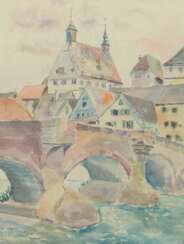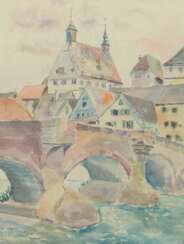caspar

Caspar David Friedrich was a German painter of the late eighteenth and first half of the nineteenth centuries. He is known as a painter, draughtsman, watercolorist and is considered a key figure of early German Romanticism.
Caspar David Friedrich was the leader of the so-called Dresden Romantics, known for their emotionally intense landscapes. The artist himself viewed nature as a reflection of the soul and a symbol of religious experiences, creating works with deep symbolism. He actively used landscape to convey his emotions and used the technique of transporting the viewer into the virtual space of the painting. His works often depicted figures immersed in the contemplation of nature, facing infinity, which created a unique effect.


Caspar David Friedrich was a German painter of the late eighteenth and first half of the nineteenth centuries. He is known as a painter, draughtsman, watercolorist and is considered a key figure of early German Romanticism.
Caspar David Friedrich was the leader of the so-called Dresden Romantics, known for their emotionally intense landscapes. The artist himself viewed nature as a reflection of the soul and a symbol of religious experiences, creating works with deep symbolism. He actively used landscape to convey his emotions and used the technique of transporting the viewer into the virtual space of the painting. His works often depicted figures immersed in the contemplation of nature, facing infinity, which created a unique effect.
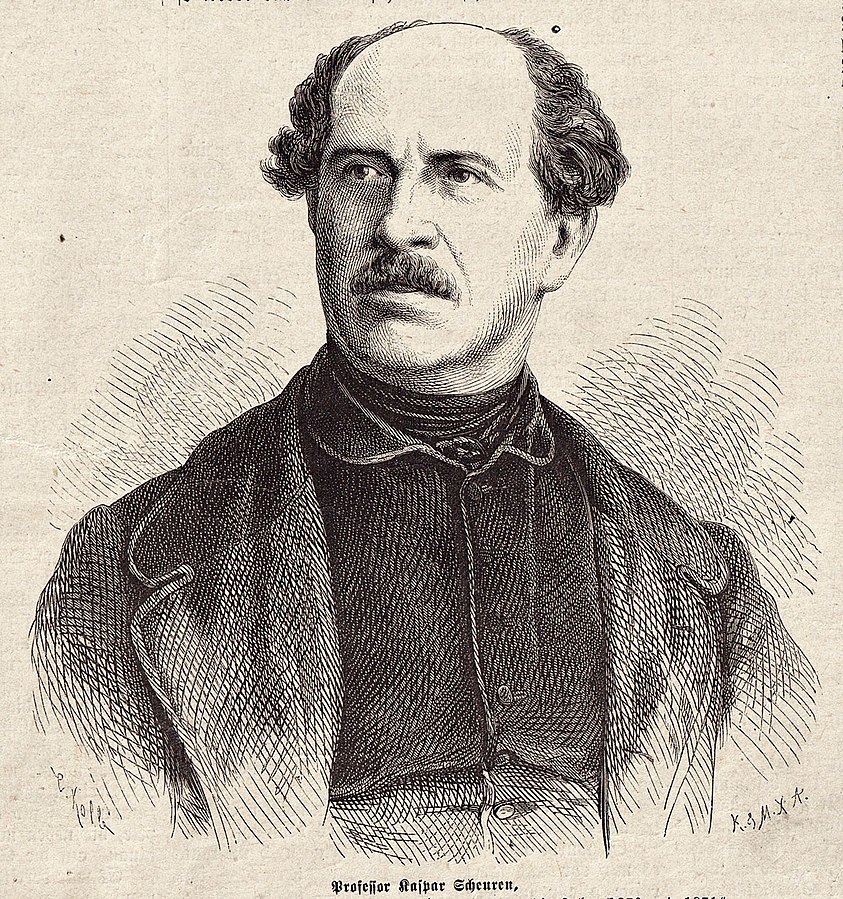


