rate maps america

William Henry Mouzon, Jr. was an American cartographer and civil engineer.
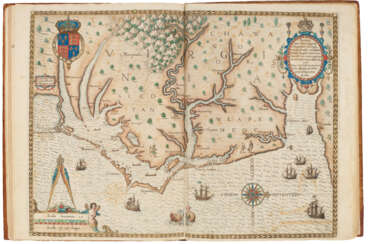
Henry Mouzon, Jr. was the grandson of a Huguenot immigrant and was sent to France at the age of eight, where he was trained as a civil engineer and surveyor. In 1771 he and Ephraim Mitchell were sent to survey the boundaries of South Carolina. As a result, a map was created and published in 1775 that included both North and South Carolina with corrections to previous maps.
This map was entitled "An Accurate Map of North and South Carolina with their Indian Boundaries," and clearly showed all the mountains, rivers, swamps, marshes, bogs, bays, creeks, harbors, sandbanks and shoals on the coasts, and gave the names of the land owners. American, British, and French troops used this map during the American Revolution. A copy of this map, owned by George Washington, is now in the library of the American Geographical Society.



Peter Jefferson was an American cartographer and surveyor, father of the third President of the United States, Thomas Jefferson.
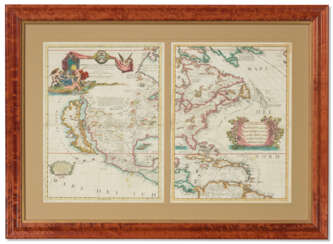
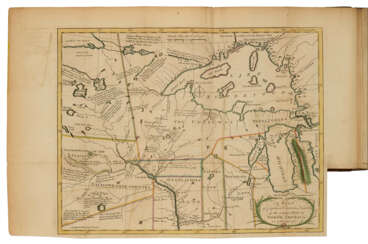
Peter Jefferson was the son of a large landowner in Virginia, and served as sheriff, surveyor, and justice of the peace. He was also a cartographer and surveyor. Along with Colonel and County Surveyor Joshua Fry, he spent several years exploring new lands. In 1750, Lewis Burwell, acting governor of Virginia, commissioned Frye and Jefferson to map the colony, which was done.
This map of early America was based on Frye and Jefferson's meticulous research and accurately delineated the boundaries, roads, settlements, and trails of the original inhabitants. It also included significant new geographic information reported by early wilderness travelers, including George Washington, Christopher Gist, and John Dalrymple. The map was completed in 1751 and engraved and published a few years later. Afterward, Jefferson worked on numerous surveying projects throughout Virginia.

Joshua Fry was a British and American politician and planter, surveyor and cartographer.
Educated at Oxford University, Fry emigrated to the colony of Virginia around 1726. He soon founded a grammar school for the sons of the local gentry, then headed the mathematics department of the college, and worked as a professor of philosophy. Through a successful marriage, he became a large landowner and gained prominence, serving as a member of the House of Burgesses and justice of the peace in Essex County and later in Albemarle.
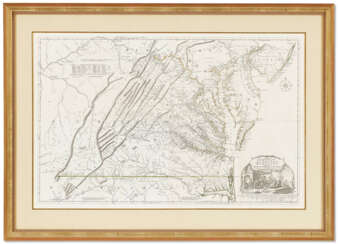
When Albemarle County was established in Virginia in 1745, Joshua Fry was appointed here as chief surveyor in charge of land surveying. Beginning in 1746, Fry was assisted throughout his work by his close friend Peter Jefferson, father of future U.S. President Thomas Jefferson. Together they not only explored new lands, but also created maps that documented the new territories with great accuracy. Their main project was the so-called Frye-Jefferson map, published in 1751, depicting Virginia and Maryland.
This map was unique for its time because it was based on actual geodetic data. The map showed the "Great Road from the Yadkin River through Virginia to Philadelphia 455 miles."
At the outbreak of the Seven Years' War, Joshua Fry was appointed head of the Virginia Regiment and died of his injuries in the campaign on May 31, 1754.


