
Printed books — The Alphabet of Genius: Important Autograph Letters and Manuscripts
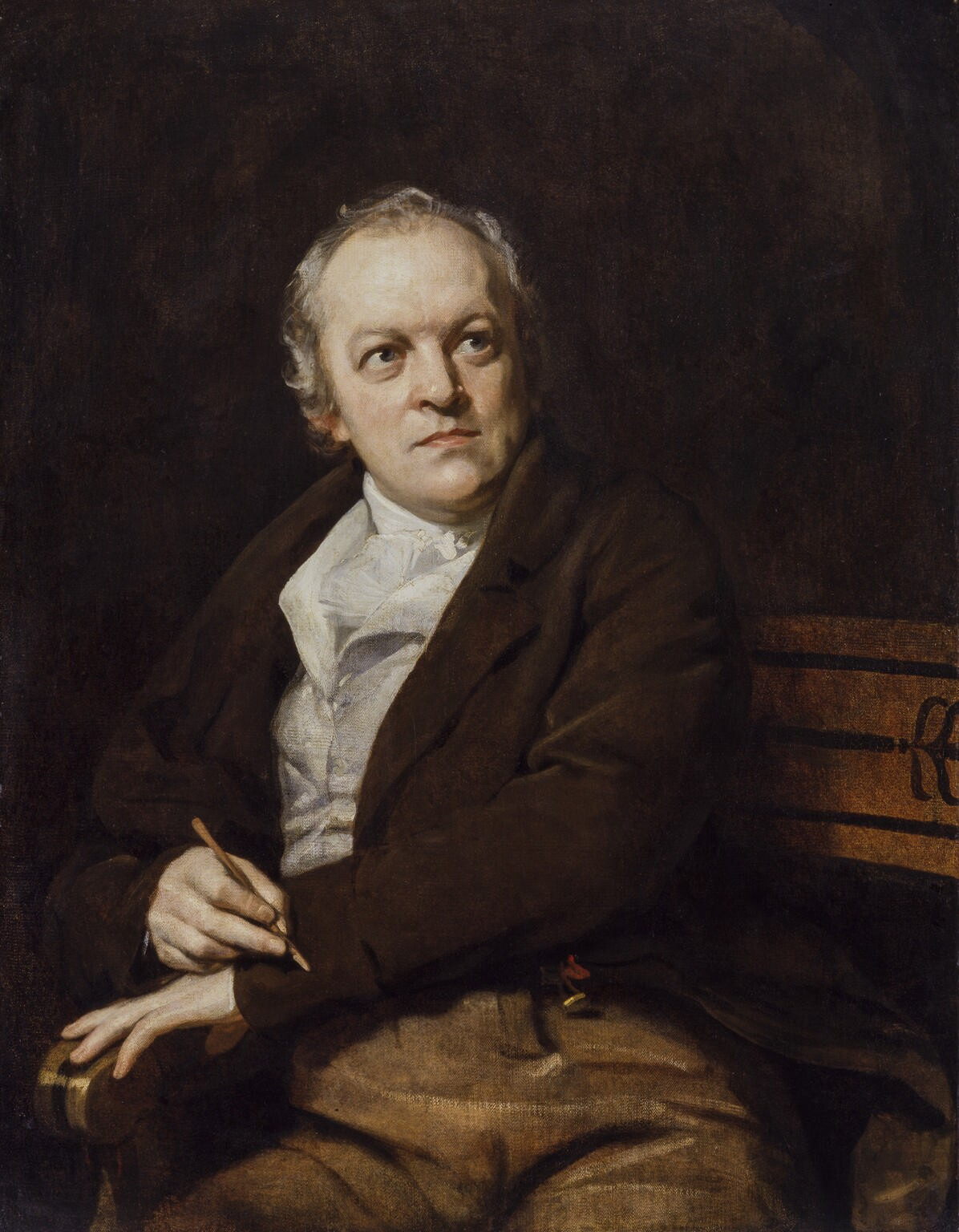
William Blake was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. What he called his "prophetic works" were said by 20th-century critic Northrop Frye to form "what is in proportion to its merits the least read body of poetry in the English language". His visual artistry led 21st-century critic Jonathan Jones to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced". In 2002, Blake was placed at number 38 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. While he lived in London his entire life, except for three years spent in Felpham, he produced a diverse and symbolically rich collection of works, which embraced the imagination as "the body of God" or "human existence itself".
