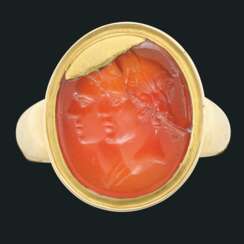
two-profile


Heinrich Eberhard was a German modernist painter.
Eberhard studied at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Stuttgart, and was decisively influenced in his artistic development by the modernist pioneer Adolf Helzel (1853-1934). In 1920 he became a member of the Stuttgart "Üecht Group", which also included Willy Baumeister and Oskar Schlemmer, and was a member of the legendary Hölzelkreis.
Eberhard's oeuvre includes oil paintings, drawings, prints and stained glass windows and is characterized by a stylistic pluralism between expressive naturalism, cubist influences and abstraction.
During the Nazi "Degenerate Art" campaign in Germany in 1937, some of the artist's paintings were removed from galleries and destroyed, but in 1943 he was allowed to exhibit one canvas that met the tastes of the authorities. After the war, Eberhard continued to create with success, participating in exhibitions.
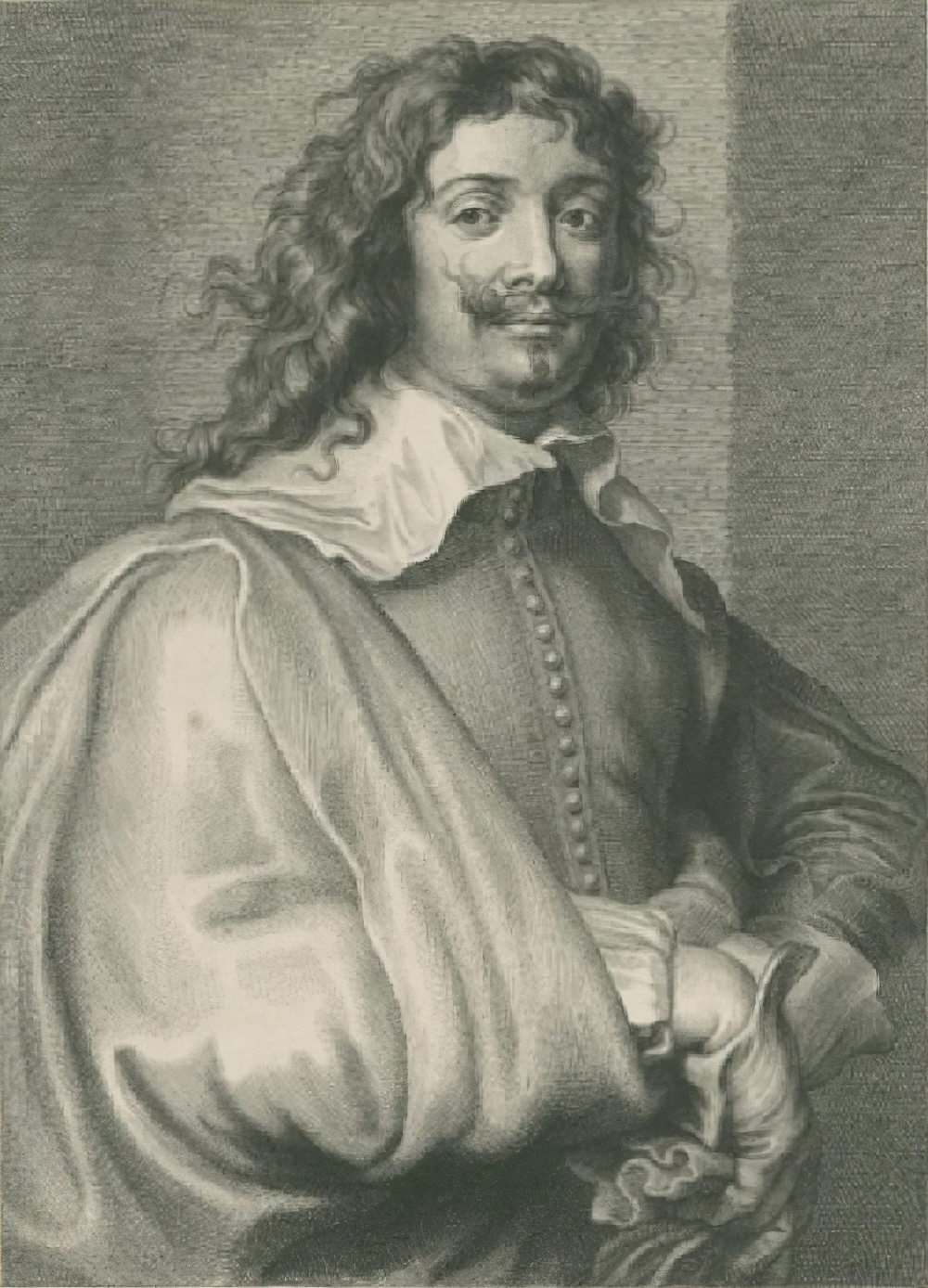


