Poets 19th century

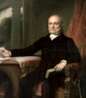
John Quincy Adams was an American politician and statesman, the sixth President of the United States (March 4, 1825 - March 4, 1829).
John Quincy Adams was the son of John Adams, the second President of the United States, and, of course, public service was his destiny. As a child, in 1778 he traveled to France with his father, who was then U.S. Commissioner to France. At the age of 14, Adams became personal secretary to Francis Dana, the U.S. Minister to Russia, serving as his father's secretary as well during the negotiation of the Treaty of Paris (1783). In 1787, the twenty-year-old Adams graduated from Harvard University and, after studying law, began practicing in Boston.
In addition to numerous diplomatic appointments, Quincy Adams served as a U.S. Senator from Massachusetts from 1803 to 1808. President James Madison appointed Adams U.S. minister to Russia in 1809, and Adams served until 1814. And under President James Monroe, he served as Secretary of State from 1817 to 1825 and is considered one of the best Secretaries of State in U.S. history.
John Quincy Adams won the 1824 presidential election in a four-way race against Henry Clay, William Crawford, and Andrew Jackson. As president, Adams supported a program to modernize the U.S. economy. But his popularity declined because of his approach to Native Americans, whom he supported against the demands of settlers from the west.
After losing the 1828 presidential election to Andrew Jackson, John Quincy Adams was elected to the House of Representatives, where he served as a representative from Massachusetts for the next 17 years. In the House of Representatives, Adams became one of the most vocal opponents of slavery. He consistently defended abolitionist views and policies, denouncing slavery as an immoral institution and attacking the interests of Southern slaveholders. During the U.S.-Mexican War of 1848, Adams was a leading opponent of the annexation of Texas, farsightedly predicting that it would lead to civil war.
After suffering two strokes, Adams died on February 23, 1848, at the age of 80. Had fate not predestined him to pursue politics, John Quincy Adams would have become a famous poet. He spent his life composing poems in various genres. After his death, many of his poems were collected and published in Poems on Religion and Society (1848).


Paul Allen is an American editor, historian, and poet.
He attended Brown University and later moved to Philadelphia, where he was editor of The Port Folio, The Gazette of the United States, and The Federal Republican. Success came to Allen in Baltimore, where he served as editor until his death at the Baltimore Morning Chronicle newspaper. Paul Allen also joined the Delphic Club, and his epic poem Noah (1821) was a success.


Richard Alsop was an 18th-century American writer and poet.
Alsop was one of the founders of the later famous literary group, the Hartford Witters. He wrote poetry in the journals The Political Greenhouse and The Echo, the latter soon becoming primarily concerned with satirical parodies of public speeches and articles of a political nature.
Alsop also published various translations from French and Italian.


Guillaume Apollinaire, real name Wilhelm Albert Vladimir Apollinaris de Wąż-Kostrowicki, a French poet of Polish descent, was a towering figure in the early 20th century's literary and art scenes. Known for his experimental verse and support of avant-garde art movements like Cubism and Surrealism, Apollinaire's work pushed the boundaries of traditional aesthetics and inspired a generation of artists and writers.
Guillaume Apollinaire's literary contributions were vast and varied. He was an early advocate for Cubism, a relationship most prominently seen in his collaborations with artists like Pablo Picasso. He not only wrote about art but also collected it, surrounding himself with works by modernist masters such as Henri Rousseau and Georges Braque. His Paris apartment was a small museum of modern art, filled with pieces he often sold to support his literary endeavors. This vibrant artistic environment fueled his creativity, leading to major works such as Alcools and Calligrammes, which explored the possibilities of poetic form and typography to represent visual and verbal content in a unified way.
Despite his innovative work in poetry and art criticism, Guillaume Apollinaire's life was marked by personal challenges, including a grievous injury during World War I. Yet, even these difficulties did not hinder his prolific output. Among his notable works during this period was the play Les Mamelles de Tirésias, which was performed in 1917 and is considered a precursor to theatrical Surrealism.
Apollinaire's influence extended beyond his lifetime, particularly through his mentoring of future Surrealist leaders like André Breton. His forward-thinking approach to art and literature made him a central figure in the transition from traditional to modernist forms in both fields.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Guillaume Apollinaire's work represents a nexus of literary brilliance and pivotal artistic movements. His life and work provide fascinating insights into the dynamic and transformative world of early 20th-century art and literature.
Sign up for updates on auctions and sales events featuring items related to Guillaume Apollinaire. Stay informed about opportunities to acquire unique artifacts that celebrate his legacy in the realms of poetry and art.


Antoine Vincent Arnault was a French playwright, fable poet and statesman.
Arnault was one of the most popular playwrights of the French Revolution and the First Empire and, like many writers of the time, he was also politically active. He carried out commissions for Napoleon Bonaparte and served him faithfully throughout his life.
Arnault wrote many plays and poems, among which his poem "Listok" about the fate of the emigrant was especially popular, it was repeatedly translated into different languages, including Russian.
His son was the playwright Lucien Arnault (1787-1863).


Sabine Baring-Gould was a Victorian British clergyman, poet, writer and folklorist.
He traveled extensively in Europe, studied at Clare College, Cambridge, was ordained in the Church of England in 1864, and was appointed vicar at Horbury. Baring-Gould was a polyglot and knew six languages. Despite his ministry, he had a serious interest in supernatural phenomena and in 1865 published a book called The Book of Werewolves.
In addition to this, Baring-Gould was interested in a wide range of subjects. His work is diverse and covered theology, history, poetry, hymns, fiction, biography, travel, social commentary, and folklore. Baring-Gould collected the folk songs of old English singers, personally visiting them and recording the words and music. In 1889 he published a collection of Songs of the West in four parts, of which he was proud, and also wrote several patriotic hymns.
Baring-Gould was a very prolific writer: during his life he wrote many novels, published short stories in periodicals, the popular "Curious Myths of the Middle Ages," and others, his bibliography numbering some 1,250 works.


Joel Barlow was an American statesman, diplomat, French politician and poet.
A graduate of Yale University, he briefly served as a chaplain in the Revolutionary Army. In 1784, Barlow founded the American Mercury, a weekly newspaper in Hartford, Connecticut, and was admitted to the bar in 1786. Along with John Trumbull and Timothy Dwight, he was a member of the Hartford Witters, a group of young writers.
Joel Barlow's fame was brought to him by his poetic work The Vision of Columbus (1787). It is a dialog between Christopher Columbus and an angel and covers the entire history of America to the end of the American Revolution. The poem was signed by many leading figures of the time, including George Washington and Benjamin Franklin, and was popular on both sides of the Atlantic. The author later reworked the poem into a more cynical epic called Columbiad.
In 1788, Barlow traveled to France as an agent for the Scioto Land Company and persuaded a group of Frenchmen to emigrate to America, who eventually founded the town of Gallipolis, Ohio. In Paris he became a liberal in religion and an advanced republican in politics; he took part in the French Revolution and was granted French citizenship.
In the literary field, Barlow is also known for his work The Hasty Pudding (1796). It is a humorous poem inspired by a longing for New England and cornmeal, containing vivid descriptions of rural scenes.
In 1795-97. Barlow was sent to Algeria on a diplomatic mission and returned to the United States in 1805. In 1811 he was appointed U.S. plenipotentiary to France. Barlow participated in Napoleon's retreat from Russia and died in Poland.


