Tables — Design
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
.jpeg)
Jean Dunand was a Swiss and French painter, sculptor, metal craftsman and interior designer during the Art Deco period. He was particularly known for his lacquered screens and other art objects.
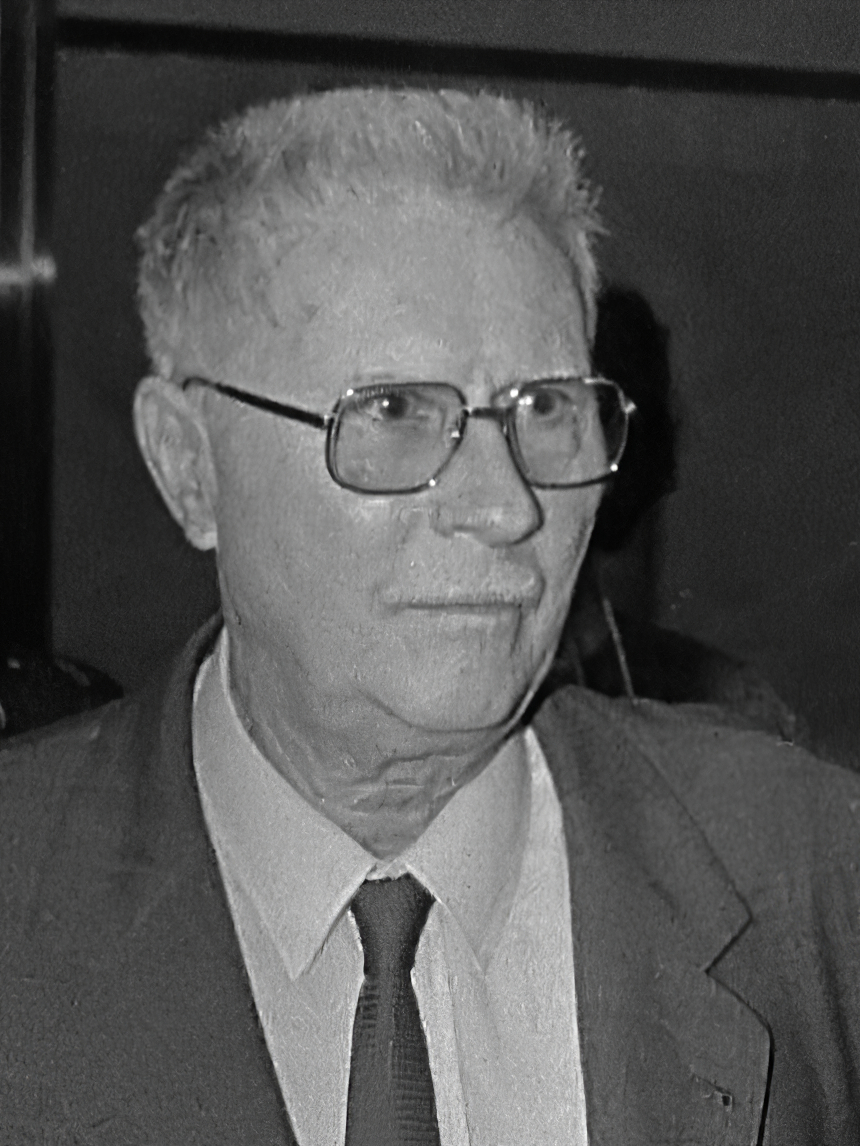

Jean Prouvé was a French metal worker, self-taught architect and designer. Le Corbusier designated Prouvé a constructeur, blending architecture and engineering. Prouvé's main achievement was transferring manufacturing technology from industry to architecture, without losing aesthetic qualities. His design skills were not limited to one discipline. During his career Jean Prouvé was involved in architectural design, industrial design, structural design and furniture design.
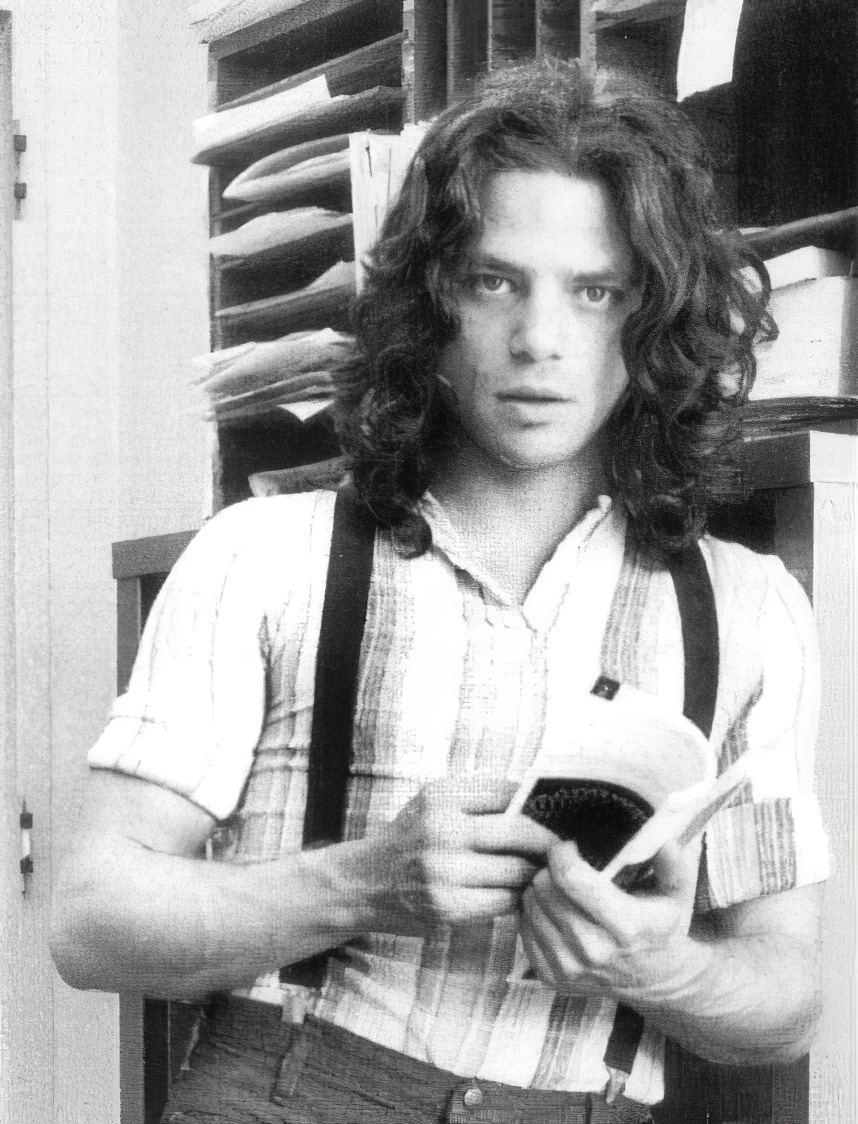

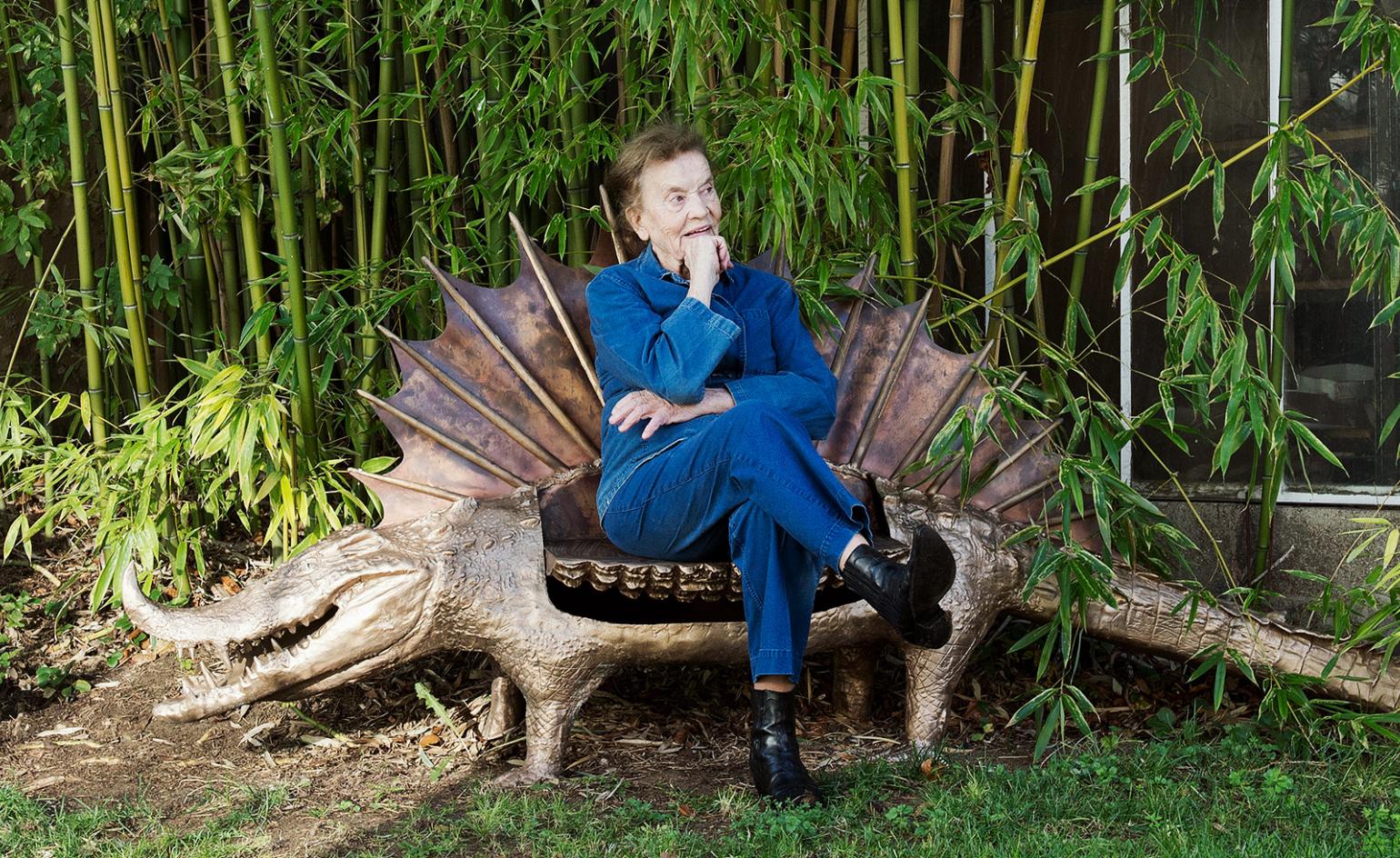
Scott Burton was an American sculptor and performance artist best known for his large-scale granite and bronze furniture sculptures.
Burton's work was aimed at blurring the boundaries between art and functional objects. He challenged the traditional notion of sculpture as an object to be admired from a distance, creating sculptures designed for audience interaction and use. His work often incorporated elements of furniture and architectural design, combining art with the practical aspects of everyday life.
Burton's approach to art was influenced by his interest in minimalism and the conceptual art movement. He believed that art should not be confined within the confines of galleries and museums, but should exist as part of the everyday environment. By integrating his sculptures into public spaces, Burton sought to change viewers' perception of both the artwork and the environment.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)
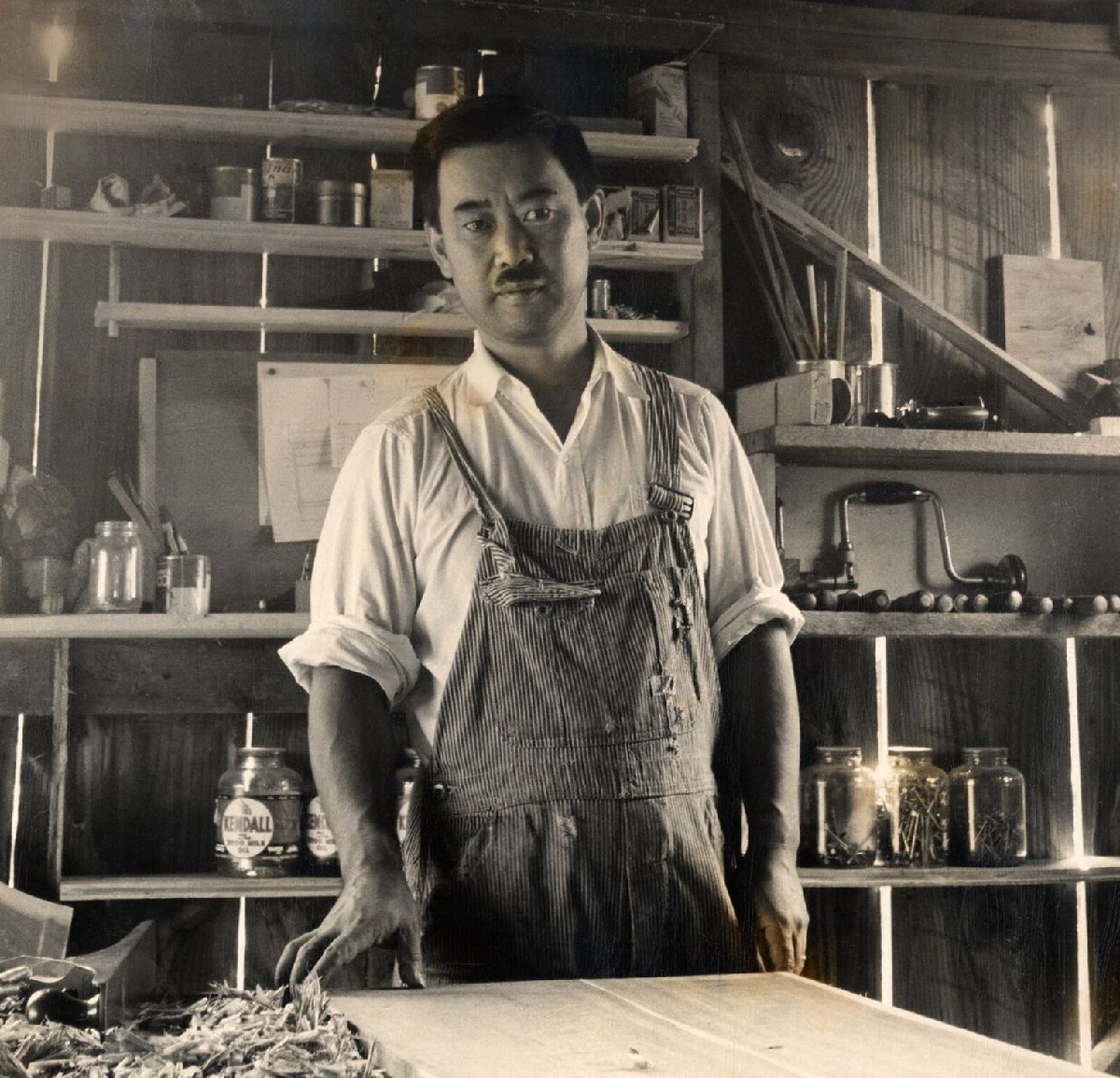

George Nakashima (Japanese: 中島勝寿) was an influential Japanese-American artist, architect, and furniture maker. He is renowned for his mastery of woodworking and his philosophy of incorporating natural materials and traditional craftsmanship into his designs.
Nakashima's furniture designs emphasized simplicity, functionality, and the integration of nature into the living space. He believed in the spiritual essence of the materials he used and aimed to create pieces that harmonized with their surroundings and brought a sense of peace and tranquility to the users.
His signature designs often featured clean lines, elegant proportions, and meticulous joinery techniques. Nakashima's work showcased a blend of Japanese aesthetics, American modernism, and his own unique artistic vision.
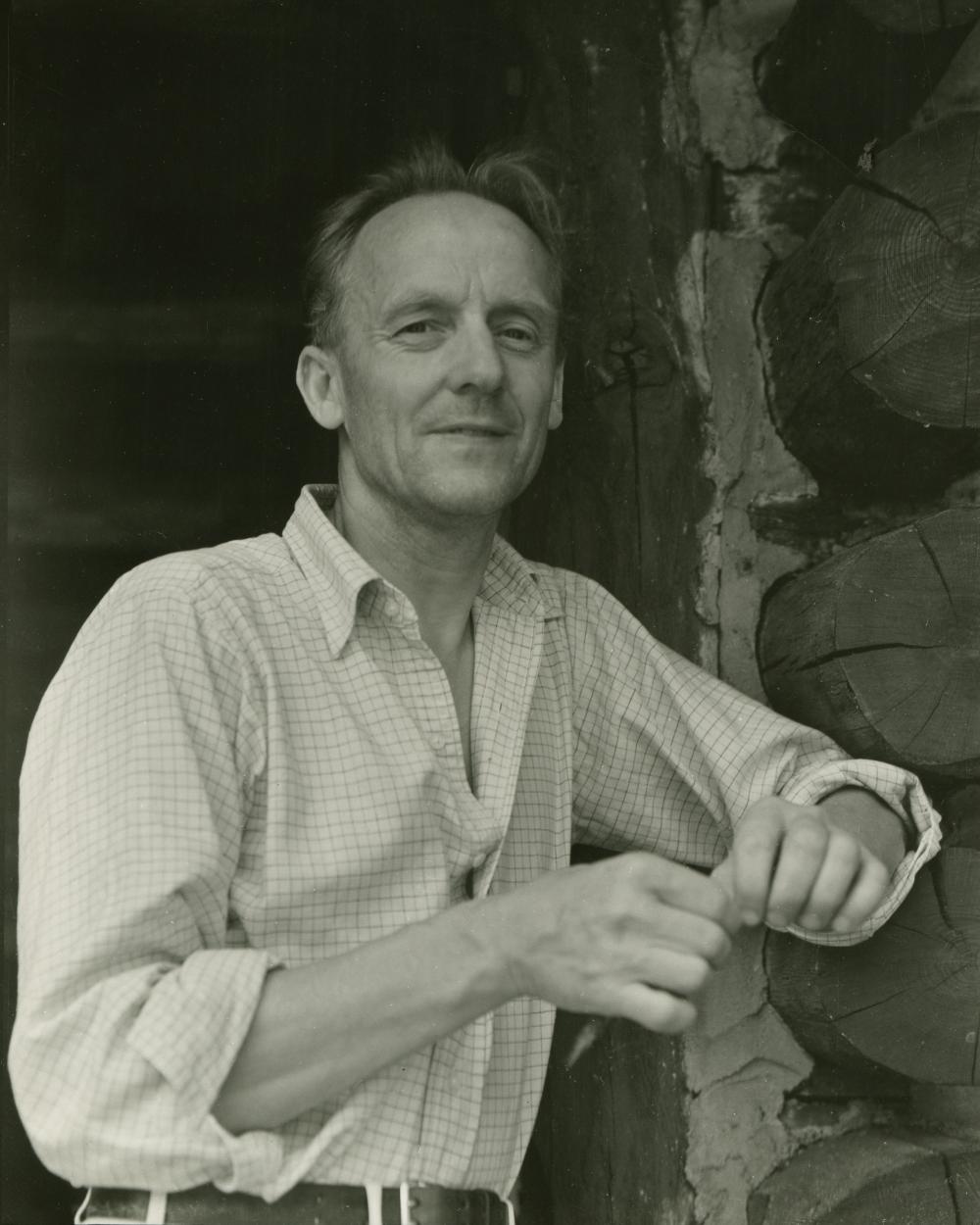

Wharton Esherick is an American artist and sculptor known for his innovative and organic approach to woodworking. He is considered one of the pioneers of the American studio furniture movement and is known for his sculptural furniture, functional objects and architectural woodworking.
Esherick's creative journey led him to experiment with various mediums, including painting, printmaking and sculpture, but it was his work in woodworking that brought him the most recognition.
Esherick developed a distinctive style characterized by organic forms, sculptural detailing and an emphasis on the natural qualities of wood. He believed that furniture design should reflect the inherent qualities of the materials used. Esherick adhered to the concept of "truth of materials", allowing wood to guide his artistic process and shape the final form of his creations.
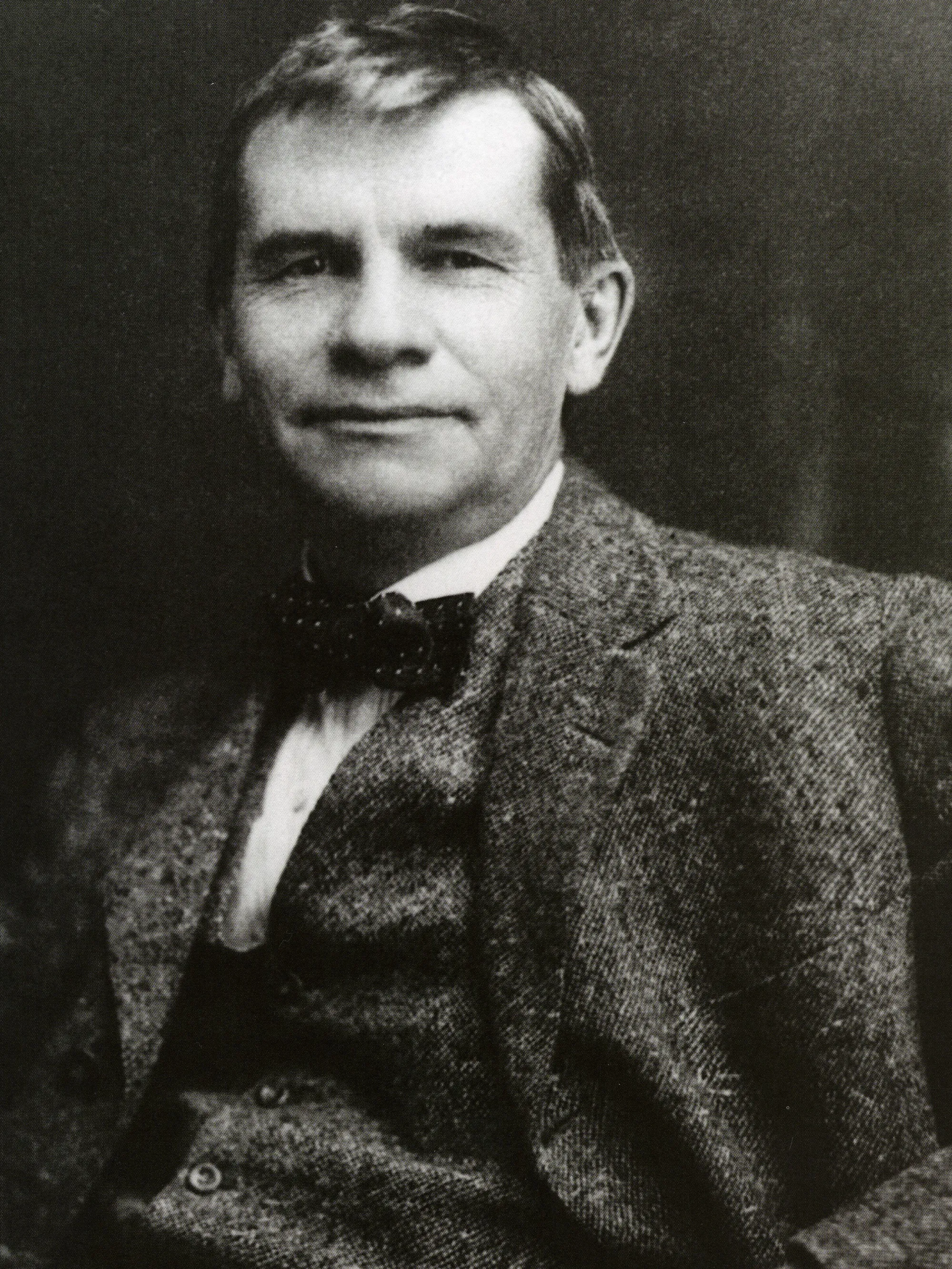

Gustav Stickley was an American furniture designer, architect, and leader of the American Arts and Crafts movement. He is renowned for his contribution to the design and production of high-quality, handcrafted furniture that emphasized simplicity, functionality, and craftsmanship.
In 1898, he established his own furniture company called the Gustav Stickley Company, later known as Craftsman Workshops. Stickley's furniture designs became synonymous with the Craftsman style, which advocated for well-crafted, and functional pieces.
One of Stickley's most iconic furniture designs was the Morris chair, which became synonymous with the Craftsman movement. The Morris chair featured a reclining back, adjustable angles, and typically incorporated cushioned upholstery.
Stickley's furniture designs were characterized by sturdy construction, visible joinery, and the use of native American woods. He emphasized the beauty of natural materials and the integrity of the craftsman's handwork. Stickley's designs were a reaction against the ornate and mass-produced furniture of the time, and he sought to bring back traditional craftsmanship and simplicity.



























