Scientists 16th century


Cornelius Gerardi Aurelius, also called Goudanus, was a Dutch humanist scholar, writer, and historian.
Aurelius was a permanent canon (monk) of the Augustinian monastic order and is one of the first humanists of the Netherlands in the 16th century. He wrote poetry, historiography, hagiography, political and theological works. Aurelius also corresponded with many of the famous men of his day, especially Erasmus.


Johann Hartmann Beyer was a German physician, mathematician and statesman.
He earned a master's degree in liberal arts at the University of Strasbourg, and then graduated from the University of Tübingen with a doctorate in medicine. In 1588 Beyer returned to his native Frankfurt and began working as a physician; a year later he was appointed Physicus ordinarius - his duties included overseeing the city's health care and pharmacy system.
In 1614 Beyer took up the position of senior burgomaster of Frankfurt, but during the Fetmilch Rebellion he became involved in conflict, was forced to resign and returned to science.
He had the richest library of scientific books, numbering about 2500 volumes, wrote scientific works on astronomy and mathematics, engaged in medical activity, having invented the famous Frankfurt pills. Beyer carried on a lively correspondence with scientists, including mathematician Johannes Kepler, dealing with decimal fractions. Beyer bequeathed his rich inheritance to the city and to charity.


Tycho Brahe, born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, more commonly called Tycho, was a prominent Danish astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist of the Renaissance.
As a young man he traveled extensively throughout Europe, studying in Wittenberg, Rostock, Basel, and Augsburg and acquiring mathematical and astronomical instruments. In 1572 Tycho unexpectedly even for himself discovered a new star in Cassiopeia, and the publication of this turned the young Dane into an astronomer of European reputation. For further astronomical research he established an observatory and gathered around him modern progressive scientists.
Besides practicing astronomy, Tycho was an artist, scientist, and craftsman, and everything he undertook or surrounded himself with had to be innovative and beautiful. He even founded a printing house to produce and bind his manuscripts in his own way, and he perfected sanitary ware for convenience. His development of astronomical instruments and his work in measuring and fixing the positions of the stars laid a solid foundation for future discoveries.
Tycho's observations - the most accurate possible before the invention of the telescope - included a comprehensive study of the solar system and the precise positions of more than 777 fixed stars. What Tycho accomplished using only his simple instruments and intellect remains a remarkable achievement of the Renaissance.
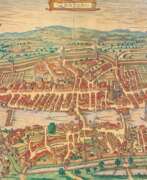

Georg Braun was a German topographical geographer, cartographer and publisher.
Braun was the editor-in-chief of the Civitates orbis terrarum, a groundbreaking atlas of cities, one of the major cartographic achievements of the 16th century. It was the first comprehensive and detailed atlas, with plans of the world's famous cities and bird's-eye views, and became one of the best-selling works of the time.
The book was prepared by Georg Braun in collaboration with the Flemish engraver and cartographer Frans Hoogenberg. Braun, as editor-in-chief, acquired tables, hired artists, and wrote the texts. They drew on existing maps as well as maps based on drawings by the Antwerp artist Joris Hofnagel and his son Jacob. Other authors include Pieter Bruegel the Elder (c. 1525-1569), Jacob van Deventer (c. 1505-1575), and more than a hundred other artists and engravers.


Nicolaus Copernicus (Polish: Mikołaj Kopernik) was a Polish and German scientist, astronomer, mathematician, mechanic, economist, and Renaissance canonist. He was the author of the heliocentric system of the world, which initiated the first scientific revolution.
Copernicus studied the humanities, including astronomy and astrology, at the University of Krakow and at the University of Bologna in Italy. Together with other astronomers, including Domenico Maria de Novara (1454-1504), he was engaged in observing the stars and planets, recording their movements and eclipses. At the time, medicine was closely related to astrology, as the stars were believed to influence the human body, and Copernicus also studied medicine at the University of Padua between 1501 and 1503.
Nicolaus Copernicus, based on his knowledge and observations, was the first to suggest that the Earth is a planet that not only revolves around the sun every year, but also rotates once a day on its axis. This was in the early 16th century when people believed the Earth to be the center of the universe. The scientist also suggested that the Earth's rotation explained the rising and setting of the Sun, the movement of the stars, and that the cycle of the seasons was caused by the Earth's rotation around itself. Finally, he correctly concluded that the Earth's motion in space causes the planets to move backwards across the night sky, the so-called retrograde direction.
Although Copernicus' model was not completely correct, it laid a solid foundation for future scientists, such as Galileo, who developed and improved mankind's understanding of the motion of celestial bodies. Copernicus completed the first manuscript of his book De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (On the Rotation of the Celestial Spheres) in 1532. In it, the astronomer outlined his model of the solar system and the paths of the planets. However, he published the book only in 1543, just two months before his death, and dedicated it to Pope Paul III. Perhaps for this reason, and also because the subject matter was too difficult to understand, but the church did not finally ban the book until 1616.


Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance, celebrated as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. His remarkable abilities and innovative thinking made him an epitome of the Renaissance humanist ideal. Born in Vinci, near Florence, in 1452, Leonardo was educated in Florence by Andrea del Verrocchio, a renowned painter and sculptor. He began his career in Florence, later working in Milan, Rome, and France, where he died in 1519.
Da Vinci is revered for his artistic mastery, technological innovation, and scientific inquiry. Despite having fewer than 25 major works attributed to him, including several unfinished ones, his influence on Western art is profound. His magnum opus, the "Mona Lisa," housed in the Louvre Museum, Paris, is considered the world's most famous painting. "The Last Supper," his most reproduced religious painting, showcases his mastery of dramatic narrative and pictorial illusionism. Both paintings exhibit Leonardo's unique ability to convey complex human emotions and his innovative use of techniques like sfumato and chiaroscuro.
Leonardo's interests extended far beyond fine art. He was a visionary in multiple fields, including anatomy, physics, architecture, and mechanics. His notebooks reveal designs for machines like bicycles, helicopters, and military tanks, centuries ahead of their time. However, due to his diverse interests, he left many projects and paintings incomplete. Leonardo's final years were spent in France, where he continued his artistic and scientific pursuits until his death.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Leonardo da Vinci remains a figure of endless fascination. His works not only embody the pinnacle of Renaissance art but also provide insights into the era's scientific and philosophical inquiry. To stay updated on new sales and auction events related to Leonardo da Vinci, sign up for our newsletter. This subscription is a gateway to exploring the rich legacy of this unparalleled artist and inventor.


Estienne de la Roche, also known as Estienne de Villefranche, was a French mathematician.
He is known for having taught mathematics in Lyon for 25 years as a professor of mathematics. In 1520 he published the Arismatics, considered at the time the best reference book on algebra.


Johann Dryander, born Johann Eichmann, was a German medical anatomist, mathematician and astrologer.
He studied anatomy and medicine at the University of Paris and the University of Erfurt, and in 1535 became professor of medicine at the University of Marburg. A year later, Dryander performed two public autopsies, making the first illustrated description of the dissection of the human brain. Dryander titled his book Anatomiae, hoc est, corporis humani dissectionis pars prior ("Anatomy, that is, the dissection of the human body, part one," suggesting a sequel, which, however, did not follow.
His work made a significant contribution to the development of modern anatomy. Toward the end of his life, Dryander also dabbled in astrology and mathematics.


Albrecht Dürer, born on May 21, 1471 in Nuremberg, Germany, is widely regarded as the greatest German Renaissance painter. His contribution to painting and engraving is quite significant and has left a notable mark on the art world. Dürer's early life was spent in Nuremberg, a city that played a crucial role in his development as an artist and was also the site of his death on April 6, 1528. He was the son of the goldsmith Albrecht Dürer the Elder, from whom he initially learned the basics of drawing and metalworking.
Dürer's work is characterized by a combination of Gothic elements with the emerging Renaissance style, which is evident in his woodcuts and engravings. His oeuvre encompasses many themes, including religious works, altarpieces, portraits, and self-portraits. His outstanding prints, such as The Knight, Death and the Devil (1513), St. Jerome in his Study (1514) and Melencolia I (1514), are known for their intricate detail and artistic skill. Dürer was also one of the earliest European landscape painters, as evidenced by his watercolor paintings.
Equally significant are his theoretical writings on mathematics, perspective, and ideal proportions in art. Dürer was not only an artist but also a keen intellectual, his interests encompassing various aspects of culture and science. He served as court painter to Holy Roman Emperors Maximilian I and Charles V, completing several significant art projects for them. Dürer's keen mind and versatile interests brought him into contact with the most prominent figures of his time, including theologians and scientists of the Reformation era.
Dürer's self-portraits are particularly famous, demonstrating not only his artistic skill but also his self-awareness and personal style. These portraits attest to his growing success and confidence as an artist. Dürer's legacy is immense; he influenced not only the art of his time, but also left an indelible mark on the history of European art.
For those interested in the work and legacy of Albrecht Dürer, we recommend subscribing to our updates. Our subscription service is designed to provide information about new sales and auction events related to this remarkable artist. Join us to keep up to date on the latest art and antiques related to Albrecht Dürer.