Joseph Bartlett was an American lawyer, politician, and poet.
Bartlett graduated from Harvard and began his law practice in Woburn. In 1782, he was elected a member of the Harvard chapter of the PBK. In 1803 he moved to Saco, Maine, where he was elected state senator the following year.
Joseph Bartlett was a man of eccentricity, with a very peculiar taste. His charisma and sharp wit ensured the success of his lectures. Bartlett is the author of the satirical poem Physiognomy, a Poem (1799).


Aubrey Vincent Beardsley was an English artist and illustrator, whose brief yet impactful career left an indelible mark on the art world. Born in Brighton, England, in 1872, Beardsley's work was instrumental in the development of the Art Nouveau movement, and he is often remembered for his bold, innovative illustrations that challenged Victorian sensibilities with their erotic and often grotesque imagery.
Beardsley's artistic journey was characterized by his unique ability to blend influences from Japanese woodcuts with the aesthetic of the English Art Nouveau movement. His illustrations are distinguished by their stark contrasts of black and white, intricate details, and the absence of middle tones, creating a dramatic and unmistakable style. He was particularly known for his illustrations for the limited edition of "Le Morte D'Arthur," which were celebrated for their elaborate detail and pre-Raphaelite influences, despite their sometimes grotesque details. This work, along with his contributions to "The Yellow Book" and illustrations for Oscar Wilde's "Salome," showcased his talent for capturing the decadent and the macabre, earning him both acclaim and controversy (Wikipedia, The Collector).
Beardsley's career, though short-lived due to his untimely death at the age of 25 from tuberculosis, was marked by significant contributions to various publications, including "The Studio" and "The Savoy," which he co-founded. His work for "The Yellow Book," where he served as art editor, was particularly influential. The magazine, using the latest image-reproduction technology of the time, allowed Beardsley to make dramatic use of black and white space, reflecting his vision of modern life and aesthetics (V&A Museum).
Despite facing health challenges and controversies, including being dismissed from "The Yellow Book" during the scandal surrounding Oscar Wilde's arrest, Beardsley continued to work on projects that pushed the boundaries of conventional morality and art. His illustrations for works like Aristophanes' "Lysistrata" and his retelling of the Tannhäuser legend are testament to his enduring creative spirit and his willingness to explore themes of decadence, sexuality, and the grotesque.
Beardsley's legacy extends beyond his death, influencing not only the Art Nouveau movement but also future generations of artists and illustrators. His work continues to be celebrated for its daring originality and its challenge to the norms of his time. The Victoria and Albert Museum, among others, has celebrated Beardsley's contributions to art and culture, showcasing his ability to intertwine the beautiful and the grotesque in ways that remain provocative and engaging to this day.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Beardsley's work offers a fascinating glimpse into the aesthetic and cultural shifts of the late 19th century. His influence on poster art, illustration, and the broader Art Nouveau movement underlines the significant impact he had during his brief career. To stay updated on sales and auction events related to Aubrey Vincent Beardsley's work, signing up for updates can provide exclusive access to the continuing legacy of this remarkable artist.


Harriet Beecher Stowe, full name Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe, was an American writer and poet, an activist for the eradication of slavery in the country.
Beecher Stowe is the author of the world-famous novel Uncle Tom's Cabin. Published first in a newspaper and first published as a book in 1852, it aroused widespread anger in the country and galvanized the fight against slavery in the southern United States. This novel was later reprinted many times in all languages of the world and has been screened more than once.
In her youth, Beecher Stowe received an academic education, wrote poetry, notes and essays on social topics. In addition to "The Shack", she wrote several other novels and was engaged in teaching.


Abijah Bigelow is an American legislator, U.S. Representative from Massachusetts, poet and publicist.
Bigelow attended Dartmouth College in Hanover and became a lawyer. Between 1810 and 1815, he represented Massachusetts in the U.S. House of Representatives, where he strongly opposed the War of 1812. He also served as a justice of the peace from 1809 until his death.
As an author and poet, Bigelow published his work in Worcester newspapers throughout his life. Six essays entitled "Political Reflections" were published in the Massachusetts Spy in 1812, and a series of articles on slavery, signed by him as "The Unprofessional," were printed in the Worcester Palladium in 1838. Bigelow was also a member of the American Antiquarian Society.
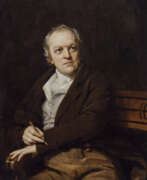

William Blake was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. What he called his "prophetic works" were said by 20th-century critic Northrop Frye to form "what is in proportion to its merits the least read body of poetry in the English language". His visual artistry led 21st-century critic Jonathan Jones to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced". In 2002, Blake was placed at number 38 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. While he lived in London his entire life, except for three years spent in Felpham, he produced a diverse and symbolically rich collection of works, which embraced the imagination as "the body of God" or "human existence itself".


Eugène Boch was a Belgian painter, celebrated for his vibrant contributions to the Post-Impressionist movement. Boch was part of a prominent family known for their fine china business, Villeroy & Boch. He pursued his passion for art in Paris, studying under notable teachers such as Léon Bonnat and Fernand Cormon.
Eugène Boch's artistry is marked by his distinct style and use of color, which earned him spots in prestigious exhibitions like the Salon in Paris during the 1880s. His works, characterized by their emotional depth and innovative techniques, reflect the bold spirit of the Post-Impressionist era. He was not only a painter but also a visionary, whose works resonated with the aesthetic shifts of his time.
One of Eugène Boch's most notable associations was with Vincent van Gogh, who painted Boch in the famous portrait "The Poet," which Van Gogh described as a vision of idealistic and artistic purity. This painting is now housed at the Musée d'Orsay, symbolizing their profound connection and mutual respect. Boch's own works, like "The Red Roofs," demonstrate his unique ability to blend reality with his visionary outlook, showcasing scenes filled with vivid colors and dynamic compositions.
Eugène Boch's legacy extends beyond his paintings. Upon his death in 1941, he left a significant impact on the cultural heritage of Europe, influencing future generations of artists. His works continue to be celebrated in major museums and galleries, reminding us of his pivotal role in the development of modern art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Boch's works offer a timeless exploration of Post-Impressionist vibrancy. Sign up for updates and stay informed about new sales and auction events featuring Eugène Boch’s timeless works, ensuring you never miss an opportunity to own a piece of art history.


Hugh Henry Brackenridge was an American writer and poet, jurist and Pennsylvania Supreme Court Justice.
Hugh Henry graduated from the College of New Jersey (now Princeton University), learned Latin and Greek, and became a teacher. He later served in George Washington's army and published two verse dramas on revolutionary themes. He worked with the poet Philip Morin Freneau (1752-1832) on satirical and political publications.
Hugh Henry Breckenridge founded the Pittsburgh Academy, now the University of Pittsburgh, and the Pittsburgh Gazette, which is still published today.
Breckenridge is also known as the author of the first novel about frontier life in the United States after the Revolutionary War, Modern Chivalry. Considered one of the earliest American novels, this book was published in installments beginning in 1792 over a period of 23 years. In the latest edition, Captain John Farrago, along with his own Sancho Panza, Teague, leaves his farm in western Pennsylvania and sets out to find adventure in the big world.


