neti
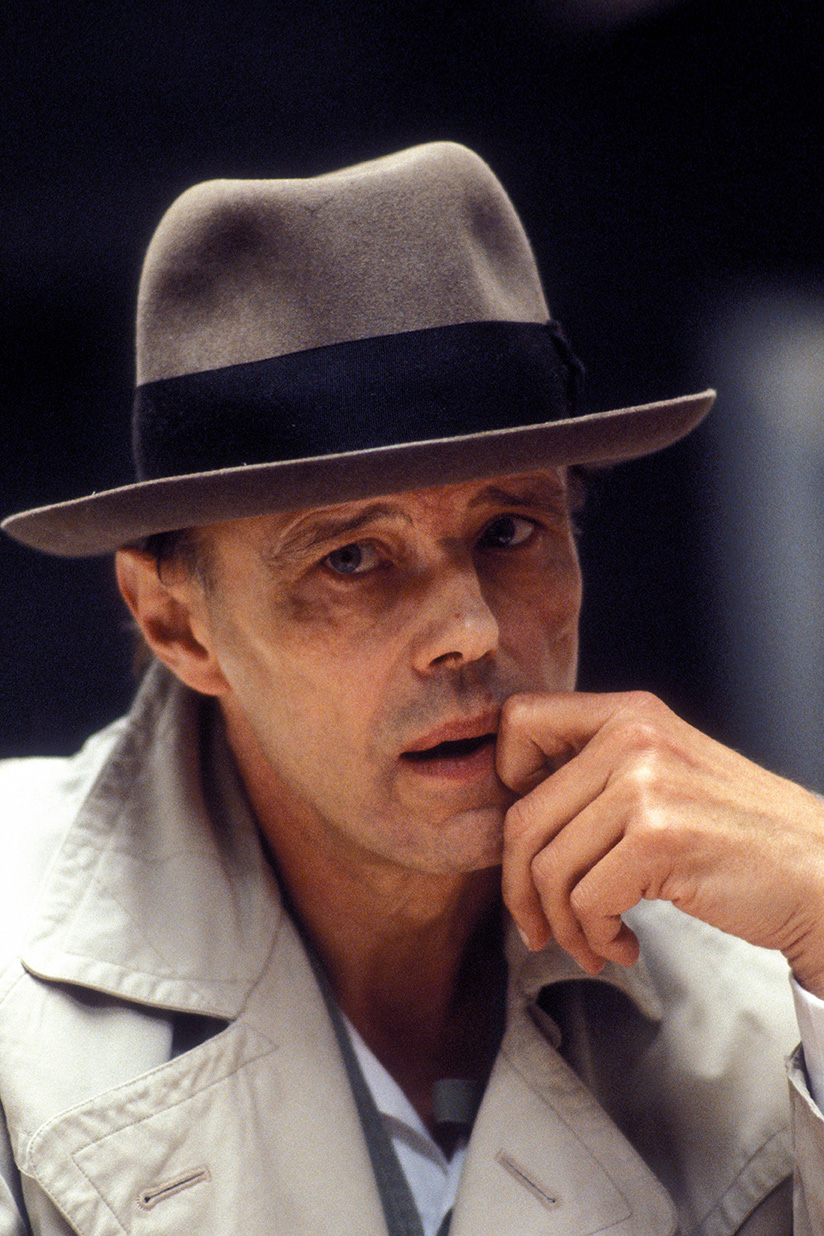

Joseph Heinrich Beuys was a German artist, renowned for his significant contributions to the realms of sculpture, painting, and installation art, which have left a lasting impact on the culture and art world. His work transcended traditional boundaries, merging art with social theory and politics, thus redefining the role of the artist in society. Beuys's unique approach to materials, incorporating substances like fat and felt, symbolized healing and insulation, reflecting his broader philosophical and ecological concerns.
Beuys's art was deeply influenced by his experiences during World War II and his academic background in natural sciences and sculpture. His concept of "social sculpture" proposed that art could transform society, emphasizing creativity as a fundamental component of human existence. This vision led him to use his performances, or "actions," as a medium to communicate his ideas, making him a pivotal figure in the Fluxus movement. Notable works such as "How to Explain Pictures to a Dead Hare" and "7000 Oaks" exemplify his innovative use of performance and environmental art to engage and challenge the public.
