médecine
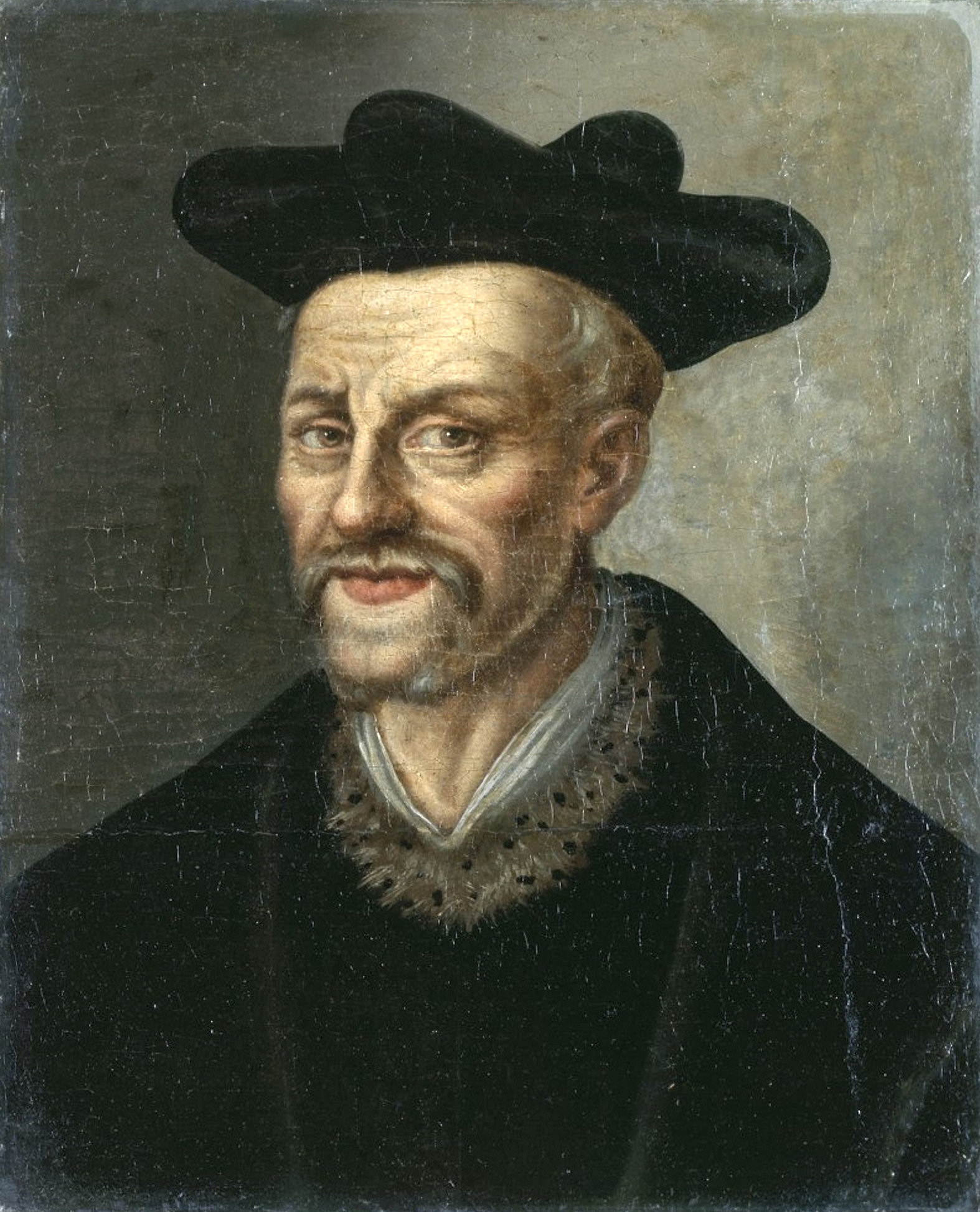


François Rabelais was a French Renaissance writer, physician, Renaissance humanist, monk and Greek scholar. He is primarily known as a writer of satire, of the grotesque, and of bawdy jokes and songs.
