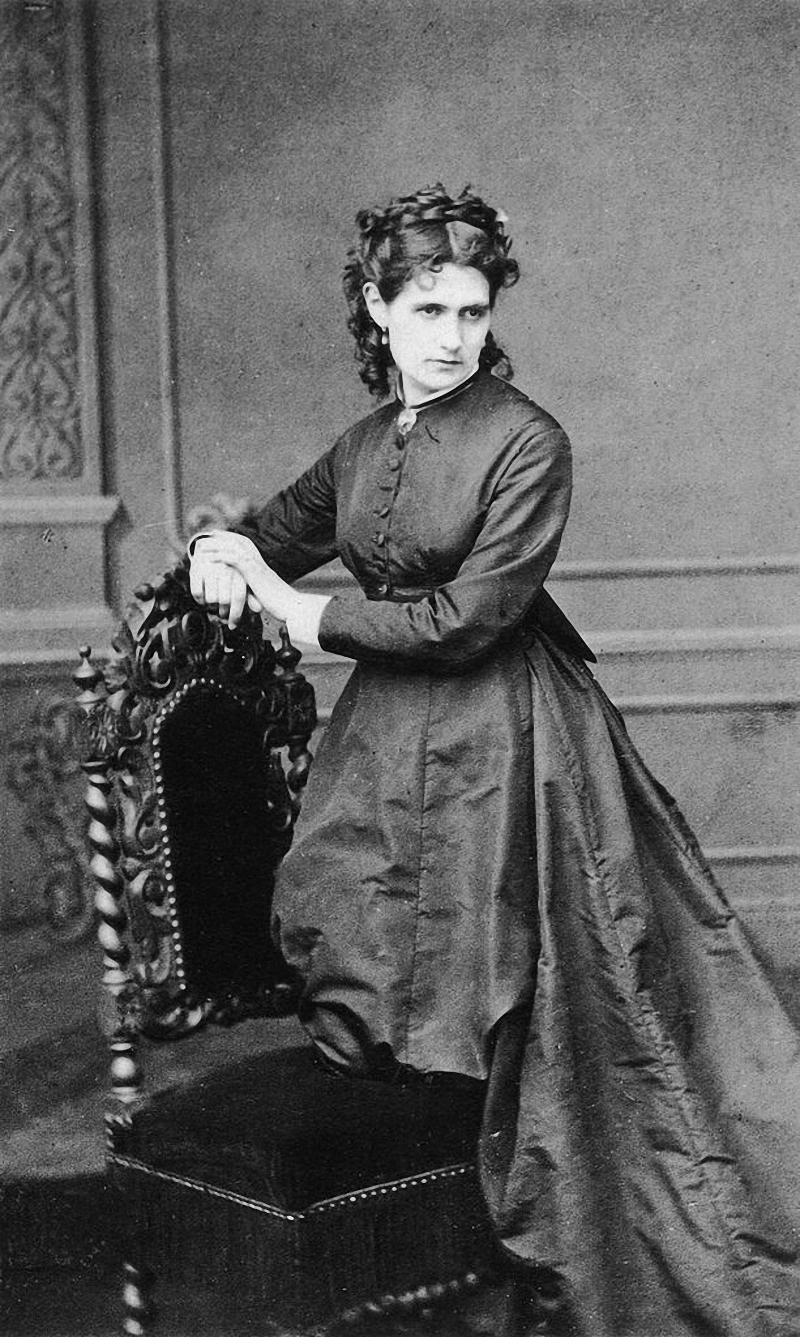


Berthe Morisot was a French painter, renowned for her pivotal role in the Impressionist movement. Born into an affluent family in 1841, Morisot's upbringing was steeped in culture, and she received a comprehensive art education alongside her sisters. Despite societal constraints, she pursued a career in art, initially exhibiting at Paris' salons before transitioning to the more avant-garde Impressionist exhibitions.
Berthe Morisot's artistry is characterized by a unique blend of color, light, and texture, embodying a distinctly "feminine" style that garnered admiration from her peers and critics alike. Her works, such as "The Cradle" and "Hanging the Laundry out to Dry," showcase her ability to capture the ephemeral qualities of everyday life with a tender and nuanced touch. Morisot's palette, dominated by pastel tones and an interplay of light, lends her paintings an ethereal quality, while her brushwork reflects a freedom and delicacy that became her signature.
Throughout her career, Berthe Morisot's evolving style reflected broader artistic trends, integrating influences from photography and Japanese prints. Yet, she remained faithful to the Impressionist ethos, capturing the transient moments of life with grace and sensitivity. Today, her works are celebrated in museums like the Musée d'Orsay, testament to her enduring influence in the realm of art and culture.
As we remember Berthe Morisot, her legacy continues to inspire art collectors and enthusiasts, reminding us of the profound impact one individual can have on the course of art history. For those captivated by Berthe Morisot's contribution to art and culture, we invite you to sign up for updates on upcoming sales and auction events featuring her works. Join us in celebrating the timeless beauty and historical significance of Morisot's artistry.














![[ÉTAT ET MENU GÉNÉRAL DE LA DÉPENSE].](/assets/image/picture_2735040/c5a9a/d83810beb9c5f3c8e2277956725aa38a1679526000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[ÉTAT ET MENU GÉNÉRAL DE LA DÉPENSE].](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2735040/c5a9a/d83810beb9c5f3c8e2277956725aa38a1679526000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)