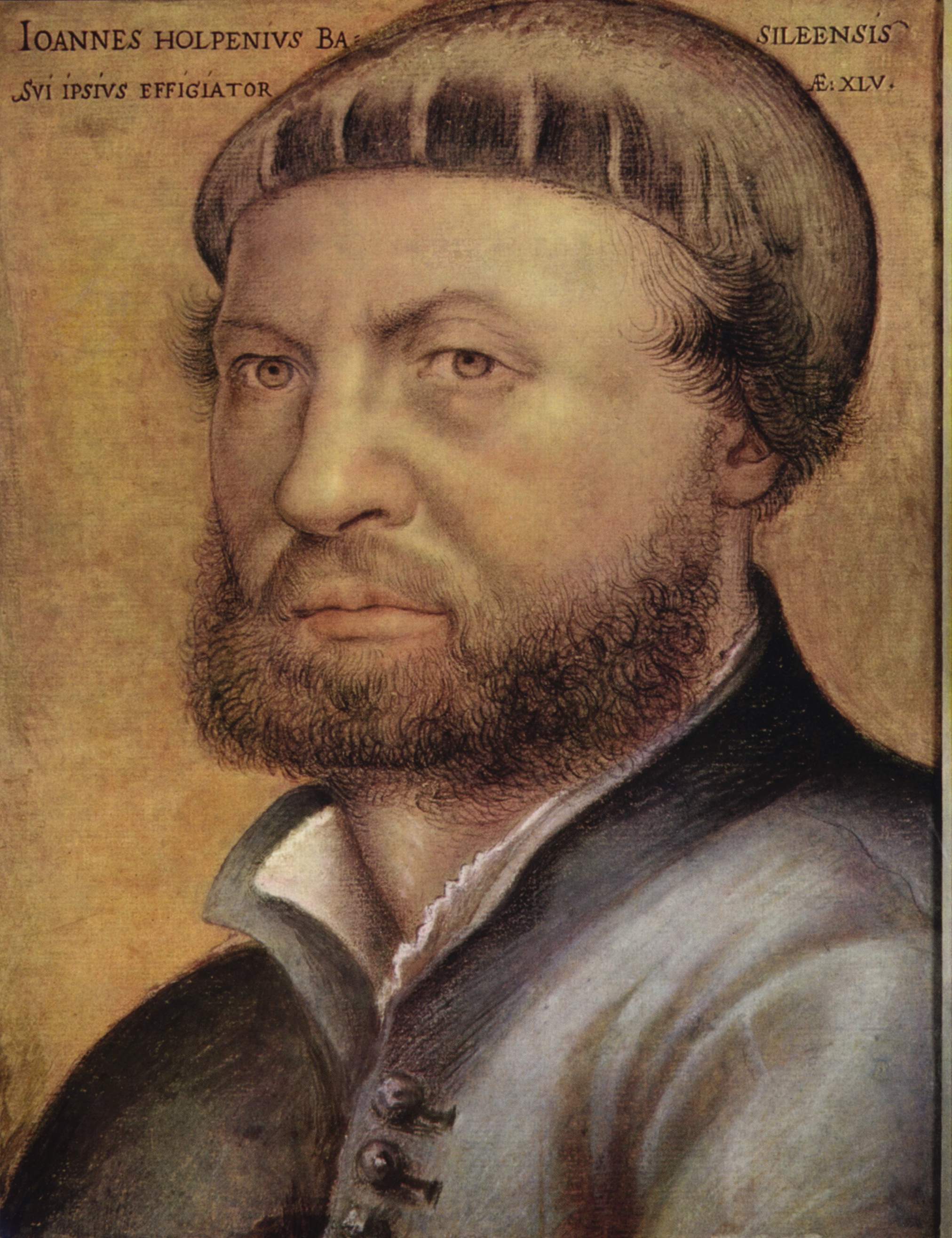

Hans Holbein the Younger was a German-Swiss painter and printmaker who worked in a Northern Renaissance style, and is considered one of the greatest portraitists of the 16th century. He also produced religious art, satire, and Reformation propaganda, and he made a significant contribution to the history of book design. He is called "the Younger" to distinguish him from his father Hans Holbein the Elder, an accomplished painter of the Late Gothic school.