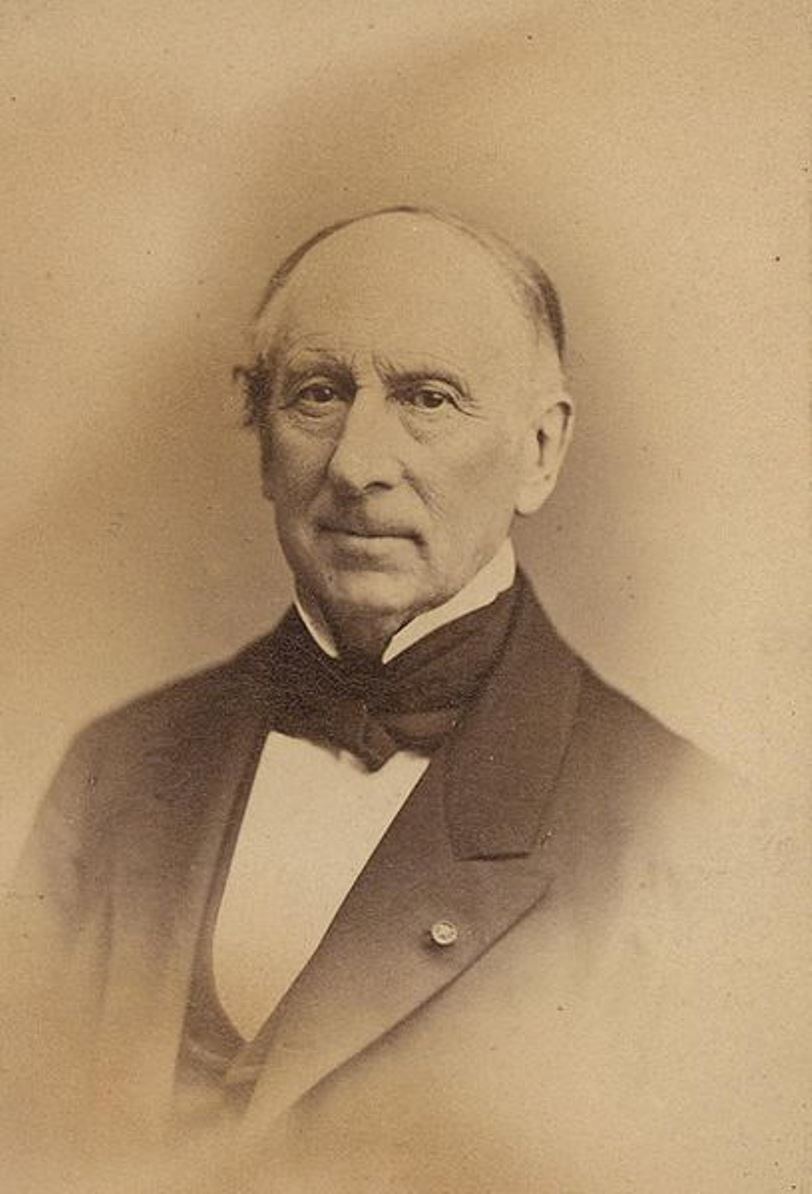


Augustin Louis Cauchy was a French mathematician and mechanic, military engineer, and founder of mathematical analysis.
Cauchy studied at the École Polytechnique and at the Paris School of Bridges and Roads. After becoming a military engineer, he went to Cherbourg in 1810 to work on harbors and fortifications for Napoleon's English invasion. Here he began independent mathematical research. Cauchy returned to Paris in 1813, and Lagrange and Laplace convinced him to devote himself entirely to mathematics. The following year he published a memoir on definite integrals, which formed the basis of the theory of complex functions. From 1816, Cauchy held professorships at the Faculty of Natural Sciences, the Collège de France, and the École Polytechnique in Paris.
Cauchy developed the foundation of mathematical analysis, and made enormous contributions to analysis, algebra, mathematical physics, and many other areas of mathematics. He almost single-handedly founded the theory of functions of a complex variable, which has extensive applications in physics. Cauchy's greatest contributions to mathematics are published primarily in three of his treatises, "Courses in Analysis at the Royal Polytechnic School" (1821), "Summary of Lessons on Infinitesimal Calculus" (1823), and "Lessons on the Application of Infinitesimal Values in Geometry" (1826-28). In all, Augustin Louis Cauchy wrote about 800 scientific articles.
Cauchy was a member of the Paris Academy of Sciences, the Royal Society of London, the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and other academies.
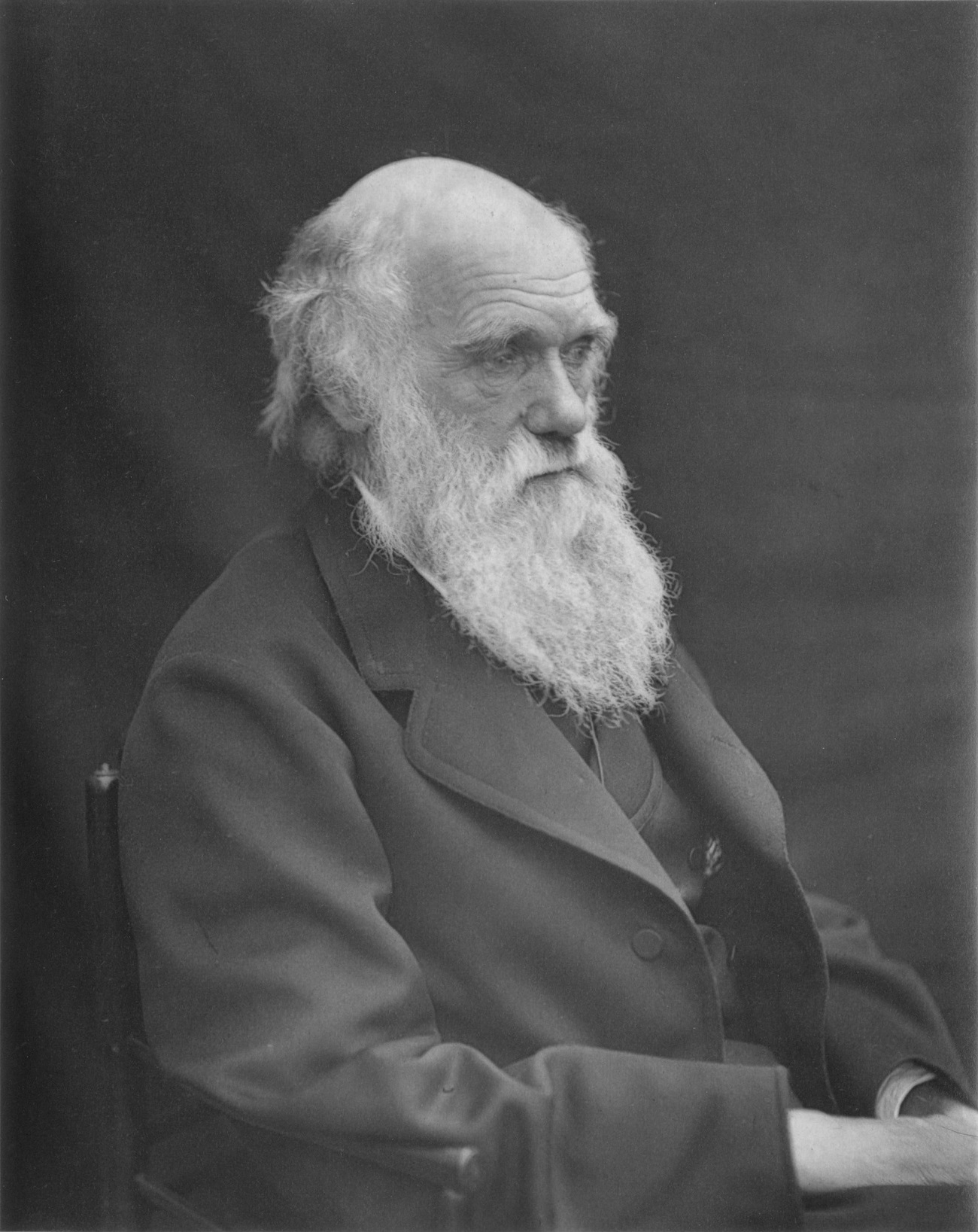


Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for contributing to the understanding of evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history, and he was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.