Georg Galgemair (1564 - 1619) — Auction price

Galileo Galilei was an Italian naturalist, physicist, mechanic, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician.
Using his own improved telescopes, Galileo Galilei observed the movements of the Moon, Earth's satellites, and the stars, making several breakthrough discoveries in astronomy. He was the first to see craters on the Moon, discovered sunspots and the rings of Saturn, and traced the phases of Venus. Galileo was a consistent and convinced supporter of the teachings of Copernicus and the heliocentric system of the world, for which he was subjected to the trial of the Inquisition.
Galileo is considered the founder of experimental and theoretical physics. He is also one of the founders of the principle of relativity in classical mechanics. Overall, the scientist had such a significant impact on the science of his time that he cannot be overemphasized.
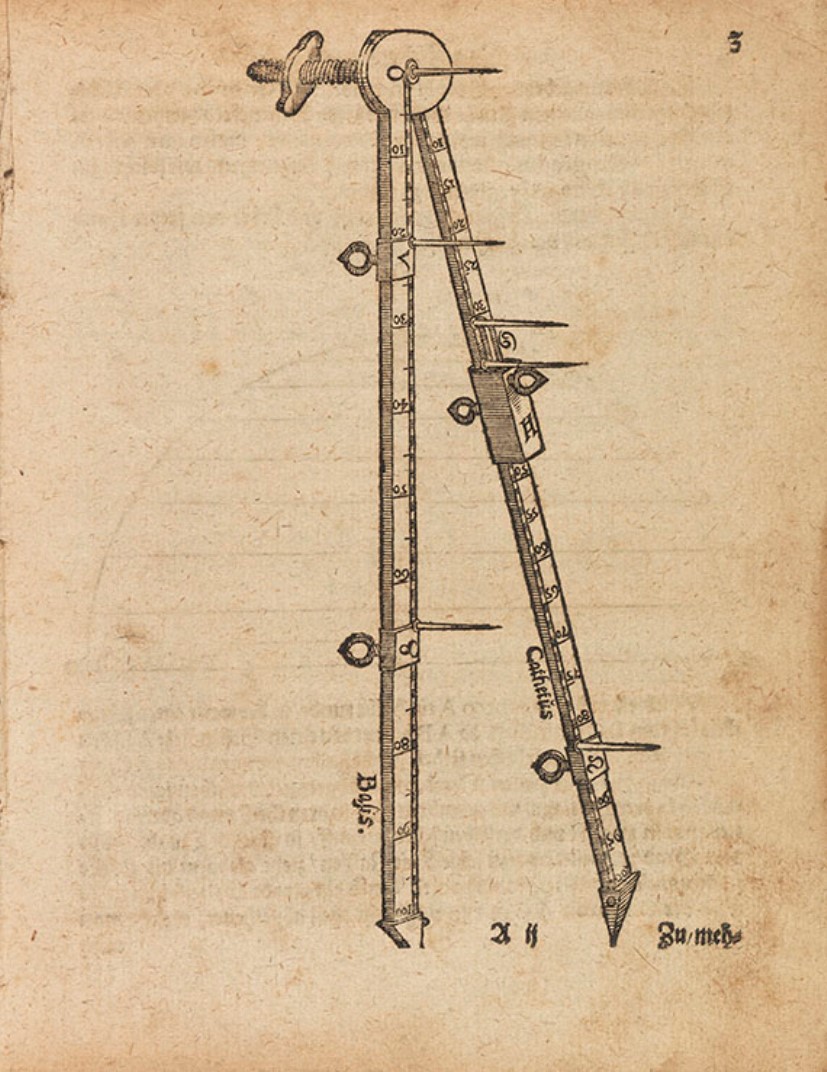
Georg Galgemair was a German mathematician and astrologer.
He was born into the family of the burgomaster of Donauwörth, was a pupil of Philip Apian, and then a master of mathematics at the University of Tübingen in 1585. After completing his studies, Galgemair began teaching at Lauingen in 1588.
His work on proportional circles led to the development of gnomonics. In the history of science, Galgemair is known for his works on mathematical instruments. As a calendar maker, he succeeded in 1606 in obtaining an imperial privilege for his calendars.
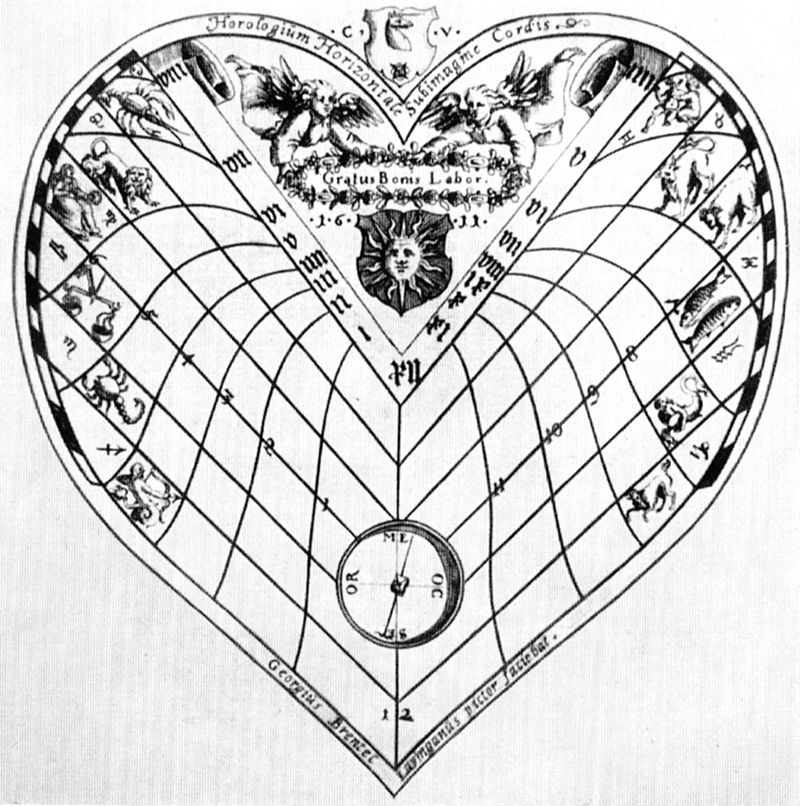
Georg Brentel the Younger was a German draftsman, engraver, and author of works on sundials and instrumentation.
He was the son of the cartographer Hans Brentel (1532-1614) and nephew of the armorial artist Georg Brentel the Elder (1525-1610). He always showed an interest in mathematics and astronomy, writing papers on these subjects and making instruments.
Brentel was particularly fond of designing sundials, and wrote several instructions for assembling various types of sundials - round and cubic, cross-shaped and heart-shaped.