Design
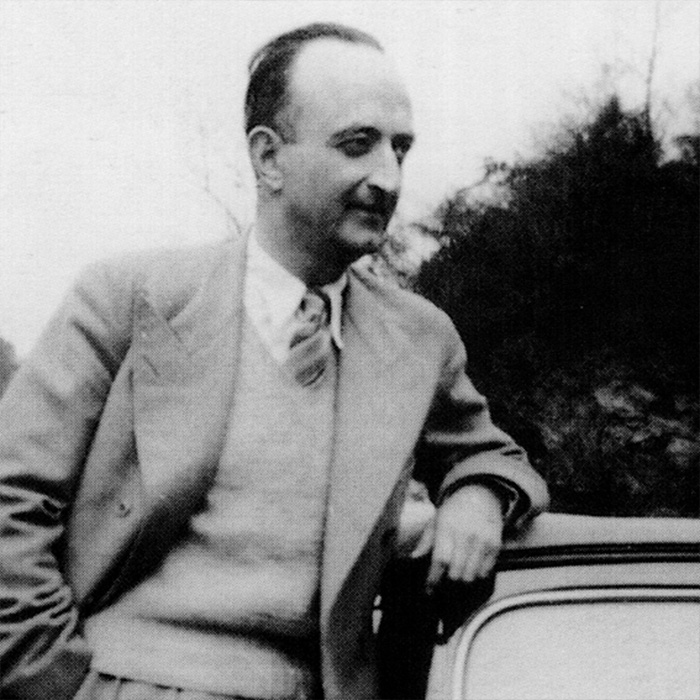
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
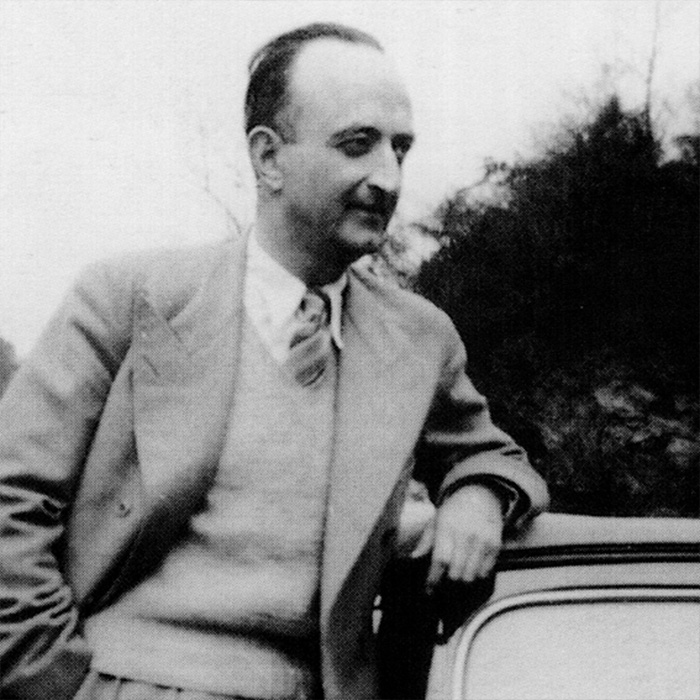
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
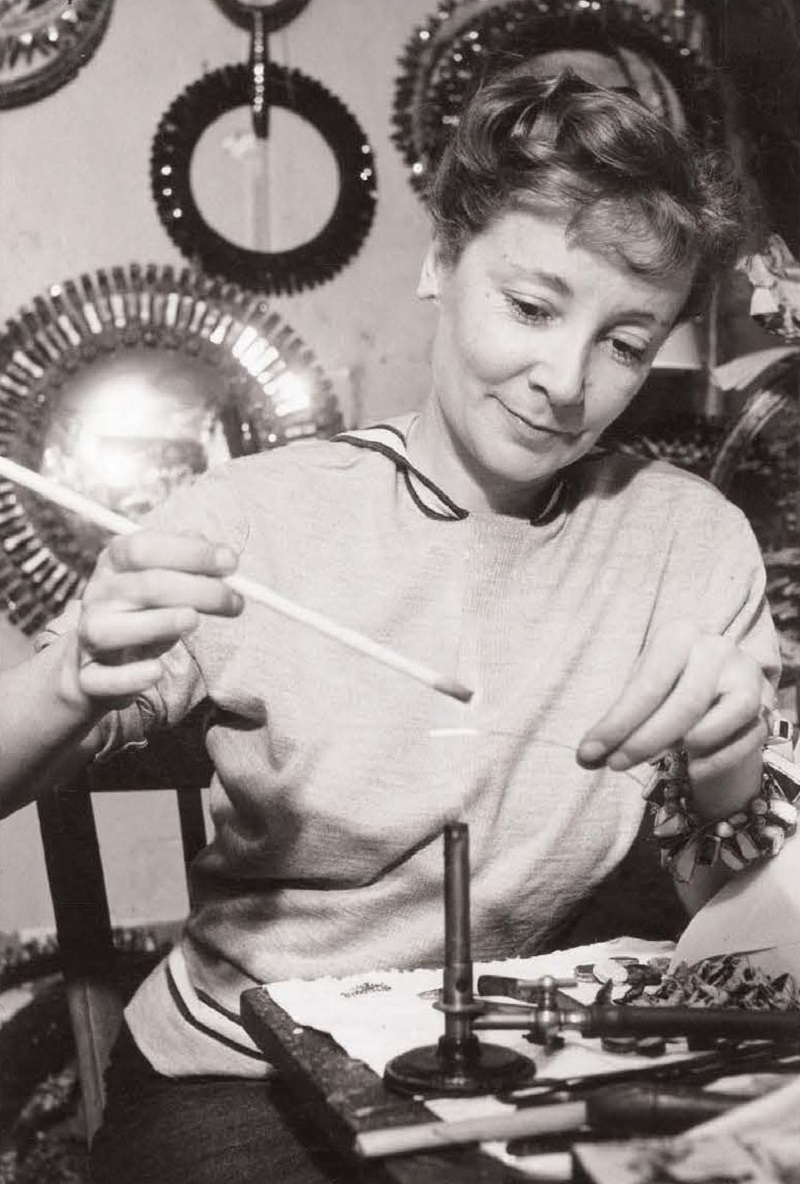

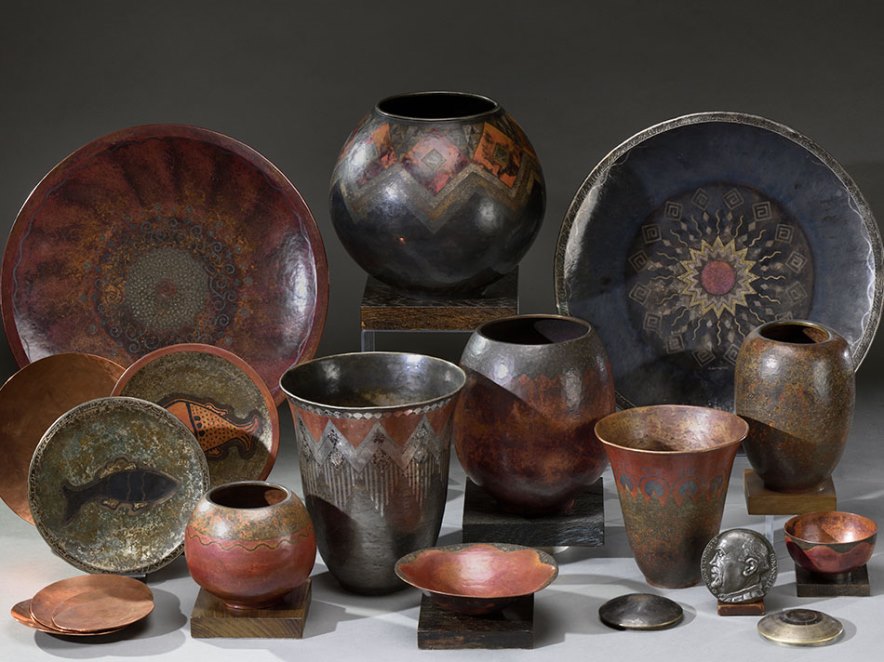
Line Vautrin is a French artist, jeweller and designer.
Her work ranges from jewellery to objects such as mirrors, trays and boxes. Devoted to experimentation, she opened A.D.A.M. (Association for the Development of Handmade Arts), a craft school where she taught metalwork and jewellery making and also sold the raw materials she used in her practice.

Line Vautrin is a French artist, jeweller and designer.
Her work ranges from jewellery to objects such as mirrors, trays and boxes. Devoted to experimentation, she opened A.D.A.M. (Association for the Development of Handmade Arts), a craft school where she taught metalwork and jewellery making and also sold the raw materials she used in her practice.

Line Vautrin is a French artist, jeweller and designer.
Her work ranges from jewellery to objects such as mirrors, trays and boxes. Devoted to experimentation, she opened A.D.A.M. (Association for the Development of Handmade Arts), a craft school where she taught metalwork and jewellery making and also sold the raw materials she used in her practice.
