
Art & Design : un certain regard sur le XXè siècle
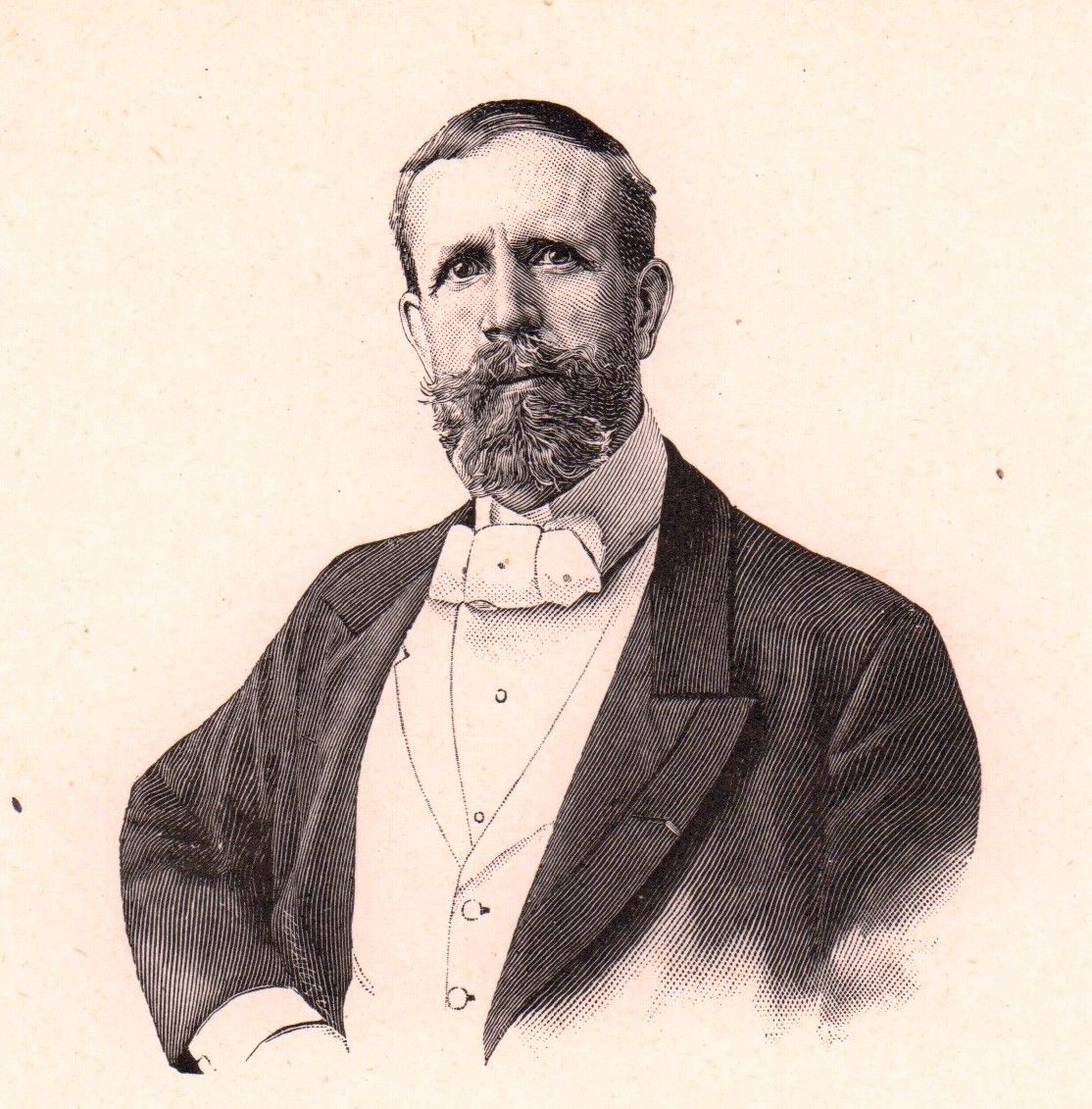

Frederick Arthur Bridgman was an American artist. He was known for his paintings in the Orientalist style.