His legacy is preserved in major museums and galleries worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Modern in London. These institutions house key pieces that exemplify Beuys's diverse artistic output, from his early drawings and sculptures to his later installations and public interventions. His influence extends beyond the art world, impacting environmental activism and educational reform, underscoring his belief in the transformative power of art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Joseph Heinrich Beuys remains a figure of immense interest, not only for his groundbreaking artworks but also for his profound impact on contemporary art theory and practice. To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Beuys, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription ensures you are always in the loop regarding opportunities to engage with the enduring legacy of one of the most influential artists of the 20th century.
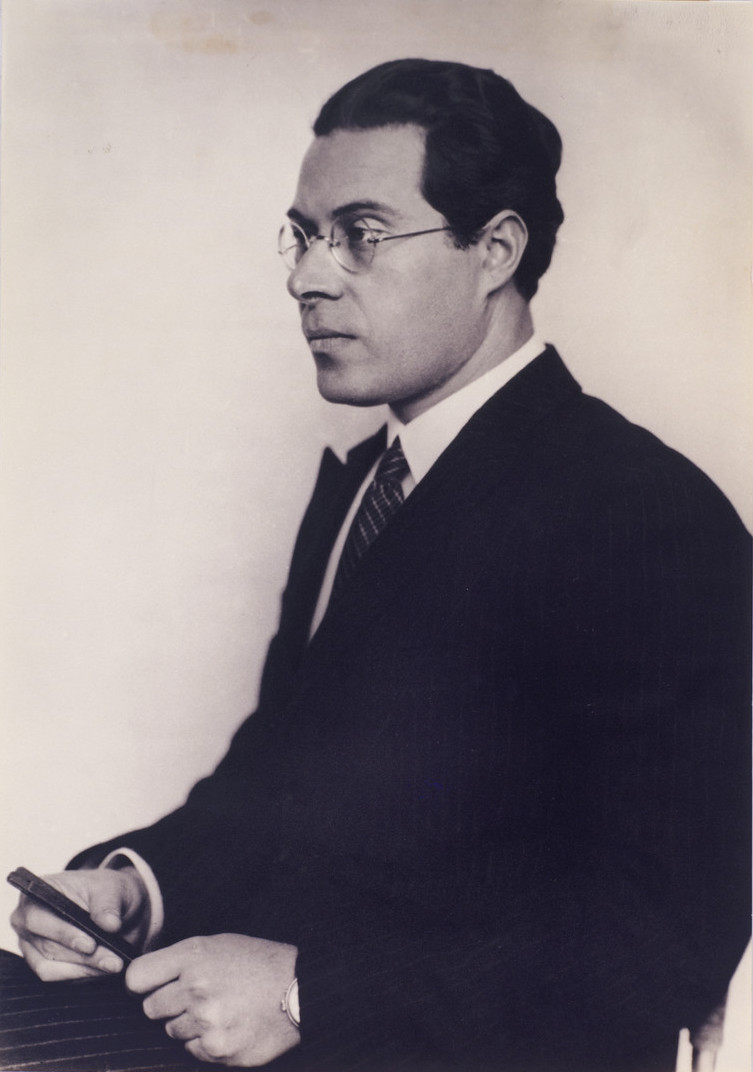


Laszlo Moholy-Nagy, a Hungarian-American artist, was a visionary in the integration of technology and art, profoundly influencing modern art education in the United States. His journey began in post-World War I Europe, where he immersed himself in the avant-garde art scene, eventually joining the Bauhaus school in Germany. There, Moholy-Nagy embraced various mediums, from photography and film to painting and sculpture, pioneering the movement known as the New Vision, which emphasized the unique perspectives that photography and film could offer compared to the human eye.
Laszlo Moholy-Nagy's innovative approach extended to photograms, a camera-less photographic technique that captures the shadows and silhouettes of objects placed on photosensitive paper. His exploration of light and shadow in this medium underscored his belief in the transformative power of art and technology. Beyond his technical achievements, Moholy-Nagy was a dedicated educator, shaping future generations of artists at the Bauhaus and later in Chicago, where he founded the New Bauhaus, which evolved into the Illinois Institute of Technology's Institute of Design.