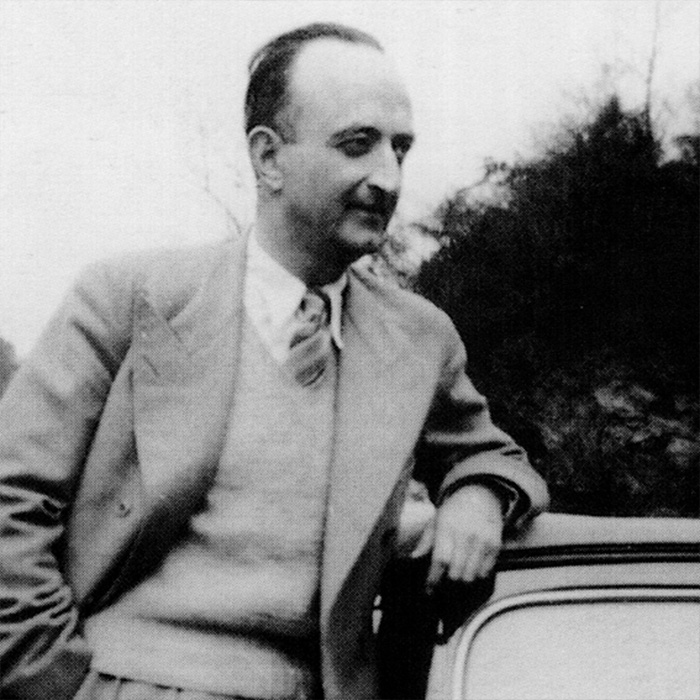
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
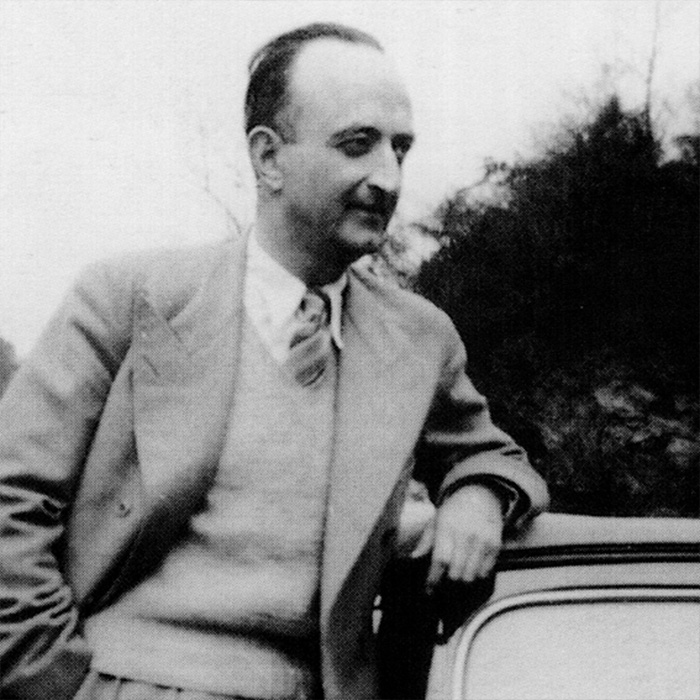
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
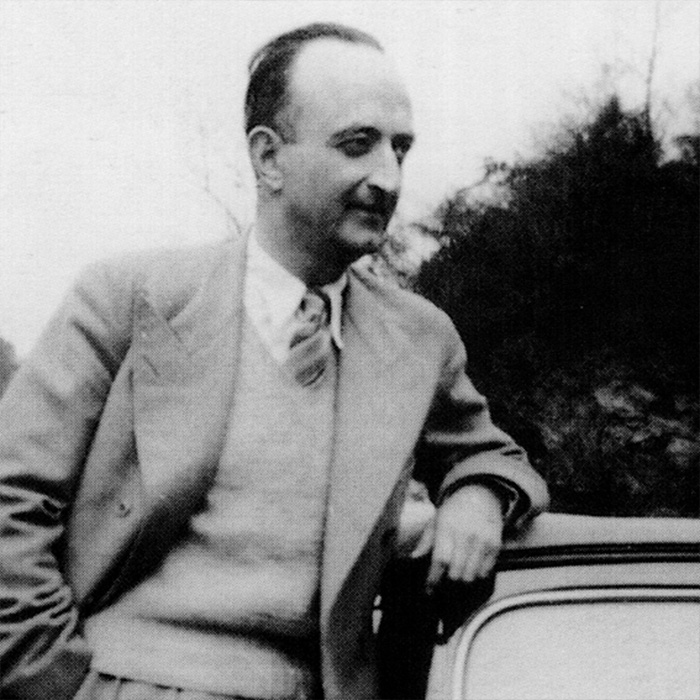
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
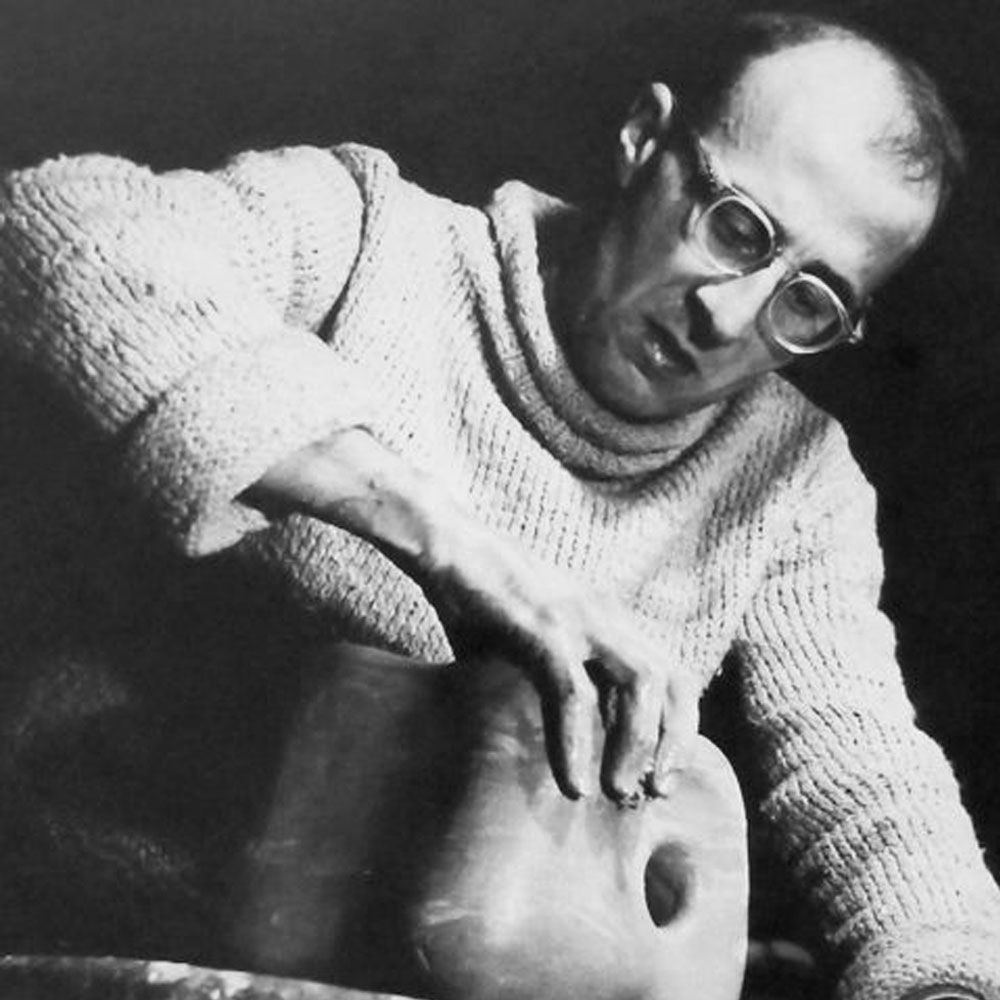

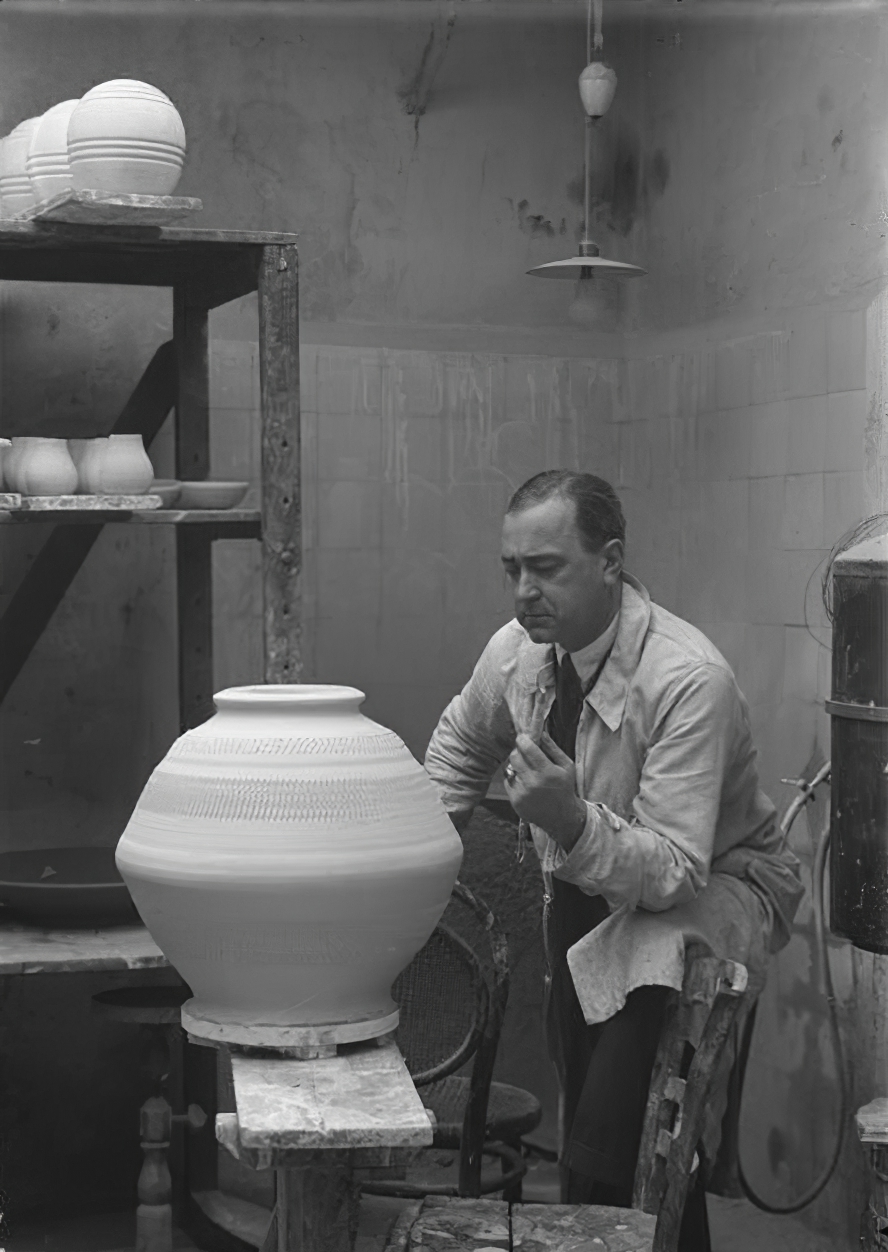
Georges Jouve was an important ceramist of the 20th century. At 17 years old, Jouve enrolled at the prestigious Ecole Boulle in Paris where he received theoretical instruction in Art History in addition to his technical studies as a sculptor. After Graduation in 1930 he first embarked on his artistic career as a theatrical set designer. During World War II, Jouve was captured by the Germans and interned in a German camp. After several attempts he escaped from the camp and took refuge at his step parents home in a potters village in the South of France called Dieulefit. In 1944, Jouve and his family moved back to Paris. He opened his studio in Paris and was invited by Jacques Adnet to participate in the exhibition “La Ceramique Contemporaine” by the Compagnie des Arts Francais. He then participated annually in numerous 'Salons' in France and internationally such as the “Salon des Artistes Decorateurs” in Paris, Association Francaise d'Action Artistique in Rio de Janeiro, and Vienna, Toronto, Rome, Milan, and Cairo.