Frederick Arthur Bridgman studied art at the Brooklyn Art Association and the National Academy of Design in New York. In 1866 he went to Paris to continue his studies at the École des Beaux-Arts. There he worked in the studio of Jean-Léon Gérôme, who at the time was a leading Orientalist painter. Bridgeman painted scenes of everyday life in the area, as well as historical and religious subjects. His paintings were notable for their vivid colours, attention to detail and dramatic compositions.
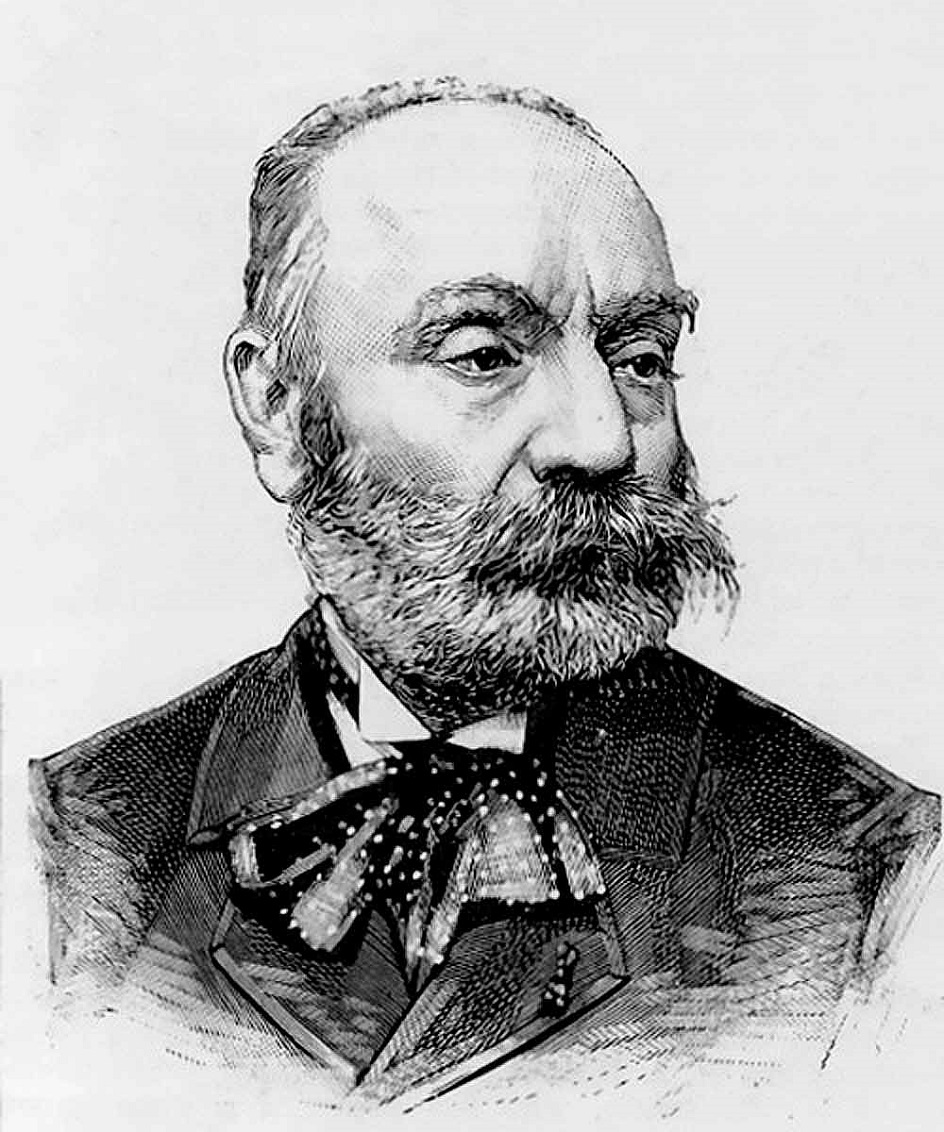

Gustave Clarence Rodolphe Boulanger was a French painter renowned for his classical and Orientalist themes. He was born in Paris and became an accomplished academic artist, earning accolades such as the Prix de Rome in 1849.
Gustave Boulanger's paintings often focused on historical subjects, with influences from Greek and Roman mythology, as well as Orientalism, particularly Middle Eastern themes. He also depicted scenes of daily life in ancient civilizations and had a knack for blending the ancient with the modern. Notable works by Boulanger include "Répétition théâtrale dans la maison d’un poète romain" (1855), presented at the Salon of 1855, which later inspired the Pompeiian palace inauguration. His style was known for its theatricality and ability to bridge the past with contemporary aesthetics.
Some of his significant works are housed in various museums and galleries, including the British Museum, the Art Institute of Chicago, and the Hermitage Museum. Examples of his works include "The Flute Concert," "The Slave Market," and "Theatrical Rehearsal in the House of an Ancient Roman Poet".
Gustave Boulanger also played a role in the cultural landscape of his time, teaching at the Académie Julian, where he influenced a generation of artists. His contributions to art and his ability to capture the spirit of different eras continue to be celebrated by collectors and experts in art and antiques.
If you are interested in updates on Gustave Boulanger-related auctions and sales, consider subscribing to a newsletter that provides such information. This subscription is designed solely for alerting you to new product sales and auction events related to Boulanger's work, without any additional promotional content.

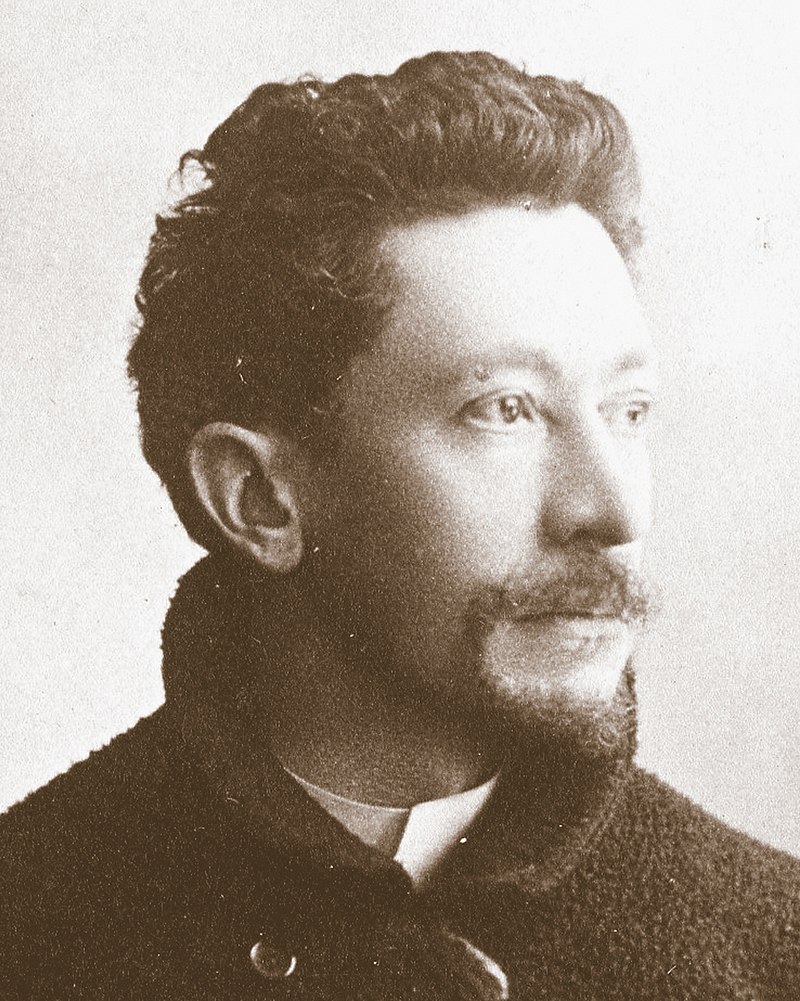
Louis-Ernest Barrias was a French sculptor of the Beaux-Arts school. In 1865 Barrias won the Prix de Rome for study at the French Academy in Rome.