His work is celebrated in various prestigious collections, including MoMA and the Smithsonian American Art Museum, where his contributions to modernism and design are acknowledged and revered. Moholy-Nagy's legacy is not only in his artistic output but also in his profound impact on art education and the philosophical discourse around art and technology.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Laszlo Moholy-Nagy's work offers a deep dive into the intersection of art, technology, and education. To stay informed about exhibitions and auctions related to Moholy-Nagy's works, consider subscribing to updates from art galleries and auction houses, ensuring you remain connected to the evolving appreciation and understanding of this pivotal figure's contributions.
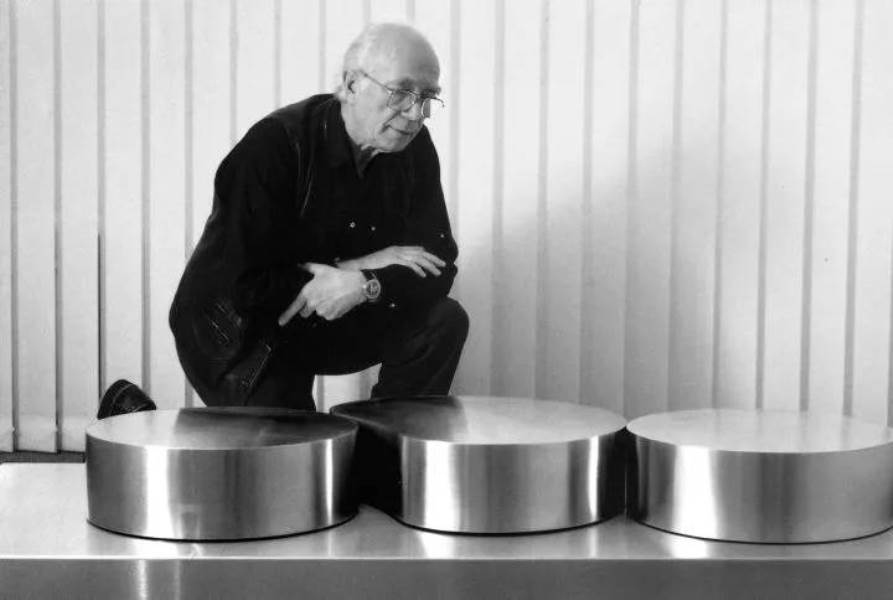



Friedrich Becker was a German artist, jeweler, and inventor of kinetic jewelry.
Friedrich Becker is one of the most influential jewelers of the second half of the twentieth century. He became known primarily for his avant-garde projects of kinetic jewelry and large kinetic objects.
Becker was interested in kinetics, the interaction of force and motion already during his apprenticeship years. He first trained as a mechanical engineer, then joined the aviation department. Only after World War II did he "make the reckless decision to become a jeweler." After training as a jeweler, he studied at the Werkkunstschule and then founded his own workshop in Düsseldorf, becoming a professor at the Düsseldorf University of Applied Sciences.
Becker experimented and supplemented various jewelry pieces with interchangeable stones and eventually developed kinetic jewelry. He was not only the inventor of kinetic jewelry, but also revolutionized the jewelry market with the introduction of stainless steel and synthetic gemstones. Each kinetic piece by Friedrich Becker is a perfect symbiosis of form, color and material.


Friedrich Becker was a German artist, jeweler, and inventor of kinetic jewelry.
Friedrich Becker is one of the most influential jewelers of the second half of the twentieth century. He became known primarily for his avant-garde projects of kinetic jewelry and large kinetic objects.
Becker was interested in kinetics, the interaction of force and motion already during his apprenticeship years. He first trained as a mechanical engineer, then joined the aviation department. Only after World War II did he "make the reckless decision to become a jeweler." After training as a jeweler, he studied at the Werkkunstschule and then founded his own workshop in Düsseldorf, becoming a professor at the Düsseldorf University of Applied Sciences.
Becker experimented and supplemented various jewelry pieces with interchangeable stones and eventually developed kinetic jewelry. He was not only the inventor of kinetic jewelry, but also revolutionized the jewelry market with the introduction of stainless steel and synthetic gemstones. Each kinetic piece by Friedrich Becker is a perfect symbiosis of form, color and material.
