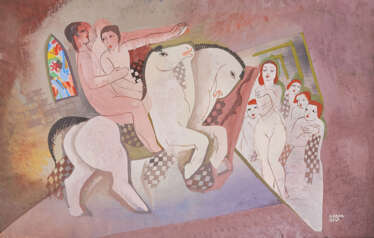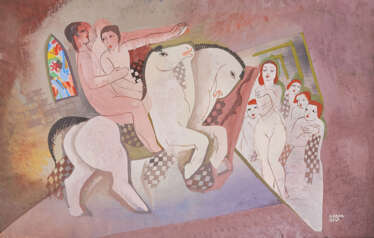Modern Art — A1144: Modern Art
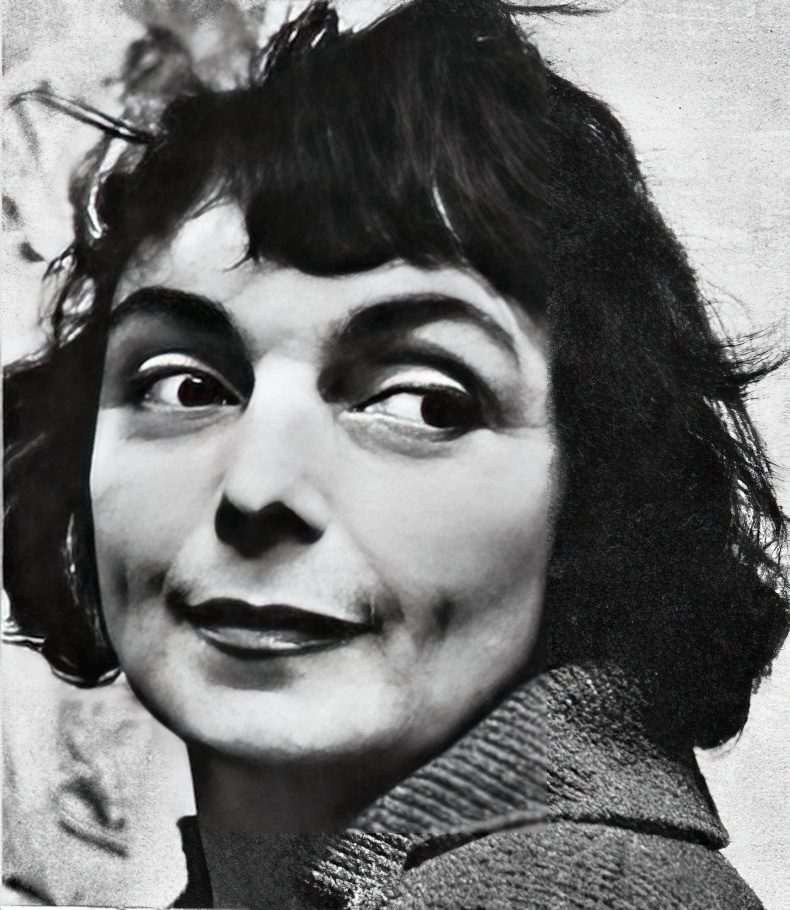

Bele Bachem (real name Renate Gabriele Bachem) was a German painter, graphic designer, book illustrator, interior designer and writer. In 1997 Bachem was awarded the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany.
Bachem is considered one of the most important post-war German artists and one of the few surrealists in the illustration of German literature.

Ernst Rudolf Baerwind was a German painter. Baerwind studied at the art academies in Munich, Berlin and Paris. Baerwind's work was initially based on early German Expressionism. After a surrealist phase, he was influenced in Paris by the painting of the École de Paris and by Informel and then found his way to the International Style.
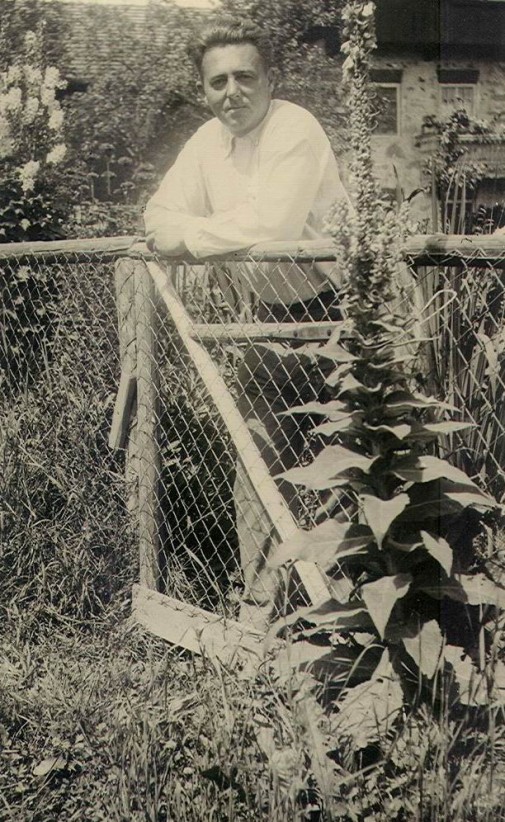