Barrias was involved in the decoration of the Paris Opéra and the Hôtel de la Païva in the Champs-Élysées. His work was mostly in marble, in a Romantic realist style indebted to Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.
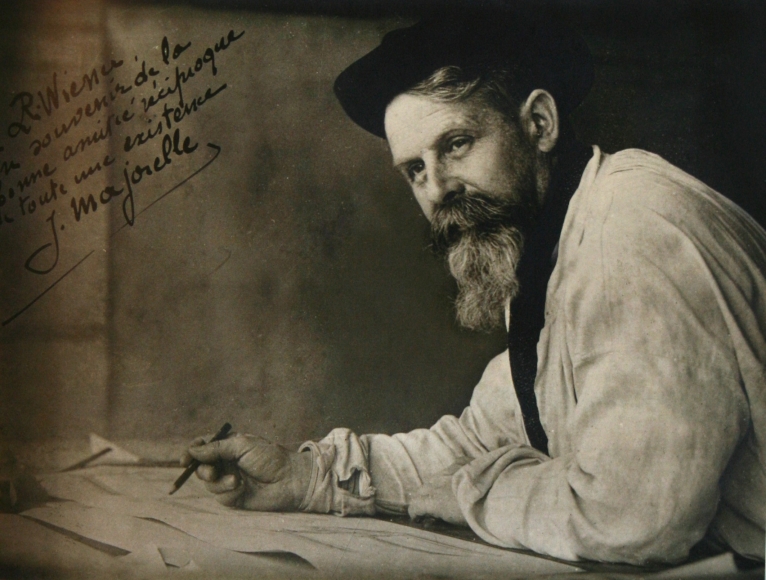

Louis Majorelle was a prominent French artist, cabinetmaker, furniture designer, and a leading figure of the Art Nouveau movement. Trained initially as a painter, Majorelle shifted focus to furniture design, taking over his family's business and emerging as a dynamic force within the École de Nancy.
Louis Majorelle was instrumental in the Art Nouveau style's development, known for his innovative and nature-inspired designs. He was one of the founding members of the École de Nancy, a collective that aimed to promote Lorraine's decorative arts. Louis Majorelle's work, particularly in furniture and interior design, showcased his skill in integrating natural forms with functional pieces. His use of materials such as mahogany and his incorporation of floral and organic motifs were distinctive of his work. Notably, Majorelle's Nénuphar bed, displaying water lily motifs, stands as a testament to his design philosophy and can be seen at the Musée d'Orsay in Paris.
The Villa Majorelle, his own residence in Nancy, serves as an embodiment of Art Nouveau architecture, featuring intricate ironwork and woodwork crafted by Louis Majorelle himself. This house not only served as his home but also as a beacon of Art Nouveau's architectural potential, showcasing the movement's aesthetic in a living environment.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Louis Majorelle's work represents the pinnacle of Art Nouveau's embrace of naturalistic designs and the seamless blend of art and craftsmanship. His contributions to the movement have left an indelible mark on the history of decorative arts.
To stay informed about new discoveries and interpretations related to Louis Majorelle and his era, signing up for updates is highly recommended. This subscription will ensure you're alerted to new product sales, auction events, and exhibitions related to this significant figure in art and design history.

Louis Majorelle was a prominent French artist, cabinetmaker, furniture designer, and a leading figure of the Art Nouveau movement. Trained initially as a painter, Majorelle shifted focus to furniture design, taking over his family's business and emerging as a dynamic force within the École de Nancy.
Louis Majorelle was instrumental in the Art Nouveau style's development, known for his innovative and nature-inspired designs. He was one of the founding members of the École de Nancy, a collective that aimed to promote Lorraine's decorative arts. Louis Majorelle's work, particularly in furniture and interior design, showcased his skill in integrating natural forms with functional pieces. His use of materials such as mahogany and his incorporation of floral and organic motifs were distinctive of his work. Notably, Majorelle's Nénuphar bed, displaying water lily motifs, stands as a testament to his design philosophy and can be seen at the Musée d'Orsay in Paris.