Adriaen Brouwer was a Flemish painter active in Flanders and the Dutch Republic in the first half of the 17th century. Brouwer was an important innovator of genre painting through his vivid depictions of peasants, soldiers and other "lower class" individuals engaged in drinking, smoking, card or dice playing, fighting, music making etc. in taverns or rural settings. Brouwer contributed to the development of the genre of tronies, i.e. head or facial studies, which investigate varieties of expression. In his final year he produced a few landscapes of a tragic intensity. Brouwer's work had an important influence on the next generation of Flemish and Dutch genre painters. Although Brouwer produced only a small body of work, Dutch masters Peter Paul Rubens and Rembrandt collected it.

Giovanni (Gio) Ponti was an Italian architect, industrial designer, furniture designer, artist, teacher, writer and publisher.


Giovanni (Gio) Ponti was an Italian architect, industrial designer, furniture designer, artist, teacher, writer and publisher.
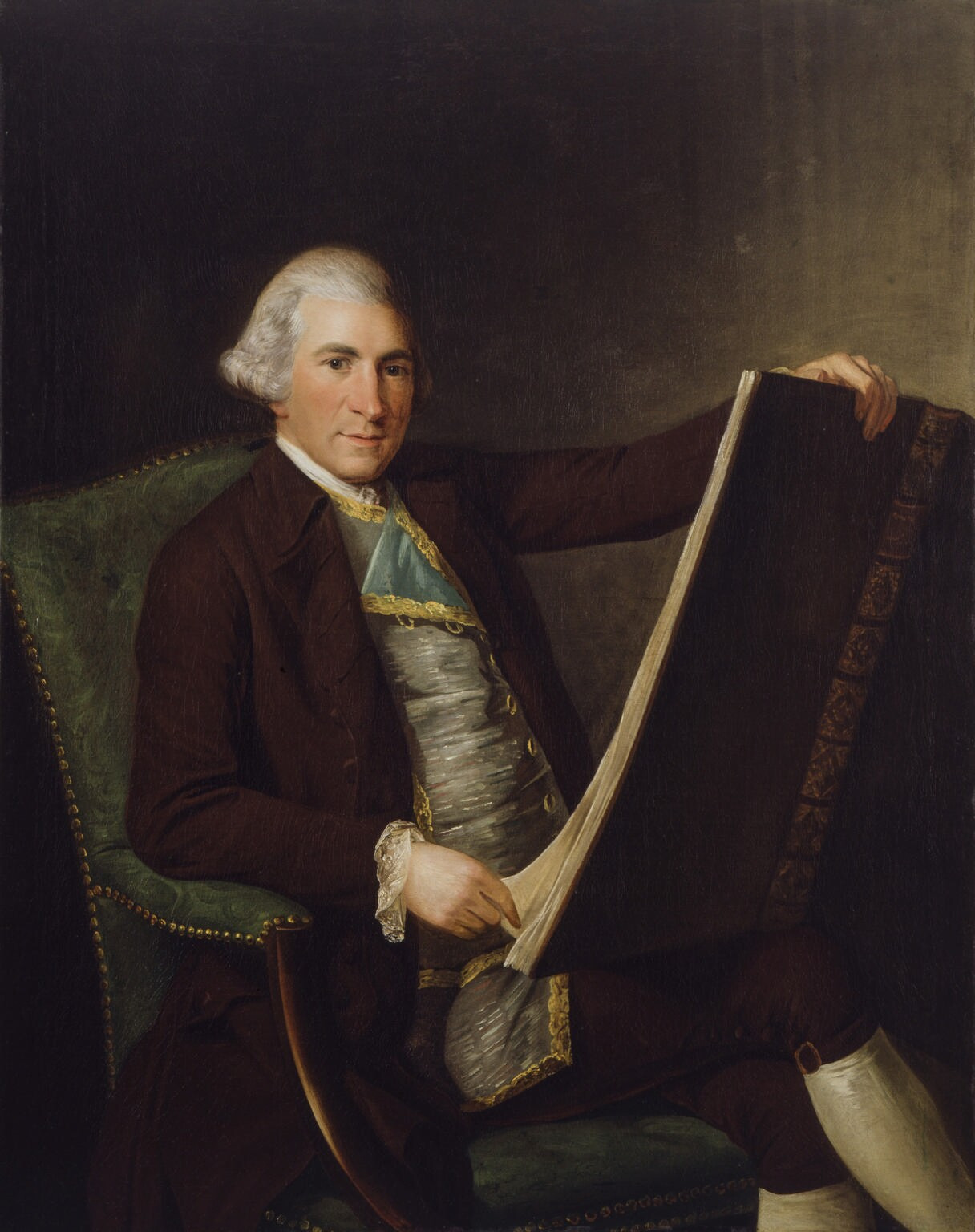