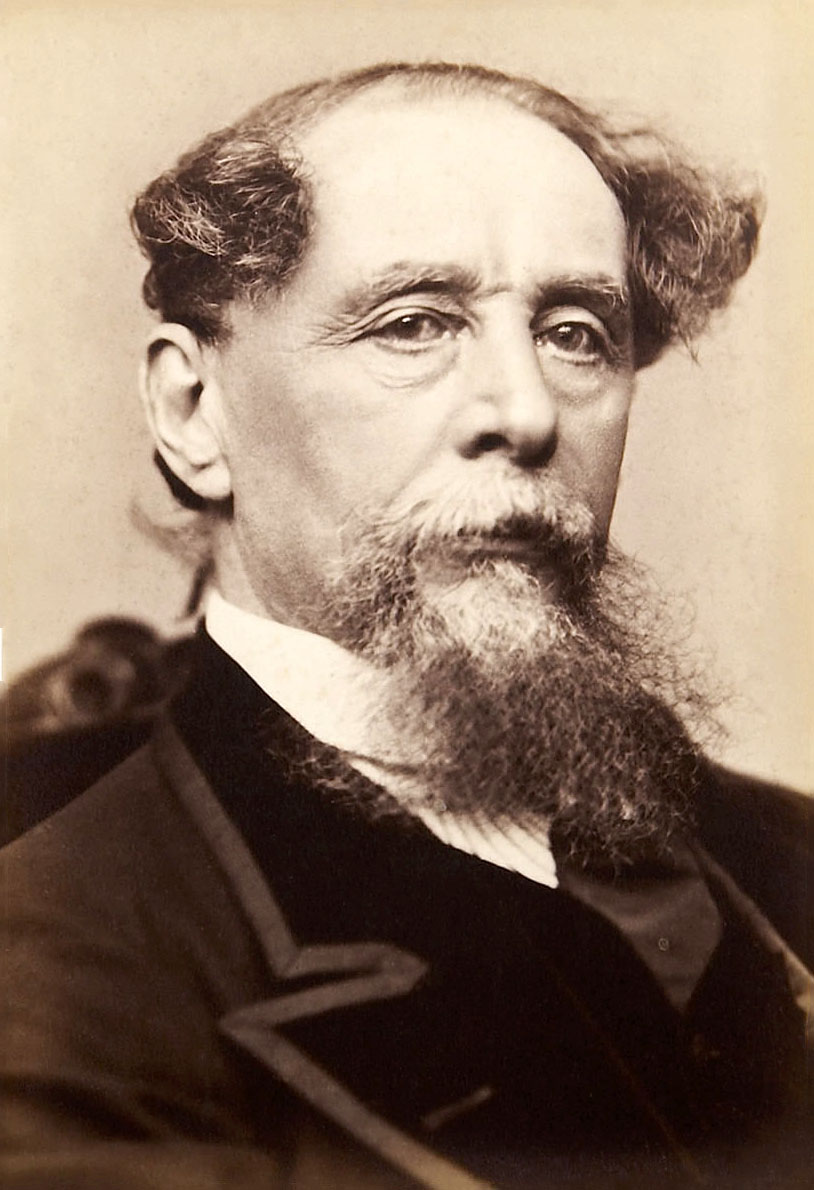

Charles Dickens, full name Charles John Huffam Dickens, is the most famous British writer of the Victorian era, a classic of world literature.