Arnold Balwé was a German post-impressionist painter.
He studied at the Antwerp Academy of Art and the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich, traveled extensively and painted landscapes he saw. Balwe's work is characterized by color intensity and vitality.
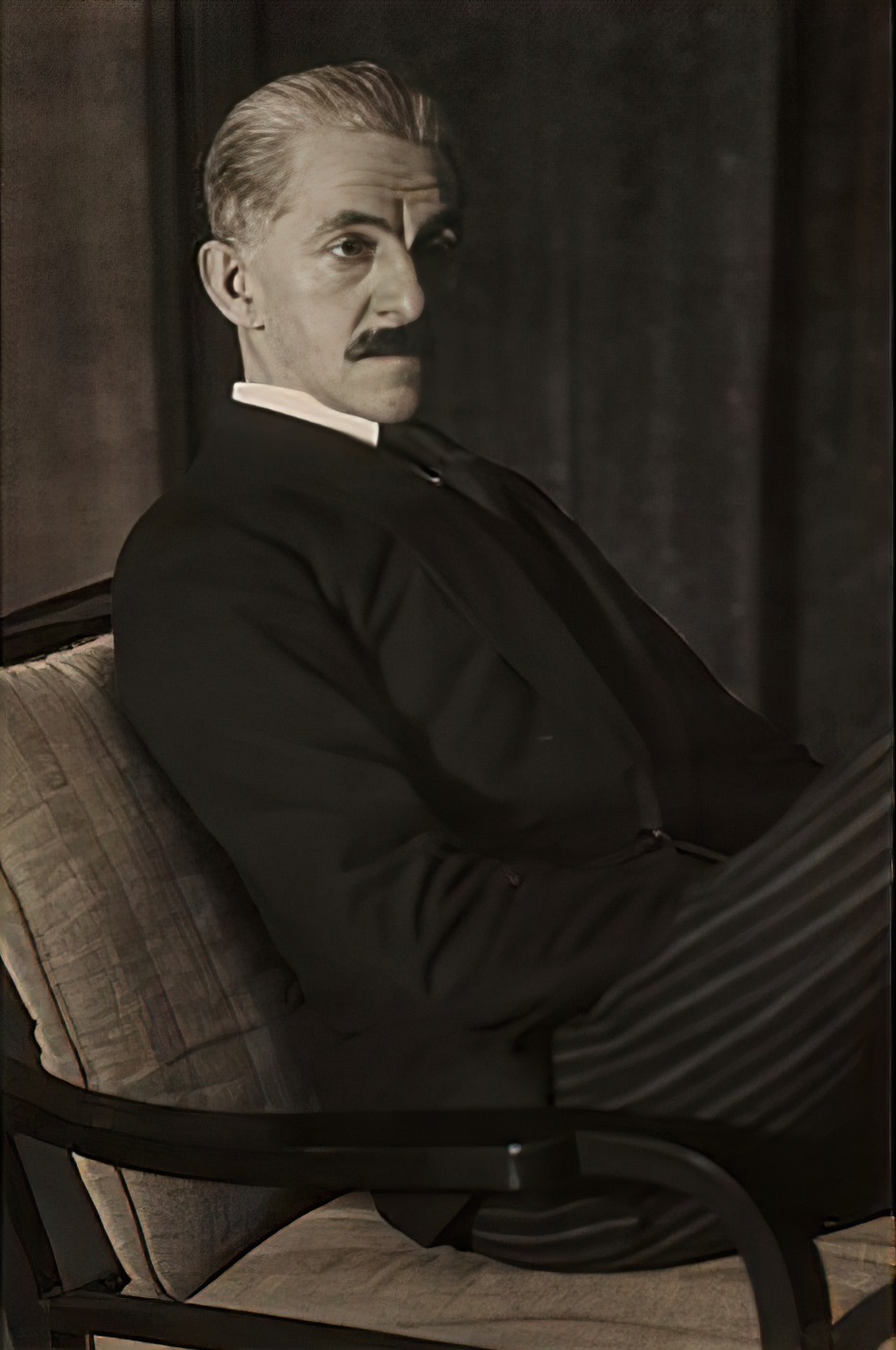

Alexander Georg Rudolf Bauer was a German-born painter who was involved in the avant-garde group Der Sturm in Berlin, and whose work would become central to the non-objective art collection of Solomon R. Guggenheim.

Arthur Brusenbauch was an Austrian painter. Arthur Brusenbauch learned from Johann Kautsky and then worked as a stage decorator himself. He studied in Vienna at the Staatsgewerbeschule and the Academy of Fine Arts, interrupted by military service and imprisonment. In 1920 he became a member of the Vienna Secession, and in 1939 he moved to the Künstlerhaus. In 1928 he had represented Austria in the art competitions of the 1928 Olympic Games. From 1937 to 1941 he participated in all major German art exhibitions in Munich with seven oil paintings. There, in 1939, Hitler acquired the picture of Melk an der Donau in festive decorations. Brusenbauch, who is attributed to late impressionism, dealt with fresco painting and graphics.

Carl Buchheister was a German constructivist artist noted for his multiple series of "model paintings"at Galerie Lambert Weyl, Paris. which he began in 1925. He was born in Hanover, Germany. Although he was not officially part of the Bauhaus movement, Buchheister was a close friend of Wassily Kandinsky and paralleled many of the social and artistic goals of the Bauhaus school. With regard to constructivism, Buchheister was typically more playful and improvisational than his contemporaries, becoming interested in the Dada movement after a collaboration with Kurt Schwitters in the late 1920s which led him to incorporate more varied materials such as acrylic glass, aluminum, wood, and twine into his compositions. This direction was given much freer rein after World War II and the end of Nazism. He died in Hanover in 1964.

Arthur Degner was a German painter, graphic artist and sculptor. Degner studied between 1906 and 1908 at the Art Academy in Königsberg under Ludwig Dettmann and Otto Heichert. In 1909 he came to Berlin after a stay in Munich. In 1912 he exhibited in the gallery of Paul Cassirer, at whose suggestion he had traveled to Paris in 1910. In 1919 he became a board member of the Free Secession, of which he had been a member since 1911. In 1920 he was appointed to the Königsberg Academy. In 1925 he returned to Berlin, where he taught at the Academy of Fine Arts (HBK). From 1931 to 1933 he was chairman of the Berlin Secession. After the National Socialists seized power, he was banned from working and exhibiting. Nevertheless, the Villa Romana Prize of the German Association of Artists enabled him to study in Florence in 1936 and in 1937 he became a member of the Association of Berlin Artists.
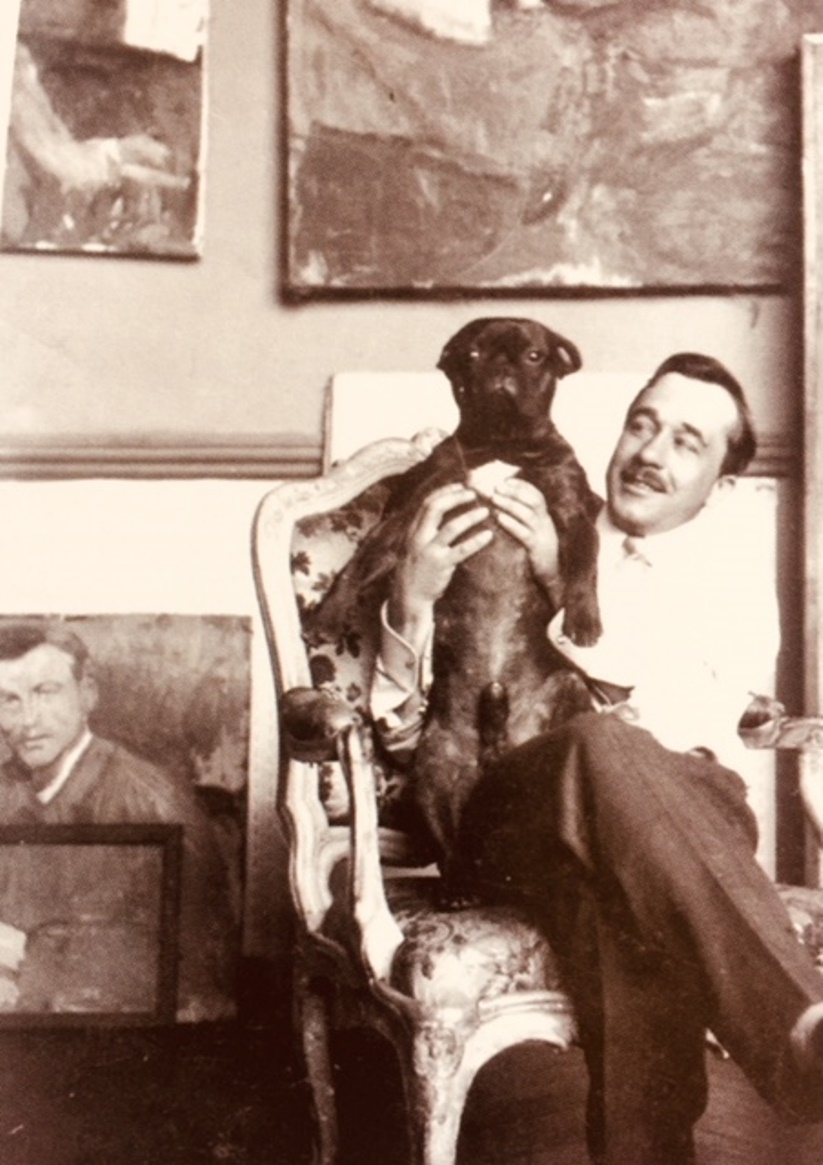

Serge Férat, born Count Sergei Nikolaevich Iastrebtsov (Russian: Сергей Николаевич Ястребцов), was a Russian and French avant-garde artist, painter, graphic artist and scenographer.
Sergei Iastrebtsov was born into a Moscow noble family, studied at the Kiev Art School, and in 1902 moved to Paris and entered the Académie Julian in Paris. In France, he first took the pseudonym Alexander Rudnev, and then began to sign his works with the name Serge Ferat. In the magazine Les Soirées de Paris he signed his publications with the pseudonym Jean Cérusse.
In 1910, Ferat began working on still lifes, combining the techniques of cubism with the warm colors of Russian folklore. Until the 1920s, Serge Fera painted in the style of Picasso's cubism, and on glass. Serge Ferat knew and was friends with many contemporary European artists, including Guillaume Apollinaire and Amedeo Modigliani. In the surrealist production of Apollinaire's play Mamelles de Tirésias (Théâtre René Mobel, Montmartre), he contributed to the set and costume design.
Ferat was engaged in book graphics and scenography, was a member of the group "Golden Section", and collaborated with the Russian magazine "Blow". In 1949 he took part in the design of the anthology Poetry of the Unrecognized, and in 1953 his works were exhibited at the Great Exhibition of Cubism at the Museum of Modern Art in Paris.
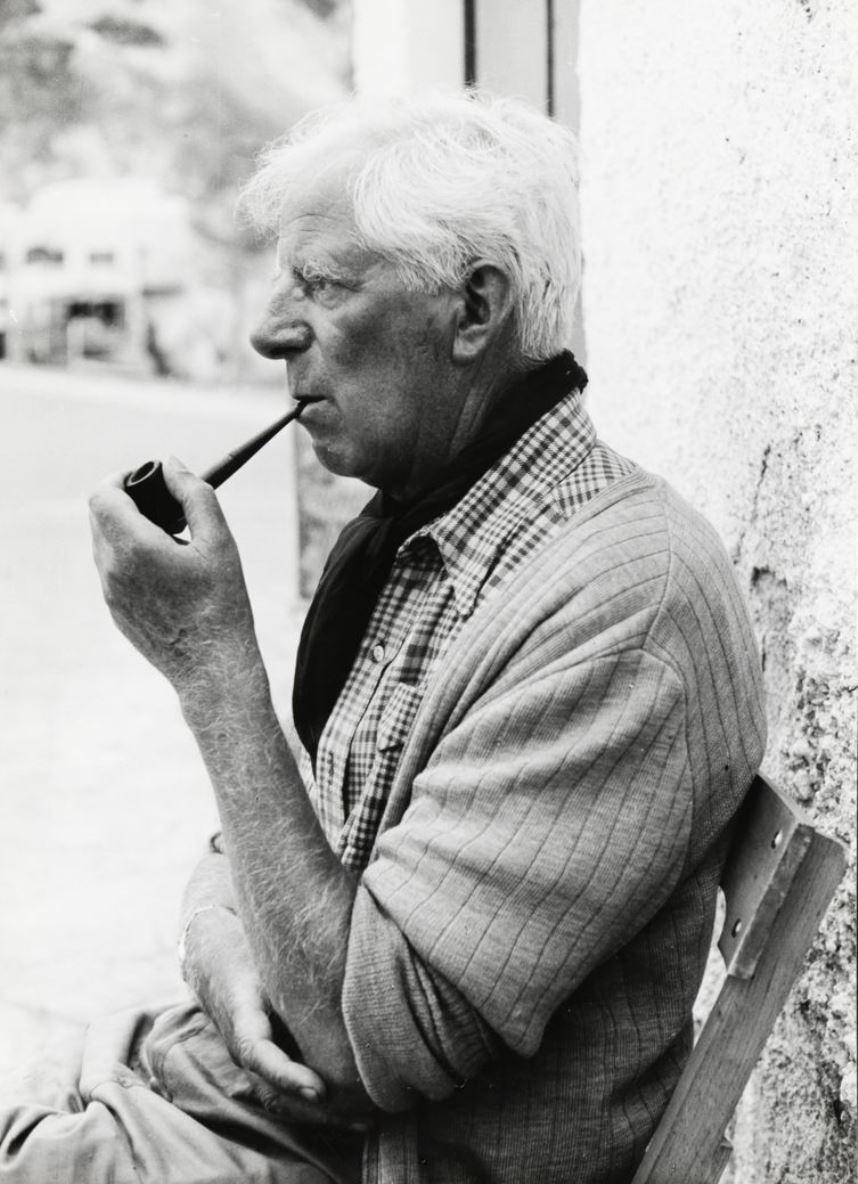

Werner Gilles was a German artist.
He was a member of the Bauhaus school of art and design. After arriving on the Italian island of Ischia in 1932, Gilles found inspiration for painting. In his oil paintings and watercolors, the artist depicts the cheerful and menacing aspects of this primitive landscape and captures its basic nature.
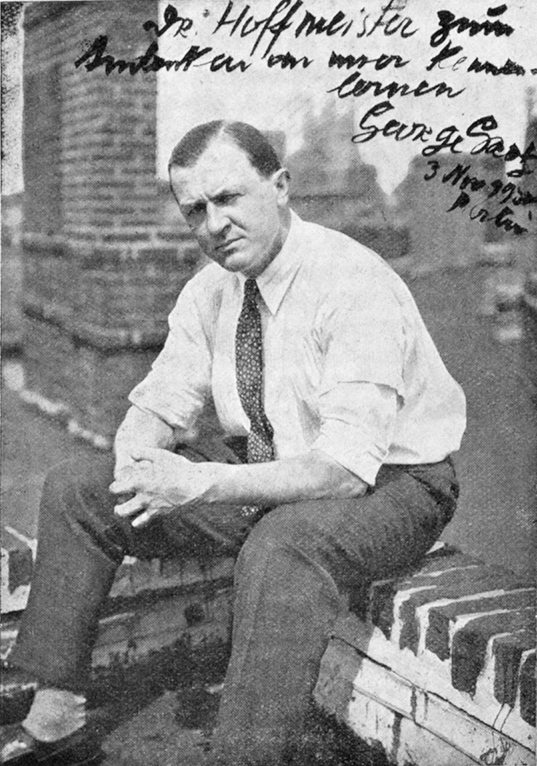

George Grosz was a twentieth-century German painter, graphic artist, and cartoonist. In his work one can find features of various styles of avant-garde art, including Dadaism, Expressionism, and Futurism.
George Grosz drew in every style in a sharp-grotesque and satirical spirit, ridiculing the vices of society. The erotic theme, which occupied a prominent place in Gross's work, was executed in the same spirit.
Grosz devoted more than 20 years to teaching at the Art Students League of New York, and was elected an honorary member of the American and Berlin Academies for his outstanding services to the arts.
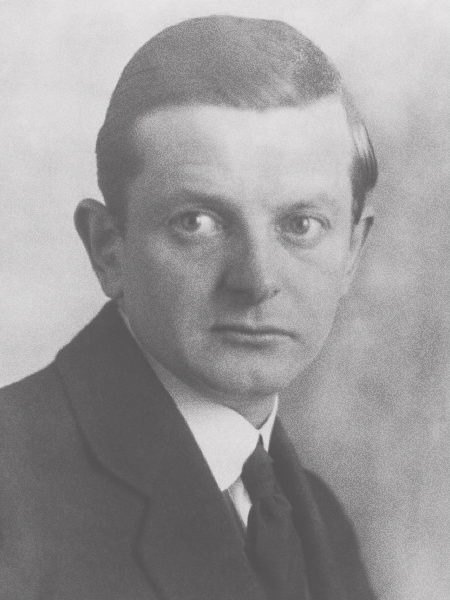
Franz Heckendorf was a German painter and graphic artist who was particularly successful during the Weimar Republic. During the National Socialist era, he was sentenced to ten years in prison after helping Berlin Jews threatened with deportation to extermination camps to escape to Switzerland.
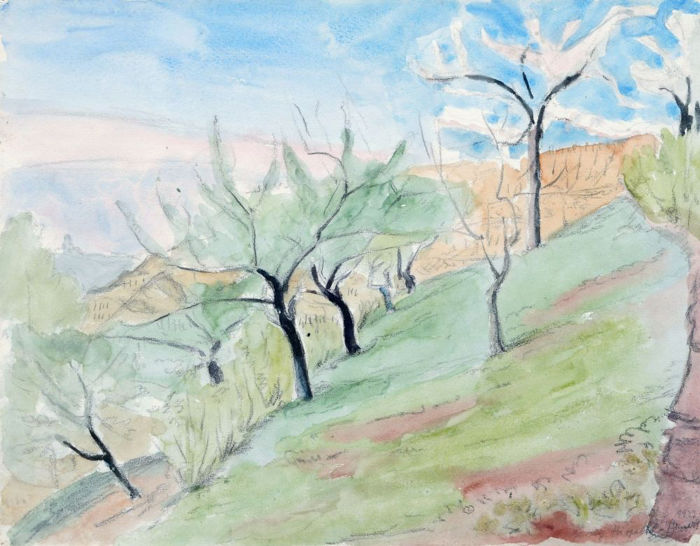

Gussy Erika Edith Hippold-Ahnert, née Ahnert, was a German painter and master student of Otto Dix. The early work of the Dix student, such as the painting Lying Nude from 1931, shows her closeness to Dix's New Objectivity or Verism. She reached her artistic peak in 1932/1933, when she developed a painting style of her own, unmistakable character in the glazing technique taught by Dix. Hippold-Ahnert's late work is closely connected to the works of her husband Erhard Hippold and other artists of this region and time.
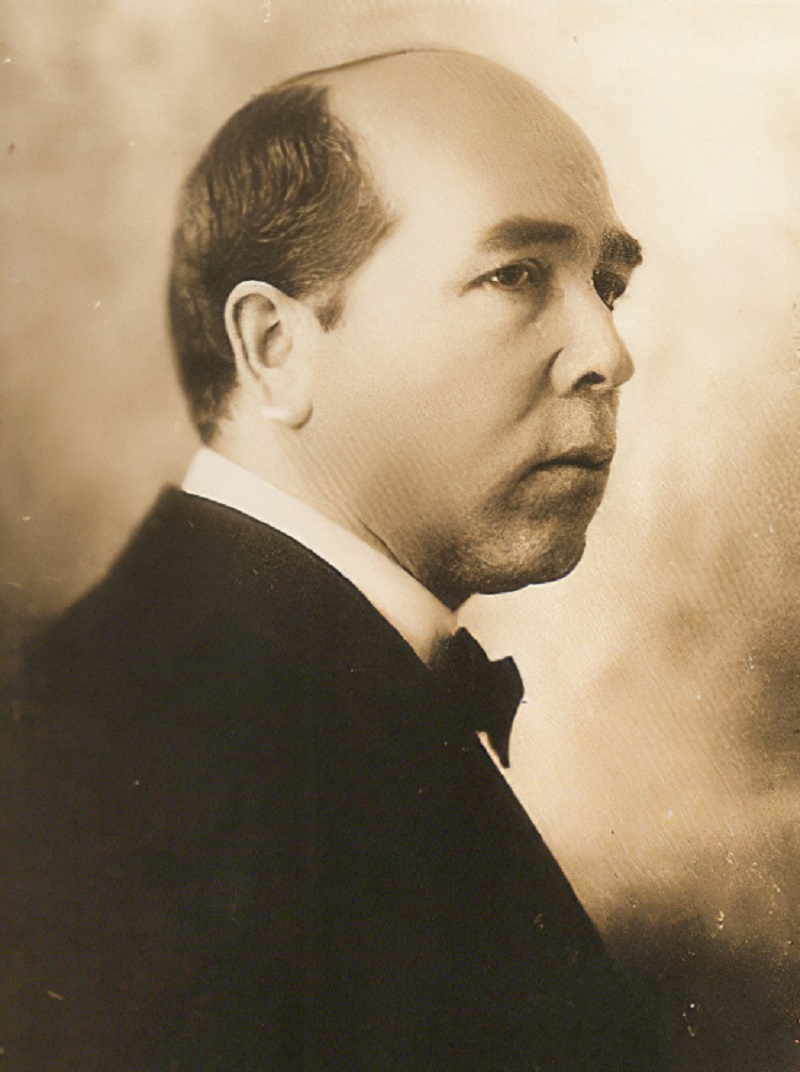

Bernhard Hoetger is a German painter, sculptor, graphic artist and architect. He studied at the Dusseldorf Academy of Art.
In 1937, as part of the Nazi "Degenerate Art" campaign, many works by Bernhard Hoetger were destroyed.
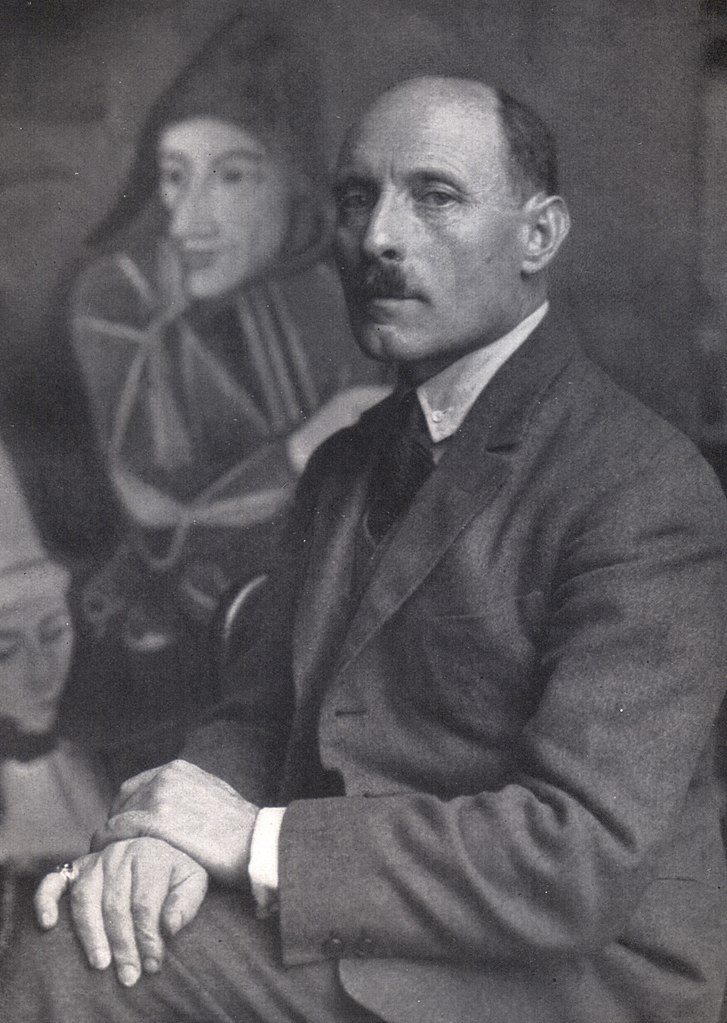

Karl Hofer was a German expressionist painter. He was director of the Berlin Academy of Fine Arts.
One of the most prominent painters of expressionism, he never was a member of one of the expressionist painting groups, like "Die Brücke", but was influenced by their painters. His work was among those considered degenerate art by the Nazis, but after World War II he regained recognition as one of the leading German painters.

Karl Hofer was a German expressionist painter. He was director of the Berlin Academy of Fine Arts.
One of the most prominent painters of expressionism, he never was a member of one of the expressionist painting groups, like "Die Brücke", but was influenced by their painters. His work was among those considered degenerate art by the Nazis, but after World War II he regained recognition as one of the leading German painters.

Karl Hofer was a German expressionist painter. He was director of the Berlin Academy of Fine Arts.
One of the most prominent painters of expressionism, he never was a member of one of the expressionist painting groups, like "Die Brücke", but was influenced by their painters. His work was among those considered degenerate art by the Nazis, but after World War II he regained recognition as one of the leading German painters.
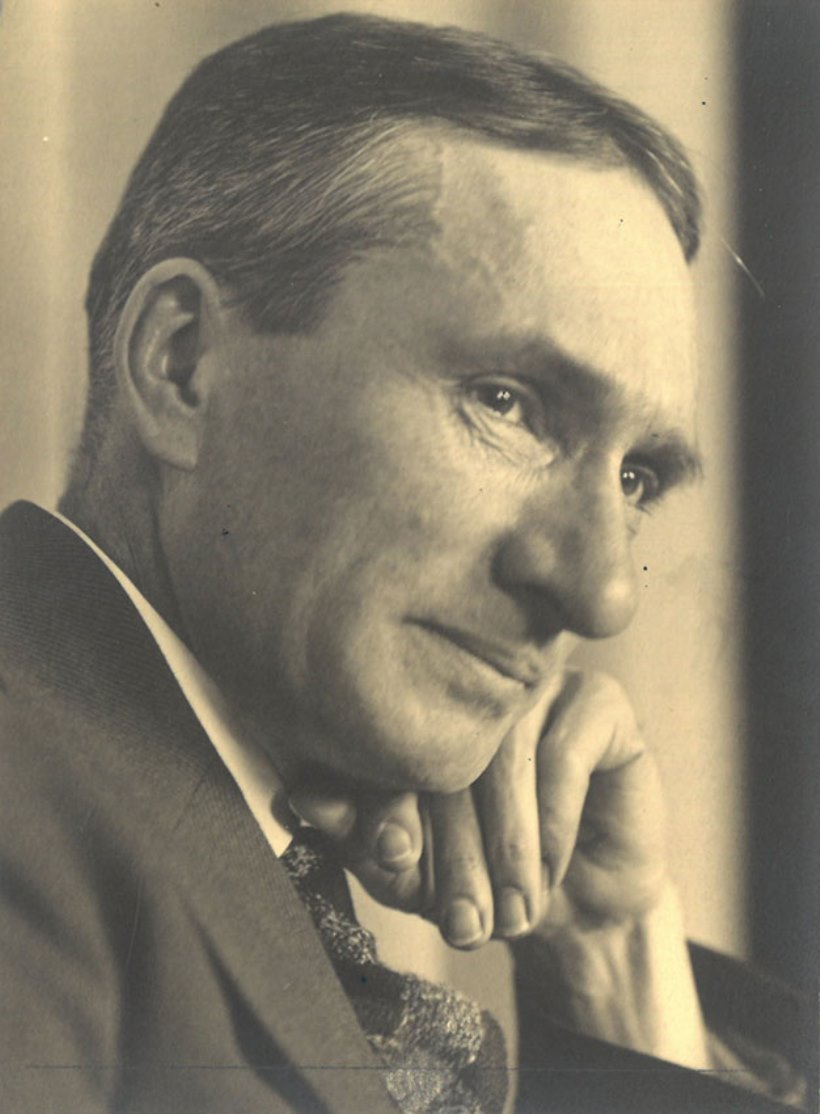

Holmead, born Clifford Holmead Phillips, was a painter. From about 1920 he joined various artist colonies in New England. In 1923, some of his paintings were shown for the first time as part of an Art Association exhibition. They were delicate, airy idylls, traditional landscapes in a brittle, silvery light, lonely farmhouses and trees. But he found the painting practiced there to be too beautiful and looked for new inspiration. In Paris, seeing a work by the French Expressionist and Fauvist Maurice de Vlaminck caused a fundamental change in his view of art. Vlaminck's dynamic lines and strong colors impressed Clifford Holmead Phillips so much that he increasingly followed the expressive direction, but later defined his style as "Crude Expressionism". From the 1920s to 1940, he celebrated international success and exhibited in important galleries and museums on both continents.

Holmead, born Clifford Holmead Phillips, was a painter. From about 1920 he joined various artist colonies in New England. In 1923, some of his paintings were shown for the first time as part of an Art Association exhibition. They were delicate, airy idylls, traditional landscapes in a brittle, silvery light, lonely farmhouses and trees. But he found the painting practiced there to be too beautiful and looked for new inspiration. In Paris, seeing a work by the French Expressionist and Fauvist Maurice de Vlaminck caused a fundamental change in his view of art. Vlaminck's dynamic lines and strong colors impressed Clifford Holmead Phillips so much that he increasingly followed the expressive direction, but later defined his style as "Crude Expressionism". From the 1920s to 1940, he celebrated international success and exhibited in important galleries and museums on both continents.




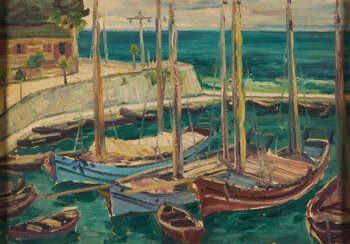








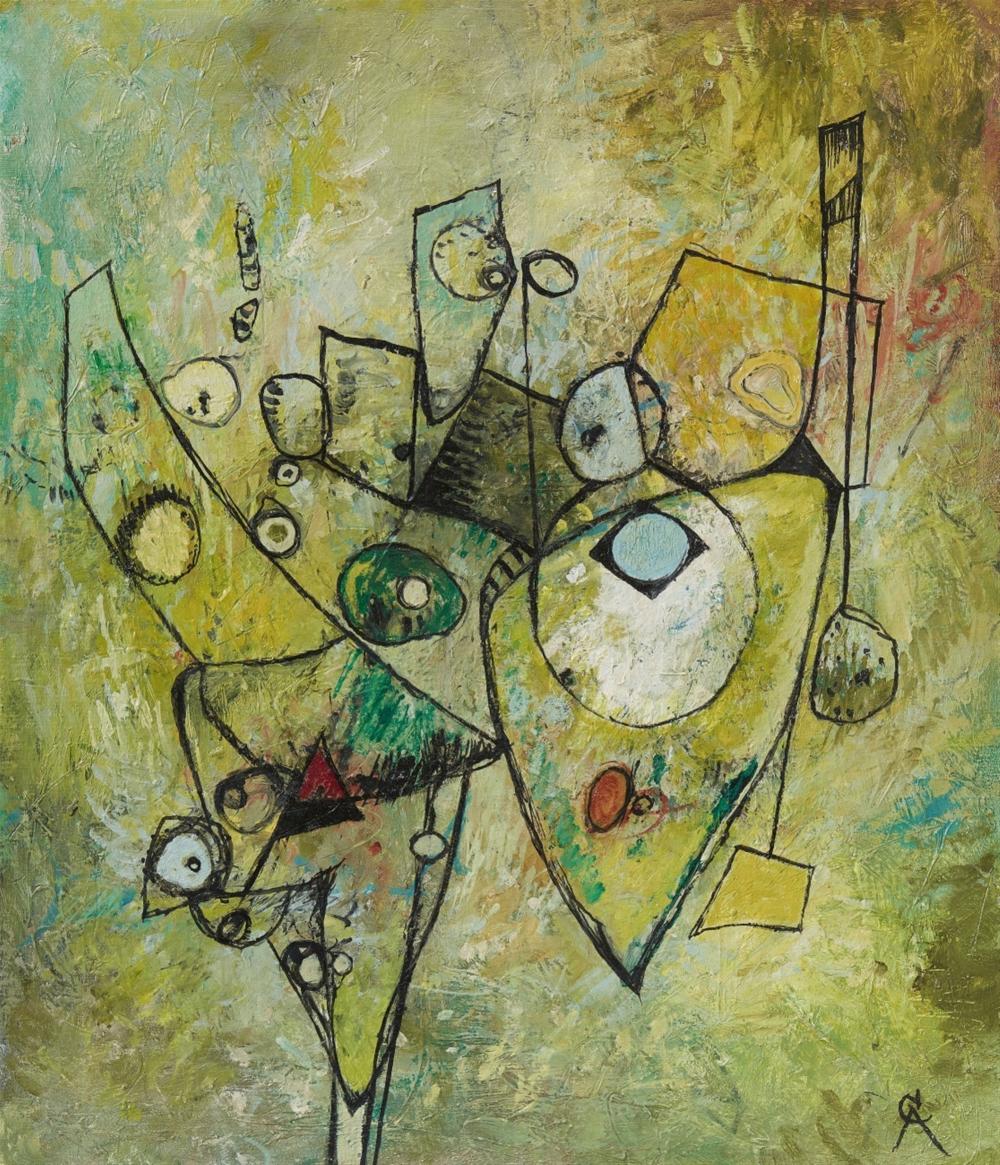



































.jpg)