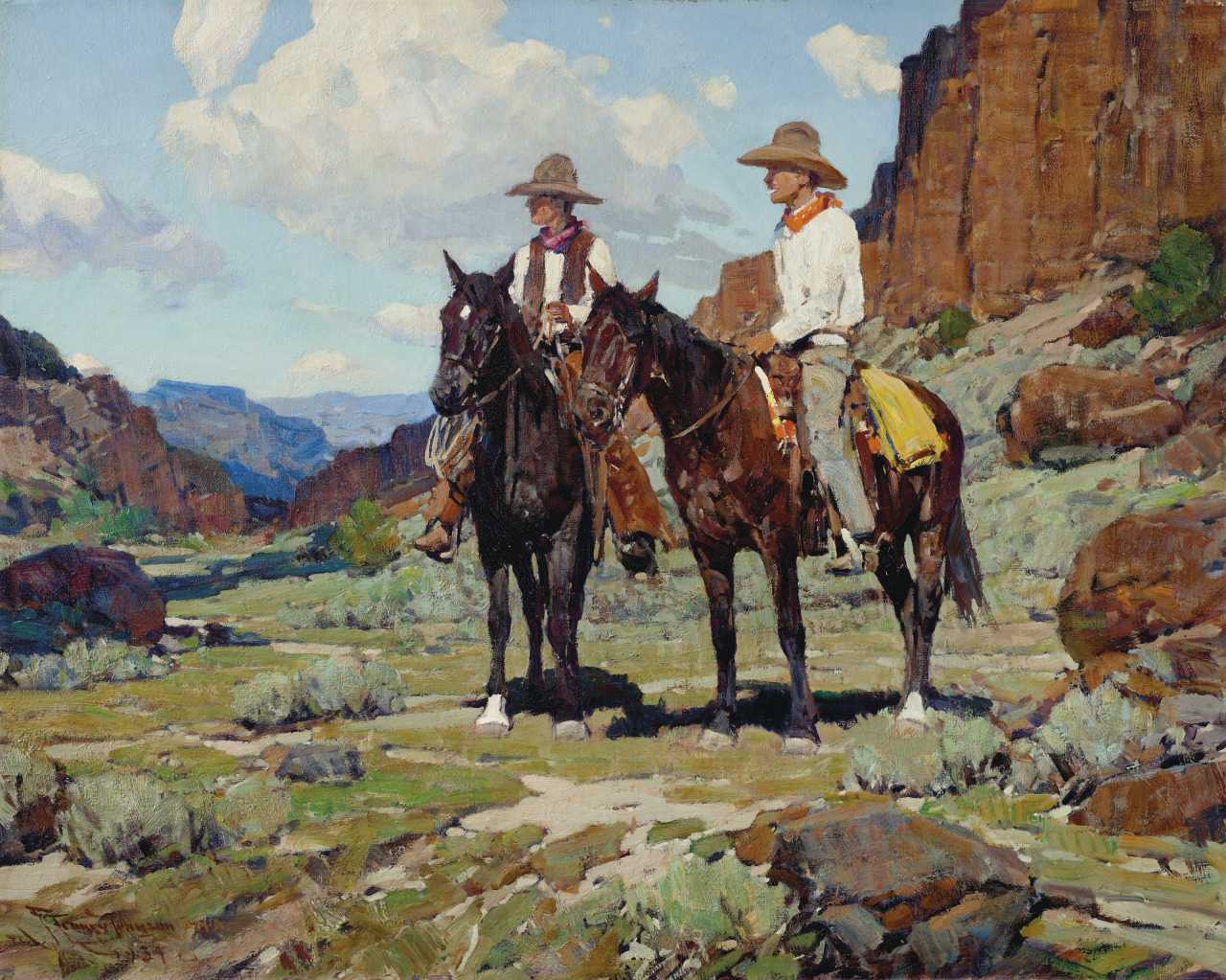
Paintings — The Legend of the West: Iconic Works from the T. Boone Pickens Collection
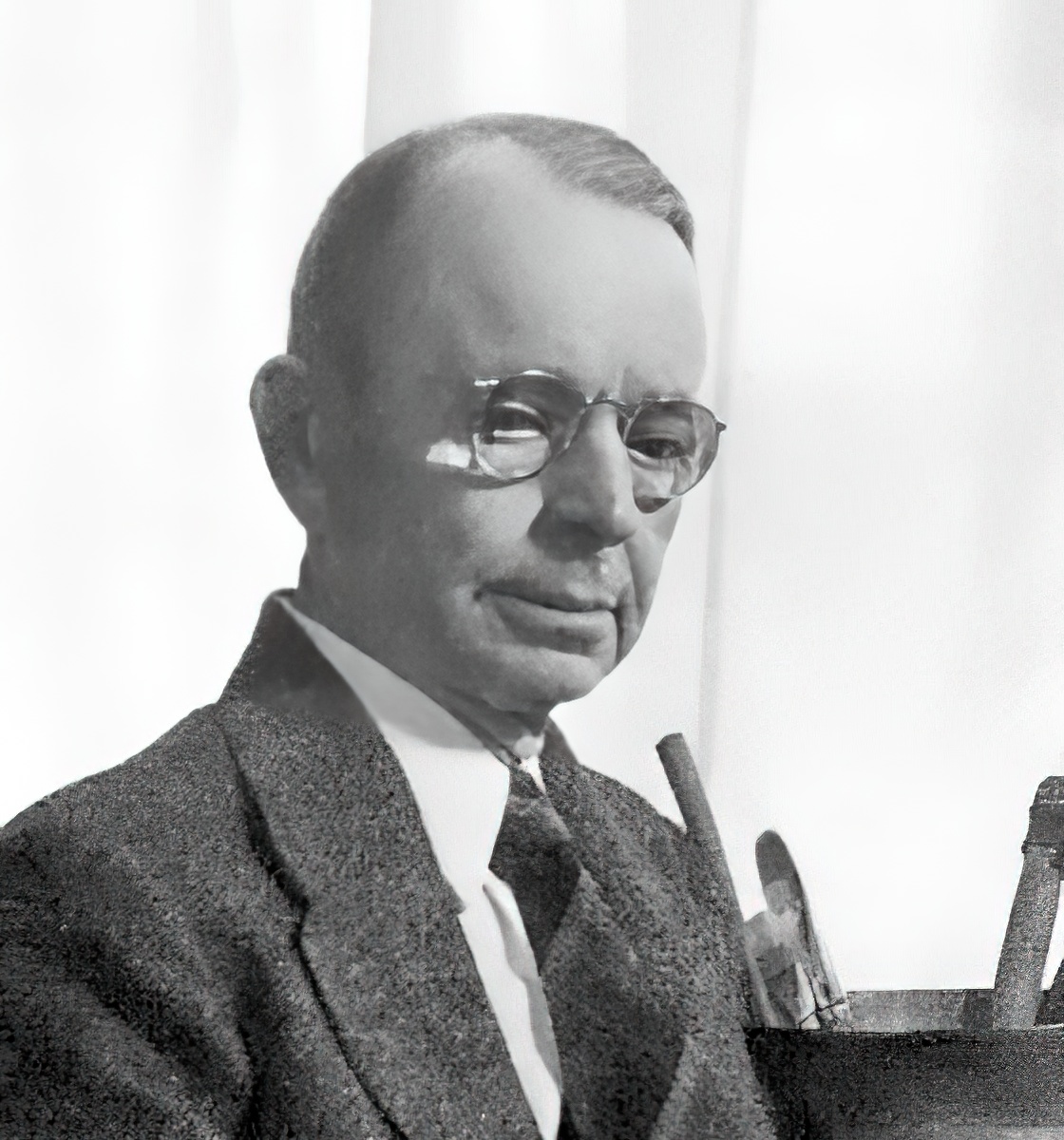

Oscar Edmund Berninghaus was an American artist and a founding member of the Taos Society of Artists. He is best known for his paintings of Native Americans, New Mexico and the American Southwest. His son, Charles Berninghaus (1905–1988), was also a Taos artist.

Charles Marion Russell, also known as C. M. Russell, Charlie Russell, and "Kid" Russell, was an American artist of the American Old West. He created more than 2,000 paintings of cowboys, Native Americans, and landscapes set in the western United States and in Alberta, Canada, in addition to bronze sculptures. He is known as "the cowboy artist" and was also a storyteller and author. He became an advocate for Native Americans in the west, supporting the bid by landless Chippewa to have a reservation established for them in Montana. In 1916, Congress passed legislation to create the Rocky Boy Reservation.