From childhood the future writer learned all the hardships of life in poverty: his father in prison for debts, hard work in a factory. Then service stenographer in court and reporter developed in him a strong attachment to journalism and contempt for both the law and parliament.
Dickens had many talents: in addition to literary work, he was an actor, published periodicals, arranged numerous literary readings, where he reveled in the admiration and love of the public. Fecund and versatile, Charles Dickens wrote many brilliant and often comic works. His novels cover a wide range of social, moral, emotional and other aspects. As a subtle psychologist, he is also very interested in the most ordinary people, but also the eccentric, the flawed, and even the insane.
Dickens was immensely popular around the world during his lifetime. His intellect, worldview, and deep reflections on society and its faults enriched his novels and made him one of the great figures of nineteenth-century literature, an influential spokesman for the conscience of his time.
Dickens' best-known and most popular novels are The Pickwick Club Posthumous Notes, Oliver Twist, Nicholas Nickleby, David Copperfield, Cold House, A Tale of Two Cities, Our Mutual Friend, Great Expectations, and The Mystery of Edwin Drood.

Charles Dickens, full name Charles John Huffam Dickens, is the most famous British writer of the Victorian era, a classic of world literature.
From childhood the future writer learned all the hardships of life in poverty: his father in prison for debts, hard work in a factory. Then service stenographer in court and reporter developed in him a strong attachment to journalism and contempt for both the law and parliament.