Peter Jefferson was an American cartographer and surveyor, father of the third President of the United States, Thomas Jefferson.
Peter Jefferson was the son of a large landowner in Virginia, and served as sheriff, surveyor, and justice of the peace. He was also a cartographer and surveyor. Along with Colonel and County Surveyor Joshua Fry, he spent several years exploring new lands. In 1750, Lewis Burwell, acting governor of Virginia, commissioned Frye and Jefferson to map the colony, which was done.
This map of early America was based on Frye and Jefferson's meticulous research and accurately delineated the boundaries, roads, settlements, and trails of the original inhabitants. It also included significant new geographic information reported by early wilderness travelers, including George Washington, Christopher Gist, and John Dalrymple. The map was completed in 1751 and engraved and published a few years later. Afterward, Jefferson worked on numerous surveying projects throughout Virginia.

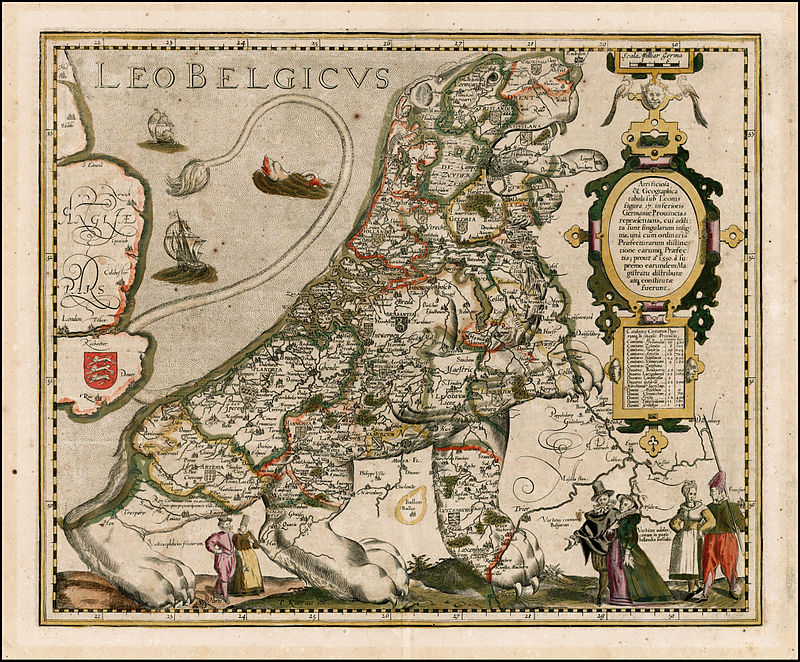
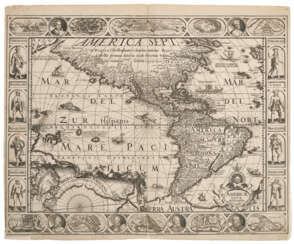
Pieter van der Keere (Latin: Petrus Kaerius) was a Flemish engraver, publisher, cartographer and globe maker.
His father was the master of typefaces Hendrik van der Keere (c. 1540-1580); in 1584 he fled from the Netherlands to London, where he lived most of his life. Pieter van der Keere produced engravings and atlases. From 1603, Kere began to produce large city panoramas, including Utrecht, Cologne, Amsterdam and Paris.
An atlas of the Netherlands was published in 1617, with der Keere's name as publisher and his full signature on several maps. He also produced topographical maps of Amsterdam and Nuremberg, as well as a world map ("Nova totius terrarum orbis..."), which was printed by Jan Janszoon in Amsterdam.
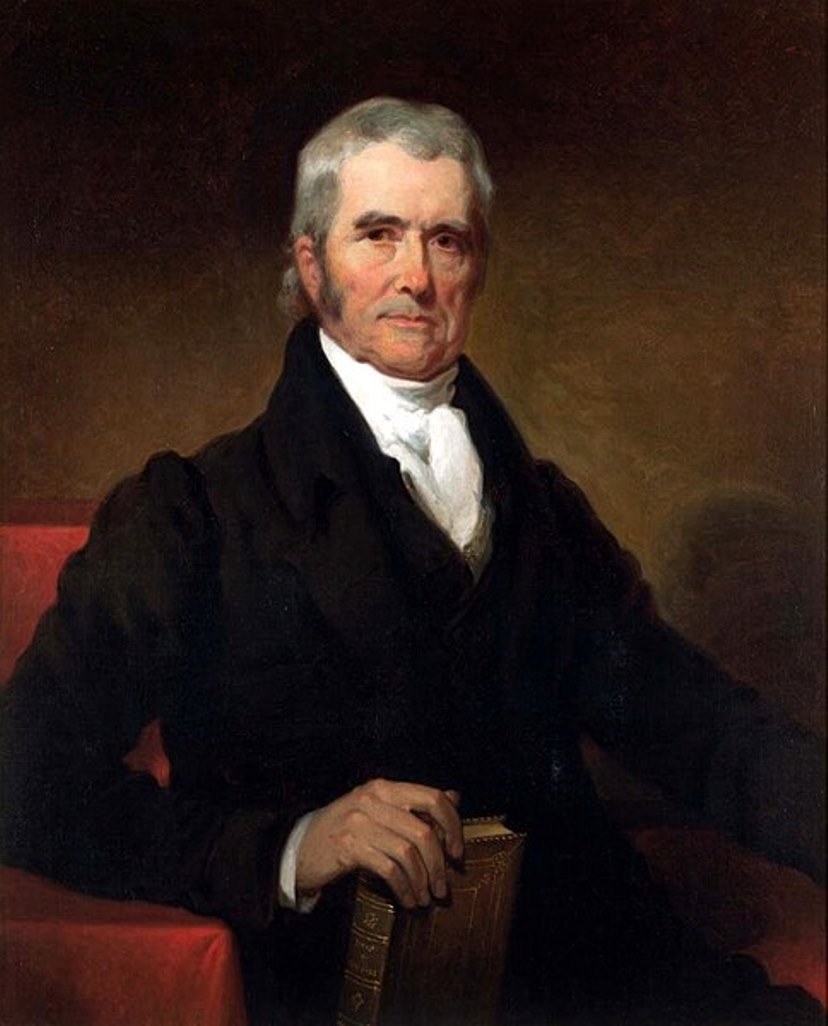