Robert Adam was a Scottish architect and interior designer, best known for his work during the Rococo and Neoclassical periods in Britain. He was born in 1728 in Kirkcauld, Scotland, and studied at the University of Edinburgh.
Adam began his career as an architect in 1754 and quickly became known for his innovative approaches to architecture and interior design. He developed his own style, which combined elements of rococo, classicism and antiquity.
He designed many buildings, including residences, palaces, churches, bridges and furniture. He also participated in designs for gardens and landscapes. One of Adam's best known projects is the Admiralty Building in London, built in the 1760s.
Adam was also known for his experiments with colour and form in interior design. He often used light colours, mirrors and mouldings to create larger and lighter spaces.
Robert Adam died in London in 1792, but his legacy continues to influence architecture and design in Britain and around the world.

Joseph Fernand Henri Léger was a French artist renowned for his innovative approach to Cubism and his transition towards a figurative, populist style. Born in Argentan, Orne, Lower Normandy, Léger's early career was marked by a stint as an architectural draftsman and a series of educational pursuits that eventually led him to Paris, where he embraced painting seriously. His artistic journey was significantly influenced by the bold abstractions of Cubism, characterized by geometric shapes and a vibrant palette, distinguishing his work from his contemporaries with what came to be known as "Tubism".
Léger's service in World War I profoundly impacted his artistic direction, leading him to adopt a 'mechanical' style that depicted the modern industrial world with sleek, tubular forms. This period saw creations like "Soldier with a Pipe" and "The Card Players," reflecting his war experiences and the mechanical aesthetics of the time. The post-war era encouraged Léger to explore the mechanical style further, evident in works like "The Bargeman" and "Mechanical Elements," highlighting the pace of technological advancement.