Georges Jouve was an important ceramist of the 20th century. At 17 years old, Jouve enrolled at the prestigious Ecole Boulle in Paris where he received theoretical instruction in Art History in addition to his technical studies as a sculptor. After Graduation in 1930 he first embarked on his artistic career as a theatrical set designer. During World War II, Jouve was captured by the Germans and interned in a German camp. After several attempts he escaped from the camp and took refuge at his step parents home in a potters village in the South of France called Dieulefit. In 1944, Jouve and his family moved back to Paris. He opened his studio in Paris and was invited by Jacques Adnet to participate in the exhibition “La Ceramique Contemporaine” by the Compagnie des Arts Francais. He then participated annually in numerous 'Salons' in France and internationally such as the “Salon des Artistes Decorateurs” in Paris, Association Francaise d'Action Artistique in Rio de Janeiro, and Vienna, Toronto, Rome, Milan, and Cairo.
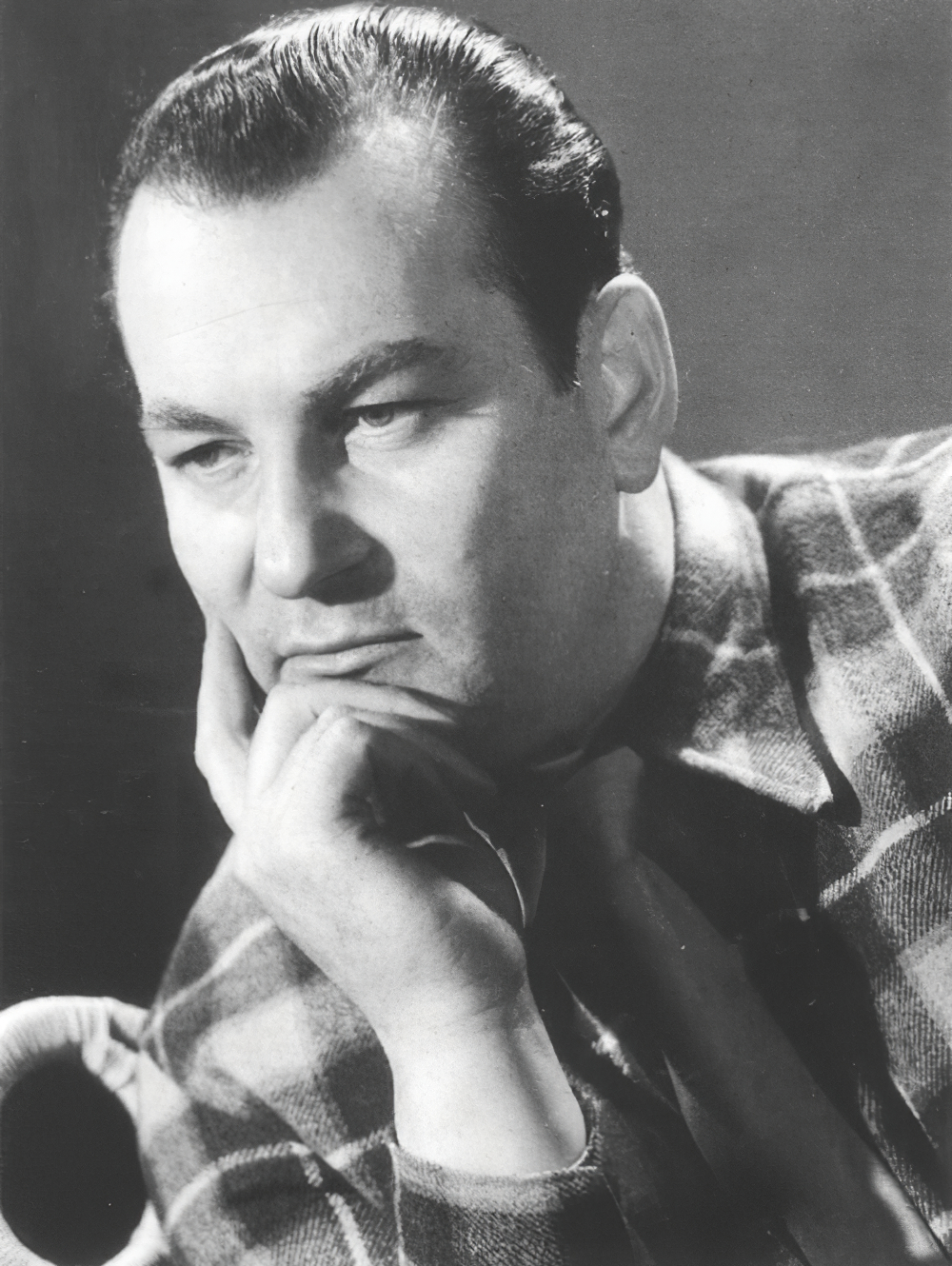

Mathieu Matégot was a Hungarian / French designer and material artist. He was one of the most renowned French designers of the 1950s.