The Villa Majorelle, his own residence in Nancy, serves as an embodiment of Art Nouveau architecture, featuring intricate ironwork and woodwork crafted by Louis Majorelle himself. This house not only served as his home but also as a beacon of Art Nouveau's architectural potential, showcasing the movement's aesthetic in a living environment.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Louis Majorelle's work represents the pinnacle of Art Nouveau's embrace of naturalistic designs and the seamless blend of art and craftsmanship. His contributions to the movement have left an indelible mark on the history of decorative arts.
To stay informed about new discoveries and interpretations related to Louis Majorelle and his era, signing up for updates is highly recommended. This subscription will ensure you're alerted to new product sales, auction events, and exhibitions related to this significant figure in art and design history.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Louis-Ernest Barrias was a French sculptor of the Beaux-Arts school. In 1865 Barrias won the Prix de Rome for study at the French Academy in Rome.
Barrias was involved in the decoration of the Paris Opéra and the Hôtel de la Païva in the Champs-Élysées. His work was mostly in marble, in a Romantic realist style indebted to Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

Emile Gallé was a French artist and designer who worked in glass, and is considered to be one of the major innovators in the French Art Nouveau movement. He was noted for his designs of Art Nouveau glass art and Art Nouveau furniture, and was a founder of the École de Nancy or Nancy School, a movement of design in the city of Nancy, France.

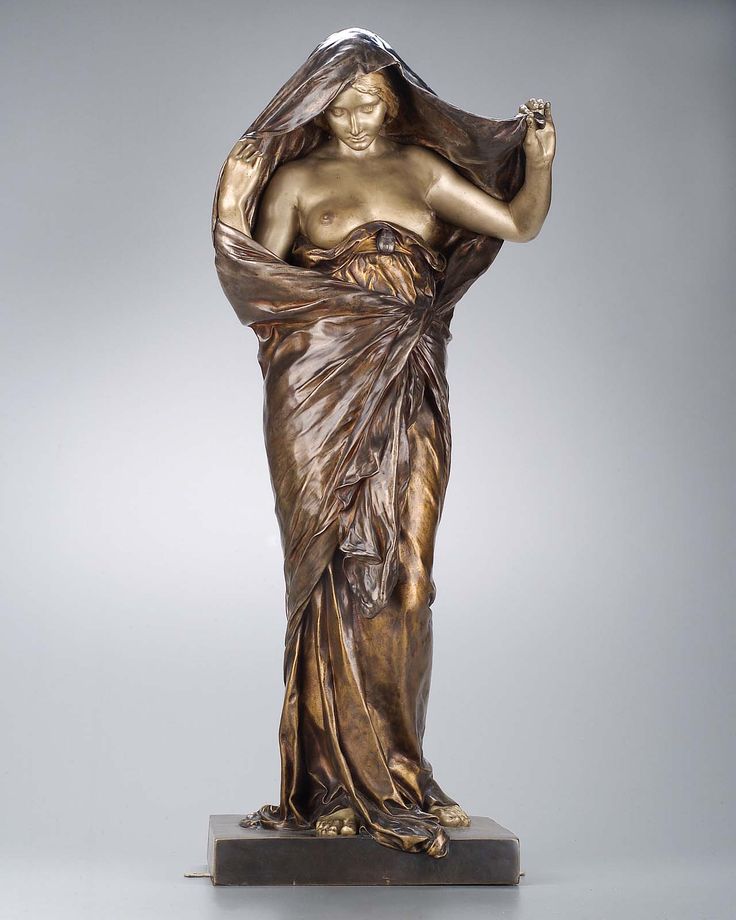
François-Raoul Larche was a French Art Nouveau sculptor whose work included several figures of Christ, but who may be better known for his numerous female figures, both nude and draped.
He was one of several artists inspired by the dancer Loie Fuller; one of his best-known statues depicts Fuller dancing with part of her drapery billowing above and behind her head like a flame.