Caspar Johann Nepomuk Scheuren is a German painter and illustrator.
After receiving an elementary art education from his painter father Egidius Scheuren, he studied landscape painting at the Düsseldorf Academy of Art, where he later became a professor.
Caspar Scheuren gradually developed an allegorical style of landscape painting, including motifs from stories and legends of the Rhine. He produced more than 300 oil paintings, 600 watercolors and 400 engravings.
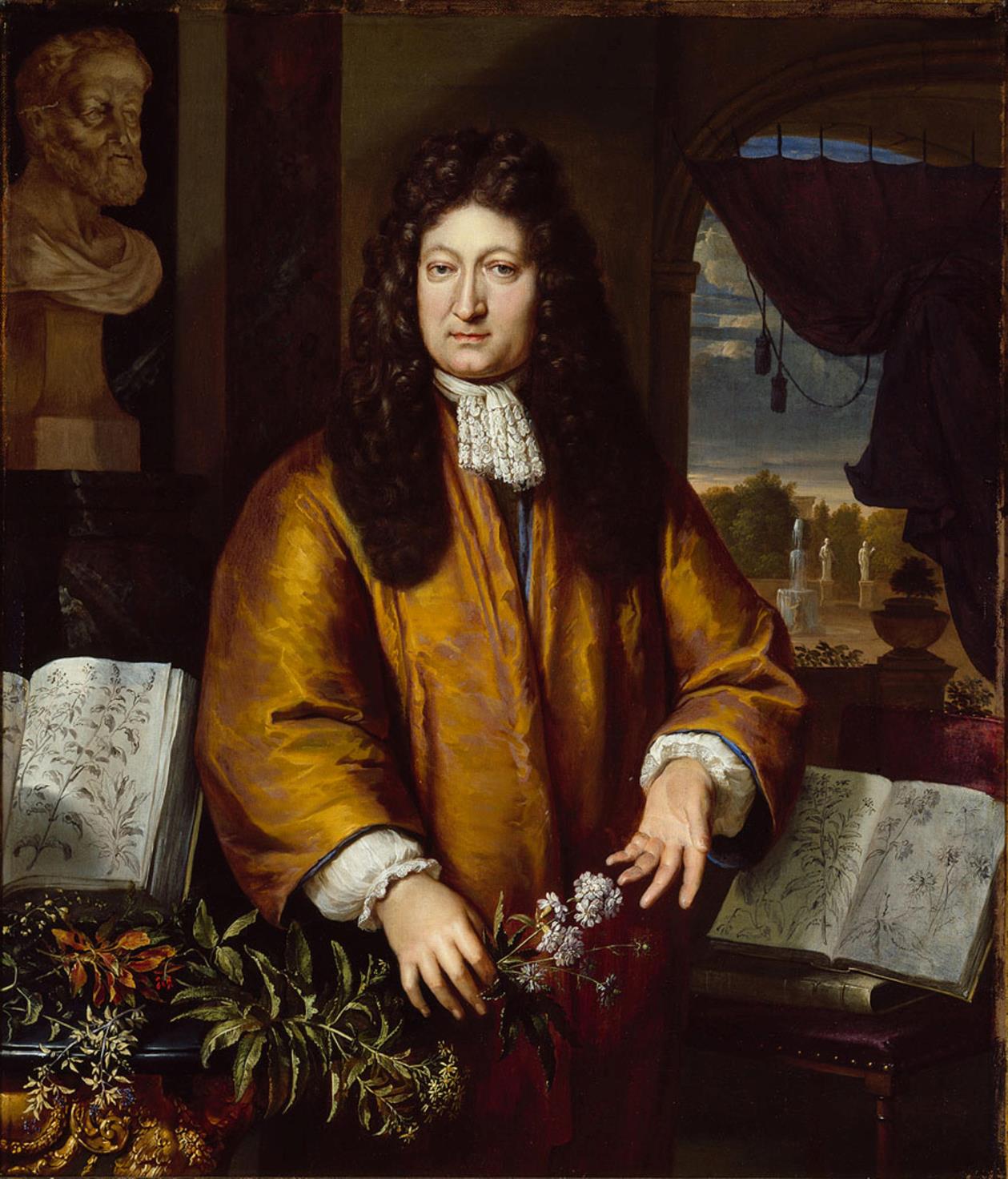

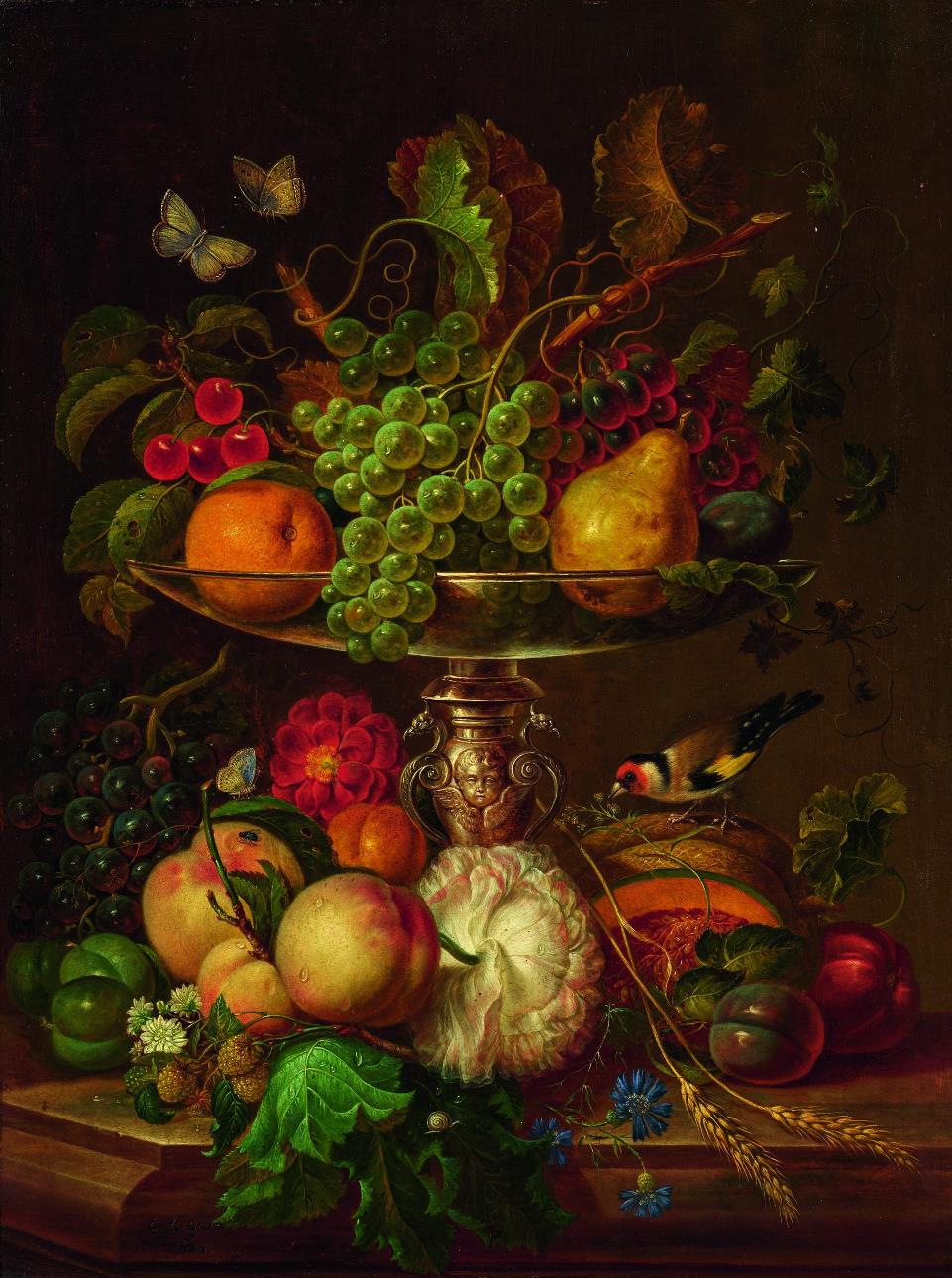


Jan Commelin (Dutch: Jan Commelin or Jan Commelijn), also Johannes Commelin, was a Dutch botanist.
Jan Commelin is the son of the historian Isaac Commelin. He was a professor of botany and director of the Amsterdam Botanical Gardens. Jan Commelin wrote many scientific works on botany, notably compiling the first volume of descriptions of East and West Indian plants. The second volume was written by Jan's nephew, the botanist Caspar Kommelin, who expanded the earlier descriptions and added notes on African plants.

Caspar Commelin was a Dutch botanist and mycologist.
Caspar Commelin was trained as a medical doctor, practiced botanical science and worked on books that were left unfinished due to the death of his uncle, botanist Jan Commelin. Caspar was mainly interested in exotic plants.
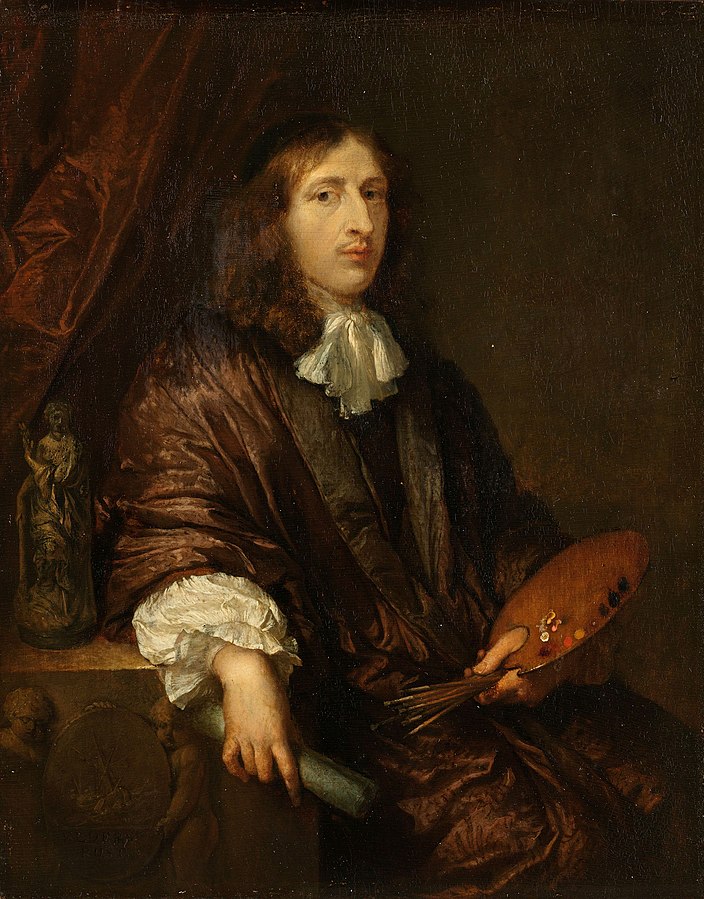


Caspar Netscher was a Dutch painter of the Golden Age of Dutch painting, known for his portraits. Netscher chose subjects from the life of the Dutch elegant and wealthy class; he painted many small portraits - mostly of women; some of them historical. After spending some time in Paris, he painted several persons belonging to the court of Louis XIV. In addition to the above-mentioned usual subjects, he depicted sometimes historical and biblical scenes.
Caspar Netscher's paintings were kept in many art galleries: in the Louvre, Amsterdam, Florence, in several private collections in England and in many other places. In the Hermitage at the beginning of the 20th century there were six of his paintings, including a portrait of the artist himself and a portrait of Mary Stuart, painted in 1683; today only two works have survived.


Jan Commelin (Dutch: Jan Commelin or Jan Commelijn), also Johannes Commelin, was a Dutch botanist.
Jan Commelin is the son of the historian Isaac Commelin. He was a professor of botany and director of the Amsterdam Botanical Gardens. Jan Commelin wrote many scientific works on botany, notably compiling the first volume of descriptions of East and West Indian plants. The second volume was written by Jan's nephew, the botanist Caspar Kommelin, who expanded the earlier descriptions and added notes on African plants.

Caspar Commelin was a Dutch botanist and mycologist.
Caspar Commelin was trained as a medical doctor, practiced botanical science and worked on books that were left unfinished due to the death of his uncle, botanist Jan Commelin. Caspar was mainly interested in exotic plants.
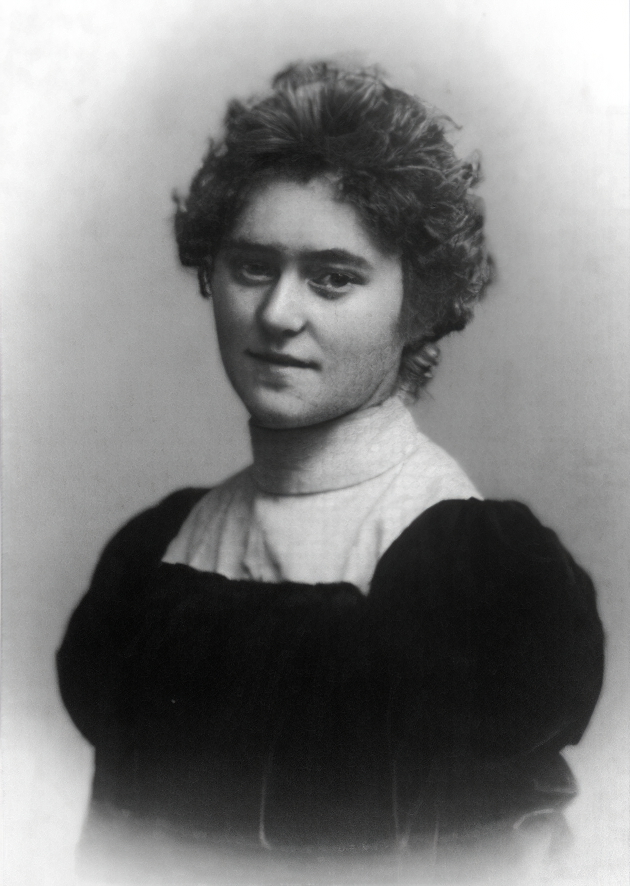


Maria Caspar-Filser was a German painter. She lived and worked mainly in Munich.
In 1913, she was the only woman among the founding members of the artists' association Münchener Neue Secession. In 1925 she became the first German woman painter to be awarded the title of professor. She taught at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich.
Caspar-Filser primarily painted flowers, gardens and landscapes, influenced equally by Impressionism and Expressionism.
The Nazis considered Caspar-Filser's paintings "degenerate".
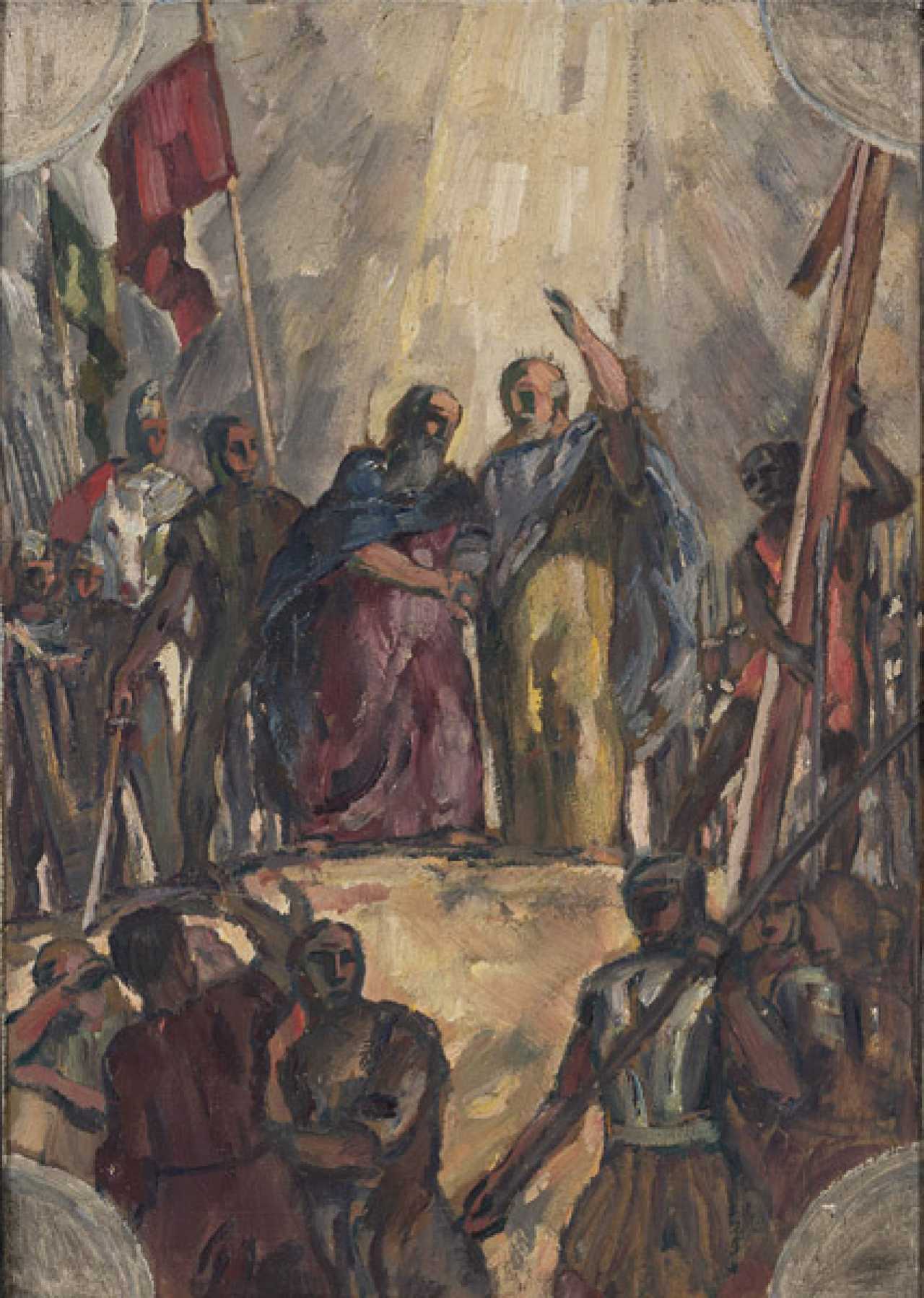


Karl Caspar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Caspar studied at the Art Academy in Stuttgart and the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich. In 1904 he became a member of the Stuttgart Artists' Union (Stuttgarter Künstlerbund), in 1906 he joined the German Artists' Union (Deutscher Künstlerbund). In 1913 he became one of the founders of the New Munich Secession, becoming its chairman in 1919.
Karl Caspar's creative field was painting and drawing with Impressionist and Expressionist influences in various genres, from Christian subjects to the nude genre.
From 1922 to 1937, Karl Caspar was professor and then president of the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich. In 1937, his works were exhibited at the Exhibition of Degenerate Art organized by the Nazis in Munich, but many of them were then withdrawn from German museums and state collections and destroyed. After the end of World War II, Karl Caspar returned to teaching: in 1948 he became one of the founders of the Bavarian Academy of Fine Arts, and in 1955 he became an academician of the Berlin Academy of Arts. He participated in the Venice Biennale and was awarded the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1950.
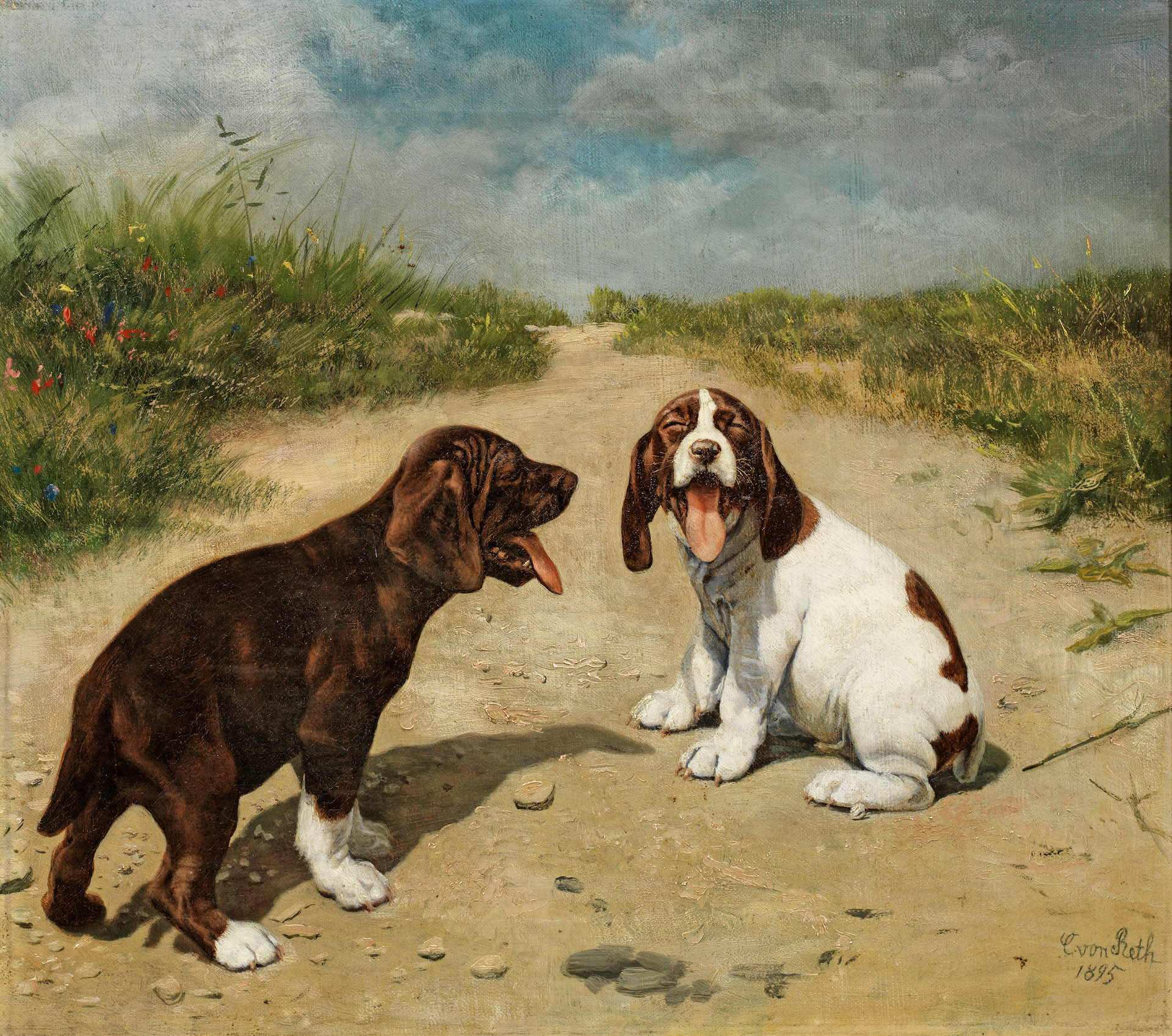