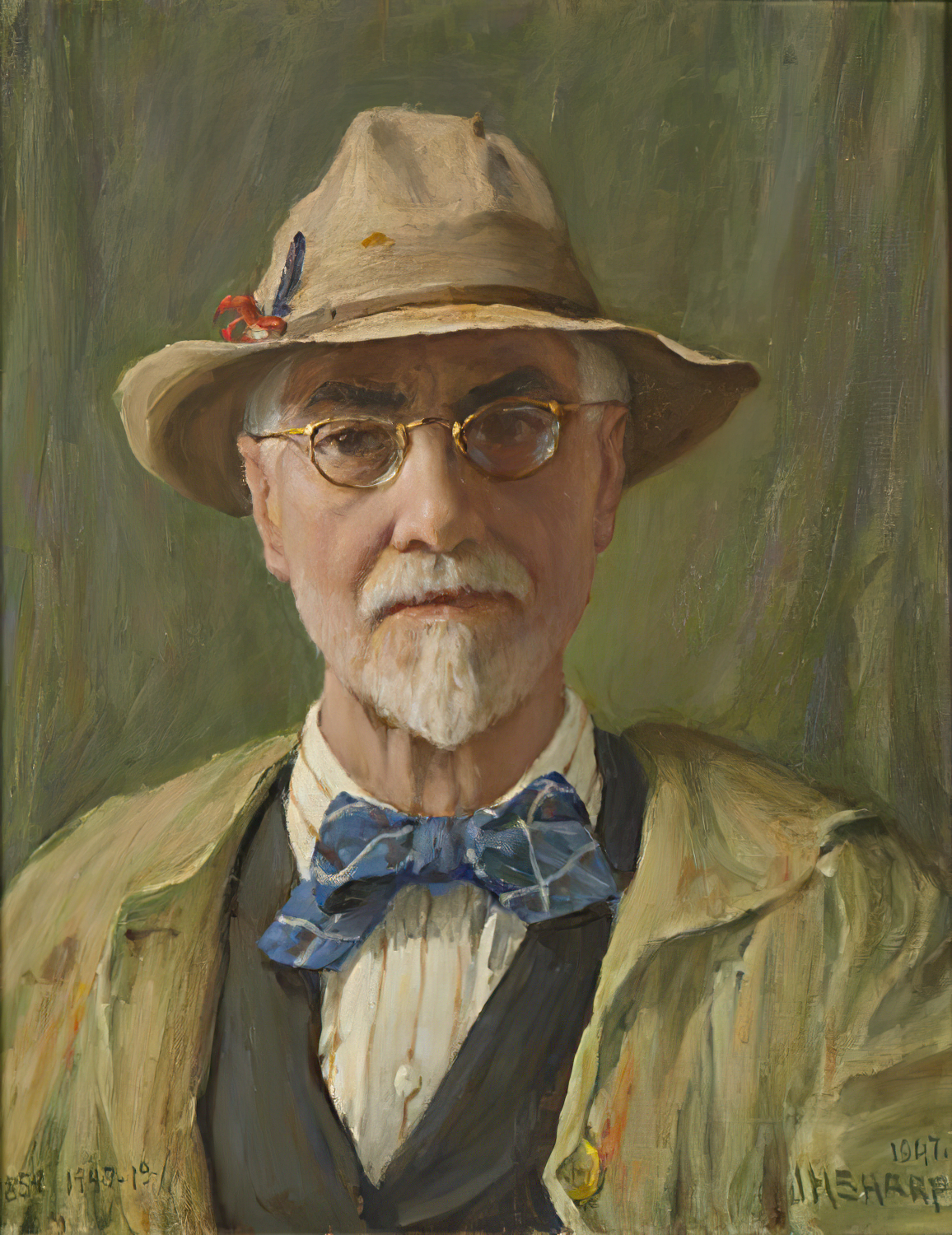

Joseph Henry Sharp was an American artist and one of the founders of the Taos Society of Artists. He painted portraits, landscapes as well as paintings of Native American cultural life.
Joseph Henry Sharp began his career as an artist in the 1880s, working in New York and Paris. His colourful and emotional paintings were characterised by a high degree of realism and detail.

Newell Convers Wyeth, better known as N.C. Wyeth, was an American painter and illustrator, celebrated for his vivid and dramatic illustrations that brought to life classic literature for the Scribner’s Illustrated Classics series. Born on October 22, 1882, in Needham, Massachusetts, Wyeth displayed artistic talent from an early age, encouraged by his supportive mother. He trained under the tutelage of Howard Pyle, the "father of American illustration," who influenced him deeply, instilling a penchant for romanticism and historical accuracy in his work.
Wyeth’s illustrations for books like "Treasure Island," "The Last of the Mohicans," and "Robinson Crusoe" are among his most famous and have left a lasting legacy in the field of American illustration. His work was characterized by a robust, painterly style that effectively conveyed the adventure and emotion of the stories he illustrated. Beyond book illustrations, Wyeth also excelled in creating murals and was commissioned to paint for various public and private institutions, including banks and schools, depicting scenes that ranged from historical narratives to allegorical themes.
Despite his commercial success, Wyeth often expressed a desire to be recognized for his personal paintings, and he struggled with the commercial constraints of illustration. He explored a variety of artistic styles throughout his career, including Impressionism and Realism, and was an adept muralist as well as a studio artist. His legacy continues to influence artists and captivates art collectors and experts in the field, securing his place as a key figure in American art history.
For those interested in staying updated on exhibitions and sales related to N.C. Wyeth, consider signing up for updates focused on his works and related auction events.
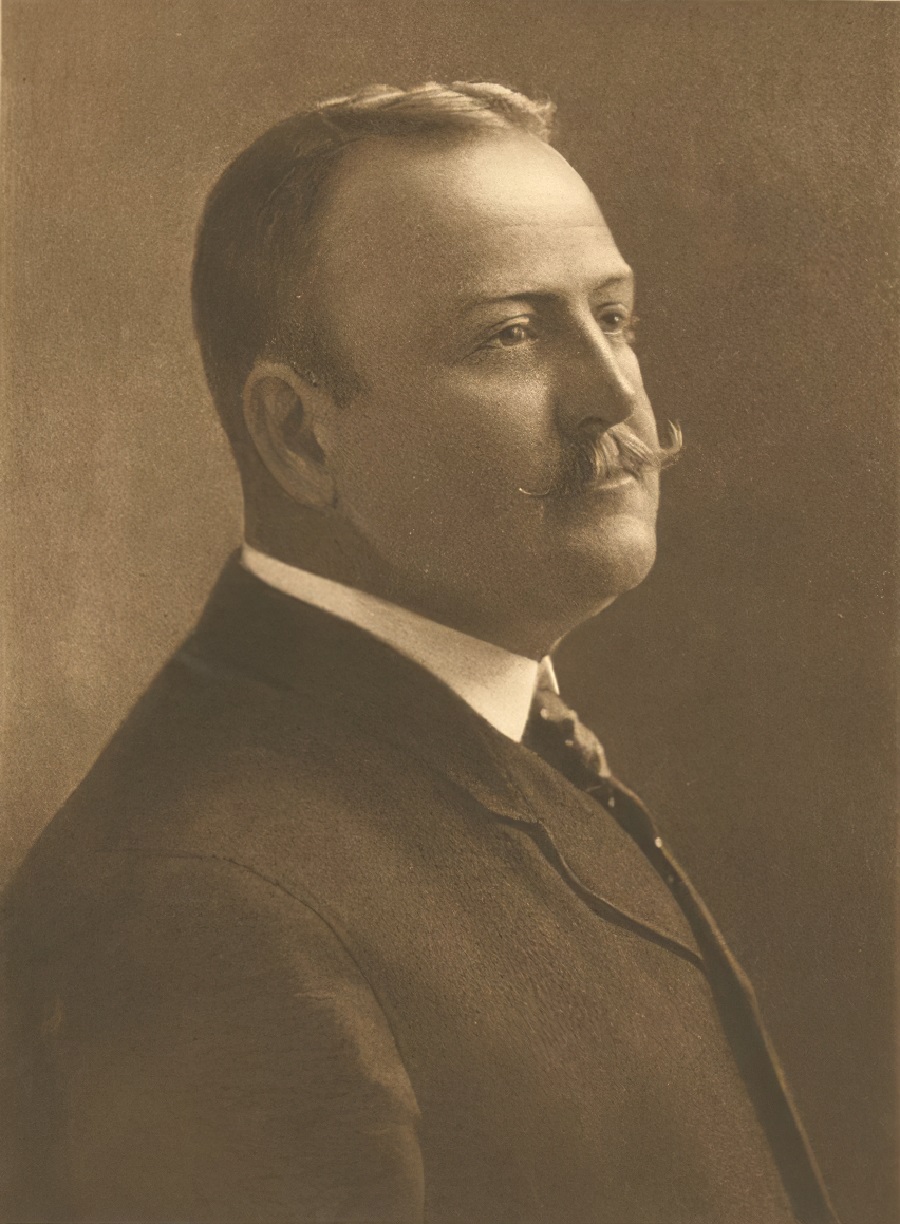

Frederic Sackrider Remington, an American artist born in 1861 in Canton, New York, is celebrated for his vivid portrayals of the American West. Specializing in painting, sculpture, and illustration, Remington captured the essence of Western life through dynamic scenes of cowboys, Native Americans, and the U.S. Cavalry, evoking a nostalgic era that was quickly vanishing by the late 19th century.
Remington's early experiences in the West, which included ventures into sheepherding and prospecting, profoundly influenced his artwork. Despite initial business failures and personal setbacks, his first-hand encounters with the rugged landscapes and frontier characters provided authentic material for his art. By the mid-1880s, Remington’s work began to gain recognition, and he quickly established himself as a significant figure in Western art, contributing illustrations to popular magazines like Harper’s Weekly.
In his later years, Remington's style evolved, displaying a notable shift towards impressionism and atmospheric mood in his "Nocturnes" series. These paintings are characterized by a dramatic use of light and shadow to convey the mystery and tension of nighttime in the West. Despite his own critical self-view, these works were highly regarded and marked a significant contribution to American art history. Remington’s art is featured in major collections, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Frederic Remington Art Museum in Ogdensburg, New York, preserving his legacy as an icon of American culture.
For those interested in exploring more about Frederic Remington’s life and works, updates on exhibitions and sales can be subscribed to, keeping enthusiasts connected to new insights and offerings related to this influential artist.