Louis Majorelle was a prominent French artist, cabinetmaker, furniture designer, and a leading figure of the Art Nouveau movement. Trained initially as a painter, Majorelle shifted focus to furniture design, taking over his family's business and emerging as a dynamic force within the École de Nancy.
Louis Majorelle was instrumental in the Art Nouveau style's development, known for his innovative and nature-inspired designs. He was one of the founding members of the École de Nancy, a collective that aimed to promote Lorraine's decorative arts. Louis Majorelle's work, particularly in furniture and interior design, showcased his skill in integrating natural forms with functional pieces. His use of materials such as mahogany and his incorporation of floral and organic motifs were distinctive of his work. Notably, Majorelle's Nénuphar bed, displaying water lily motifs, stands as a testament to his design philosophy and can be seen at the Musée d'Orsay in Paris.
The Villa Majorelle, his own residence in Nancy, serves as an embodiment of Art Nouveau architecture, featuring intricate ironwork and woodwork crafted by Louis Majorelle himself. This house not only served as his home but also as a beacon of Art Nouveau's architectural potential, showcasing the movement's aesthetic in a living environment.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Louis Majorelle's work represents the pinnacle of Art Nouveau's embrace of naturalistic designs and the seamless blend of art and craftsmanship. His contributions to the movement have left an indelible mark on the history of decorative arts.
To stay informed about new discoveries and interpretations related to Louis Majorelle and his era, signing up for updates is highly recommended. This subscription will ensure you're alerted to new product sales, auction events, and exhibitions related to this significant figure in art and design history.


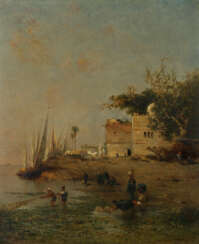
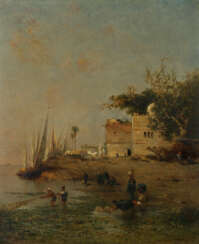
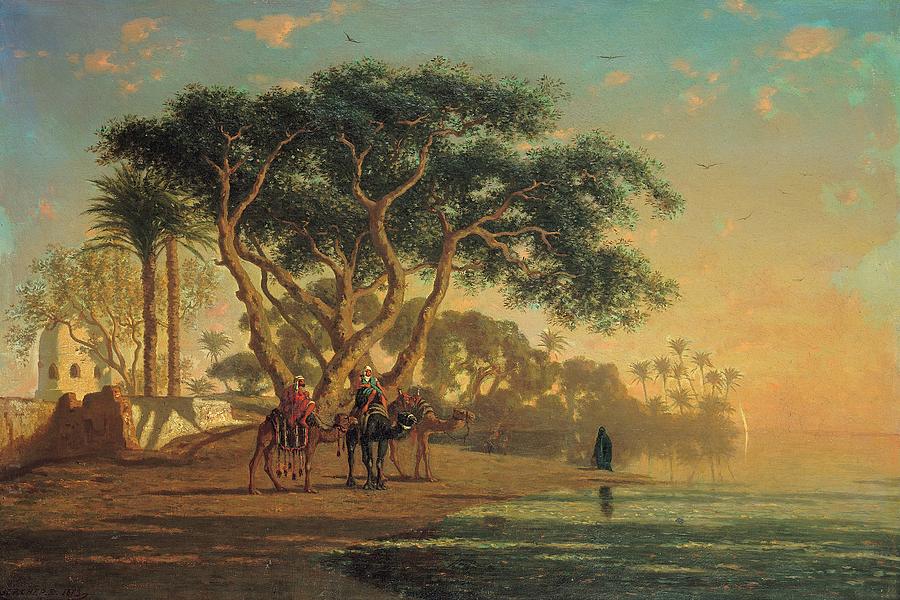




































 Севрская фарфоровая мануфактура. Леонард Агатон. Скульптура «Танец с шарфом», 1908.jpg)





