Caspar von Reth was a German realist painter. Master of hunting and domestic animal scenes.

Jan Commelin (Dutch: Jan Commelin or Jan Commelijn), also Johannes Commelin, was a Dutch botanist.
Jan Commelin is the son of the historian Isaac Commelin. He was a professor of botany and director of the Amsterdam Botanical Gardens. Jan Commelin wrote many scientific works on botany, notably compiling the first volume of descriptions of East and West Indian plants. The second volume was written by Jan's nephew, the botanist Caspar Kommelin, who expanded the earlier descriptions and added notes on African plants.

Caspar Commelin was a Dutch botanist and mycologist.
Caspar Commelin was trained as a medical doctor, practiced botanical science and worked on books that were left unfinished due to the death of his uncle, botanist Jan Commelin. Caspar was mainly interested in exotic plants.


Caspar Johann Nepomuk Scheuren is a German painter and illustrator.
After receiving an elementary art education from his painter father Egidius Scheuren, he studied landscape painting at the Düsseldorf Academy of Art, where he later became a professor.
Caspar Scheuren gradually developed an allegorical style of landscape painting, including motifs from stories and legends of the Rhine. He produced more than 300 oil paintings, 600 watercolors and 400 engravings.


Caspar von Reth was a German realist painter. Master of hunting and domestic animal scenes.


Karl Caspar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Caspar studied at the Art Academy in Stuttgart and the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich. In 1904 he became a member of the Stuttgart Artists' Union (Stuttgarter Künstlerbund), in 1906 he joined the German Artists' Union (Deutscher Künstlerbund). In 1913 he became one of the founders of the New Munich Secession, becoming its chairman in 1919.
Karl Caspar's creative field was painting and drawing with Impressionist and Expressionist influences in various genres, from Christian subjects to the nude genre.
From 1922 to 1937, Karl Caspar was professor and then president of the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich. In 1937, his works were exhibited at the Exhibition of Degenerate Art organized by the Nazis in Munich, but many of them were then withdrawn from German museums and state collections and destroyed. After the end of World War II, Karl Caspar returned to teaching: in 1948 he became one of the founders of the Bavarian Academy of Fine Arts, and in 1955 he became an academician of the Berlin Academy of Arts. He participated in the Venice Biennale and was awarded the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1950.


Maria Caspar-Filser was a German painter. She lived and worked mainly in Munich.
In 1913, she was the only woman among the founding members of the artists' association Münchener Neue Secession. In 1925 she became the first German woman painter to be awarded the title of professor. She taught at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich.
Caspar-Filser primarily painted flowers, gardens and landscapes, influenced equally by Impressionism and Expressionism.
The Nazis considered Caspar-Filser's paintings "degenerate".


Caspar David Friedrich was a German painter of the late eighteenth and first half of the nineteenth centuries. He is known as a painter, draughtsman, watercolorist and is considered a key figure of early German Romanticism.
Caspar David Friedrich was the leader of the so-called Dresden Romantics, known for their emotionally intense landscapes. The artist himself viewed nature as a reflection of the soul and a symbol of religious experiences, creating works with deep symbolism. He actively used landscape to convey his emotions and used the technique of transporting the viewer into the virtual space of the painting. His works often depicted figures immersed in the contemplation of nature, facing infinity, which created a unique effect.


Caspar Netscher was a Dutch painter of the Golden Age of Dutch painting, known for his portraits. Netscher chose subjects from the life of the Dutch elegant and wealthy class; he painted many small portraits - mostly of women; some of them historical. After spending some time in Paris, he painted several persons belonging to the court of Louis XIV. In addition to the above-mentioned usual subjects, he depicted sometimes historical and biblical scenes.
Caspar Netscher's paintings were kept in many art galleries: in the Louvre, Amsterdam, Florence, in several private collections in England and in many other places. In the Hermitage at the beginning of the 20th century there were six of his paintings, including a portrait of the artist himself and a portrait of Mary Stuart, painted in 1683; today only two works have survived.


Caspar Netscher was a Dutch painter of the Golden Age of Dutch painting, known for his portraits. Netscher chose subjects from the life of the Dutch elegant and wealthy class; he painted many small portraits - mostly of women; some of them historical. After spending some time in Paris, he painted several persons belonging to the court of Louis XIV. In addition to the above-mentioned usual subjects, he depicted sometimes historical and biblical scenes.
Caspar Netscher's paintings were kept in many art galleries: in the Louvre, Amsterdam, Florence, in several private collections in England and in many other places. In the Hermitage at the beginning of the 20th century there were six of his paintings, including a portrait of the artist himself and a portrait of Mary Stuart, painted in 1683; today only two works have survived.


Caspar Johann Nepomuk Scheuren is a German painter and illustrator.
After receiving an elementary art education from his painter father Egidius Scheuren, he studied landscape painting at the Düsseldorf Academy of Art, where he later became a professor.
Caspar Scheuren gradually developed an allegorical style of landscape painting, including motifs from stories and legends of the Rhine. He produced more than 300 oil paintings, 600 watercolors and 400 engravings.


Maria Caspar-Filser was a German painter. She lived and worked mainly in Munich.
In 1913, she was the only woman among the founding members of the artists' association Münchener Neue Secession. In 1925 she became the first German woman painter to be awarded the title of professor. She taught at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich.
Caspar-Filser primarily painted flowers, gardens and landscapes, influenced equally by Impressionism and Expressionism.
The Nazis considered Caspar-Filser's paintings "degenerate".



Maria Caspar-Filser was a German painter. She lived and worked mainly in Munich.
In 1913, she was the only woman among the founding members of the artists' association Münchener Neue Secession. In 1925 she became the first German woman painter to be awarded the title of professor. She taught at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich.
Caspar-Filser primarily painted flowers, gardens and landscapes, influenced equally by Impressionism and Expressionism.
The Nazis considered Caspar-Filser's paintings "degenerate".


Maria Caspar-Filser was a German painter. She lived and worked mainly in Munich.
In 1913, she was the only woman among the founding members of the artists' association Münchener Neue Secession. In 1925 she became the first German woman painter to be awarded the title of professor. She taught at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich.
Caspar-Filser primarily painted flowers, gardens and landscapes, influenced equally by Impressionism and Expressionism.
The Nazis considered Caspar-Filser's paintings "degenerate".


Caspar Netscher was a Dutch painter of the Golden Age of Dutch painting, known for his portraits. Netscher chose subjects from the life of the Dutch elegant and wealthy class; he painted many small portraits - mostly of women; some of them historical. After spending some time in Paris, he painted several persons belonging to the court of Louis XIV. In addition to the above-mentioned usual subjects, he depicted sometimes historical and biblical scenes.
Caspar Netscher's paintings were kept in many art galleries: in the Louvre, Amsterdam, Florence, in several private collections in England and in many other places. In the Hermitage at the beginning of the 20th century there were six of his paintings, including a portrait of the artist himself and a portrait of Mary Stuart, painted in 1683; today only two works have survived.


Caspar Johann Nepomuk Scheuren is a German painter and illustrator.
After receiving an elementary art education from his painter father Egidius Scheuren, he studied landscape painting at the Düsseldorf Academy of Art, where he later became a professor.
Caspar Scheuren gradually developed an allegorical style of landscape painting, including motifs from stories and legends of the Rhine. He produced more than 300 oil paintings, 600 watercolors and 400 engravings.


