Books — Fine Printed Books and Manuscripts including Americana
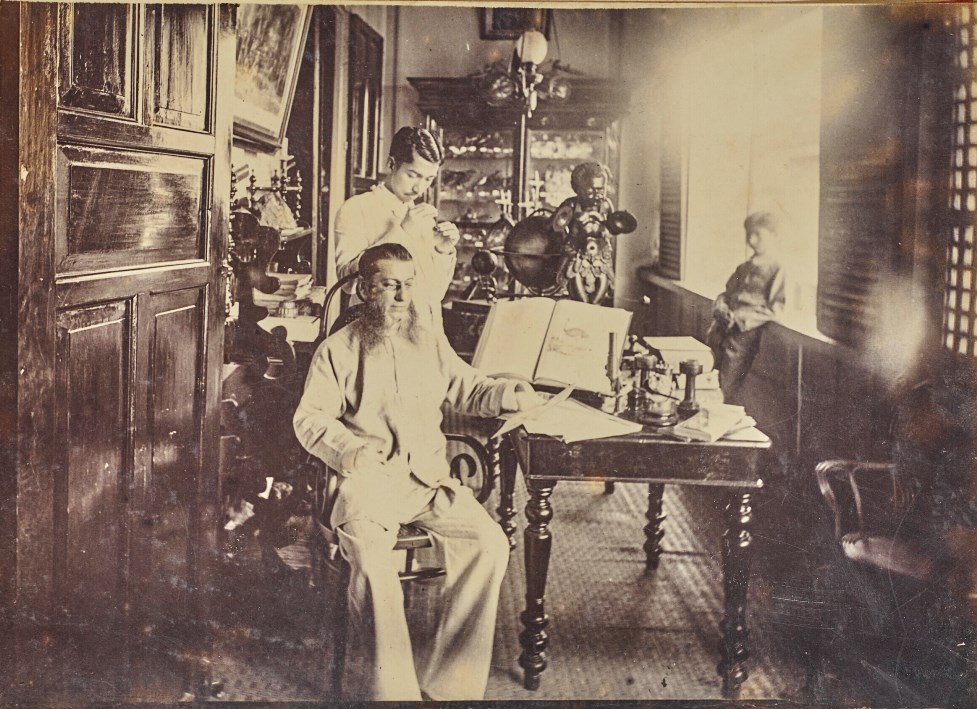

Pelayo Hipólito Fernández was a Spanish traveler and naturalist.
Fernández did extensive collecting work on the islands of Mindanao, Luzon, the Mariana Islands, and others. He founded a private zoological museum in Manila, which was incorporated into the National Museum of Natural Sciences.
In 1887, the Spanish Crown organized an exhibition to present the biodiversity of the Philippines to the Spanish public. For this exhibition, Fernández provided some 2,300 specimens of animals found in the islands, including 106 shells, among which were several type specimens. He also included ethnographic items in the exhibit, including the skulls of two outlaws.