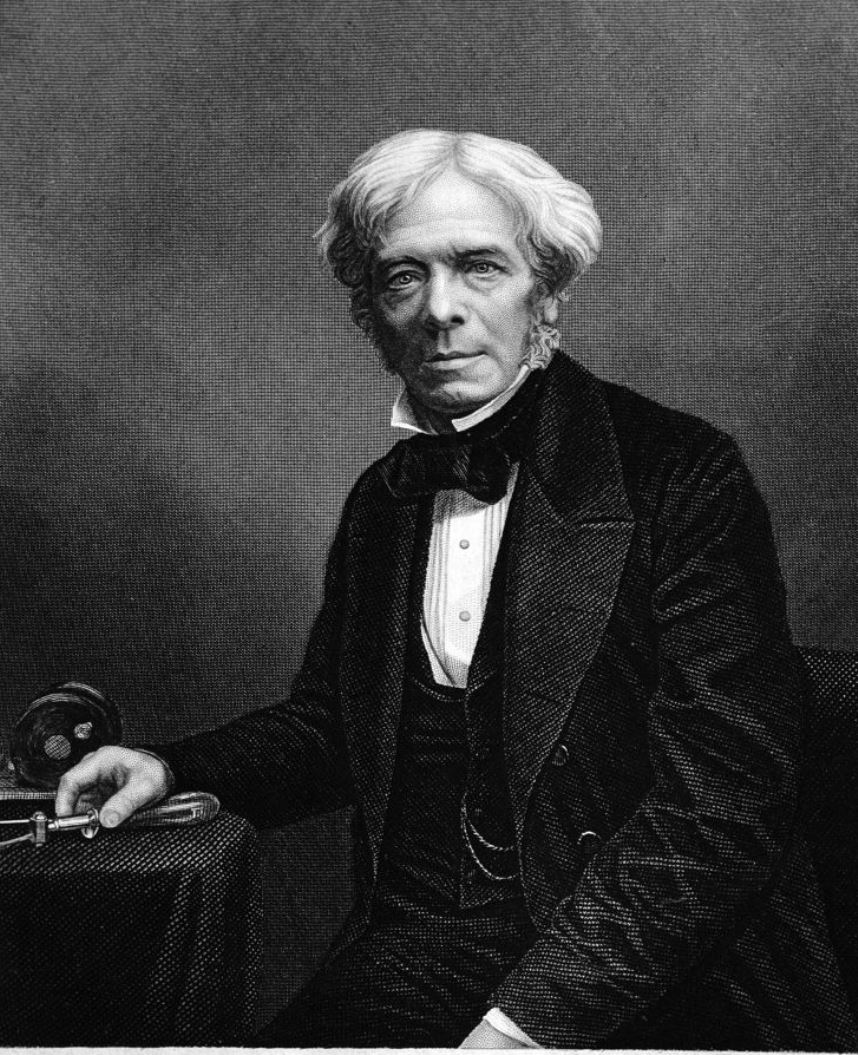


Michael Faraday was a British physicist and chemist, explorer and experimenter.
Faraday, because of his family's poverty, was unable to receive a formal education, but at the bookbinding shop in London where he worked, he read many books, including encyclopedias and textbooks on chemistry and physics. He persevered in self-education, attending hearings at the City Philosophical Society and later lectures by Sir Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution, who as a result took the able student on as an apprentice. In 1825 he replaced the seriously ill Davy in the management of the laboratory of the Royal Institution.
In 1833 Faraday was appointed to a research chair of chemistry created especially for him, where, among other achievements, the scientist liquefied various gases, including chlorine and carbon dioxide. His study of heating and lighting oils led to the discovery of benzene and other hydrocarbons, and he experimented extensively with various steel alloys and optical glasses. Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who presented his ideas in simple language. He is best known for his contributions to the understanding of electricity and electrochemistry. The concepts behind electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis were some of his most important discoveries. His electromagnetic research formed the basis of the electromagnetic equations that James Clerk Maxwell developed in the 1850s and 1860s.
Between 1831 and 1855, Faraday read a series of 30 papers before the Royal Society, which were published in his three-volume Experimental Investigations in Electricity. His bibliography numbers some 500 printed articles. By 1844 he had been elected a member of some 70 scientific societies, including the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences.