александра i
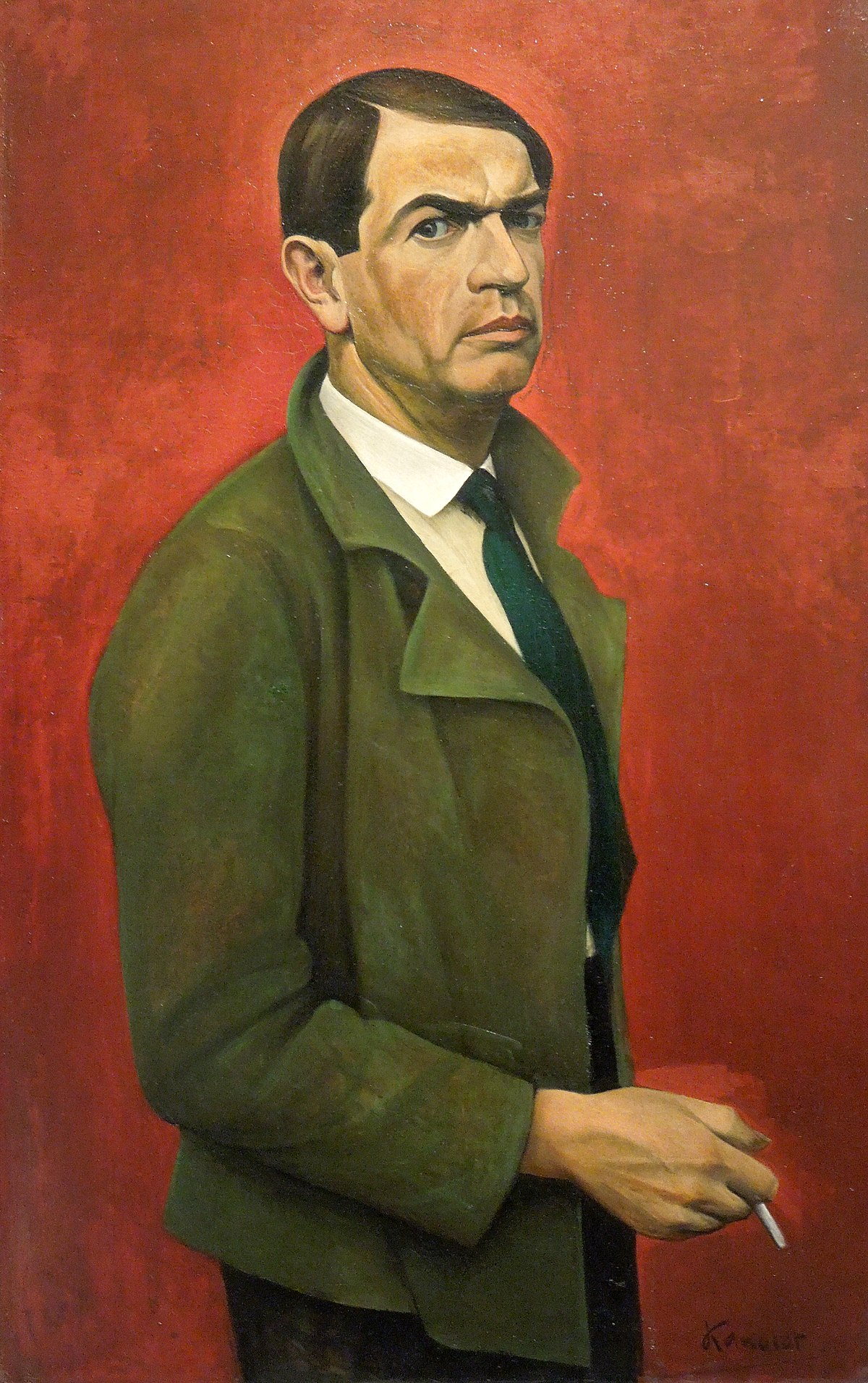








Alexander Kanoldt was a German painter of the first half of the twentieth century. He is known as a painter, landscape and portrait painter, a representative of the New Materiality movement.
Alexander Kanoldt was one of the founders of the New Munich Art Association and the Blue Rider group. His style evolved from Neo-Impressionism to magic realism, to depicting plants, objects, landscapes and people in angular forms. During the Nazi regime, he tried to adapt to the styles in demand, but many of his works were confiscated as belonging to "degenerate art."
Kanoldt was a professor at the Berlin Academy of Art and director of the State School of Art in Berlin until his retirement in 1936.


Alexander Kanoldt was a German painter of the first half of the twentieth century. He is known as a painter, landscape and portrait painter, a representative of the New Materiality movement.
Alexander Kanoldt was one of the founders of the New Munich Art Association and the Blue Rider group. His style evolved from Neo-Impressionism to magic realism, to depicting plants, objects, landscapes and people in angular forms. During the Nazi regime, he tried to adapt to the styles in demand, but many of his works were confiscated as belonging to "degenerate art."
Kanoldt was a professor at the Berlin Academy of Art and director of the State School of Art in Berlin until his retirement in 1936.
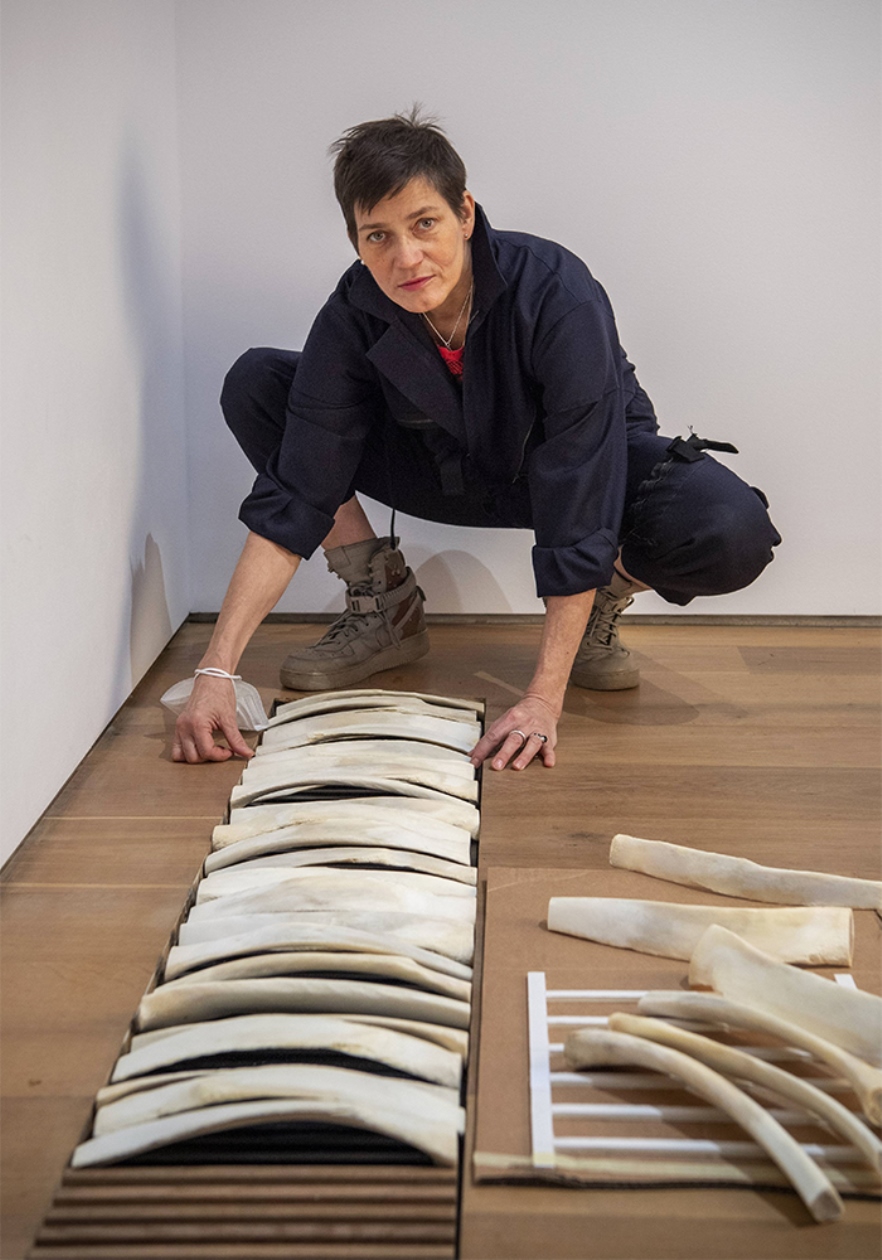


Alexandra Bircken is a German artist, designer and installer who graduated from the Central Saint Martin's College of Art and Design.
The main theme in Alexandra Birkcen's work is the shell. She explores and combines a variety of materials - wool, concrete, wood, bone, everyday objects and clothing, and creates sculptural objects from them. The artist also uses objects that she encounters in everyday life: cars, motorcycles, surgical shirts, rocking horses, skis. However, she strips them of their familiar contexts and surprises us with unusual combinations.
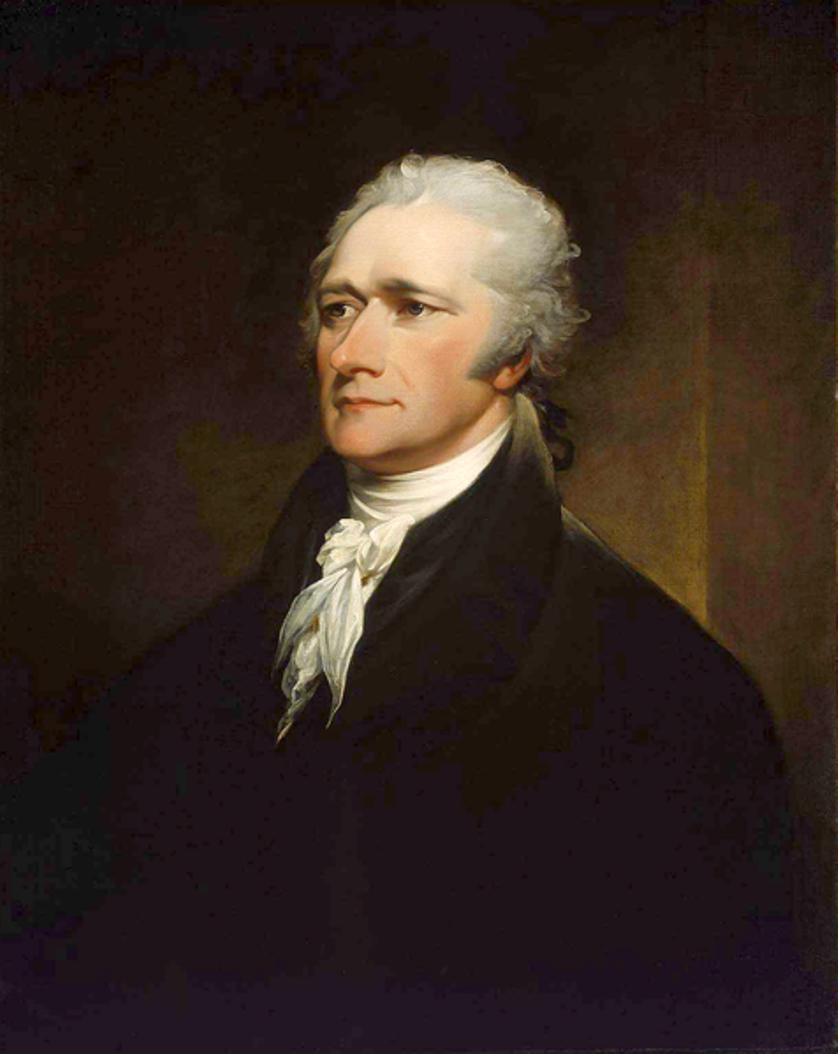






Alexander Hamilton was an American politician and statesman, the founder of the American financial system.
A native of Great Britain, Hamilton arrived in continental America in late 1772 and enrolled at King's College in New York. He became captain of an artillery company in 1776 and fought in the battles of Kips Bay, White Plains, Trenton, and Princeton during the American War of Independence. For four years he served on George Washington's staff as adjutant with the rank of lieutenant colonel. And in 1782, Hamilton was chosen by New York as a delegate to the Confederate Congress.
Alexander Hamilton was also one of New York's delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. He was a passionate advocate of the Constitution and, along with future President James Madison and John Jay, contributed to the famous book The Federalist (1788), writing most of the essays for it. After George Washington was elected the nation's first president in 1789, he appointed Hamilton Secretary of the Treasury. As the first Secretary of the Treasury (1789-1795), Hamilton developed plans to finance the national debt, secure federal credit, encourage the expansion of manufacturing, and organize a federal bank. In 1801, Hamilton founded the New York Evening Post newspaper.