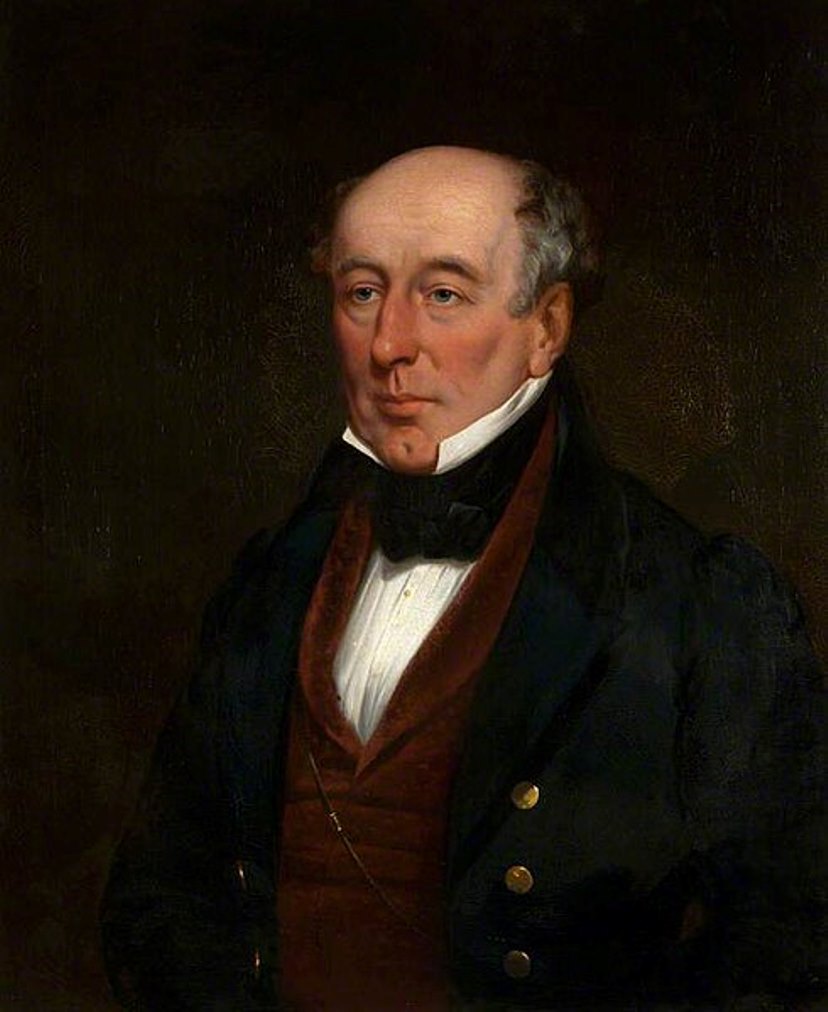

William Jardine was a Scottish naturalist, ornithologist, ichthyologist, artist and publisher of works on zoology.
Jardine studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh and was an excellent sportsman. Although his main passion was ornithology, he also studied ichthyology, botany and geology. Sir William Jardine was a prominent Scottish Victorian naturalist, author and publisher of 40 volumes of the popular Naturalist's Library (1833-43). Of these, 14 volumes were devoted to ornithology, 13 volumes to mammals, 7 volumes to entomology, and 6 volumes to ichthyology.
A series in four volumes, Illustrations on Ornithology, co-written with Prideaux John Selby, was published between 1825 and 1843. His book on burrows and fossil tracks, The Ichnology of Annandale, includes fossils from his ancestral estate. Jardine was a leading expert on salmon and trout in the British Isles. His outstanding knowledge of the species was profound that in 1860 he was appointed a member of the Royal Commission on the Salmon Fisheries of England and Wales. His research culminated in the best and most comprehensive monograph on these fish, "British Salmonids," with the remarkable illustrations by Jardine himself. William Jardine's private natural history museum and library are considered the finest in Britain.
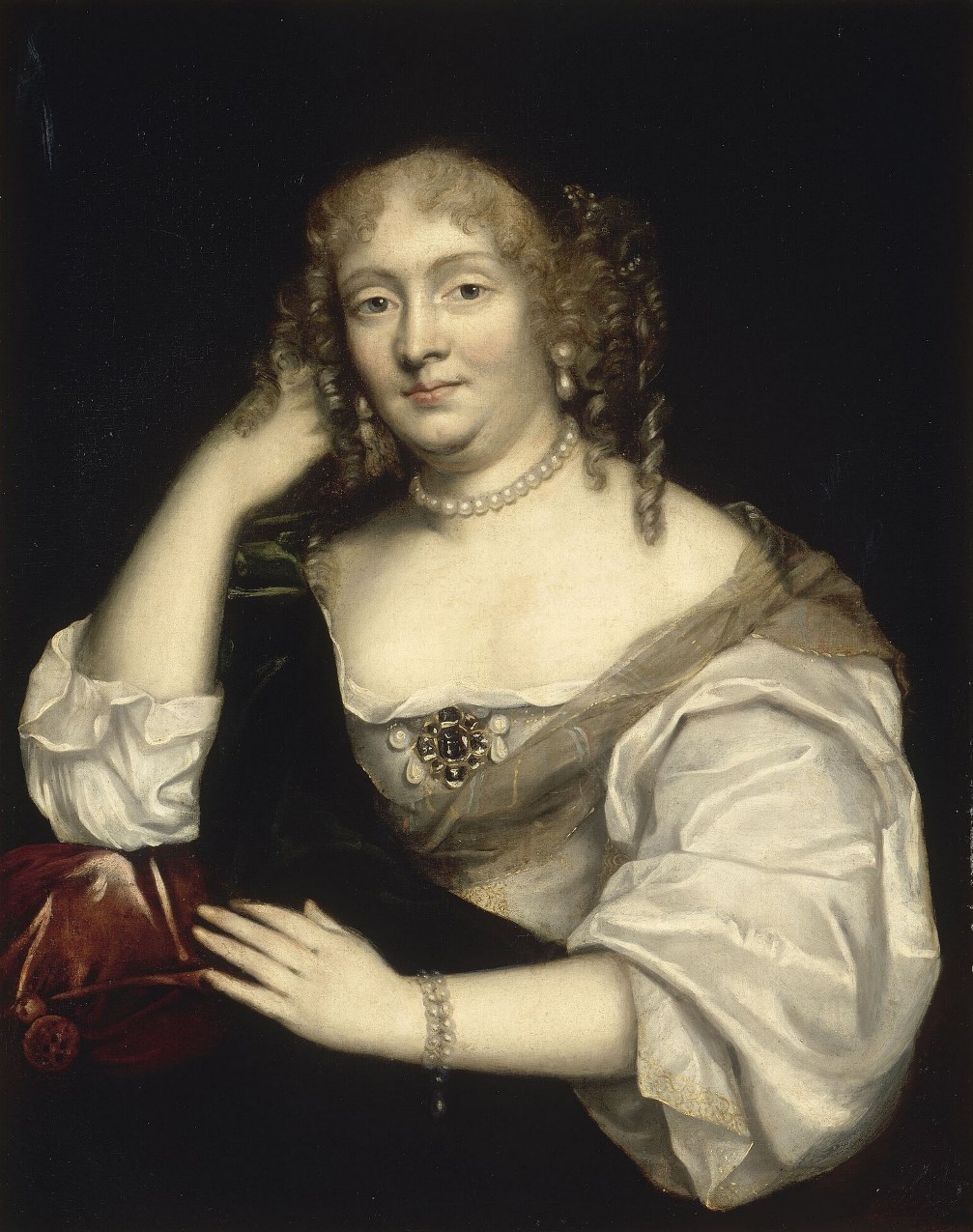

Marie de Rabutin-Chantal, marquise de Sévigné was a 17th-century French writer of epistolary genre.
Marie came from a noble family, but was orphaned at the age of six and raised by her uncle Philippe II de Coulanges. She received a good education and married Henri de Sévigné in 1644. In 1651 he was killed in a duel, and Madame de Sevigne was left a widow with two children. She led an ordinary social life, and only the marriage of her daughter, painful separation from her and loneliness suddenly revealed in the Marquise literary gift.
Since 1671 for thirty years, Madame de Sévigné wrote to her daughter about 1700 letters, and this correspondence has both historical and literary significance. In her letters, the woman relates current news and events of secular society, describes prominent people, comments on all of these, and reports on the details of her own life. Her letters reflect the intellectual sophistication of the salon culture of the period. Madame de Sévigné also touches on serious philosophical and religious topics, nature, art, morality, and psychology.
Her letters were read out in the salons, passed from hand to hand. Gradually they turned into a collection, the first edition of which was published in 1726, gradually expanding and supplementing. The popularity of the Letters of Madame de Sévigné grew over the years, becoming a source of historical study of the era and language. Francophone educational institutions in many countries around the world have included Sevigné's works in their curricula. The crater Sevigné on Venus is named in her honor.
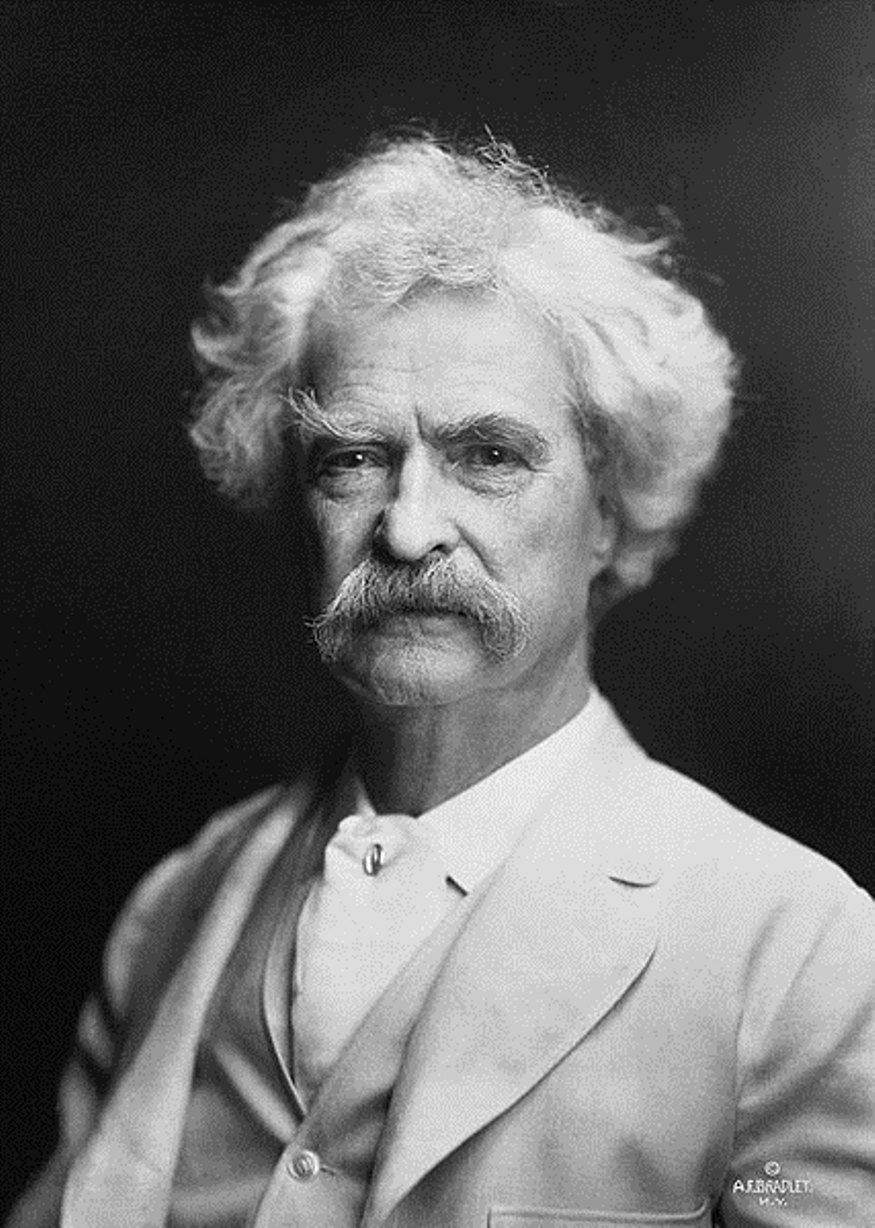

Mark Twain, real name Samuel Langhorne Clemens, was an American humanist writer, journalist, and social activist.
As a young man, Samuel worked in the printing press and in the gold mines, then went on a steamboat trip to Europe and the "Holy Land". His travel letters, full of vivid descriptions and ironic observations, were very well received by the public and were later revised into his first book, Innocents Abroad, published in 1869.
The pseudonym "Mark Twain" first appeared in 1863 under one of Samuel Clemens' short stories, and since then all his significant works have been signed by that name.
A talented storyteller, a peculiar humorist and moralist, Twain knew and loved his many diverse characters. His scandalizers and dreamers, caring aunts and ambitious politicians, grumpy widows and lying aristocrats, cunning but generous slaves, sentimental moralists, brave and naive children - all these types of American people Twain gave voice to thanks to his masterful command of colloquial language, slang and jargon. Twain wrote a lot and in a variety of genres: humor and satire, philosophical fiction and journalism and others, but he always stood on the position of humanist and democrat.
Mark Twain became world famous for his travel stories and adventure novels about his childhood, these are "The Adventures of Tom Sawyer" (1876) and "The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn" (1885). Twain is still one of America's, and indeed the world's, best and most beloved writers. His works have been and are still being published in many languages around the world.
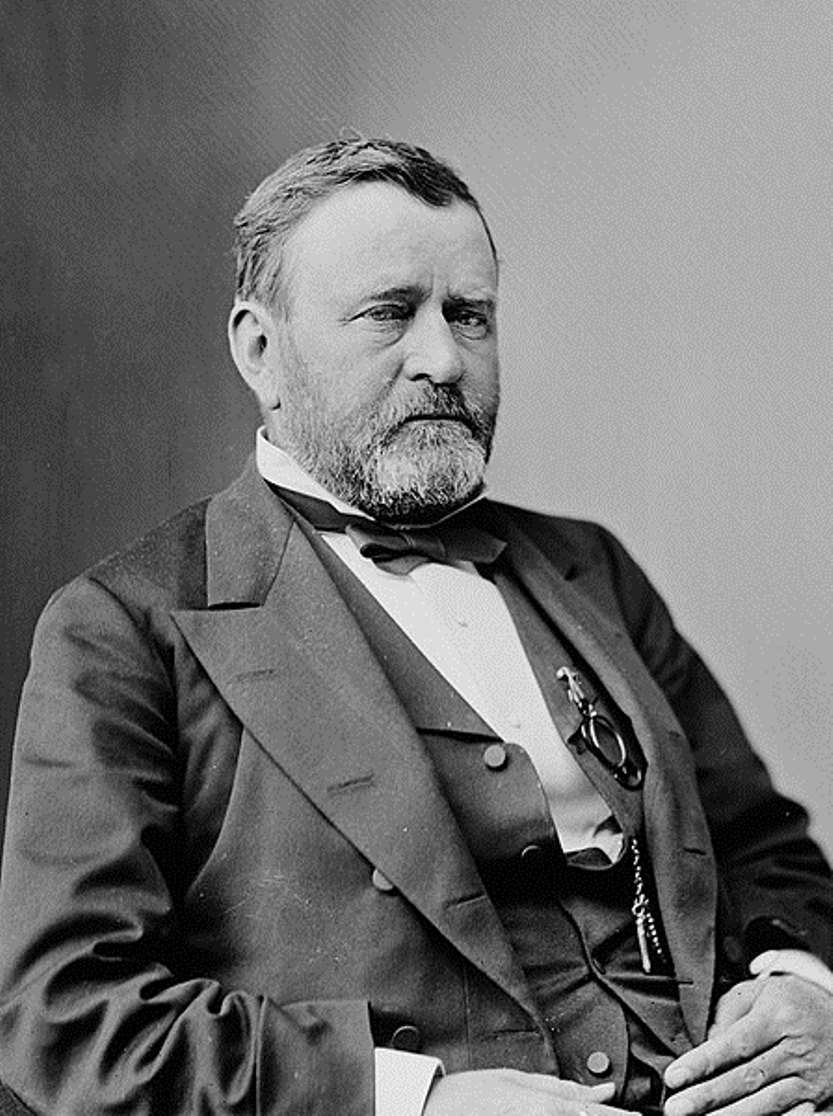

Ulysses S. Grant, born Hiram Ulysses Grant, was an American politician and military leader who was the 18th President of the United States (March 4, 1869 - March 4, 1877).
Grant's father was a tanner and enrolled his son in the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York. Ulysses Grant distinguished himself in the Mexican-American War, then fought in the Civil War, was a brigadier general, and was given command of the District of Southeast Missouri. In March, 1864, Grant became lieutenant general and was given command of all the armies of the United States. In 1866, he was promoted to the newly established rank of general in the U.S. Army.
Grant continued as commander-in-chief after Lincoln's assassination and during the administration of U.S. President Andrew Johnson. However, the situation was such that Ulysses Grant won the next presidential election and became the 18th President of the United States on March 4, 1869. He was politically inexperienced and personally clean, but his time as president was marked by corruption and scandals. During his two presidential terms, Grant worked hard to re-unite the North and South, opposing the nascent Ku Klux Klan.
In 1877, after leaving the presidency, Grant traveled around the world with his wife, and everywhere he was received with glee. Then his attempts at business led to complete bankruptcy. Ulysses Grant spent the last years of his life writing his memoirs while battling poverty and throat cancer. With the help of writer Mark Twain, his two-volume work was published in 1885, two months before the author's death.
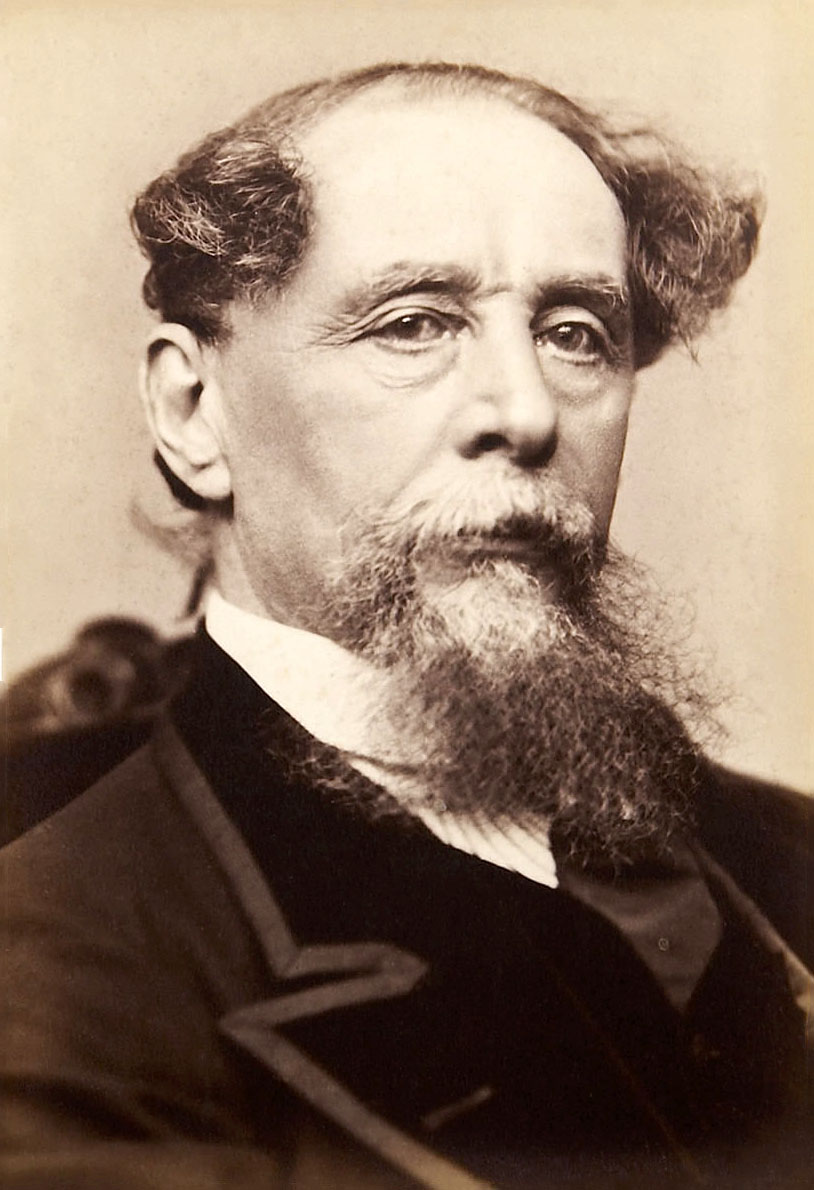

Charles Dickens, full name Charles John Huffam Dickens, is the most famous British writer of the Victorian era, a classic of world literature.
From childhood the future writer learned all the hardships of life in poverty: his father in prison for debts, hard work in a factory. Then service stenographer in court and reporter developed in him a strong attachment to journalism and contempt for both the law and parliament.
Dickens had many talents: in addition to literary work, he was an actor, published periodicals, arranged numerous literary readings, where he reveled in the admiration and love of the public. Fecund and versatile, Charles Dickens wrote many brilliant and often comic works. His novels cover a wide range of social, moral, emotional and other aspects. As a subtle psychologist, he is also very interested in the most ordinary people, but also the eccentric, the flawed, and even the insane.
Dickens was immensely popular around the world during his lifetime. His intellect, worldview, and deep reflections on society and its faults enriched his novels and made him one of the great figures of nineteenth-century literature, an influential spokesman for the conscience of his time.
Dickens' best-known and most popular novels are The Pickwick Club Posthumous Notes, Oliver Twist, Nicholas Nickleby, David Copperfield, Cold House, A Tale of Two Cities, Our Mutual Friend, Great Expectations, and The Mystery of Edwin Drood.
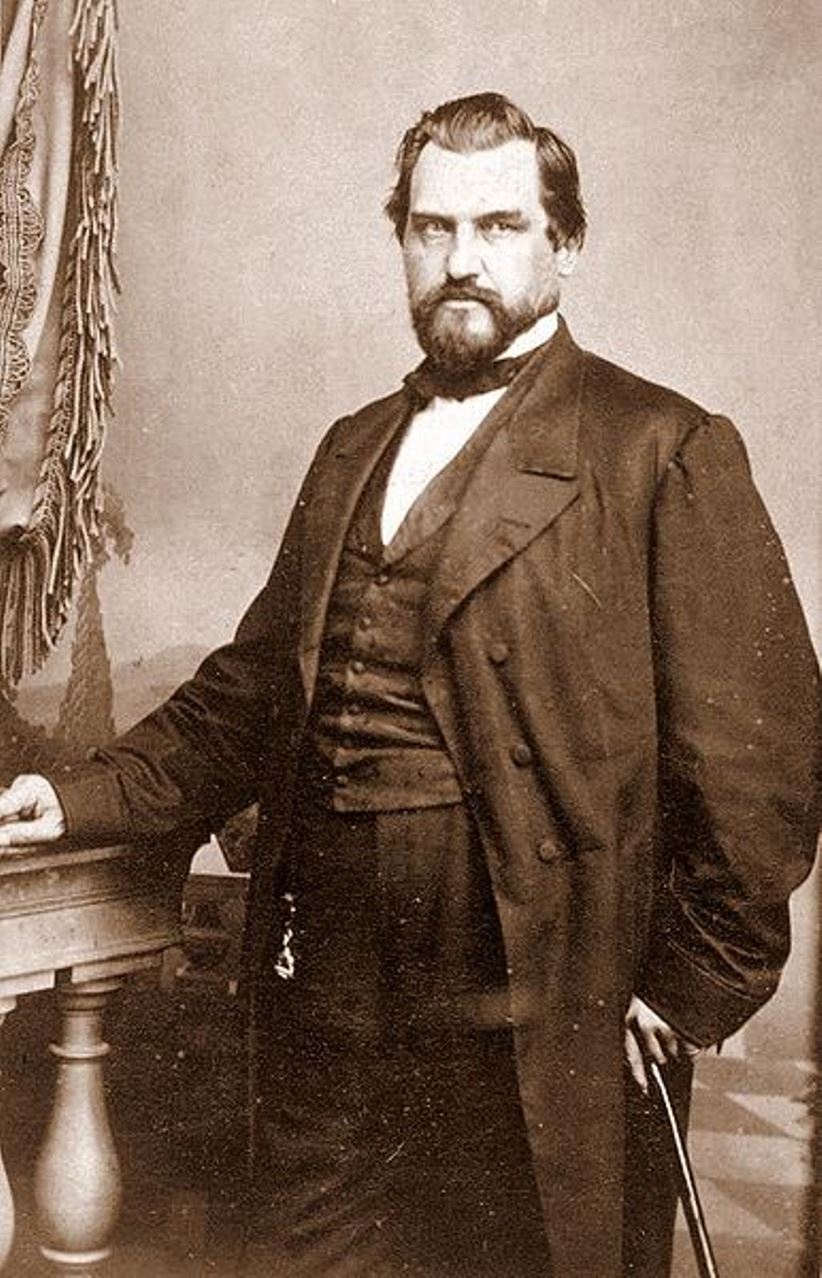

Amasa Leland Stanford was an American politician, industrialist and entrepreneur, and founder of Stanford University.
Born into a wealthy family, Stanford earned a law degree and practiced law in Wisconsin, and soon built a lucrative business selling mining equipment in northern California. And of course he became involved in politics, first as a justice of the peace and in 1861 was elected governor of California, but he didn't move away from business either.
As a member of the "Big Four" of the Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR), he was involved in planning the eastern section of the transcontinental railroad and helped secure major public investments and land grants for the railroad project. In 1863, Stanford became president of the Central Pacific Railroad and held that position for the rest of his life. He was also president of the Southern Pacific Railroad (which was acquired by the CPRR) and owned many of the construction companies that built the railroad. At the same time, he served in the U.S. Senate from 1885.
In 1891, he and his wife Jane Stanford founded Leland Stanford Junior University in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford, Jr. who died in his teens of typhoid fever during a trip to Italy.

Martin Luther King Jr, born Michael King, is an American preacher, leader of the Black Civil Rights Movement in the United States, and Nobel Laureate.
His father was the famous Baptist missionary and leader of the Civil Rights Movement Martin Luther King Sr. (1899-1984). He studied medicine and law at Morehouse College, then earned a bachelor's degree in theology at Crozer Theological Seminary in Pennsylvania, followed by a doctorate in theology at Boston University. And beginning in 1955, King Jr. became active in the community with protests over segregated seating on public buses.
On September 20, 1958, the first assassination attempt was made on Martin. Isola Ware Curry, a mentally unstable Harlem woman, stabbed King with a metal letter opener at a department store where he was signing copies of Stride Toward Freedom as part of a tour to promote the book.
Martin Luther King, Jr. was a driving force behind such watershed events as the Montgomery Bus Boycott and the 1963 March on Washington, which resulted in the historic Civil Rights Act (1964) and Voting Rights Act (1965). He was a prominent African American leader of the civil rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s. In 1964, Martin Luther King, Jr. was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his activism for civil rights and social justice. King also actively opposed the Vietnam War, calling for an end to the bombing, negotiations, and the withdrawal of U.S. troops.
On April 4, 1968, King was assassinated by gunfire on the balcony of the Lorraine Motel in Memphis. James Earl Ray, a petty criminal who had escaped from a maximum-security prison a year earlier, was blamed for the murder. Years after his death, Martin Luther King Jr. became the most famous African-American leader of his era. Today, he has a reputation as a visionary leader who was deeply committed to achieving social justice through nonviolent means. In 1983, President Ronald Reagan signed into law a U.S. federal day in King's honor; it is observed nationwide on the third Monday in January.