Caspar Netscher was a Dutch painter of the Golden Age of Dutch painting, known for his portraits. Netscher chose subjects from the life of the Dutch elegant and wealthy class; he painted many small portraits - mostly of women; some of them historical. After spending some time in Paris, he painted several persons belonging to the court of Louis XIV. In addition to the above-mentioned usual subjects, he depicted sometimes historical and biblical scenes.
Caspar Netscher's paintings were kept in many art galleries: in the Louvre, Amsterdam, Florence, in several private collections in England and in many other places. In the Hermitage at the beginning of the 20th century there were six of his paintings, including a portrait of the artist himself and a portrait of Mary Stuart, painted in 1683; today only two works have survived.
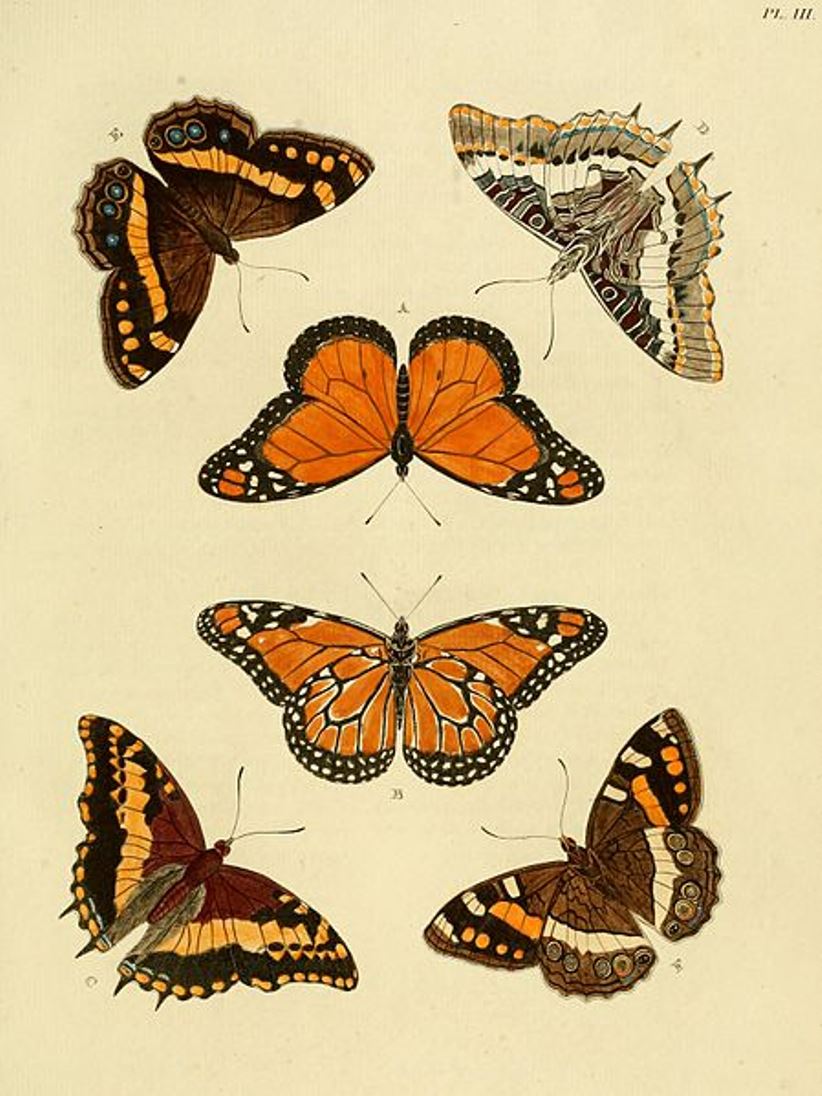


Pieter Cramer was a Dutch merchant and traveler and entomologist.
A cloth and wool merchant, Cramer traveled the world and amassed an extensive collection of sea shells, fossils, and various insects. Many colorful butterflies and moths were collected in Surinam, Ceylon, Sierra Leone, and the Dutch East Indies - countries with which Holland had colonial or trade ties. Kramer hired the artist Gerrit Wartenaar Lambertz to sketch butterfly specimens collected not only by him but also by other Dutch collectors. The illustrations were very numerous, and Kramer, together with the naturalist and entomologist Caspar Stoll, decided to publish them.
The resulting encyclopedia, De Uitlandsche Kapellen, is one of the key works in the history of entomology. The scales from Asia, Africa and the Americas are depicted in life-size and hand-colored engravings. It was the first book on exotic butterflies to use the new system of animal classification developed by Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778). Over 1,658 species of butterflies were described and illustrated on 400 plates. Many species were depicted and named for the first time.

Caspar Stoll was a Dutch naturalist and entomologist of German descent.
Caspar Stoll became known for his work on the historical illustrated encyclopedia De Uitlandsche Kapellen, a butterfly encyclopedia started by merchant and entomologist Peter Cramer. Butterflies and moths were collected by him on his travels in Surinam, Ceylon, Sierra Leone, and the Dutch East Indies, countries with which Holland had colonial or trade ties. Stoll continued and completed the publication of volumes of this work after Kramer's death. He also published several of his own works on other groups of insects.


Pieter Cramer was a Dutch merchant and traveler and entomologist.
A cloth and wool merchant, Cramer traveled the world and amassed an extensive collection of sea shells, fossils, and various insects. Many colorful butterflies and moths were collected in Surinam, Ceylon, Sierra Leone, and the Dutch East Indies - countries with which Holland had colonial or trade ties. Kramer hired the artist Gerrit Wartenaar Lambertz to sketch butterfly specimens collected not only by him but also by other Dutch collectors. The illustrations were very numerous, and Kramer, together with the naturalist and entomologist Caspar Stoll, decided to publish them.
The resulting encyclopedia, De Uitlandsche Kapellen, is one of the key works in the history of entomology. The scales from Asia, Africa and the Americas are depicted in life-size and hand-colored engravings. It was the first book on exotic butterflies to use the new system of animal classification developed by Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778). Over 1,658 species of butterflies were described and illustrated on 400 plates. Many species were depicted and named for the first time.

Caspar Stoll was a Dutch naturalist and entomologist of German descent.
Caspar Stoll became known for his work on the historical illustrated encyclopedia De Uitlandsche Kapellen, a butterfly encyclopedia started by merchant and entomologist Peter Cramer. Butterflies and moths were collected by him on his travels in Surinam, Ceylon, Sierra Leone, and the Dutch East Indies, countries with which Holland had colonial or trade ties. Stoll continued and completed the publication of volumes of this work after Kramer's death. He also published several of his own works on other groups of insects.


Maria Caspar-Filser was a German painter. She lived and worked mainly in Munich.
In 1913, she was the only woman among the founding members of the artists' association Münchener Neue Secession. In 1925 she became the first German woman painter to be awarded the title of professor. She taught at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich.
Caspar-Filser primarily painted flowers, gardens and landscapes, influenced equally by Impressionism and Expressionism.
The Nazis considered Caspar-Filser's paintings "degenerate".