Peter Hurd was an American painter whose work is strongly associated with the people and landscapes of San Patricio, New Mexico. He is equally acclaimed for his portraits and his western landscapes. His large egg tempera paintings earned him national recognition. During World War II, Hurd worked for Life magazine as a war correspondent attached to the US Air Force. He covered almost all the fronts of the far-flung battle line, creating hundreds of "War Sketches" that range from poignant to comic. Some of Hurd’s most well-known portraits were of his neighbors, family, and friends at Sentinel Ranch. He loved to paint people who were deeply connected to the land, and always showed them outdoors, against the hills and sky. Many of Hurd's works can be seen at the Hurd-La Rinconada Gallery in San Patricio, New Mexico.

Frederic Sackrider Remington, an American artist born in 1861 in Canton, New York, is celebrated for his vivid portrayals of the American West. Specializing in painting, sculpture, and illustration, Remington captured the essence of Western life through dynamic scenes of cowboys, Native Americans, and the U.S. Cavalry, evoking a nostalgic era that was quickly vanishing by the late 19th century.
Remington's early experiences in the West, which included ventures into sheepherding and prospecting, profoundly influenced his artwork. Despite initial business failures and personal setbacks, his first-hand encounters with the rugged landscapes and frontier characters provided authentic material for his art. By the mid-1880s, Remington’s work began to gain recognition, and he quickly established himself as a significant figure in Western art, contributing illustrations to popular magazines like Harper’s Weekly.
In his later years, Remington's style evolved, displaying a notable shift towards impressionism and atmospheric mood in his "Nocturnes" series. These paintings are characterized by a dramatic use of light and shadow to convey the mystery and tension of nighttime in the West. Despite his own critical self-view, these works were highly regarded and marked a significant contribution to American art history. Remington’s art is featured in major collections, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Frederic Remington Art Museum in Ogdensburg, New York, preserving his legacy as an icon of American culture.
For those interested in exploring more about Frederic Remington’s life and works, updates on exhibitions and sales can be subscribed to, keeping enthusiasts connected to new insights and offerings related to this influential artist.
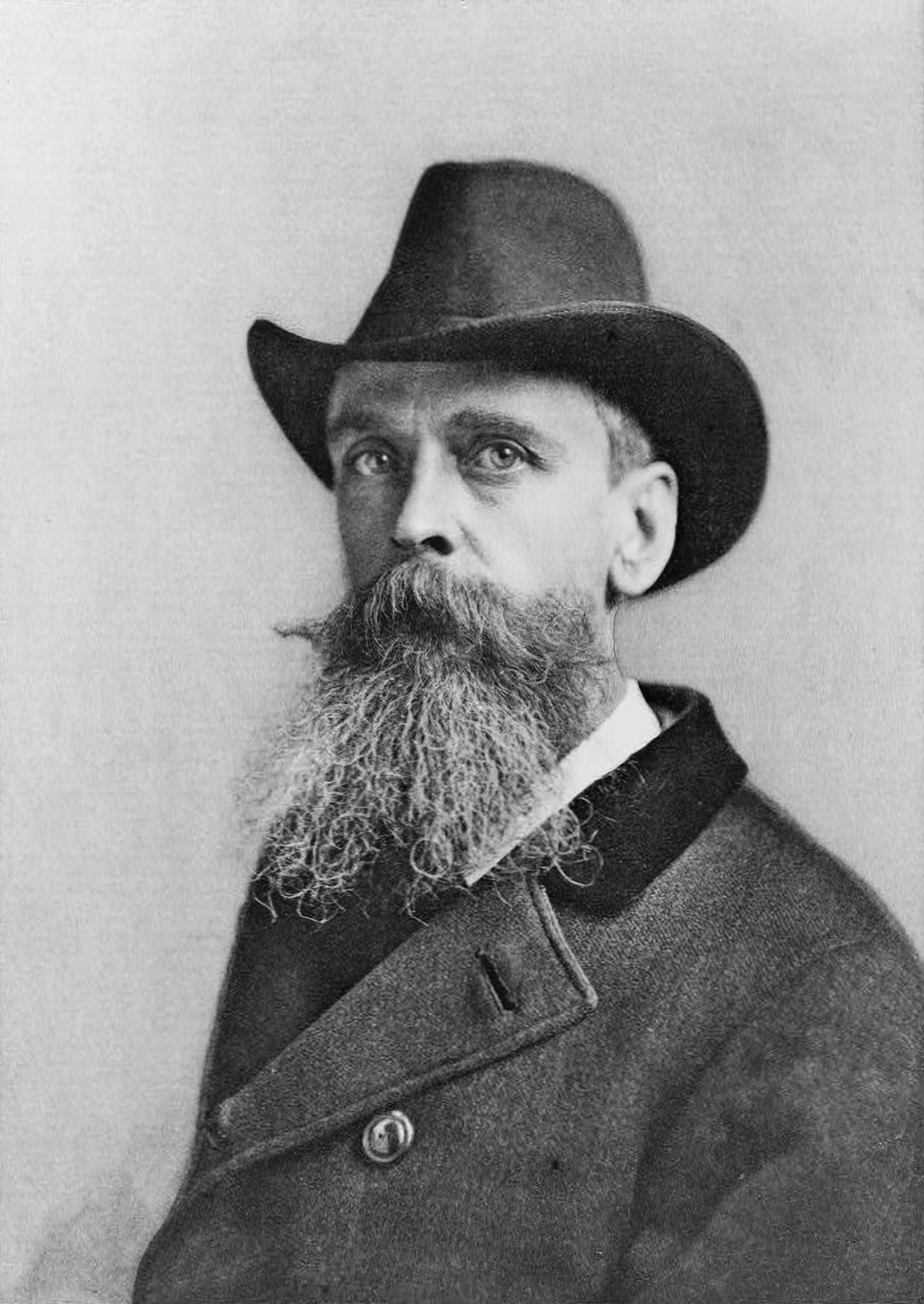

Thomas Moran was an American painter and printmaker of the Hudson River School in New York whose work often featured the Rocky Mountains. Moran and his family, wife Mary Nimmo Moran and daughter Ruth took residence in New York where he obtained work as an artist. He was a younger brother of the noted marine artist Edward Moran, with whom he shared a studio. A talented illustrator and exquisite colorist, Thomas Moran was hired as an illustrator at Scribner's Monthly. During the late 1860s, he was appointed the chief illustrator for the magazine, a position that helped him launch his career as one of the premier painters of the American landscape, in particular, the American West.
Moran along with Albert Bierstadt, Thomas Hill, and William Keith are sometimes referred to as belonging to the Rocky Mountain School of landscape painters because of all of the Western landscapes made by this group.
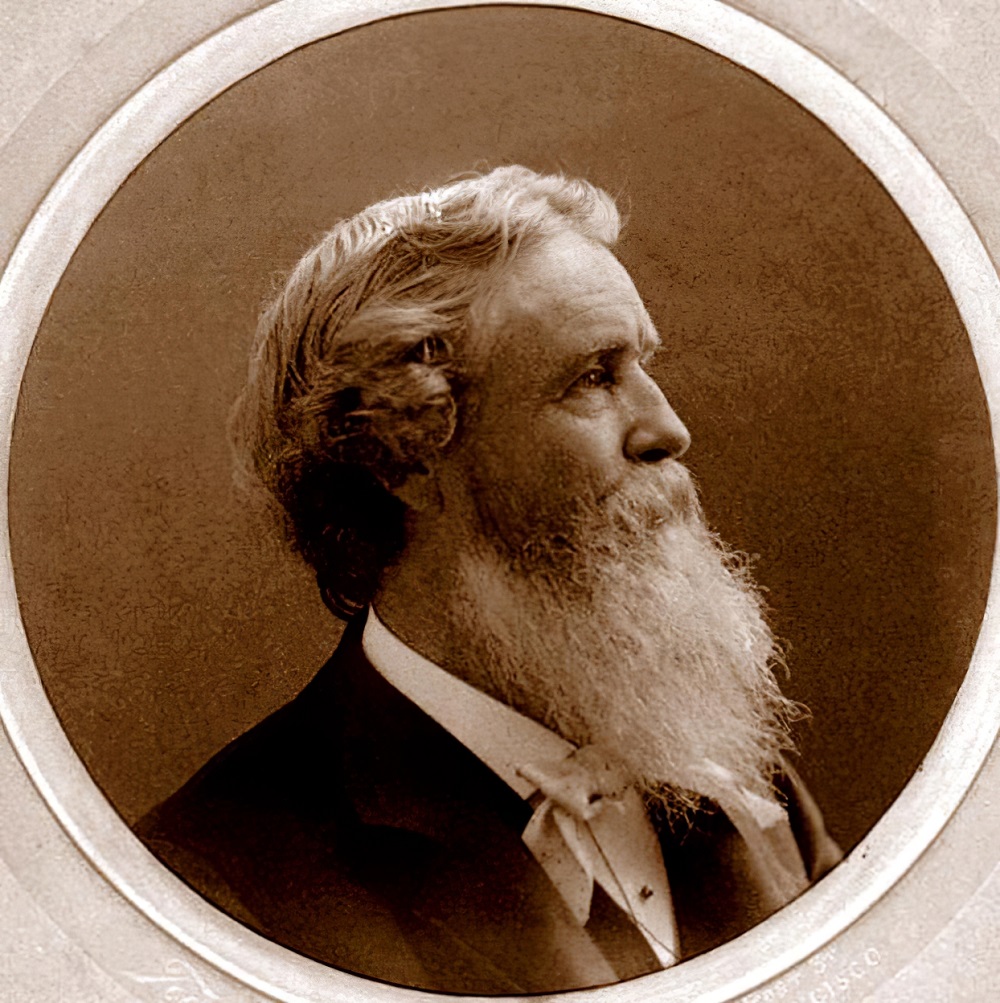

Thomas Hill was an English-born American artist of the 19th century. He produced many fine paintings of the California landscape, in particular of the Yosemite Valley, as well as the White Mountains of New Hampshire.
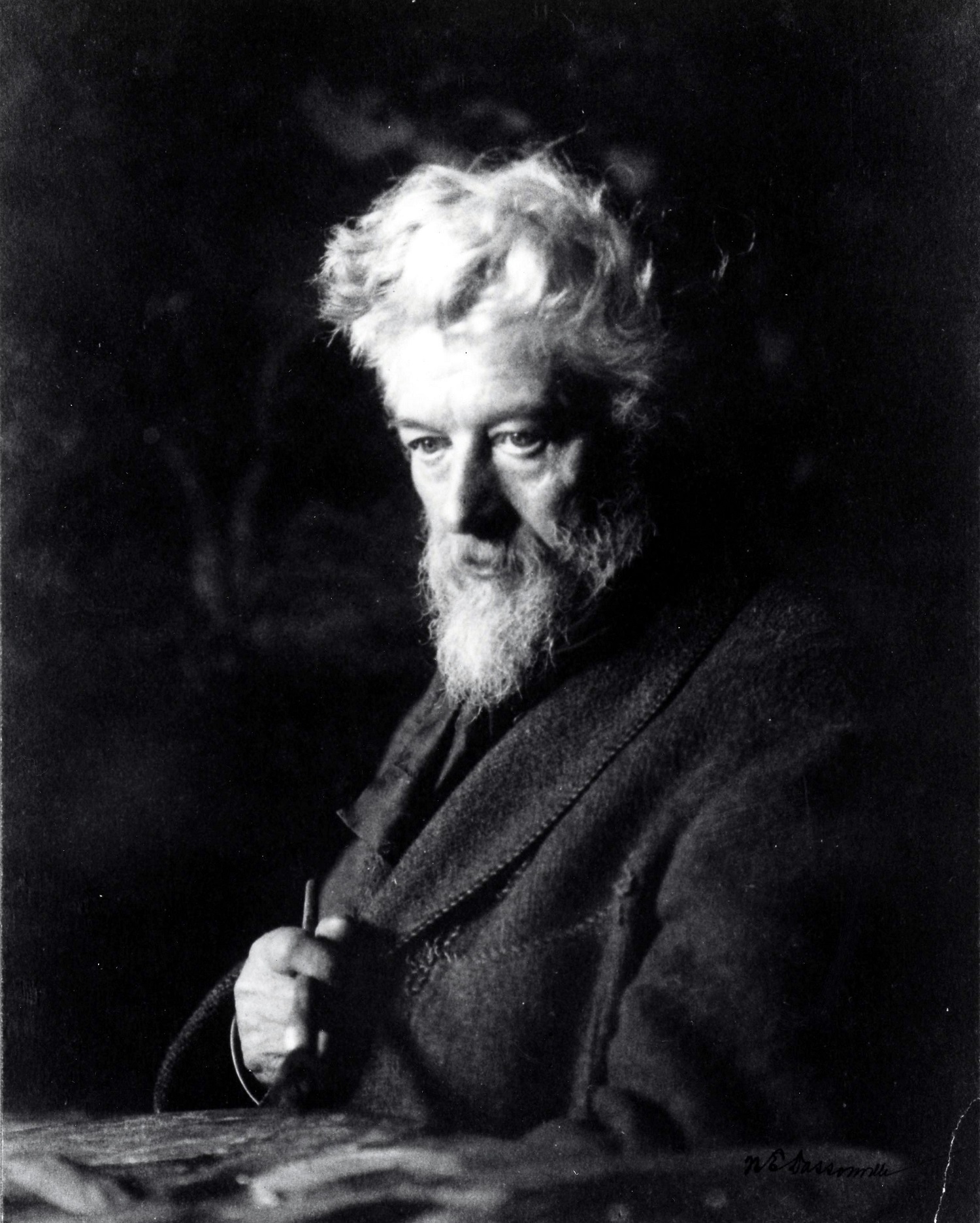

William Keith was a Scottish-American painter famous for his California landscapes. He is associated with Tonalism and the American Barbizon school. Although most of his career was spent in California, he started out in New York, made two extended study trips to Europe, and had a studio in Boston in 1871-72 and one in New York in 1880.
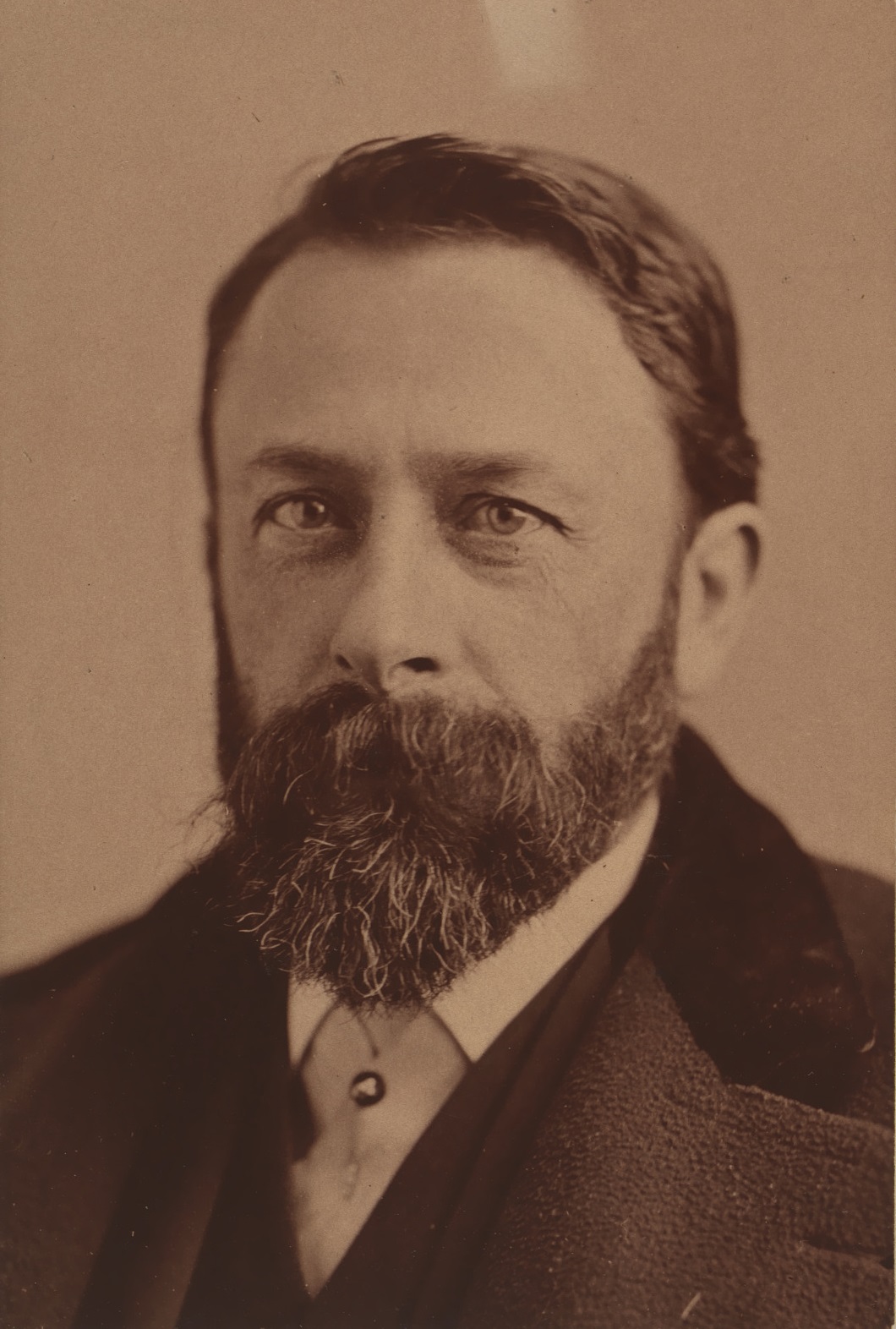

Albert Bierstadt, a German-American painter, became renowned for his expansive and romanticized landscapes of the American West. Born in Solingen, Germany, in 1830, Bierstadt moved to New Bedford, Massachusetts, at the age of two with his family. Largely self-taught, he initially worked as a drawing teacher before traveling to Europe to hone his skills. Bierstadt's European studies, particularly in Düsseldorf, greatly influenced his artistic style, equipping him with the techniques that he would later apply to his majestic depictions of the American wilderness.
Bierstadt's first major expedition to the West in 1859 marked the beginning of his lifelong fascination with the region. His works from this period, such as "The Rocky Mountains, Lander's Peak" (1863), captured the public imagination and established him as a leading figure in the Hudson River School. These paintings were celebrated for their detailed and idealized portrayal of the rugged landscapes and played a role in shaping the perception of the American West during a time of rapid territorial expansion and exploration.
Despite his success, Bierstadt's style fell out of favor towards the end of his career as tastes shifted towards realism and Impressionism. His later works, including "The Last of the Buffalo" (1888), were criticized for their perceived theatricality and excessive romanticism. Bierstadt's popularity waned, and he faced financial difficulties, but his legacy experienced a resurgence in the mid-20th century as interest in his technique and contributions to American art history grew.
For collectors and enthusiasts of American landscape painting, Bierstadt’s works offer a vivid, albeit embellished, glimpse into the 19th-century frontier spirit. His paintings are housed in major institutions like the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the National Gallery of Art, serving as testaments to his skill and vision.
To stay updated on exhibitions and sales related to Albert Bierstadt's works, consider signing up for alerts tailored to his artistic contributions. This subscription will keep you informed about new discoveries and auction events specifically linked to Bierstadt's enduring legacy.