Dickens had many talents: in addition to literary work, he was an actor, published periodicals, arranged numerous literary readings, where he reveled in the admiration and love of the public. Fecund and versatile, Charles Dickens wrote many brilliant and often comic works. His novels cover a wide range of social, moral, emotional and other aspects. As a subtle psychologist, he is also very interested in the most ordinary people, but also the eccentric, the flawed, and even the insane.
Dickens was immensely popular around the world during his lifetime. His intellect, worldview, and deep reflections on society and its faults enriched his novels and made him one of the great figures of nineteenth-century literature, an influential spokesman for the conscience of his time.
Dickens' best-known and most popular novels are The Pickwick Club Posthumous Notes, Oliver Twist, Nicholas Nickleby, David Copperfield, Cold House, A Tale of Two Cities, Our Mutual Friend, Great Expectations, and The Mystery of Edwin Drood.
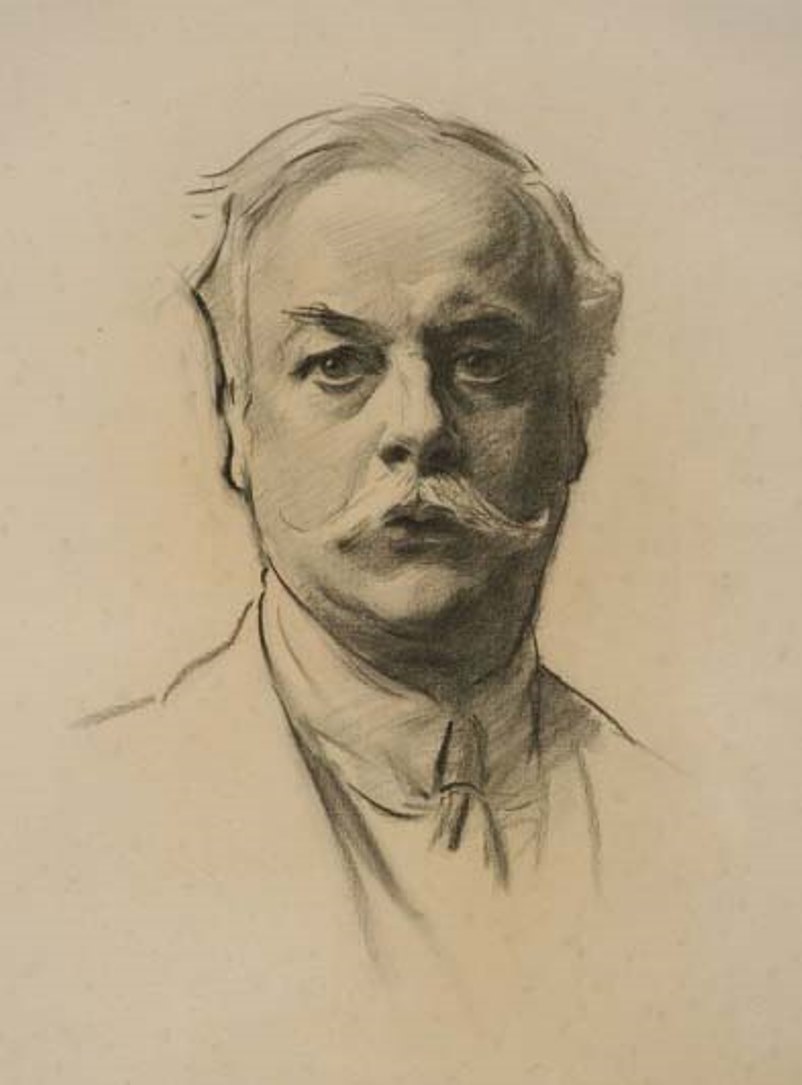

Kenneth Grahame was a Scottish and British writer, a classic of children's literature.
Kenneth was orphaned early and lived with relatives, attending St. Edward's School in Oxford. He then served at the Bank of England and published magazine articles and collections of sketches, short stories and essays - Pagan Notes (1893), The Golden Age (1895) and Dream Days (1898), The Reluctant Dragon.
The Wind in the Willows, the book that made Kenneth Grahame famous, began as bedtime stories for his son and was first published in 1908. It was later illustrated by master illustrator Arthur Rackham. Its characters are the timid Mole, the clever Rat, the Badger and the insanely energetic Toad. They all talk and act like humans and have human vices, but have typical animal behavior at the same time. Both children and adults enjoyed the story. This book, which is now considered one of the most famous works in world children's literature, has been adapted many times for stage, screen and radio.
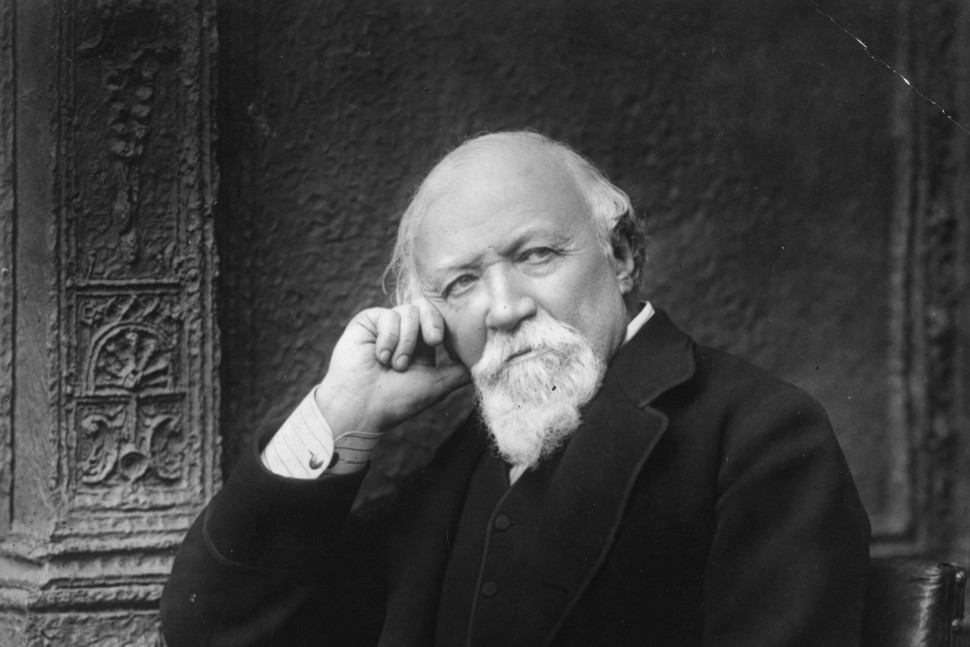

Robert Browning was an English poet and playwright of the Victorian era.