John Marshall was Chief Justice of the United States Supreme Court from 1801 to 1835, Secretary of State, and one of the founders of the American legal system.
During the Revolutionary War, Marshall served first as a lieutenant and after July 1778 as a captain in the Continental Army. In 1781 he left the service, studied law, and began practicing law in Virginia, in Fauquier County, and then in Richmond. He soon became head of the Virginia bar and was a member of the Virginia assembly. In 1788 he took a leading part in the Virginia convention convened to discuss the proposed U.S. Constitution. In 1797-98, along with Charles Cotesworth Pinckney and Elbridge, Gerry Marshall was appointed by John Adams to negotiate with France.
He was Secretary of State under President Adams from June 6, 1800 to March 4, 1801. At the same time he was appointed Chief Justice of the Supreme Court in 1801 and served in that position until 1835.
John Marshall was a personal friend of Washington, he announced his death in 1799, organized his funeral, and delivered his eulogy. Washington's relatives soon asked Marshall to write a biography of the late president. "The Life of George Washington" was published in London in 1804-1807. It includes illustrations, portraits, facsimile letters, and folding maps.
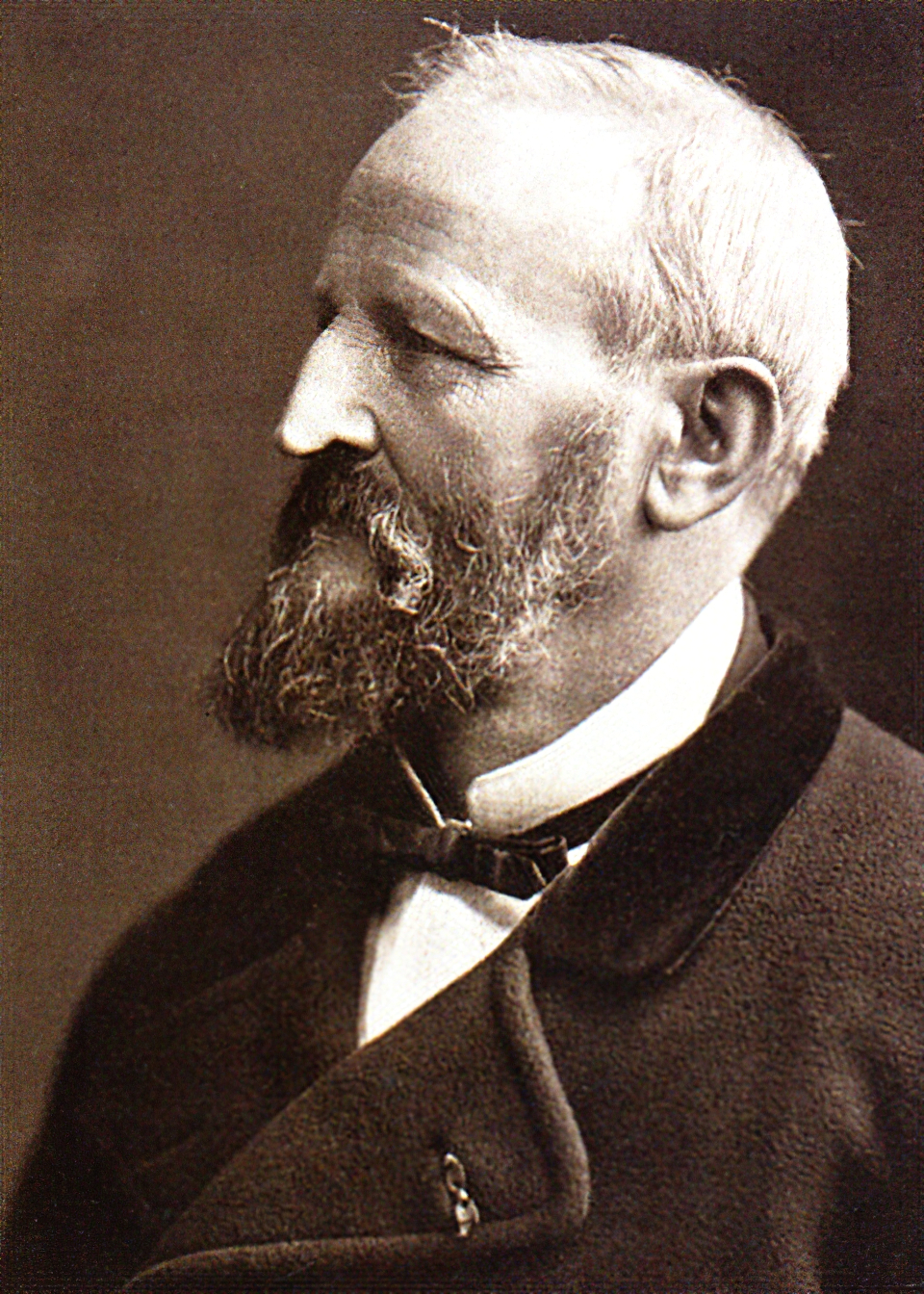