Patrick Branwell Bronte was an English painter and writer. He was the only son of the Brontë family, and brother of the writers Charlotte, Emily and Anne. Brontë was rigorously tutored at home by his father, and earned praise for his poetry and translations from the classics. However, he drifted between jobs, supporting himself by portrait-painting, and gave way to drug and alcohol addiction, apparently worsened by a failed relationship with a married woman. Brontë died at the age of 31, insisting on standing in his final moments.


Solyman Brown was an American dentist, creator of the first U.S. National Dental Society and the first U.S. Dental Journal, as well as a poet and artist.
Brown received his bachelor's, master's, and doctor of medicine degrees from Yale University, and also worked as a minister. He wrote many articles explaining dental principles and regulations and became one of the editors of the American Journal and Library of Dental Sciences.
Essentially, in the 19th century, American dentistry was in a terrible state. And Solyman Brown, through all his activism, contributed to the enlightenment and establishment of dentistry in the United States as a true profession and science.
Brown also wrote poetry, articles and essays, and was constantly published in the periodical press. He gained fame and notoriety as a dental poet with his epic "Dentology, a poem on the diseases of the teeth and their proper remedies," which he wrote in 1833. And many more of his poems were devoted to dental diseases, their prevention and treatment. Soliyman Brown, in addition, was a painter and sculptor, painting portraits and creating furniture in wood.
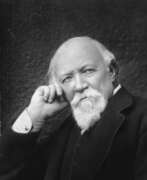

Robert Browning was an English poet and playwright of the Victorian era.
Browning's father, a bank clerk in London, was a very accomplished man, a collector of books and paintings, an artist and a scholar. He gave his son the basics of Greek and Latin, as well as classical literature. Browning re-read many books from his father's extensive library and also attended classes at the University of London. In 1834 Robert Browning traveled to St. Petersburg and later visited Italy. Between
1832-46 he wrote his early long poems and most of his plays. Browning's first published work was "Pauline" (1833); this dramatic monologue was highly emotional. In 1835 he published the poems "Paracelsus" and in 1840 "Sordello," which are about men of great talent trying to come to terms with the demands of the world.
In 1868-69. Browning published his major work, a novel in verse, The Ring and the Book, based on the trial of a murder case in Rome in 1698. Grand in conception and execution, it was immediately well received by the public, and Browning became a major figure in the history of English poetry.


William Cullen Bryant is an American poet, journalist, and editor-in-chief of the New York Post.
He began his education at Williams College, then studied law and worked as a lawyer, but a very different fate awaited him. In 1825, he moved to New York City and became co-editor of the New York Review. In 1827 he became editor of the New York Evening Post, and in 1829 he became its editor-in-chief and co-owner.
Bryant remained in this position until his death, for 50 years. He made the Post a voice for free trade, workers' rights, free speech, and abolition of the death penalty, and he was a founding member of the Republican Party.
Bryant wrote poetry from his early youth and announced himself by publishing a book of Poems (1821). His main theme was nature, and his best-known poems are "Thanatopsis" and "To a Waterfowl." In later years he devoted much time to translations and was an active patron of art and literature.


David Davidovich Burliuk (Russian: Давид Давидович Бурлюк), a pioneering figure of the Russian Futurist movement, was a Ukrainian poet, artist, and publicist, born in 1882 in Semirotovshchina, Kharkov, Ukraine, and died in 1967 on Long Island, N.Y., U.S. Known for his eclectic contributions that spanned poetry, painting, criticism, and publishing, Burliuk's work was instrumental in introducing the Russian avant-garde to Europe and the United States. Despite having a lesser volume of work in poetry and painting compared to his contemporaries, Burliuk's knack for discovering talent and promoting it was unparalleled. He was among the first to publish the works of Velimir Khlebnikov and to recognize the genius of Vladimir Mayakovsky, significantly contributing to their renown.
Burliuk's artistic journey was marked by his involvement with the Futurist and Neo-Primitivist movements. His early work, including an exhibition with the group Zveno ("The Link") in Kiev in 1908 and his participation in the Hylaea group, set the stage for his later achievements. He was a co-author of the influential Futurist manifesto "A Slap in the Face of Public Taste" in 1912, advocating for a break from traditional art forms and the embrace of modernity. Burliuk's commitment to Futurism was evident in his publishing endeavors and his collaborations with notable artists of the time.
In his later years, after emigrating to the United States in 1922, Burliuk continued to engage with the art world, contributing to pro-Soviet groups and publishing his works and those of his contemporaries. His efforts were recognized in several exhibitions, including a significant show at the Brooklyn Museum's 1926 International Exhibition of Modern Art. Despite facing challenges, such as being denied permission to visit his homeland by the Soviet government, Burliuk's influence remained steadfast. His legacy as a central figure in Russian Futurism and his contributions to the broader art movement are celebrated to this day.
To stay informed about updates and events related to David Davidovich Burliuk, including sales of his works and auction events, sign up for our newsletter. This subscription will ensure you're the first to know about new discoveries and opportunities to engage with Burliuk's enduring legacy.


Heinrich Christian Wilhelm Busch was a German humorist, poet, illustrator, and painter. He published wildly innovative illustrated tales that remain influential to this day.
Busch drew on the tropes of folk humour as well as a profound knowledge of German literature and art to satirize contemporary life, any kind of piety, Catholicism, Philistinism, religious morality, bigotry, and moral uplift.
His mastery of drawing and verse became deeply influential for future generations of comic artists and vernacular poets. Among many notable influences, The Katzenjammer Kids was inspired by Busch's Max and Moritz. Today, the Wilhelm Busch Prize and the Wilhelm Busch Museum help maintain his legacy. The 175th anniversary of his birth in 2007 was celebrated throughout Germany. Busch remains one of the most influential poets and artists in Western Europe.


George Gordon Byron was an English poet and peer. One of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, Byron is regarded as one of the greatest English poets. He remains widely read and influential. Among his best-known works are the lengthy narrative poems Don Juan and Childe Harold's Pilgrimage; many of his shorter lyrics in Hebrew Melodies also became popular.
He travelled extensively across Europe, especially in Italy, where he lived for seven years in the cities of Venice, Ravenna, and Pisa. During his stay in Italy he frequently visited his friend and fellow poet Percy Bysshe Shelley. Later in life Byron joined the Greek War of Independence fighting the Ottoman Empire and died leading a campaign during that war, for which Greeks revere him as a folk hero. He died in 1824 at the age of 36 from a fever contracted after the First and Second Sieges of Missolonghi.


Lydia Maria Child, née Francis, is an American writer and journalist, women's rights and Indian rights activist, and a prominent abolitionist.
Lydia Francis was born into a family of abolitionists, which shaped her worldview. From the age of 18, she taught, wrote historical novels and in 1826 founded a periodical for children "Juvenile Miscellany".
Her first novel, Hobomock, was published in 1824 - set in colonial New England and based on the marriage of a white woman, Mary Conant, and a Native American named Hobomock. In 1833, Lydia Child published An Appeal in Favor of the Class of Americans Called Africans, which recounted the history of slavery and decried the educational and employment inequalities of the black population in the United States. As a result, she was expectedly publicly condemned and her magazine collapsed. But this book united and empowered like-minded people in the abolitionist movement.
On the subject of inequality, Lydia Child wrote throughout her life, and she also spoke out on behalf of Native American peoples. In 1861, "Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl" was published. Her many books also include Flowers for Children (1844-47), Facts and Fictions (1846), The Freedmen's Book (1865), and An Address to the Indians (1868).


