athanasius kircher

Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.


Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.


Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.


Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.


Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.



Paul Delaroche was renowned for his meticulously detailed historical scenes that captured both the essence and drama of bygone eras. Delaroche's work bridged the Neoclassical and Romantic movements, bringing to life figures and moments from both English and French history with a narrative intensity that resonated across Europe.
Paul Delaroche's education under the influential history painters Antoine-Jean Gros and Watelet instilled in him a profound understanding of historical accuracy and dramatic composition. His debut at the Paris Salon in 1822 marked the beginning of a highly successful career in which he received widespread acclaim, particularly for his poignant portrayal of "The Execution of Lady Jane Grey" in 1834, a piece that remains one of his most celebrated works.
Throughout his career, Paul Delaroche was committed to the educational aspect of art. In 1833, he became a professor at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, influencing a generation of artists with his emphasis on historical fidelity and narrative depth. His major works, like the grand mural "The Hemicycle," which he completed between 1837 and 1841, showcased his talent for orchestrating large-scale compositions that featured an array of historical figures.
Paul Delaroche's approach to history painting was characterized by a "philosophical analysis" of events, aiming to link historical truth with the nineteenth-century understanding of time and morality. His attention to detail and the emotional gravity of his subjects helped forge a visceral connection with viewers, making his works a staple in both public exhibitions and private collections.
For collectors and enthusiasts wishing to delve deeper into Delaroche's legacy or view his works, ongoing exhibitions and collections can be accessed through various art galleries and museums worldwide. To stay informed about such events and opportunities, consider signing up for updates focused on Paul Delaroche's works and their exhibition schedules.


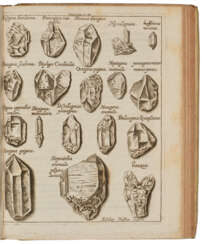
Filippo Bonanni or Buonanni was an Italian Jesuit scholar. His many works included treatises on fields ranging from anatomy to music. He created the earliest practical illustrated guide for shell collectors in 1681, for which he is considered a founder of conchology. He also published a study of lacquer that has been of lasting value since his death.
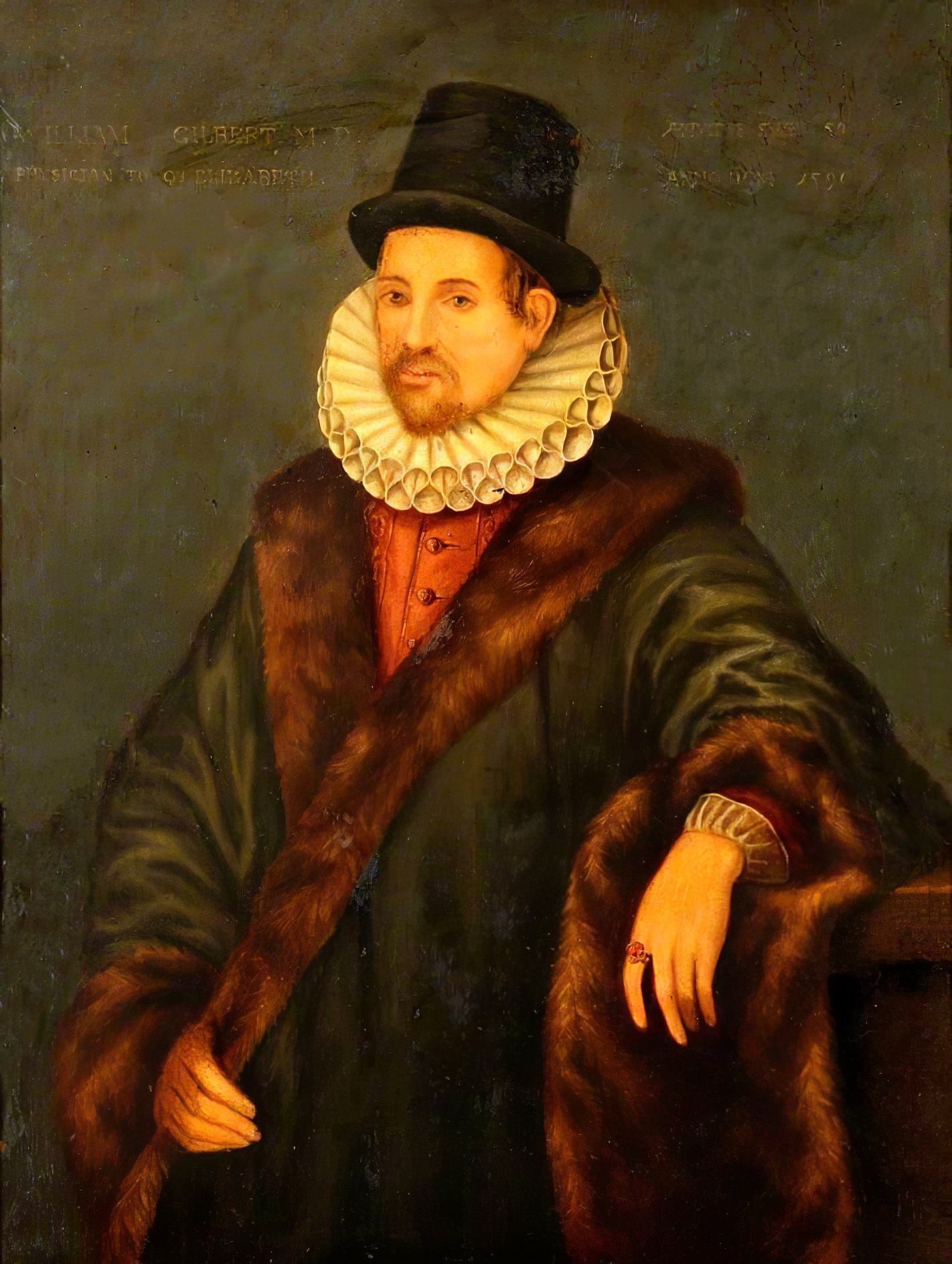