Karl Bodmer was a Swiss-French printmaker, etcher, lithographer, zinc engraver, draughtsman, painter, illustrator and hunter.


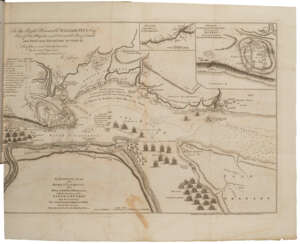
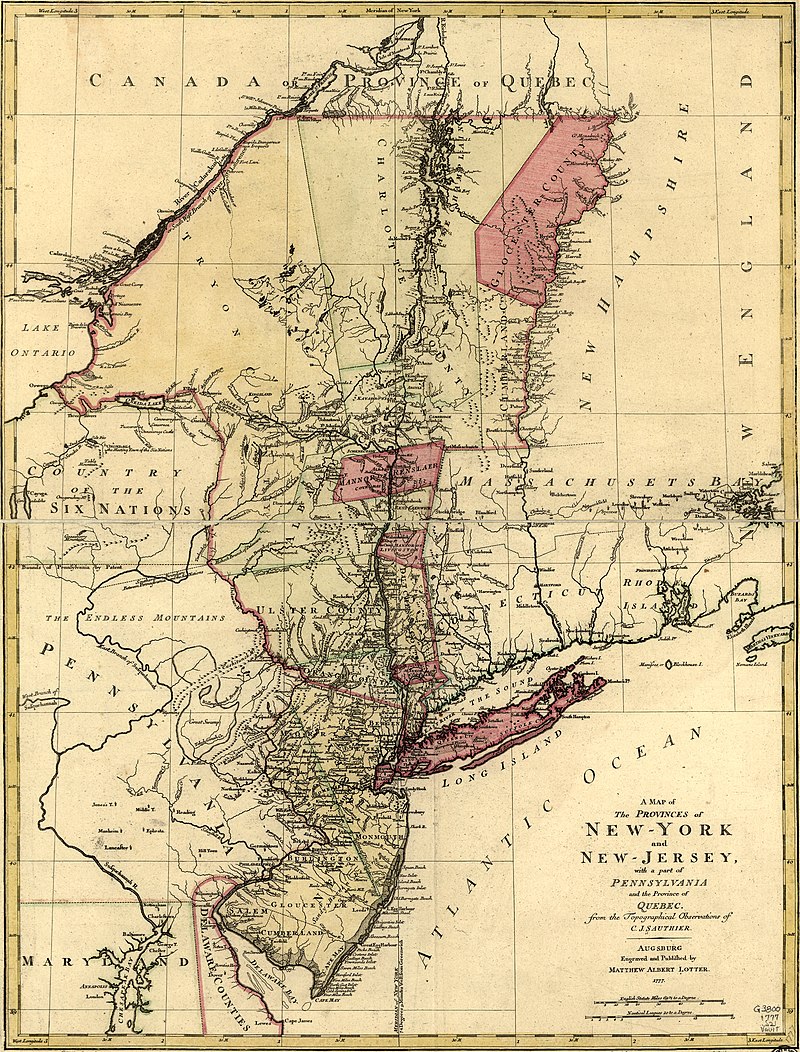
John Montresor was a British military engineer and cartographer who worked in North America.
His father was a military engineer and his youth was spent in British Gibraltar. Montresor studied in London, and in 1754 accompanied his father to North America when he was appointed chief engineer to Major General Edward Braddock's troops. John participated in various expeditions, delivered dispatches, and witnessed the sieges of Louisbourg and Quebec. During his service, he also did the necessary research and prepared maps of Acadia, the St. Lawrence River, and his route along the Kennebec River.
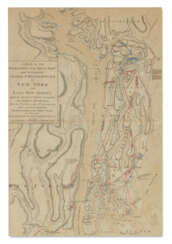
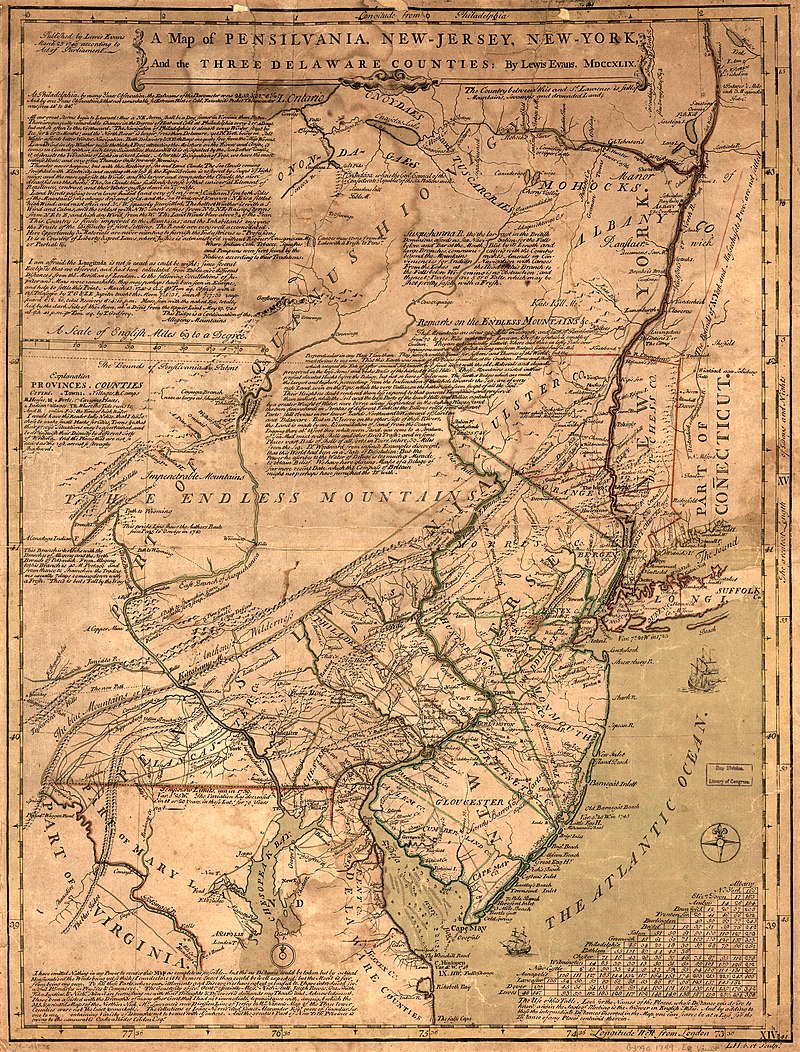
One of John Montresor's major accomplishments is the strategic map of the Hudson River, one of the most detailed maps of the New York City area during the American Revolution, first published in 1775. The map extends from Lake Champlain down the Hudson to Long Island, with insets of Lake Champlain and the White Hills in the upper Connecticut Valley.