Thomas Holley Chivers was an American physician and poet of the first half of the 19th century.
Chivers earned a medical degree from Transylvania University in Lexington, Kentucky, but rarely practiced medicine. After receiving an inheritance, he was able to live freely and travel. In the early 1830s he traveled extensively throughout the western frontier and the North. He became fascinated with Transcendentalist philosophy as well as slave poetry. A number of Cheevers's poems and plays reflected his ideological views on American Indians and their plight, inspired in part by his interactions with the Cherokee during his frontier wanderings.
During his lifetime, Chivers published eleven volumes of poems, plays, and pamphlets. He also collaborated with the leading literary periodicals and newspapers of the antebellum era, notably the Georgia Citizen, and wrote a biography of Edgar Allan Poe, his friend and soulmate. Nevertheless, the eccentric writer never achieved the critical acclaim he craved all his life.
The friendship between Chivers and Edgar Allan Poe was based on a mutual fascination with metaphysical speculation, as well as on shared literary interests. However, the close cooperation of the two poets was accompanied by a sharp rivalry, in addition, each of them began to consider the artistic borrowings of the other plagiarized. By and large, Chivers is known only for his association with Edgar Poe.


Pierre Choderlos de Laclos, full name Pierre Ambroise François Choderlos de Laclos, was a French politician, inventor, military leader, and writer.
De Laclos initially pursued a military career, but soon abandoned it, deciding that he would achieve greater fame by becoming a writer. He wrote poetry, erotic stories. His first novel "Dangerous Liaisons" (Les Liaisons dangereuses, 1782) immediately made a great impression and caused a mixed reaction in society. This is one of the masterpieces of novelistic literature of the XVIII century, which describes the love affairs of the aristocracy. On its motives, a large number of commentaries were later written, plays were staged and movies were filmed.
Later, Pierre Choderlot de Laclos worked for some time as secretary to the Duke of D'Orleans, writing several treatises on military and political topics. And in 1792 he again joined the army, where under Napoleon he rose to the rank of general, participated in the Rhine and Italian campaigns.


McDonald Clarke was an American outsider poet of the first half of the 19th century.
McDonald Clarke led an eccentric lifestyle and was nicknamed the Mad Poet of Broadway. He suffered periodic bouts of insanity, but was a regular on the New York poetry scene. Clarke was also known for sleeping in cemeteries and imitating Lord Byron. In his many poems, he covered topics ranging from social satire to sentimental romanticism.
Clarke was always virtually penniless and ended his life in a New York prison, where he was taken in another fit. The mad poet was immortalized by Walt Whitman, whom he greatly influenced as a mystical figure and outsider poet. The young Whitman was fascinated by both Clark's works and his eccentric life. Contemporaries describe Clarke as a mad child with aristocratic manners, meek and always happy, and all his oddities did no harm to those around him.


William Combe was a British writer and poet.
Combe authored a variety of prose and satirical verse, but is best known for the popular Dr. Syntax series of books published between 1812 and 1821, for which he wrote the text and artist Thomas Rowlandson did the drawings. The first book in the series, The Journey of Dr. Syntax: In Search of the Picturesque (1812), was published by the publisher Rudolf Ackerman, and he oversaw further collaboration between Combe and Rowlandson. William Combe's poems about Dr. Syntax with Rowlandson's illustrations were immensely popular in their day.


George Cumberland was an English art collector, writer and poet. He was a lifelong friend and supporter of William Blake, and like him was an experimental printmaker. He was also an amateur watercolourist, and one of the earliest members of the Bristol School of artists. He made use of his wide circle of connections to help its other members, in particular assisting and influencing Edward Bird and Francis Danby.


Alphonse Daudet was a French novelist and short-story writer, best remembered for his sentimental tales of provincial life in southern France. Born in Nîmes in 1840, Alphonse Daudet's early life was marked by financial hardship, influencing much of his later work. He moved to Paris with his brother Ernest and quickly immersed himself in the literary world, publishing his first collection of poems, Les Amoureuses, at a young age.
Alphonse Daudet's career flourished with notable works such as Le Petit Chose, Tartarin de Tarascon, and Lettres de Mon Moulin, which highlighted the charm and simplicity of rural life in Provence. His storytelling, often infused with humor and satire, made significant contributions to French literature, capturing the essence of Provencal culture.
Despite his literary success, Alphonse Daudet's personal life was fraught with challenges, including a long-term illness that he bravely depicted in his later works. He passed away in Paris in 1897, leaving behind a legacy celebrated for its profound impact on regionalist literature and its vivid portrayal of French life and culture during the 19th century.
For those interested in the intricate tapestry of French literature and the enchanting allure of Provence, Alphonse Daudet's works offer a gateway to the past, brimming with the richness of its regional heritage and the timeless appeal of its narratives. To delve deeper into Daudet's life and explore his contributions to literature, subscribing to updates on related sales and auction events can be a rewarding pursuit for collectors and enthusiasts alike, ensuring they remain informed about opportunities to engage with his enduring legacy.


Charles Leconte de Lisle, full name Charles Marie René Leconte de Lisle, was a French poet and politician, head of the Parnassus poetic movement.
He was a member of the Revolution of 1848 and initiator of the law on the abolition of slavery in the colonies. As a poet, he was highly regarded by his contemporaries, including Victor Hugo. Leconte de Lisle's poems are characterized by a clear, sculptural, "objective" form. He translated into French a number of classical Greek works.


Fortunato Depero was an Italian futurist painter, designer, sculptor and poet. In 1913 Depero comes to Rome, where he meets the futurists Giacomo Balla and Umberto Boccioni.
In the early 1920s, Fortunato Depero tries his hand as an artist in commercial advertising, designs theatrical costumes, works for magazines and as a room decorator, and participates in many art exhibitions.


Emily Elizabeth Dickinson was a 19th-century American lyric poet.
Emily led a secluded and rather unusual lifestyle, preferring active correspondence instead of personal communication. In addition to many brilliant and witty letters to her family and friends, she wrote about two thousand poems during her lifetime, but only about ten were published during her lifetime.
Dickinson possessed an extraordinary brilliance of style and integrity of vision and, along with Walt Whitman, is today considered one of the two leading American poets of the nineteenth century. She easily ignored the usual rules of versification and even grammar, and in the intellectual content of her works showed exceptional courage and originality. It is known that the poetess was particularly impressed by the poetry of Ralph Waldo Emerson, and with Charles Wadsworth she corresponded.
Today, the work of Emily Dickinson is evaluated as a bright forerunner of modernism, it is widely studied in educational institutions in the United States and Europe.