Girolamo Fabrici d'Acquapendente, also known as Girolamo Fabrizio or Hieronymus Fabricius, was an Italian anatomist and surgeon and the founder of embryology. The Latinised form of his name, under which his works can be found, is Hieronymus Fabricius (ab Aquapendente).


Wilhelm Fabry von Hilden or Fabricius von Hilden (Latin: Fabricius Hildanus) was a German and Swiss Renaissance physician and surgeon, the founder of scientific surgery.
In 1576 he began a four-year apprenticeship as a surgeon with a barber in Neuss. Surgery at that time was considered the craft of bath and barbers; surgeons or wound doctors treated wounds, broken bones, inflammations, and many other ailments. After completing his apprenticeship, Fabry worked for five years as an assistant wound surgeon to Cosmas Slot (died 1585) at the court of Duke Wilhelm V in Düsseldorf. To expand his anatomical knowledge, Fabry constantly dissected and prepared cadavers. In later years, he also encouraged his students to do so and conducted public autopsies to draw attention to the importance of anatomical knowledge. He also made it a habit to do practice procedures on a cadaver before surgery.
In 1615 Fabry was appointed city physician of Bern. Here he wrote several books on gunshot wounds. In 1623 the versatile physician published a small book, "Christian and Good-Hearted Caution against Drunkenness," which he republished in more detail the following year under the title Christlicher Schlafftrunck. Fabry's most important surgical treatise was Observationem et curationem chirurgicam centuriae sex ("Six hundred surgical observations and cures"), first published in 1606. This compilation remained the most important book of German surgery until Lorenz Heister. It describes new surgical methods and surgical instruments for the treatment of amputations, nasal polyps, bladder stones, dropsy, hernias, ascites, etc., etc., etc.
For centuries, Fabricius remained one of the most respected surgeons not only in Germany and Switzerland, but throughout Europe. Among his many accomplishments in the field of surgery may be enumerated his innovation in the amputation of the thigh, for which he invented a special tourniquet; the excision of involved axillary glands in breast cancer; the first classification of burns into three degrees with the appropriate treatment for each variety; and the first description of a medical field chest for military purposes.
Although in his later years Fabritius had already given up practicing medicine, he continued to write medical papers and maintain an active scientific correspondence until his death. He authored some 20 medical books. It was his surgical works, translated into German, French, Latin, English and Dutch, that ensured his recognition centuries later.


Gabriele Falloppio was an Italian physician and anatomist of the Renaissance.
Originally a priest, Falloppio soon left for Ferrara to study medicine and was later appointed anatomy professor there, and in 1548 he became head of the anatomy department at Pisa. Three years later he accepted the offer of the Venetian Senate to become professor of anatomy, surgery, and botany at Padua, where he remained for the rest of his life. It was in this city that he made his most famous discoveries, was director of the famous botanical garden, and wrote two medical textbooks.
He also gained a reputation as an excellent teacher and lecturer, attracting many Italian and foreign students to the medical faculty of the University of Padua. As a physician, he made a thorough study of the clinical aspects and treatment of syphilis, and proposed the condom as a defense against venereal disease.
Falloppio was a versatile scientist and an able physician and surgeon, describing, among other things, the semicircular canals, the cuneiform sinuses, the trigeminal, auditory and lingual pharyngeal nerves, the canal of the facial nerve, and the fallopian tubes, named Fallopian tubes in his honor. Falloppio described his discoveries in his three-volume work Opera genuina omnia, published in Frankfurt in 1600 and in Venice in 1606.


Gemma Frisius, born Jemme Reinerszoon Frisius, was a Dutch mathematician, physician, cartographer, philosopher, engraver, and master of astronomical instruments.
He taught mathematics and medicine at the University of Leuven and applied his mathematical knowledge to astronomy, geography, and map-making. Frisius participated in the creation of the latest globes and used mathematics in geodesy and navigation in new ways and invented or improved many instruments, including the cross staff, the astrolabe, and the astronomical rings (also known as "Gemma rings"). He ran a workshop for making such instruments.
Frisius is credited with being one of the founders of the Dutch school of cartography.


Leonhart Fuchs was a German humanist scientist, botanist, and physician.
Fuchs received a humanistic education under Catholic guidance, but later became a Protestant. He studied medicine and became a professor in Tübingen. He was most interested in the medicinal properties of plants. Well acquainted with the Greek and Latin classics and an excellent observer, he gave precise descriptions, and his beautiful engravings of plants established the tradition of depicting plants with precise illustrations and in alphabetical order.
In 1542 Fuchs published his most important work, De Historia Stirpium Commentarii Insignes (Famous Commentaries on the History of Plants). The book was a great success, especially because of the magnificent woodcuts and the 487 plants, which were described for the first time in such a systematic form. De Historia Stirpium survived several editions and was translated into Dutch and German.


Galileo Galilei was an Italian naturalist, physicist, mechanic, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician.
Using his own improved telescopes, Galileo Galilei observed the movements of the Moon, Earth's satellites, and the stars, making several breakthrough discoveries in astronomy. He was the first to see craters on the Moon, discovered sunspots and the rings of Saturn, and traced the phases of Venus. Galileo was a consistent and convinced supporter of the teachings of Copernicus and the heliocentric system of the world, for which he was subjected to the trial of the Inquisition.
Galileo is considered the founder of experimental and theoretical physics. He is also one of the founders of the principle of relativity in classical mechanics. Overall, the scientist had such a significant impact on the science of his time that he cannot be overemphasized.




William Gilbert was a British physicist and medical scientist famous for pioneering the study of magnetic and electrical phenomena.
After receiving a medical degree, Gilbert settled in London and began his research. In his major work De Magnete, Magneticisque Corporibus, et de Magno Magnete Tellure (On Magnetic Stones and Magnetic Bodies and the Great Magnet of the Earth), published in 1600, the scientist describes in detail his studies of magnetic bodies and electric attraction.
After years of experimentation, he came to the conclusion that the compass arrow points north-south and downward because the Earth acts as a rod magnet. He was the first to use the terms electric attraction, electric force, and magnetic pole. Gilbert came to believe that the Earth rotates on its axis and that the fixed stars are not all the same distance from the Earth, and believed that the planets are held in their orbits by magnetism.


Fortunio Liceti (Latin: Fortunius Licetus) was an Italian physician, natural philosopher, writer and educator.
Liceti studied philosophy and medicine at the University of Bologna and earned doctorates in these disciplines. He taught logic and philosophy at the University of Pisa, and became professor of philosophy at the University of Padua and the University of Bologna. At the University of Padua, Liceti became friends with Galileo Galilei.
Liceti's inquisitive mind was interested in a wide range of subjects: from genetics and reproduction to gems and animals. In general, Fortunio Liceti was a very industrious and prolific scientist: he published a book each year, writing more than seventy works on a wide range of subjects, including the human soul, reproduction, and birth defects.
In 1616, Liceti wrote and published the first edition of De monstruorum causis, natura et differentiis (On the Causes, Nature, and Differences of Monsters), a chronologically ordered catalog of monsters from antiquity to the seventeenth century. Among these monsters were infants with congenital malformations. Liceti was one of the first scholars to attempt to systematically categorize birth defects according to their causes, including numerous causes not related to the supernatural. This topic interested the scientist greatly and he returned to it several times during his life, supplementing it with illustrations, among other things. From 1640 to 1650. Liceti also wrote and published seven different volumes in which he answered questions from famous people on a wide variety of medical topics.


Pietro Andrea Gregorio Mattioli was a 16th-century Italian physician, botanist and pharmacist.
Mattioli studied medicine in Padua and obtained a medical practice first in his hometown. Later, in the 1555-1560s, he served as personal physician to the imperial court of Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria, and Emperor Maximilian II. This high position allowed him to test the effects of poisonous plants on prisoners for scientific purposes.
Mattioli published several scientific works in which he included many of his own observations on the flora of the Alps, including previously unexplored plants. These works, based on the study of books by predecessor scientists, gave impetus to the development of botany throughout Italy at the time. Mattioli kept up a lively correspondence with other researchers, describing specimens of rare plants received from them. The genus of flowering plants Matthiola is named after Mattioli.


Thomas Moffet was a British naturalist-naturalist and physician.
After receiving his MD degree in 1580, Thomas Moffet studied the anatomy of the mulberry silkworm in Italy, then returned to England to study arthropods in general, especially spiders. He edited and expanded the work Insectorum sive Minimorum Animalium Theatrum ("Insect Theater"), an illustrated guide to the classification and life of insects.
Moffet was also an ardent supporter of the Paracelsian system of medicine.


Sebastian Münster was a German Renaissance scholar, cartographer and cosmographer, historian and linguist-translator.
Münster studied at the University of Tübingen and later taught at the Universities of Basel and Heidelberg. He published several editions of Hebrew grammars and translations from that language, and was the first German to produce an edition of the Hebrew Bible.
In 1544 Münster published his Cosmographia, which was the earliest description of the history, geography, and organization of the world in German. This book was a great success, translated into many European languages and reprinted more than twenty times. "Cosmographia" contained many illustrations and geographical maps of the continents of the world, created by the best engravers of the time.
Among his other works were the "Trilingual Dictionary" (1530) in Latin, Greek, and Hebrew and the "Map of Europe" (1536).


Paolo Ricci (Italian: Paolo Ricci, Latin: Paulus Ricius, German: Paul Ritz), also known as Ritz, Riccio, or Paulus Israelita, was a humanist convert from Judaism, a writer-theologian, Kabbalist, and physician.
After his baptism in 1505 he published his first work, Sol Federis, in which he affirmed his new faith and sought through Kabbalah to refute modern Judaism. In 1506 he moved to Pavia, Italy, where he became a lecturer in philosophy and medicine at the university and met Erasmus of Rotterdam. Ricci was also a learned astrologer, a professor of Hebrew, philosophy, theology, and Kabbalah, a profound connoisseur and translator of sacred texts into Latin and Hebrew, and the author of philosophical and theological works.
Paolo Ricci was a very prolific writer. His Latin translations, especially the translation of the Kabalistic work Shaare Orach, formed the basis of the Christian Kabbalah of the early 16th century.


Celio Rodigino (Latin: Caelius Rhodiginus), real name Ludovico Ricchieri, was an Italian writer, educator and Renaissance humanist.
Rodigino studied in Ferrara and Padua, and then was professor of Greek and Latin at Rovigo. In 1515 he became chair of Greek at the University of Milan.
His principal work was Antiquarum Lectionum in sixteen books, published in Venice in 1516. In this work Rodigino collected a considerable number of short essays and notes on Latin and Greek antiquity, from literature, philology, and science to philosophy, history, anthropology, and morality, as well as reflections on ancient music. He also wrote commentaries on Virgil, Ovid, and Horace.


Werner Rolewinck (Latin: Wernerus Rolewinkius) was a German chronicler, historian, and theologian.
Werner Rolewinck was a Cartesian monk. His best known and most important work is Fasciculus temporum, a history from the creation of the world to Pope Sixtus IV. Already during his lifetime this work was republished many times in Latin, French, Dutch, and German. Drawing on major Christian historiographical sources such as Orosius and Eusebius, Fasciculus presents the history of the world in the form of a genealogy, a traditional historiographical structure dating back to late antiquity.
Another famous work by Rolewink is a description of the manners and customs of his homeland entitled De laude veteris Saxsoniæ nunc Westphaliæ dictæ.


Eucharius Rösslin the Elder or Eucharius Rößlin was a German medieval scholar, physician-midwife, and pharmacist.
In 1493 Eucharius became apothecary in Freiburg, and 13 years later was elected physician of the city of Frankfurt am Main. From there he moved to Worms, in the service of Katherine, Princess of Saxony and Duchess of Brunswick and Lüneburg. One of his duties was to oversee and supervise the city's midwives, whose ignorance led to a high infant and female mortality rate.
In order to remedy this, Eucharius wrote and published a book on midwifery called Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden for Pregnant Women and Midwives") in Strasbourg in 1513. It was in German and contained several engravings. The book proved very popular and soon became the standard medical textbook for midwives. For nearly two centuries it was the authoritative guide to midwifery in Europe, translated into seven languages and reprinted over a hundred times.
In 1517 Rösslin returned to work in Frankfurt and remained in that position until his death in 1526. His son, also named Eucharius Rösslin, succeeded him as city physician.


Desiderius Erasmus, also Erasmus of Rotterdam, or simply Erasmus (Latin: Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus, Dutch: Gerrit Gerritszoon) was a Dutch humanist, philosopher, and the greatest scholar of the Northern Renaissance.
He was illegitimate and brought up under the name Gerhard Gerhards, later in Latin his name was dubbed Desiderius Erasmus. At the age of 13, the boy was sent to a monastery, where he later took the ministry. Erasmus read a lot, improving in Latin and Ancient Greek, studied oratory. A few years later he received the post of secretary to the bishop of the French city of Cambre. From 1493 to 1499 Rotterdam lived in Paris, then in London he was introduced to Thomas More, John Fisher, and John Colet.
Erasmus was constantly on the move, rarely staying in one place and traveling frequently between the Netherlands, Britain, France and Italy. In Turin he earned a doctorate in theology and was received by the Pope, then taught ancient Greek and theology at Cambridge. He corresponded with the rulers of various countries, popes and cardinals, and with statesmen, answering their questions of a scientific, political, and philosophical nature. As a true humanist, Erasmus of Rotterdam adhered to the ideas of a scientific spirit that favored research and true knowledge.
Among the merits of Rotterdamsky study of religious texts from a scientific position, critical interpretation of theology. Erasmus was able to lay the groundwork for historical-critical study of the past, especially in his studies of the Greek New Testament and the church fathers. His educational writings helped to replace the old school curriculum with a new humanistic emphasis on the classics.
In 1501, Erasmus produced a religious and ethical treatise, The Arms of the Christian Warrior, published in 1504. His work entitled "The Praise of Folly" was reprinted 40 times only during the author's lifetime, the book has been translated into all popular languages of the world. The series "Conversations in a Simple Way" (1518-1533) is among the most popular books on pedagogy. Erasmus promoted respect and care for children, opposing violence and corporal influence. He also promoted the idea that education should be compulsory for everyone.


Hartmann Schedel was a German humanist, medical scientist, historian and chronicler.
Schedel was the first to compile a world chronicle, the so-called Visual History of the Earth from the Creation of the World to the 1490s, known as Schedelsche Weltchronik (Schedel's World Chronicle). It was published in 1493 in Nuremberg. About 600 woodcuts for this book were created by the artists and engravers Michael Wolgemuth (1434-1519) and Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528). The illustrations depict biblical scenes, family trees, portraits of famous personalities, and fairy tale or legendary creatures. However, the main ones here were maps of the world, Germany and Central Europe.
Hartmann Schedel was one of the first cartographers to use machine printing. He was also a renowned collector of books, artworks and engravings by old masters.


Marco Aurelio Severino was an Italian surgeon, anatomist and zoologist, one of the founders of comparative anatomy.
From childhood Severino studied Latin, Greek, rhetoric, poetry and law in various schools in Calabria, then continued his studies in Naples, soon moving from law to medicine. In Naples he met Tommaso Campanella, who had a great influence on the formation of his worldview. After receiving a medical degree in Salerno in 1606, he studied surgery in Naples with Giulio Jasolino. In 1615 Severino was appointed the first surgeon at Ospedale degli Incurabili. Severino made significant contributions to the transformation of naturophilosophy, medical and surgical practice, to which much of his printed work is devoted.
Severino's main contribution, however, lies in his anatomical works, especially the Zootomia Democritea. This work may be called the earliest comprehensive treatise on comparative anatomy. Severino is considered one of the pioneers of comparative anatomy.
Severino's cultural interests extended far beyond medicine. He corresponded with many prominent physicians and scientists of his time, including William Harvey and John Houghton in England, Thomas Bartolin and Ole Worm in Denmark, J.G. Volkamer and Johannes Wesling in Germany, and Campanella, Jasolino, and Tommaso Cornelio in Italy. Severino was tried by the Inquisition for allegedly unorthodox religious and philosophical views, but was eventually acquitted. He died of the plague in Naples.


Andreas Vesalius (Dutch: Andries van Wesel) was a Flemish physician, one of the first anatomists of the Renaissance.
Vesalius came from a family of physicians and apothecaries, studied at the Catholic University of Leuven and at the medical school of the University of Paris, where he learned to dissect animals. He also had the opportunity to dissect human cadavers and devoted much time to the study of human bones. He later went to the University of Padua and, after earning his MD degree, was appointed professor of surgery, whose duties included anatomical demonstrations.
Vesalius revolutionized the study of biology and medical practice through his careful description of the anatomy of the human body. Based on observations made by himself, he wrote and illustrated the first complete textbook of anatomy. In 1543 his major work De humani corporis fabrica libri septem ("Seven Books on the Structure of the Human Body"), commonly known as Fabrica, was printed. In this epochal work, Vesalius gave far more extensive and accurate descriptions of the human body than anything that had been done by his predecessors.
In the same year, 1543, the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V appointed him staff physician of his house, and in 1559 Vesalius became physician to the Madrid court of Charles V's son, Philip II.
Vesalius' work made anatomy a scientific discipline with far-reaching implications not only for physiology but for all of biology.