Browning's father, a bank clerk in London, was a very accomplished man, a collector of books and paintings, an artist and a scholar. He gave his son the basics of Greek and Latin, as well as classical literature. Browning re-read many books from his father's extensive library and also attended classes at the University of London. In 1834 Robert Browning traveled to St. Petersburg and later visited Italy. Between
1832-46 he wrote his early long poems and most of his plays. Browning's first published work was "Pauline" (1833); this dramatic monologue was highly emotional. In 1835 he published the poems "Paracelsus" and in 1840 "Sordello," which are about men of great talent trying to come to terms with the demands of the world.
In 1868-69. Browning published his major work, a novel in verse, The Ring and the Book, based on the trial of a murder case in Rome in 1698. Grand in conception and execution, it was immediately well received by the public, and Browning became a major figure in the history of English poetry.
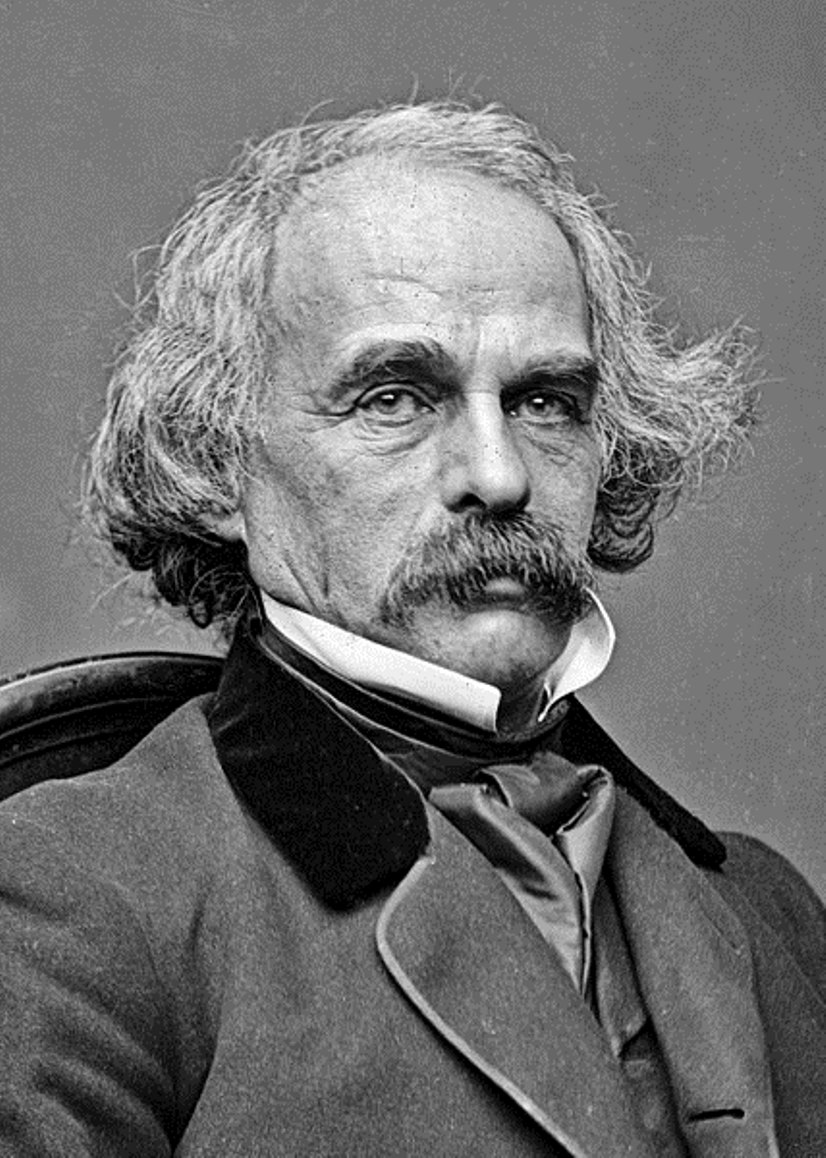


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.