John Montresor was promoted to captain in 1776, returned to England in 1779, and retired from the army. He died in prison 20 years later, accused of excessive spending while in the service.






























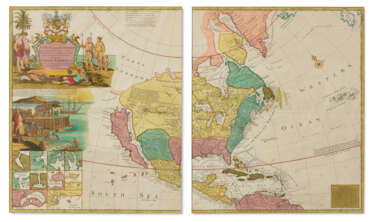




















![[FOSTER, George (fl. 1735-1740)] – Robert SAYER (1735-1794).](/assets/image/picture_4084812/eead4/rh5-akqejyjmaug43ncvjup-kaf74qit0wesbihrffucjgdpjhfhqhahybonknkw1719908507jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[FOSTER, George (fl. 1735-1740)] – Robert SAYER (1735-1794).](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4084812/eead4/rh5-akqejyjmaug43ncvjup-kaf74qit0wesbihrffucjgdpjhfhqhahybonknkw1719908507jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


![[FOSTER, George (fl. 1735-1740)] – Robert SAYER (1735-1794).](/assets/image/picture_4361590/74b5a/13dca103bbf8f022f3e8439e6036e3811733871600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[FOSTER, George (fl. 1735-1740)] – Robert SAYER (1735-1794).](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4361590/74b5a/13dca103bbf8f022f3e8439e6036e3811733871600jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)