William Gilbert was a British physicist and medical scientist famous for pioneering the study of magnetic and electrical phenomena.
After receiving a medical degree, Gilbert settled in London and began his research. In his major work De Magnete, Magneticisque Corporibus, et de Magno Magnete Tellure (On Magnetic Stones and Magnetic Bodies and the Great Magnet of the Earth), published in 1600, the scientist describes in detail his studies of magnetic bodies and electric attraction.
After years of experimentation, he came to the conclusion that the compass arrow points north-south and downward because the Earth acts as a rod magnet. He was the first to use the terms electric attraction, electric force, and magnetic pole. Gilbert came to believe that the Earth rotates on its axis and that the fixed stars are not all the same distance from the Earth, and believed that the planets are held in their orbits by magnetism.


Filippo Bonanni or Buonanni was an Italian Jesuit scholar. His many works included treatises on fields ranging from anatomy to music. He created the earliest practical illustrated guide for shell collectors in 1681, for which he is considered a founder of conchology. He also published a study of lacquer that has been of lasting value since his death.


Georg Hieronymus Welsch (or Welschius) was a German physician, translator and writer.
He studied medicine in Tübingen, Strasbourg and Padua. Having lost the ability to speak as a result of illness, he decided to settle in Augsburg and educate himself. Welsch studied Greek, Latin, Hebrew and Arabic. Then in Italy he visited numerous libraries, including the Vatican library, and collected books, including the Turkish calendar.
Georg Welsch wrote several books on medicine and fossil curiosities, and researched texts on astronomy and medicine from the Ottoman Empire. He is best known for his translation of the calendar of Avicenna and Sheikh Abul-Wafa. Welsch was also a member of the Academia Naturae Curiosorum.