Alan Alexander Milne was a British journalist, playwright and children's author.
While studying at Trinity College, Cambridge, Milne began writing for Granta magazine, and in 1906 he joined the humor magazine Punch, where he wrote humorous poems and quirky essays until 1914. During World War I he served as a communications officer, and afterward, in 1920, Milne had a son, Christopher Robin, whose name soon became known to the world.
From 1921 Milne wrote several comedy plays and also began writing children's poetry and prose for his young son, having finally found his calling. Milne's major successes were his books Winnie the Pooh (1926) and The House on Pooh Corner (1928). These two volumes tell the adventures of a boy named Christopher Robin and his playmates - animals that were "born" from the toys of the real Christopher Robin. The central character is Winnie the Pooh Bear, accompanied by the fussy Rabbit, the sullen Donkey Ia, the bouncy tiger Tigger, the kind kangaroo Kanga and her baby Roo, the wise Owl and the timid Piglet. The adventures of Pooh and his friends in the forest of One Hundred Acres with illustrations by Ernest Shepard became bestsellers.
They were translated into different languages of the world and reprinted many times, filmed cartoons. In 1929 Milne adapted another children's classic, Kenneth Graham's The Wind in the Willows, for stage production as Toad of Toad Hall. Ten years later he wrote an autobiography, Now It's Too Late.
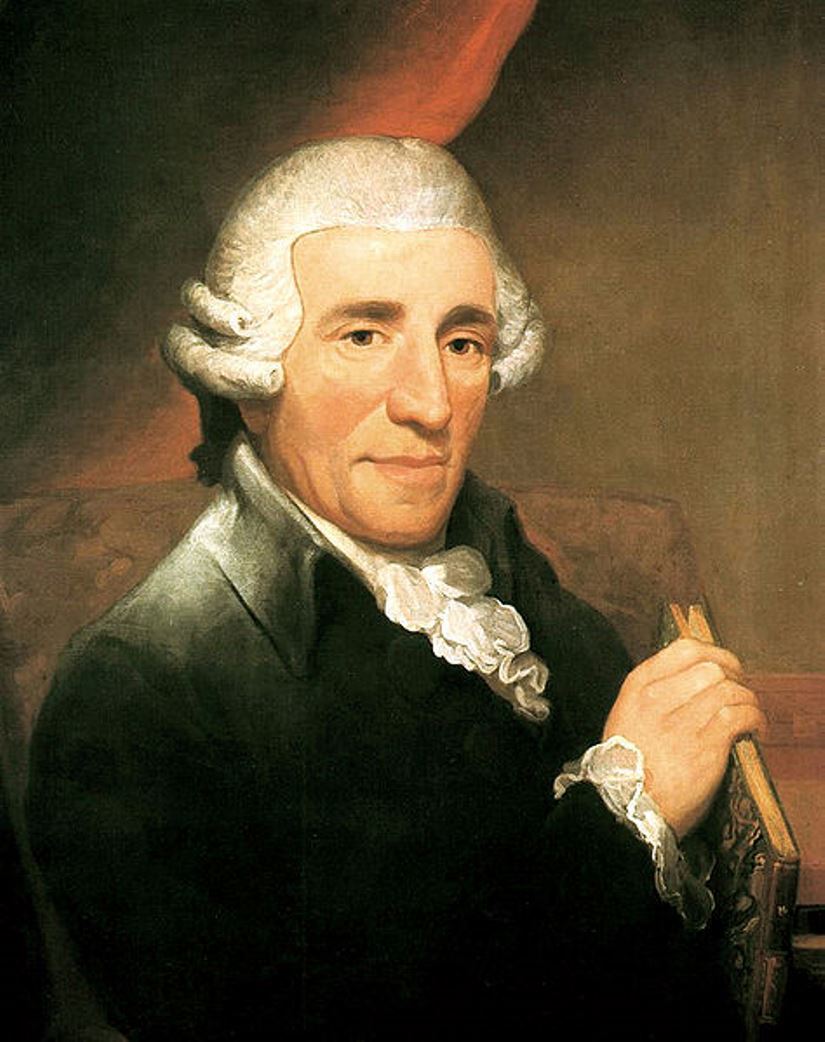

Franz Joseph Haydn was an Austrian composer of the classical school, who created the string quartet and symphony forms.