Throughout his career, Léger's work evolved, notably in the 1920s, where he aligned with Purist ideas, blending classicism with modernity. This phase is exemplified in "Woman with a Cat," showcasing a classical form with a modern, polished finish. By the 1930s, Léger's art took a more figurative, populist turn, aiming to democratize contemporary art and make it more accessible. His commitment to art education, especially for the common worker, underscored his belief in the social role of art.
For those intrigued by Joseph Fernand Henri Léger's groundbreaking contributions to modern art, his works can be found in prestigious museums worldwide. His legacy continues to inspire art collectors and enthusiasts alike. To stay updated on exhibitions and auction events featuring Léger's work, sign up for updates and embrace the unique opportunity to explore the richness of his artistic endeavors.
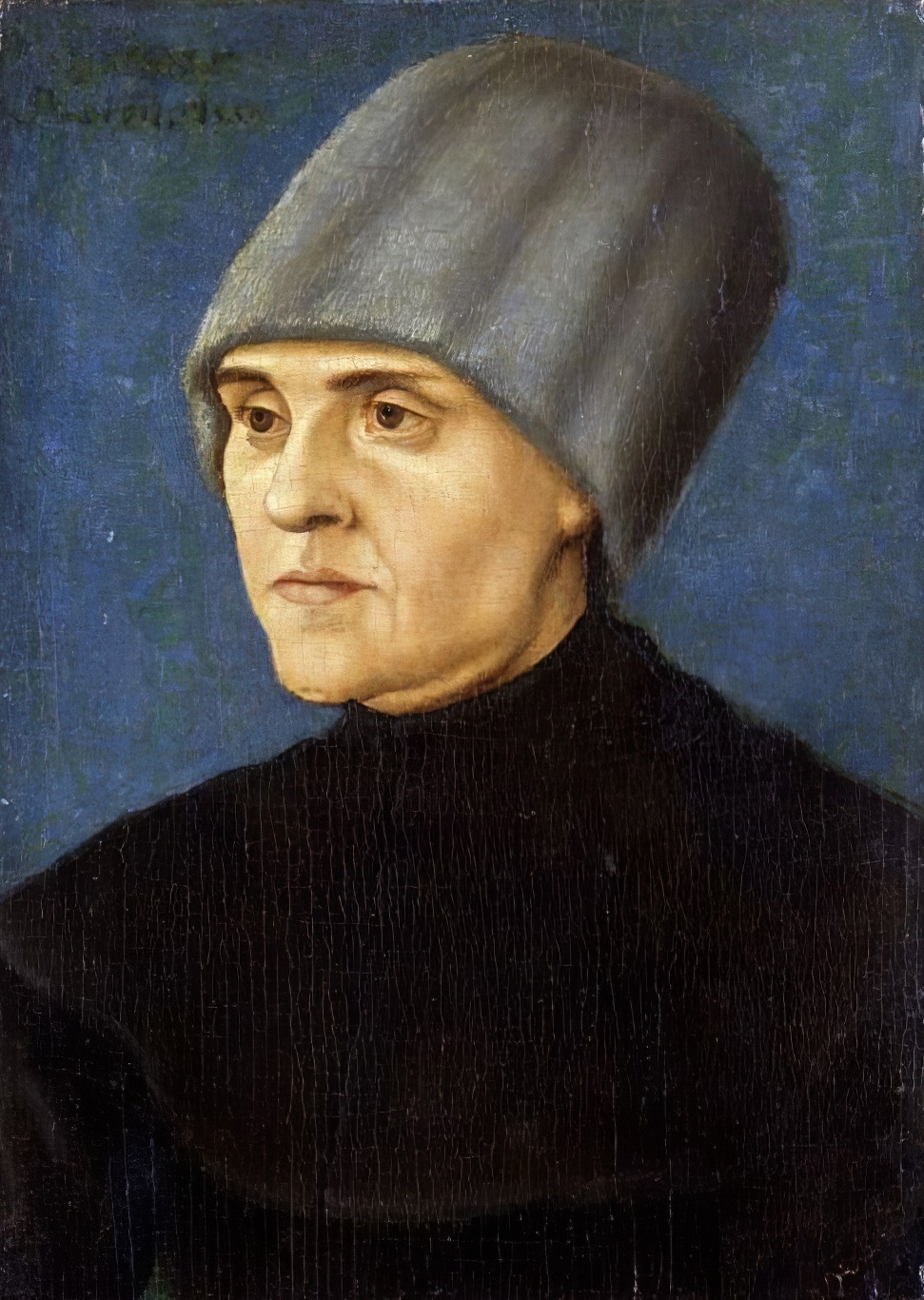


Hans Burgkmair the Elder was a German Renaissance painter, graphic artist and sculptor. He came from a family of painters. He studied painting with Martin Schongauer in Colmar from 1488.
Hans Burgkmayr was a versatile artist, working in various techniques including painting, woodcuts, stained glass designs and tapestries. He was known for his complex and detailed style, which included elements of naturalism and symbolism.
Burgkmayr's paintings often depicted religious and mythological themes, as well as historical events. His style is influenced by the Italian Renaissance, particularly in its attention to anatomical accuracy and use of perspective.
One of Hans Burgkmayr's significant contributions was in the field of engraving. His woodcuts were highly regarded for their technical skill and artistic quality.