Following the war, Matégot established a workshop for making handcrafted furniture using a variety of materials such as metal, rattan, glass, formica, and perforated sheet metal. The workshop made chairs, tables, sideboards, desks and other objects that he had designed. At first based in Paris, the workshop later moved to Casablanca. All the furniture and other objects had clever, practical and amusing designs. Distributed to decoration shops in editions of 200, his work was extremely successful.
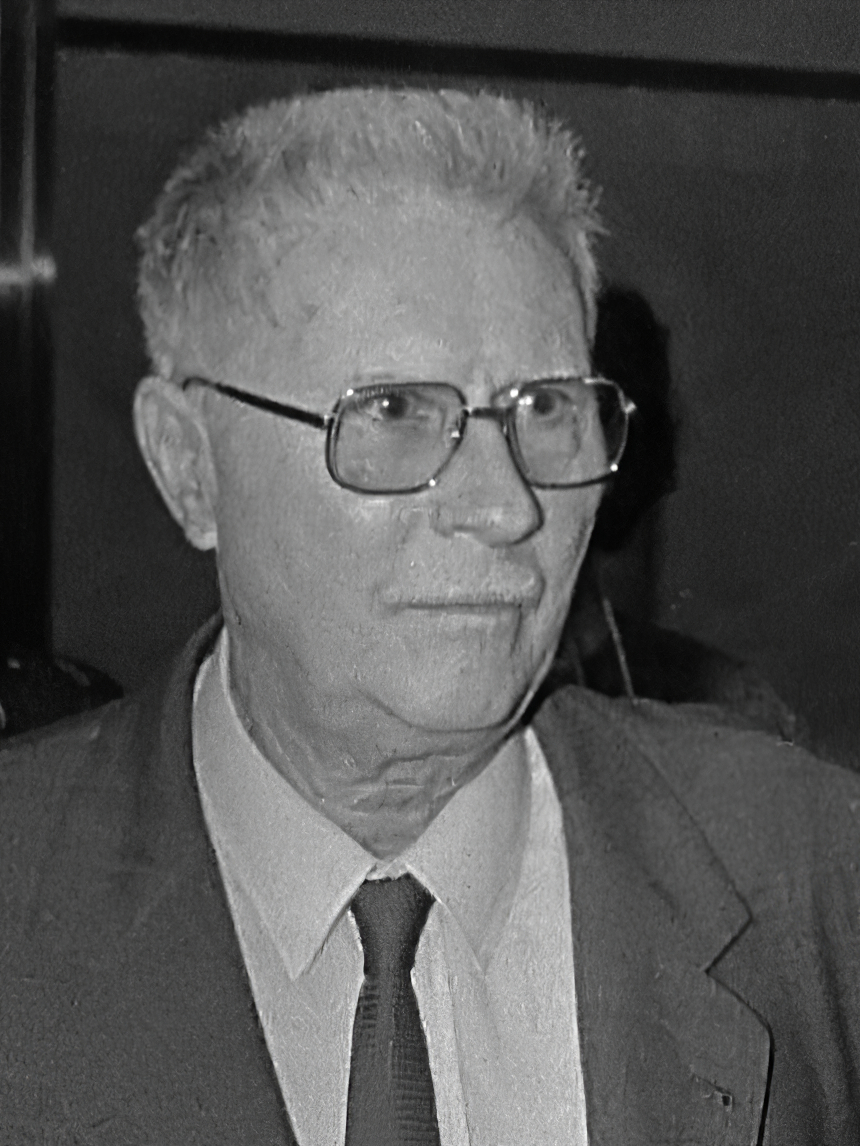

Jean Prouvé was a French metal worker, self-taught architect and designer. Le Corbusier designated Prouvé a constructeur, blending architecture and engineering. Prouvé's main achievement was transferring manufacturing technology from industry to architecture, without losing aesthetic qualities. His design skills were not limited to one discipline. During his career Jean Prouvé was involved in architectural design, industrial design, structural design and furniture design.
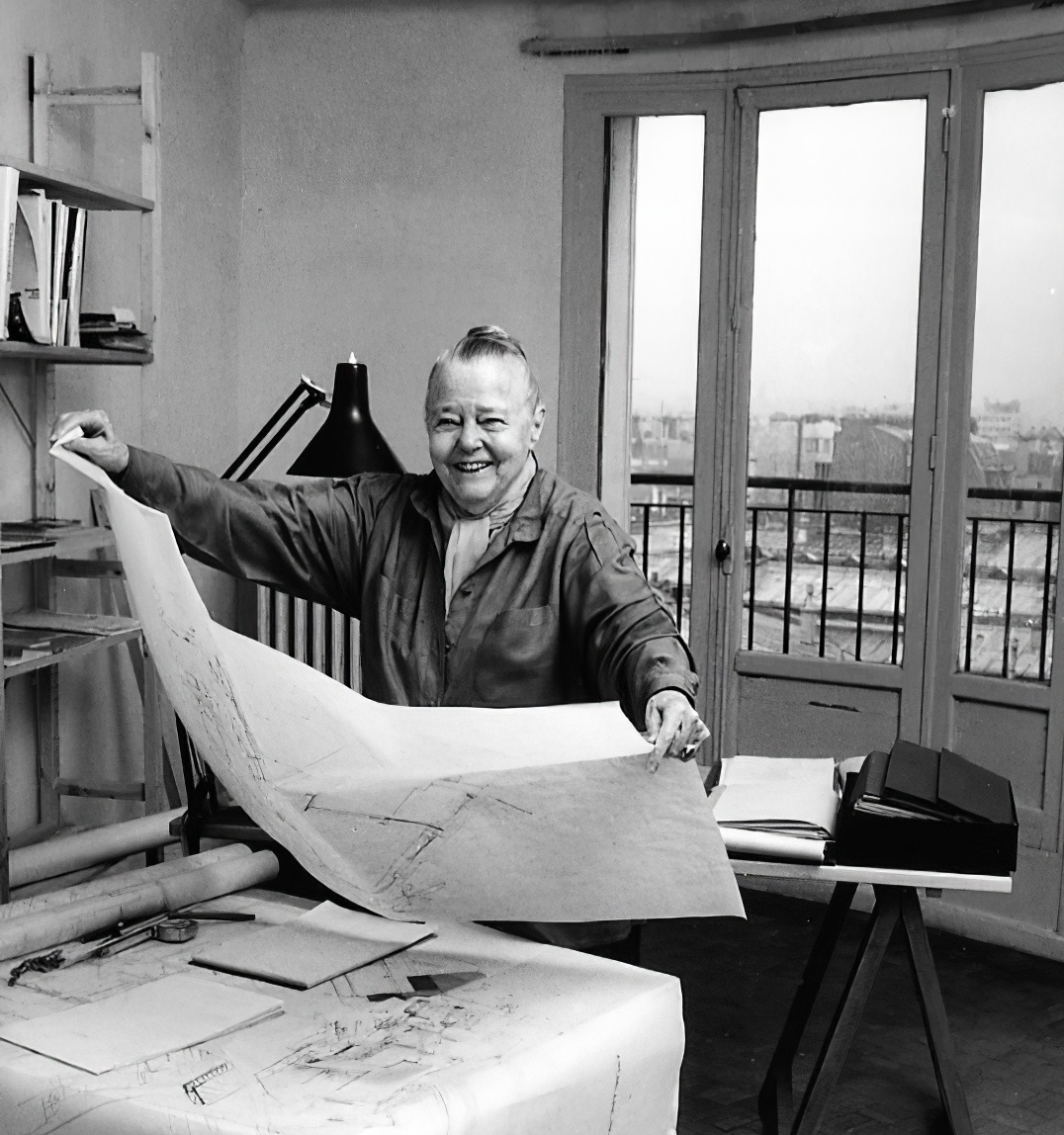

Charlotte Perriand was a French architect and designer. Her work aimed to create functional living spaces in the belief that better design helps in creating a better society. In her article "L'Art de Vivre" from 1981 she states "The extension of the art of dwelling is the art of living — living in harmony with man's deepest drives and with his adopted or fabricated environment." Charlotte liked to take her time in a space before starting the design process.

Charlotte Perriand was a French architect and designer. Her work aimed to create functional living spaces in the belief that better design helps in creating a better society. In her article "L'Art de Vivre" from 1981 she states "The extension of the art of dwelling is the art of living — living in harmony with man's deepest drives and with his adopted or fabricated environment." Charlotte liked to take her time in a space before starting the design process.

Georges Jouve was an important ceramist of the 20th century. At 17 years old, Jouve enrolled at the prestigious Ecole Boulle in Paris where he received theoretical instruction in Art History in addition to his technical studies as a sculptor. After Graduation in 1930 he first embarked on his artistic career as a theatrical set designer. During World War II, Jouve was captured by the Germans and interned in a German camp. After several attempts he escaped from the camp and took refuge at his step parents home in a potters village in the South of France called Dieulefit. In 1944, Jouve and his family moved back to Paris. He opened his studio in Paris and was invited by Jacques Adnet to participate in the exhibition “La Ceramique Contemporaine” by the Compagnie des Arts Francais. He then participated annually in numerous 'Salons' in France and internationally such as the “Salon des Artistes Decorateurs” in Paris, Association Francaise d'Action Artistique in Rio de Janeiro, and Vienna, Toronto, Rome, Milan, and Cairo.

Jean Prouvé was a French metal worker, self-taught architect and designer. Le Corbusier designated Prouvé a constructeur, blending architecture and engineering. Prouvé's main achievement was transferring manufacturing technology from industry to architecture, without losing aesthetic qualities. His design skills were not limited to one discipline. During his career Jean Prouvé was involved in architectural design, industrial design, structural design and furniture design.

Charlotte Perriand was a French architect and designer. Her work aimed to create functional living spaces in the belief that better design helps in creating a better society. In her article "L'Art de Vivre" from 1981 she states "The extension of the art of dwelling is the art of living — living in harmony with man's deepest drives and with his adopted or fabricated environment." Charlotte liked to take her time in a space before starting the design process.
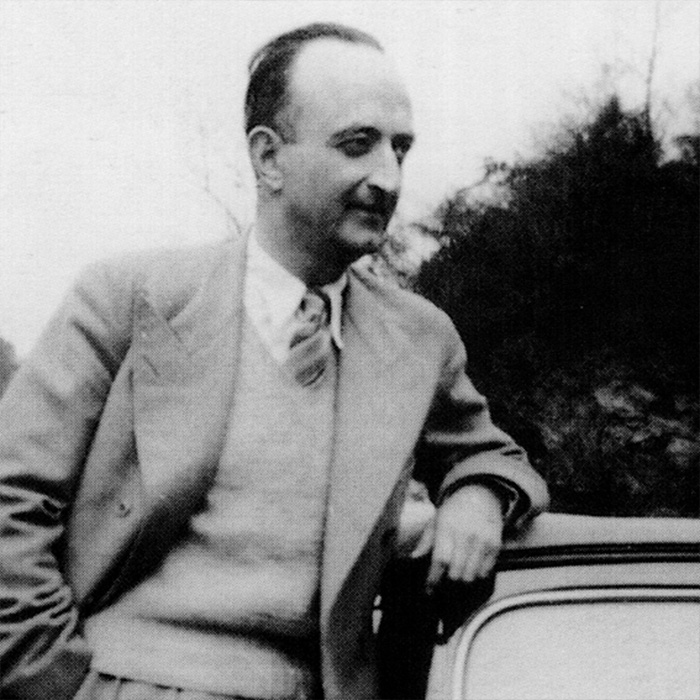
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
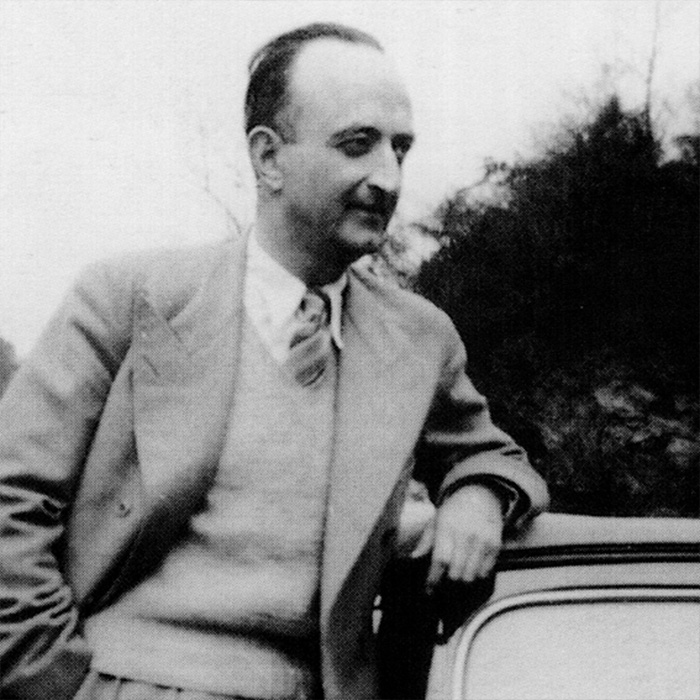
Jean Royère was a French designer.
A key figure of the avant-garde in the 1950s, Royère tackled all kinds of decoration work and opened branches in the Near East and Latin America. Among his patrons were King Farouk, King Hussein of Jordan, and the Shah of Iran, who were captivated by his freedom of creation and his elegance and entrusted him with the layout of their palaces. Royère pioneered an original style combining bright colors, organic forms and precious materials within a wide range of imaginative accomplishments. In 1980, he left France for the United States, where he lived until his death.
.jpeg)
Jean Dunand was a Swiss and French painter, sculptor, metal craftsman and interior designer during the Art Deco period. He was particularly known for his lacquered screens and other art objects.

Alberto Giacometti was a Swiss sculptor, painter, draftsman, and printmaker, renowned for his distinctive elongated sculptures of solitary figures. Born in Borgonovo, Switzerland, in 1901, into a family of artists, Giacometti's talent was evident from an early age, encouraged by his father, Giovanni, a post-Impressionist painter, and his godfather, Cuno Amiet, a Fauvist painter. Moving to Paris in 1922 to study under the sculptor Antoine Bourdelle, Giacometti became a pivotal figure in Surrealism before focusing intensely on the human form, leading to his signature style of thin, elongated figures that evoke feelings of solitude and existential dread.
Giacometti's work spans several decades and various phases, including his early involvement with Surrealism and his later, more recognized existential and figurative sculptures. Notably, his sculptures, such as "Walking Man I" and "The Palace at 4 a.m.," reflect his unique view of reality and his relentless pursuit to capture the human essence. His approach was influenced by his associations with prominent figures of the art world, including Miró and Picasso, and intellectuals like Jean-Paul Sartre.
Despite facing challenges, including periods of self-doubt and the physical toll on his health, Giacometti's legacy as a master sculptor and artist remains influential. His works are celebrated worldwide and featured in major museums, such as the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Gallery in London, testament to his enduring impact on the art world.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques continue to revere Giacometti's work for its emotional depth and unique aesthetic. For those interested in the pioneering spirit of modern sculpture, Alberto Giacometti's oeuvre offers a profound exploration of the human condition and the artist's relentless pursuit of reality through art.
To stay updated on sales and auction events related to Alberto Giacometti's work, sign up for updates. This subscription is an excellent opportunity for collectors and enthusiasts to remain informed about new discoveries and opportunities related to Giacometti's enduring legacy.































