Haydn discovered unusual musical abilities very early, but the poverty of his family did not favor the development of his talents. He was a singer, interrupted earnings and engaged in musical self-education. Fate led young Haydn to Prince Pal Antal Esterhazy, whose wealthy and influential family of the Austrian Empire maintained his own orchestra. In 1766, Haydn became music director at the Esterhazy court and remained in that service for the rest of his life. In addition to his operas for the court, Haydn composed symphonies, string quartets and other chamber music. On one of his visits to Vienna, Haydn met Wolfgang Mozart, and their interactions brought many benefits to both great composers and musicians.
In the 1760s, Haydn's fame began to spread throughout Europe. In 1792, he met the young Ludwig van Beethoven and foreshadowed his greatest fame as a composer.
Haydn was an extremely prolific composer. He created 108 symphonies, many quartets, oratorios, sonatas, concertos, etc. As a true representative of the Enlightenment, Haydn was the most famous composer in Europe in the 18th century.













![[Charles Dickens (1812-1870)] – Hablot Knight Browne ['Phiz'] (1815-1882)](/assets/image/picture_3619865/cc723/6e06e3e46ec063690ea5de1f3fe4402b1701428400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Charles Dickens (1812-1870)] – Hablot Knight Browne ['Phiz'] (1815-1882)](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3619865/cc723/6e06e3e46ec063690ea5de1f3fe4402b1701428400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Charles Dickens (1812-1870)] – auction catalogue](/assets/image/picture_3643863/6839e/4ib1nwl9x4jpu-nyuizaua9cp89td-jlnkksdkv9bfeeepvbj2huleq8ctlm0gm1701505094jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Charles Dickens (1812-1870)] – auction catalogue](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3643863/6839e/4ib1nwl9x4jpu-nyuizaua9cp89td-jlnkksdkv9bfeeepvbj2huleq8ctlm0gm1701505094jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


![[D.H. Lawrence (1885-1930)] – Robert Browning (1812-1889)](/assets/image/picture_3643917/78168/nsx1mcglqntcbud3m0hynfmrqoipi7iioqejtkyukv8sx8jslibvanbgvmfygqze1701505298jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[D.H. Lawrence (1885-1930)] – Robert Browning (1812-1889)](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3643917/78168/nsx1mcglqntcbud3m0hynfmrqoipi7iioqejtkyukv8sx8jslibvanbgvmfygqze1701505298jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[D.H. Lawrence (1885-1930)] – Nathaniel Hawthorne (1804-1864)](/assets/image/picture_3643920/42c3e/dhgyeqmhvqzrf2jksesrm4tm8jmwv8oowk-rcfxvshw895ypwrimpmlzhn5ivgas1701505309jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[D.H. Lawrence (1885-1930)] – Nathaniel Hawthorne (1804-1864)](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3643920/42c3e/dhgyeqmhvqzrf2jksesrm4tm8jmwv8oowk-rcfxvshw895ypwrimpmlzhn5ivgas1701505309jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)