Timothy Dwight IV was an American clergyman, teacher, author, and satirical poet.
Dwight was the eldest son of farmer and merchant Timothy Dwight III. He graduated from Yale University, was a schoolmaster, a Massachusetts state legislator, and a chaplain in the Continental Army. In 1783 he opened a successful school in Greenfield Hill, Connecticut, where he became pastor of the Congregational Church.
In Connecticut, Dwight began writing poetry, such as Greenfield Hill (1794), and epics, including The Conquest of Canaan (1785), an allegory of the conquest of Connecticut from the British. His works are characterized by moralizing and moralizing. Dwight was also the author of political satire, as well as a verse satire on Voltaire, "The Triumph of Infidelity." He and his brother Theodore were members of a group of writers known as the Hartford Witters, centered around Yale University.
From 1795 to 1817. Dwight served as president of Yale University and was extremely influential in modernizing the curriculum. He was an active and eloquent professor of theology; his sermons were published in Theology; Explanation and Defense, 5 volumes (1818-19).
Dwight was also a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and an early member of the American Antiquarian Society.


Emily Eden was a British writer and poet, as well as an amateur painter.
Emily Eden, daughter of William, first Baron Auckland, accompanied her brother, George, Lord Auckland (1784-1849), to India, where he served as Governor-General from 1835-1842. A gifted amateur artist and writer, Eden recorded her observations of life in India during this period in the form of letters and an extensive collection of sketches. On her return to England in 1842, Eden published her work. It chronicles Indian princes and members of the higher castes, as well as their servants, their families, and religious believers, Pathans, Tibetans, and others. In addition, she has carefully and accurately described the political events she witnessed.
Emily Eden also published two novels that wittily and satirically describe life in England in the early 19th century.


Ralph Waldo Emerson was an American philosopher, lecturer and poet, one of the most prominent thinkers and writers in the United States, and the originator of transcendentalism.
Ralph studied at Boston State Latin School and then at Harvard College (later Harvard University), began to preach, but soon doubted his chosen path and resigned his ministry. Emerson went to Europe, where new acquaintances and knowledge led him to new thoughts, and, returning to the United States in 1833, he began writing his famous book "Nature", where he first formulated a philosophy called transcendentalism. Soon other thinkers rallied around him, forming a group of like-minded thinkers.
In the essay "Nature," published in 1836, and in the following works, "The American Scholar" and "An Address in the School of Theology," Emerson consistently developed his ideas. Emerson's doctrine of the self-sufficiency and self-reliance of the individual stems from his view that a person need only look into his own heart to receive the spiritual guidance that has hitherto been the prerogative of the official churches. One must then have the courage to be oneself and trust the inner power within oneself, living one's life according to the commandments one has intuitively derived. These thoughts are not new, but Emerson put them in imaginative and accessible language.
Emerson's speeches led to his being ostracized at Harvard for many years. However, the informal Transcendental Club, founded in 1836, was joined and supported by his young students. The world fame of the brilliant thinker Emerson brought his "Essays" in two volumes, published in 1841 and 1844. As the main representative of transcendentalism, Emerson gave direction to the religious, philosophical and ethical movement, which above all emphasized belief in the spiritual potential of each person.
A later work of confession, The Conduct of Life (1860), demonstrates the author's developed humanism and full awareness of human limitations. The voluminous collection of poems cemented Emerson's reputation as a major American poet.


Léon-Paul Fargue was a French poet and novelist, journalist and publicist.
Léon-Paul studied at the Lycée Henry IV in Paris and as a young man became a member of the Symbolist circle associated with Le Mercure de France. His first collection of poems was published in 1912 and reprinted in 1918. After 1930, Fargue practiced journalism almost exclusively, writing newspaper columns and lyrical essays on Parisian life.
Léon Fargue's work encompasses various literary movements, being a kind of bridge from Symbolism to Surrealism. His work has also been associated with the Dadaists and the Cubists, but he followed his own path throughout his life. Fargue was among the founders of the Nouvelle Revue Française in 1912 and participated in the first issue of the surrealist journal Literature in 1919, and was one of the leaders of the experimental journal Commerce in the 1920s. Farg was friends with many writers, artists and composers, including Pablo Picasso and Igor Stravinsky.
In 1937, Léon-Paul Fargue was elected a member of the Académie Mallarmé, and in 1946 he won the Grand Poet Laureate of Paris.


Philip Morin Freneau was an American publicist, editor, and known as the "poet of the American Revolution".
After graduating from Princeton University, Freneau taught school and studied to become a minister. With the outbreak of the American Revolution, he began writing scathing satire on the British and the Tories. During a two-year voyage to the Caribbean islands, he created the poems "The Beauties of Santa Cruz" and "The House of Night," and in 1778 he became involved in the war. After his release from British captivity, Freneau wrote a book in verse, "The British Prison Ship" (1781).
After serving as a sea captain for several years, Freneau took up journalism. In his National Gazette newspaper in Philadelphia, he sharply criticized George Washington.
Freneau's poetry, which accompanied him throughout his life, covers a variety of subjects, including political situations, American Indians, nature, the sea, and naval battles. His political poems are often satirical, but his nature poems are very lyrical.


Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.


Elena Genrikhovna Guro (Russian: Еле́на Ге́нриховна Гуро́), born in 1877 in St. Petersburg, Russia, and passing in 1913, was a pioneering figure in the Russian Futurist movement. As a multifaceted artist, she delved into painting, writing, and poetry, marking her as a versatile and innovative force in the early 20th century Russian avant-garde. Guro's work is distinguished by its embrace of Futurism, a movement that sought to break away from traditional art forms and explore dynamic means of expression. Her contributions were not only limited to visual arts but also extended to literature, where she experimented with narrative forms and language, often incorporating nonsensical elements to challenge conventional aesthetics.
Guro's literary works, such as "The Little Camels of the Sky," demonstrate her experimental approach to language and form, embodying the Futurist fascination with the aesthetic possibilities of words. This approach is evident in her poetry and short stories, where she utilized single-word sentences and nonsense words to capture the essence of moments or convey a childlike perspective. Such techniques allowed her to explore the texture of language and its visual and auditory qualities, making her work resonate with the innovations of the Futurist and Dada movements.
Despite her early death at the age of 36, Guro's legacy continues to be celebrated for its contribution to the evolution of Russian modernism. Her work bridged the gap between the Symbolist movement and Futurism, contributing significantly to the dialogue around art and literature in her time. Her husband, Mikhail Matyushin, further propagated her artistic theories, ensuring that her innovative approach to color and form continued to influence Russian art and literature after her passing.
Elena Genrikhovna Guro remains an inspirational figure in the world of art and literature, embodying the spirit of innovation and exploration that defined the early 20th century avant-garde. Her works, which blend poetic language with vivid imagery, invite audiences to reconsider the boundaries between different art forms and the potential of language as an artistic medium.
For those intrigued by the rich tapestry of Russian Futurism and the unique voice of Elena Guro, signing up for updates on her works, sales, and auction events can deepen your appreciation and understanding of this pivotal artist's contributions. This subscription will ensure you stay informed about the latest insights and opportunities related to Elena Genrikhovna Guro's enduring legacy.


Sarah Josepha Buell Hale, born Sarah Josepha Buell, was an American writer, magazine editor, and civic activist.
Sarah Buell received a good home education and married David Hale in 1813, but, finding herself in financial difficulty after her husband's death, she turned to literary work in the 1820s. Her poems were published in local journals and in the collection The Genius of Oblivion (1823). Sarah also wrote several novels during her lifetime.
In 1828, she became editor of the new Boston edition of Ladies' Magazine (from 1834, American Ladies' Magazine). Hale herself wrote much of the wide variety of material for each issue-literary criticism, essays on American life, essays, and poetry, and she supported patriotic and humanitarian organizations, notably the Boston Ladies' Peace Society and the Sailors' Aid Society, which she founded in 1833. She was a lifelong advocate of women's education. During this period she also published Poems for Our Children (1830), containing her most famous work, Mary Had a Little Lamb.
In 1837, in Philadelphia, Hale became editor of Lady's Book, soon to be known as Godey's Lady's Book. During her years as editor, this publication became the most influential and circulating women's magazine published in the country at the time. Hale encouraged American writers: Edgar Allan Poe, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Harriet Beecher Stowe, and other women writers published in the magazine.
Hale's major accomplishment was Woman's Record; or, Sketches of Distinguished Women, published in 1853, 1869, and 1876. For this project, she produced some 36 volumes describing biographies of women, emphasizing their influence in history on social organization and literature.
Sarah Hale is considered one of the main organizers of the Thanksgiving holiday, and she helped shape the worldview of women of her time.


Edward Everett Hale was an American clergyman, preacher and writer, abolitionist and pacifist.
Hale demonstrated outstanding literary ability from an early age. He went to Harvard College and became a minister and preacher. Grandnephew of Revolutionary hero Nathan Hale and nephew of orator Edward Everett, Hale worked for his father's newspaper, the Boston Daily Advertiser. And for 70 years he never stopped writing newspaper articles, historical essays, short stories, pamphlets, and sermons for the North American Review, The Atlantic Monthly, and the Christian Examiner. From 1870 to 1875 he published and edited the Unitarian magazine Old and New.
Hale wrote several novels, of which the most popular were East and West (1892) and In His Name (1873). Hale's most famous novel, A Man Without a Country, first published in The Atlantic Monthly in 1863, was written to evoke patriotism during the Civil War. It is a political fable about a man who renounces his American citizenship and greatly regrets it.
Many of Hale's 150 books and pamphlets were tracts in support of the ideas of Negro education, worker's housing, and world peace. The moralistic novel Ten Times One is Ten (1871) was the impetus for the organization of several youth groups.
In 1847, Hale was elected a member of the American Antiquarian Society and remained a member for the rest of his life. A 10-volume collection of Edward Hale's writings was published between 1898 and 1900. In 1903 he was appointed chaplain of the United States Senate and joined the Literary Society of Washington. The following year he was elected a member of the Academy of Arts and Sciences.


Bret Harte, born Francis Bret Harte, is an American poet and writer, one of the founders of the Western genre in literature.
From his youth, Bret worked in various professions in California, published a newspaper and a magazine, collaborating for a time with Mark Twain. He wrote several novels and many short stories about the Gold Rush era, of which the best known is the later trilogy "The Steppe Finder", "Susie" and "Clarence", set during the American Civil War.
In 1878 Harte began working at the consulate in Krefeld, Germany, and then in Glasgow, Scotland. In 1885 Harte settled in London and lived there until the end of his days, continuing to write short stories, parodies, and other works of enduring success.
Harte's works about Californian life became popular in Russia, thanks to N.G.Chernyshevsky, who was engaged in their translations from the early 1870s. Russian venerable writers M.E. Saltykov-Shchedrin and N.S. Leskov spoke very flatteringly of him. And in 1895 in St. Petersburg published a collection of works by Bret Harte in six volumes. Already in the USSR in 1977 the movie "Armed and Very Dangerous" was filmed based on his stories. Alexey Rybnikov's musical "Juno and Avos", the most popular for decades, is based on Bret Harte's ballad "Concepcion de Arguello".


Christian Johann Heinrich Heine was a German poet and writer, known for his lyric poetry that has been set to music as Lieder by composers such as Schumann and Mendelssohn. Born as Harry Heine in Düsseldorf, he later became one of the most significant figures in German Romantic literature. His works exhibit a range of themes, from the humorous to the serious, and he is celebrated for making the language of everyday life suitable for poetry.
Heine's contributions to literature go beyond poetry; he was also a journalist and essayist. His prose works, like "Reisebilder," mix travelogue with literary critique, and his sharp wit and satire often targeted the social and political issues of his time. These features made him a pioneering figure in the transition from German Romanticism to Realism.
In museums, Heine's original manuscripts and early editions of his works are prized possessions. They connect collectors and literary enthusiasts to a pivotal era of literary change. For those who cherish the romance of words intertwined with the authenticity of history, seeking out Heine’s works can be a rewarding endeavor. Explore his literary artistry and consider adding a piece of his legacy to your collection.


Hermann Karl Hesse was a German-Swiss poet, novelist, and painter, known for delving into themes of authenticity, self-knowledge, and spirituality. Born in Calw, Germany, Hesse's exploration of the individual's quest for truth won him the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1946. His storytelling weaves a rich tapestry of philosophical thought, evident in masterpieces like "Steppenwolf" and "Siddhartha," which resonate deeply with the human experience.
Renowned for his lyrical prose and profound insights into the human spirit, Hesse's works are a cornerstone of 20th-century literature. They challenge readers to seek beyond the confines of society and find a deeper sense of self. His narrative style combines simplicity with a deep philosophical undercurrent, inviting reflection and introspection.
Collectors and connoisseurs of literature hold Hesse's works in high esteem, not just for their literary merit but also for their cultural significance. For those interested in the evolution of literary thought and the pivotal role of introspective narratives, Hesse’s works are invaluable. Delve into his writings to discover the essence of early 20th-century philosophical literature and consider adding them to your collection for both their historic and artistic value.


Karl Heinrich Hoff was a German painter of the second half of the 19th century. He is known as a painter, graphic artist and poet, recognized by contemporary critics as one of the best German genre painters.
Karl Hoff traveled throughout Germany, France, Italy and Greece in search of inspiration for his work. His paintings, according to critics, were masterful in conveying the characterization of the era, types, and situations. Widely known are such works of his as "Gypsies in front of the provincial chief", "Rest during the escape", "Christening of a child born after the death of the father" and others.
Hoff was an active member of the artists' association "Malkasten".


Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. was an American physician, poet, and humor writer.
Holmes studied law at Harvard University, then medicine in Paris. He practiced medicine for 10 years, taught anatomy at Dartmouth College (Hanover, North Carolina) for two years, and became professor of anatomy and physiology at Harvard in 1847. He later became dean of Harvard Medical School and held that position until 1882. Holmes' most significant contribution to medicine was his research on the contagiousness of postpartum fever. In 1843, he published a treatise on the subject, The Infectiousness of Postpartum Fever. He also introduced the term anesthesia into scientific usage.
Today, Oliver Holmes is remembered as a gifted writer of the 19th century in the United States. Beginning in 1857, he published his "Breakfast at the Table" articles-essays in The Atlantic Monthly and later published several collections written in a conversational style, with Holmes's characteristic humor and wit. He also wrote several poems, three novels, and many poems and anecdotes.
Oliver Wendell Holmes was the father of lawyer Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. (1841-1935). According to some sources, he was the prototype of the detective Sherlock Holmes, the famous hero of writer Arthur Conan Doyle.


Victor Hugo was a French poet, novelist, dramatist, and politician, celebrated for his profound impact on art, culture, painting, and history. Born on February 26, 1802, in Besançon, France, Hugo emerged as a pivotal figure in the Romantic literary movement. His illustrious career spanned over six decades, during which he authored numerous works in various genres.
Victor Hugo's legacy is particularly notable for his novels "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame" (1831) and "Les Misérables" (1862), which have left an indelible mark on literature and culture. These works not only showcase his storytelling prowess but also reflect his deep engagement with the social issues of his time. His commitment to addressing societal concerns is further evidenced by his active political life and advocacy for causes like the abolition of capital punishment and slavery.
Beyond his literary and political contributions, Victor Hugo was also an accomplished artist, having produced over 4,000 drawings throughout his lifetime. His passion for the arts and dedication to social causes cemented his status as a national hero in France. When he passed away on May 22, 1885, his significance was underscored by a state funeral at the Panthéon in Paris, attended by over 2 million people, making it the largest in French history.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Victor Hugo's multifaceted legacy offers a rich tapestry of creativity and commitment to explore. His works not only provide profound literary enjoyment but also serve as a window into the cultural and historical milieu of 19th-century France.
To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Victor Hugo, sign up for updates. This subscription will ensure you're always in the loop regarding the latest developments related to this iconic figure's works and associated artifacts.


David Humphreys was an American soldier, statesman, diplomat, writer, poet, and biographer.
He received his bachelor's degree from Yale University, where he became a member of the Hartford Witters and taught, and went to serve in the Continental Army in the summer of 1776.
A close friend and aide to George Washington, Humphreys was an eyewitness and active participant in the early years of the United States. During his long career, Col. David Humphreys served as a soldier, secretary, diplomat, and was a writer, poet, orator, biographer, and industrialist. His speeches, poems, literary works, and correspondence with Washington and others of the founding generation serve as a valuable source for historians of the early republic in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries.
Because of his intelligence and diligence, David Humphreys had a long record of service and held many public offices, among others serving as U.S. minister to Spain from 1797 to 1801. He was a member of the Royal Society of London and the American Antiquarian Society.


Joris-Karl Huysmans, real name Harles-Georges-Marie Huysmans, was a French writer and poet, the first president of the Goncourt Academy.
Huysmans' father was Dutch, and he always emphasized this fact. At the age of 20, the aspiring writer began working as an official in the French Ministry of the Interior, where he served all his life.
Huysmans received the greatest fame thanks to the novel À rebours ("Against Nature"). The main appeal of this writer's work lies in its autobiographical content. And his style is characterized by a wide vocabulary of the French language, a wealth of detailed and sensual descriptions, as well as sharp satirical wit. The novels are also notable for their encyclopedic documentation, ranging from a catalog of decadent Latin authors in À rebours to a discussion of the symbolism of Christian architecture in La Cathédrale.
In his work, Huysmans expresses a distaste for modern life and a deep pessimism, but in his writings one can trace the stages of intellectual life in late nineteenth-century France. Joris-Karl Huysmans was one of the earliest proponents of Impressionism. He was also a renowned literary critic and one of the founders and first president of the Goncourt Academy.


William Irving was the older brother of the famous writer Washington Irving and a U.S. Congressman.
William Irving was engaged in fur trading and other businesses, and wrote several essays and poems for the satirical magazine Salmagundi, which was published by Washington Irving as a periodical and later published as a book.
In 1813. William Irving was elected by Democratic-Republicans to represent New York's 2nd Congress in the U.S. House of Representatives.


Sarah Orne Jewett, full name Theodora Sarah Orne Jewett, is an American writer and poet.
Sarah attended Berwick Academy, but did most of her education on her own. She signed her first short stories "Alice Eliot." Her many late sketches of the New England town of Deephaven, reminiscent of South Berwick, were published in The Atlantic Monthly and collected in her first book, Deephaven (1877).
She wrote three novels and several books for children, and several collections of her poems were also published. Jewett's best book, The Land of Pointed Firs (1896), like Deephaven, tells of the isolation and loneliness of a decaying port town and the unique humor of its inhabitants. Her works are reminiscent of the novels of Gustave Flaubert, whose work she admired.


James Augustine Aloysius Joyce was an Irish writer and poet, journalist and literary critic.
Joyce is a representative of the modernist avant-garde movement and is considered one of the most influential writers of the 20th century. Joyce's best known works are the novels Ulysses (1922) and A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man, and the short story collection The Dubliners.


August Kopisch was a German painter of the first half of the 19th century. He is known as a landscape painter and poet.
Kopisch began his path in art with painting, but switched to literature due to a hand injury. He studied at art academies in Dresden, Prague and Vienna. His paintings were characterized by bright colors. There are 23 known paintings by Kopisch, but some of them have not survived. One of his most notable masterpieces is the 1848 painting Pontic Moorlands at Sunset.
As a poet, Kopisch also left his mark on German literature and art. He notably translated Dante's Divine Comedy and Italian folk songs into German.


Vernon Lee, real name Violet Paget, was an English writer, translator, and author of numerous essays on art. She is best known for fantasy stories and works on aesthetic theory.
Vernon Lee wrote more than 30 books during her lifetime, including works of various genres: short stories, historical novels, mystical stories. Her art studies, written on a wide range of topics such as Shakespeare, Renaissance culture, etc., are also noted for their excellence. No less popular were her numerous travel notes on her journeys in Europe - Germany, France, Switzerland.


John Blair Linn is an American priest and poet.
Linn graduated from Columbia College and later became a priest. While in college, he published in magazines and newspapers, later writing a play and several collections of poetry and prose.


Henry Wadsworth Longfellow was the most popular American poet of the nineteenth century.
Longfellow is one of the most revered poets in the United States. His poems "Paul Revere's Ride", "Evangeline", "The Tale of Acadia" (1847) and "Psalm of Life" were included in elementary and high school curricula and have long been remembered by generations of readers who studied them as children. Longfellow revitalized American literary life by linking American poetry to European traditions outside of England.


Jane Webb Loudon, full name Jane Wells Webb Loudon, is an English futurological writer, one of the pioneers of the science fiction genre, an artist and amateur botanist.
At the age of 20, Loudon wrote the novel that brought her fame, "The Mummy!" (1827). Set in the year 2126, the novel describes an England filled with advanced technology, including automated lawyers and steam-powered surgeons, coffee makers, and an information highway resembling the modern Internet.
Loudon was married to the well-known horticulturist John Claudius Loudon, and they wrote several books together, and she also published her own very successful series of books with titles such as Gardening for Women, A Lady's Companion to the Flower Garden.


Pierre Louÿs, real name Pierre Félix Louis, was a French poet and writer.
He specialized in erotic and ancient themes in the Art Nouveau style. Louÿs's most famous work is The Songs of Bilitis. It is a collection of erotic poetry with strongly lesbian themes, written in the manner of Sappho. Although Louÿs claimed that these poems had a Greek source, this ultimately proved to be a hoax.


James Russell Lowell was an American poet, educator, and diplomat.
From 1845 to 1850, he wrote about 50 articles against slavery for periodicals. Two of Lowell's other two most important works were also published in 1848: the poem "Sir Launfal's Vision," praising the brotherhood of man, and "A Fable for Critics," a witty appraisal of contemporary American authors. These books, together with the publication in the same year of a second series of his poems, made Lowell the most popular new figure in 19th-century American literature.


Pierre Mac Orlan, real name Pierre Dumarchey, is a French writer, poet, screenwriter, playwright, artist and journalist.
Pierre Dumarchey spent his youth leading a bohemian lifestyle, but by the age of 20 he had already published several collections of short stories with his own illustrations. He socialized with many contemporary writers and artists, played the accordion, and many of his songs were quite popular in cabarets. In World War
I in 1916, Pierre Dumarchey was wounded, after which he worked as a war correspondent. In the late 1920s, he became an influential critic of film and photography. And later became a famous writer under the pseudonym Pierre Mac-Orlan. Based on his most famous novel Quai des Brumes ("Port of Shadows"), French director Marcel Carné made a movie of the same name in 1938.
In addition to his numerous novels, Mac-Orlan published under various pseudonyms in erotic magazines. Pierre Mac-Orlan was a very prolific writer: in 1969-1971, a collection of his works in 24 volumes was published, which, however, did not include his many erotic works.


Stéphane Mallarmé was a French poet and critic. He was a major French symbolist poet, and his work anticipated and inspired several revolutionary artistic schools of the early 20th century, such as Cubism, Futurism, Dadaism, and Surrealism.


Filippo Tommaso Marinetti was an Italian writer, poet, founder of Futurism and one of the ideologues of Fascism. He founded a number of futurist magazines and the publishing house Poesia.
Filippo Tommaso Marinetti - author of the first futurist manifesto, one of the founders of aerial painting. He founded his own political party in 1918 to expand and translate the ideals of the futurist movement into the political struggle.
One of the founders of Italian Fascism, he worked closely with Mussolini. In his later work, he developed an updated version of futurism, the so-called Aeropoiesis, whose manifesto he published in 1931.


Herman Melville was an American writer, poet, and sailor.
Melville's hardship-filled youth ended on a whaling ship. He returned from his adventures in the South Seas in October 1844, and wrote "Taipi" the following spring. The book was based on the events surrounding Melville's desertion from the whaling ship Acushnet in 1842 and subsequent adventures in the Marquesas Islands.
Melville wrote several other novels and short stories and many poems, but during his lifetime his works were little appreciated by his contemporaries. Only in the 1920s began to rethink Melville, and he was recognized as a classic of world literature. World fame Melville already in the 20th century brought irrational novel "Moby Dick".


Henri Michaux is a French poet and artist associated with Surrealism and the post-war avant-garde movement.
Michaux's early artistic endeavours revolved around writing and poetry. In his poetry he explored themes of existentialism, spirituality and the human condition, often experimenting with language and form. His writing style was characterised by introspection, the exploration of consciousness and the search for meaning.
In 1925, after a Surrealist exhibition he saw in Paris, Henri Michaux began to paint and draw. His visual arts encompassed a wide range of styles and techniques. Michaux experimented with ink, watercolour and oil paintings, creating evocative and energetic compositions. His works often conveyed a sense of movement, rhythm and spontaneity and were influenced by the aesthetics of calligraphy and gesticulation.


Cincinnatus Heine Miller, better known by his pen name Joaquin Miller, was an American writer and poet and journalist.
Miller spent his youth traveling across the country and in California among miners, gamblers, and Indians. During the Gold Rush, he had to endure many misadventures. He attended Columbia College (Eugene, Oregon) and was admitted to the Oregon State Bar in 1860.
From 1862-1866 he published the Eugene Democratic Register newspaper and was a county judge in Oregon. For the Register, he wrote an article in defense of Mexican bandit Joaquin Murietta, whose name he later took as a pseudonym. In the late 1860s his first collections of poems, Samples and Joaquin, were published.
In 1870 Miller traveled to England, where thanks to exotic manners and bright costume in the style of Westerns became popular among the literati and published several collections of poems. Among them was a book, Songs of the Sierra, which established his nickname "The Poet of the Sierra." He became a kind of celebrity among the Pre-Raphaelites, he was honored by the British press, he attended the Savage Club as a guest of Nathanial Hawthorne's son Julian, who called him a "licensed libertine."
Joaquin Miller's best works convey a sense of the grandeur of the Old West. His most famous poem is "Columbus."


Thomas Moore was a British poet, songwriter and composer, a representative of Irish Romanticism.
Thomas graduated from Dublin University, from the age of 14 he collaborated with various Dublin journals. In 1800 he published his "Odes of Anacreon", and a year later - a collection of Poems by the late Thomas Little ("Poems by the late Thomas Little") and became widely known. Visiting the United States, Moore published a collection of poems, where he spoke about this country very sharply.
In 1812, Thomas Moore met Byron, became his close friend and wrote one of the best biographies of him, published in 1835. Moore's most famous works are "The Last Rose of Summer" and the collection "Irish Melodies" (1807-1834), which brought him a stable income for many years. In Russia, however, he is known primarily for the poem Those evening bells from the collection published in 1818. The poem was translated by Ivan Kozlov, and it turned into the famous and beloved song "Evening Bells".


William Morris was a British artist, designer, poet, and social activist, celebrated for his profound impact on the decorative arts and his role in the Arts and Crafts movement. Born in Walthamstow, Essex, in 1834, Morris developed a fascination with medieval architecture and landscapes, influencing his artistic endeavors. He founded Morris & Company, known for producing exquisite textiles, wallpapers, and various decorative items that emphasized craftsmanship and beauty.
William Morris's Kelmscott Press, established in the 1890s, aimed to revive traditional book-making methods, producing works with high-quality materials and craftsmanship. One notable achievement was the Kelmscott Chaucer, a collaboration with Edward Burne-Jones that is still celebrated for its intricate designs and craftsmanship.
William Morris's influence extended beyond his lifetime, with his designs continuing to inspire artists and designers. His works are housed in prestigious institutions like The Metropolitan Museum of Art, reflecting his enduring legacy in the art world. His commitment to social causes, particularly through his socialist beliefs, further highlights his multifaceted contributions to culture and society.
If you're intrigued by William Morris's work and his influence on art and design, consider signing up for updates. Stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to William Morris's legacy, ensuring you don't miss out on owning a piece of this historic artistry.


William Munford was an American legislator and court reporter, writer, poet, and translator.
After receiving a law degree, Munford entered politics, represented Mecklenburg County in the Virginia House of Delegates, and was elected to the state Senate. Munford was also a legal reporter for decisions of the Virginia Supreme Court of Appeals, for which he prepared six annual issues a year.
He also published collections of poetry and engaged in translations of classical works, including Homer's Iliad.


John Neal is an American writer, editor, and community activist.
Neal served for many years as editor of the Yankee and Boston Literary Gazette periodicals, publishing critical essays and always striving to promote American literature. While living in England in the 1820s, he wrote a long series of articles published in Blackwood's Edinburgh Magazine, essentially telling the story of American literature, which helped change the perception of American art in Britain.
Back in America, he used his popularity and influence to support young writers such as Poe and Whittier. In particular, it was Neale who put Edgar Allan Poe's very name in print and the very first words of encouragement to his work.
Neal's early recognition of Poe's genius was crucial to the budding talented writer's career. John Neel also wrote long adventure novels with complex plots, of which "Rachel Dyer" is considered the best, and "Bag Otter, Chief of the Oneida" and "David Whicher" are his best stories.
John Neal was also a very active social and political activist. In his literary work and lectures, he constantly addressed issues such as feminism and women's rights, slavery, the rights of free black Americans and American Indians, temperance, sports, and many others.