On July 11, 1804, Hamilton was mortally wounded in a duel with his personal and political rival, Vice President Aaron Burr. Today, Alexander Hamilton is revered as one of the founding fathers of the United States, he is known for his role in creating America's financial system, and his portrait is on the ten dollar bill.
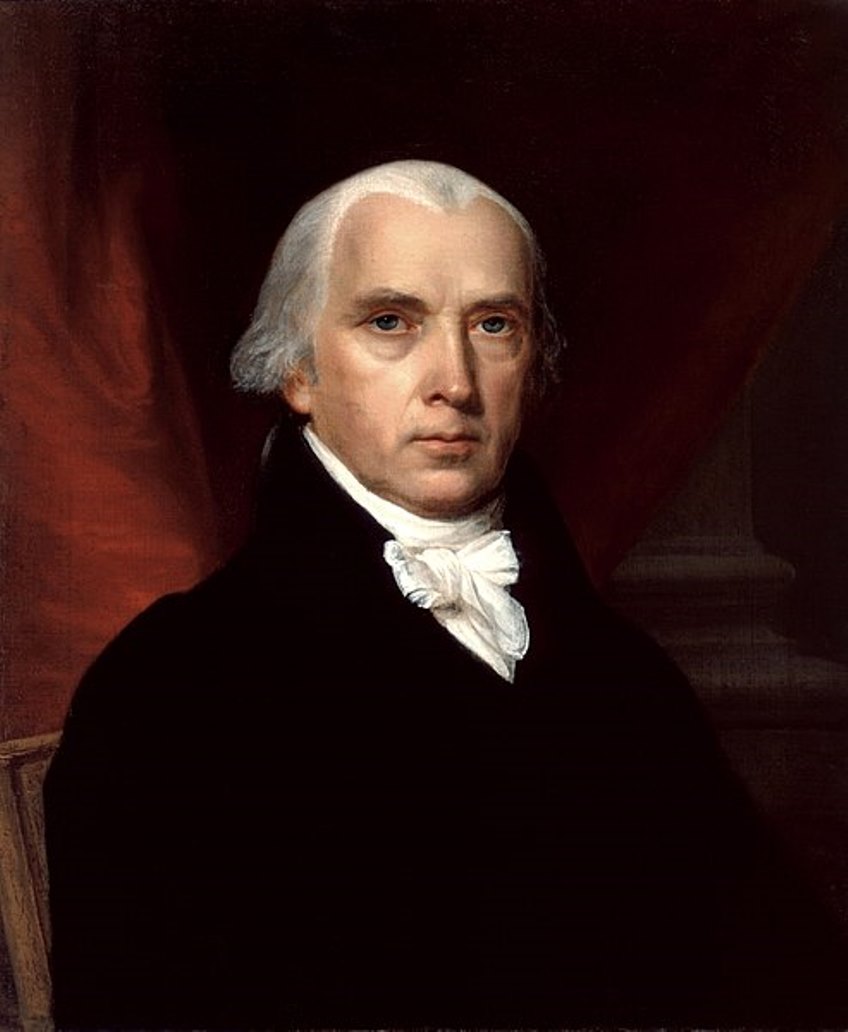






James Madison was an American politician and statesman, the fourth President of the United States (1809-1817).
Madison attended Princeton and studied history, government, and law. He participated in the drafting of the Virginia Constitution in 1776, and in 1780 was chosen to represent Virginia in the Continental Congress (1780-83 and 1786-88). James Madison contributed greatly to the ratification of the Constitution, writing, with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay, The Federalist (1788). He was later called the "father of the Constitution."
In 1792, Madison and Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) founded the Democratic-Republican Party, which has been called America's first opposition political party. When Jefferson became the third president of the United States, Madison served as his secretary of state. In Congress, he was involved in drafting the Bill of Rights and passing the first revenue legislation. As Secretary of State to President Jefferson (1801-1809), Madison protested to warring France and Great Britain that their seizure of American ships was contrary to international law.
Madison was elected president in 1808, succeeding Jefferson. Continued British interference in shipping, as well as other grievances, led to the War of 1812. During Madison's second term as president, the war was still ongoing, and he and his wife were even forced to flee in the face of advancing British troops who set Washington, D.C. on fire. Despite this, in 1815, the United States declared its victory in the war.
After the end of his second term, