рихард
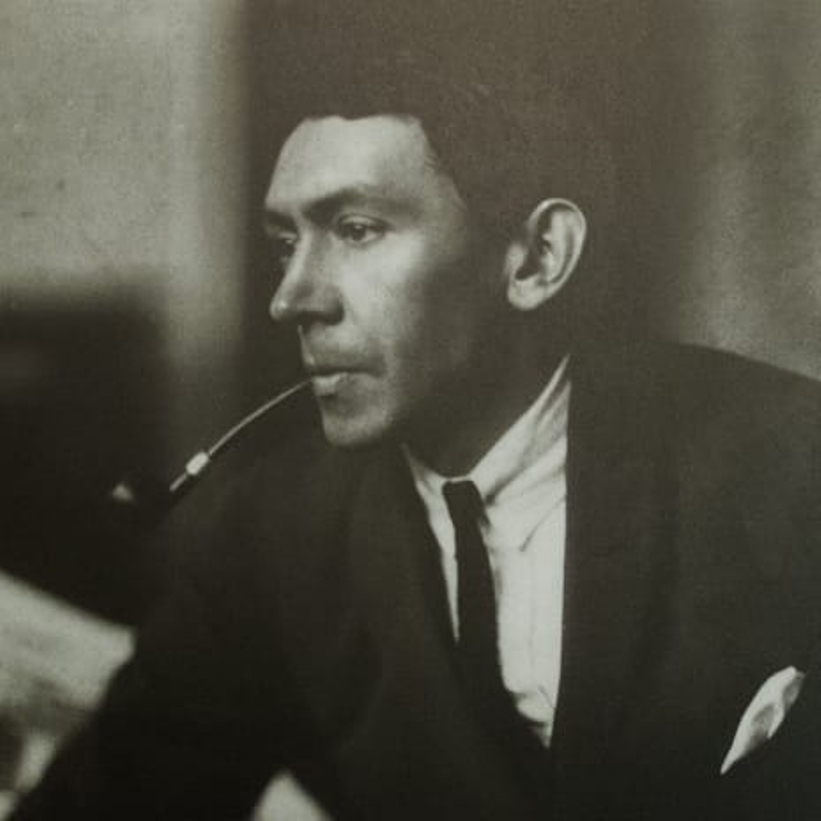

Richard Seewald was a German painter, graphic artist, illustrator and educator.
Seewald studied architecture at the Munich Polytechnic Institute, but soon turned to painting and collaborated with magazines that published his cartoons. He soon mastered etching and etching, became a member of the New Munich Secession in 1913, and illustrated an edition of Robinson Crusoe, Penthesilea (Heinrich von Kleist) and his first book.
In 1924 Seewald was appointed to a teaching position at the Werkschule in Cologne; in 1931 he settled in Ticino, where he received commissions for murals in churches and other church buildings. In 1954 Richard Seewald accepted an offer to become a professor at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich, and resigned four years later after a disagreement with the academy's presidium. After his wife's death, he burned about 150 of his paintings, as well as hundreds of sketches, drafts, and correspondence. In the late 1960s, Seewald designed windows for the Herz-Jesu-Kirche (Sacred Heart Church) in Munich-Neuhausen and St. Michael's Church in Iserlo.
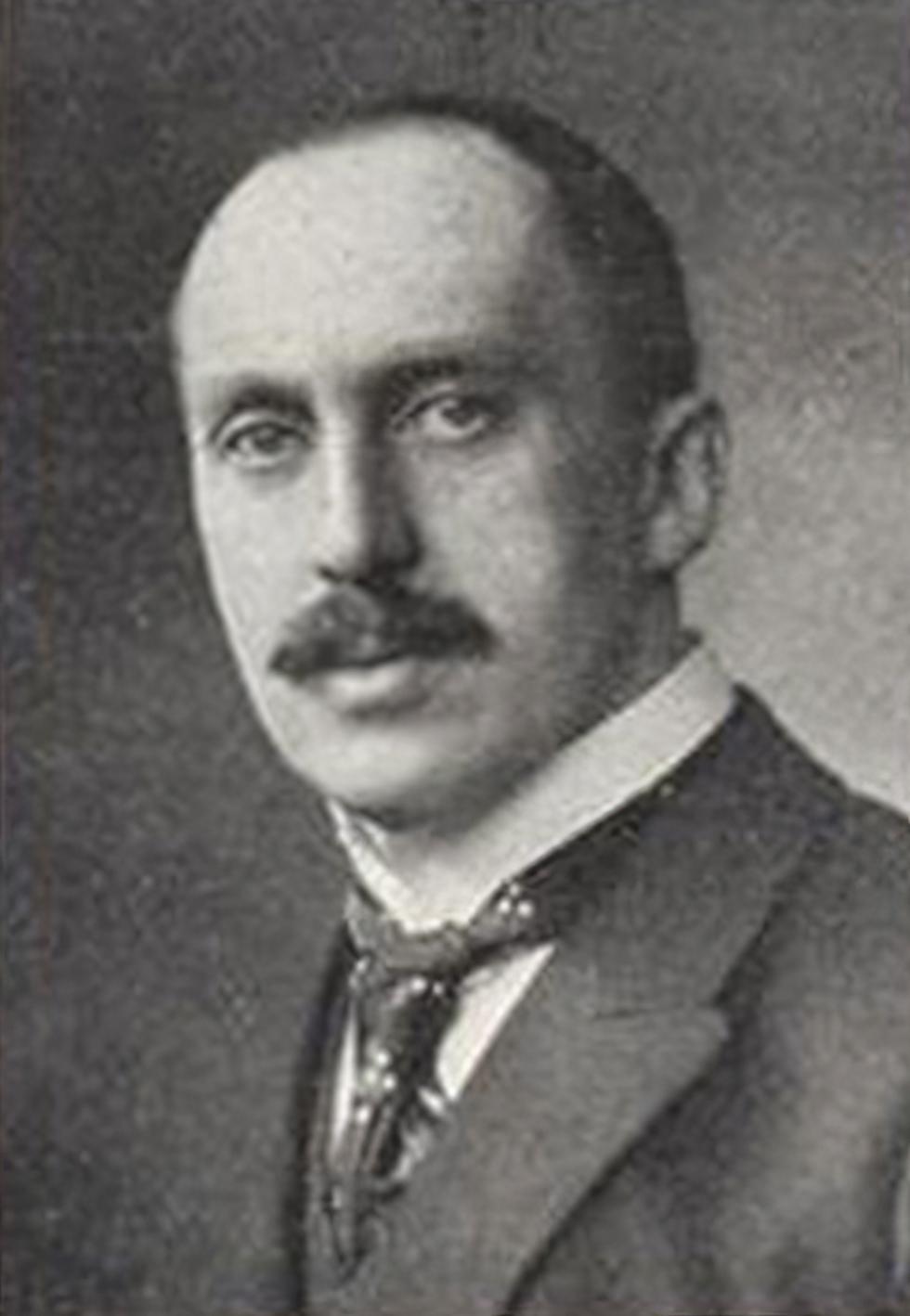


Hans Richard von Volkmann was a German illustrator and landscape painter, associated with the Düsseldorfer Malerschule.


Hans Richard von Volkmann was a German illustrator and landscape painter, associated with the Düsseldorfer Malerschule.

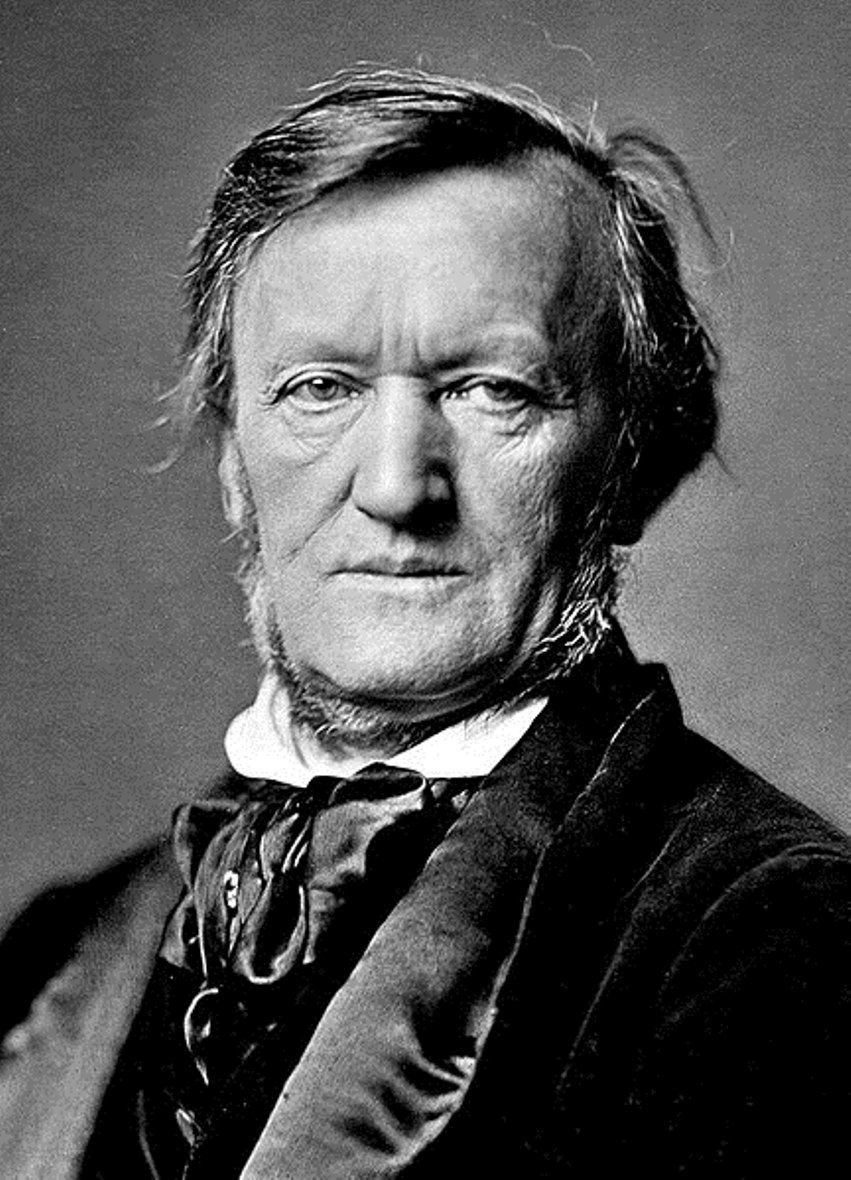
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).

























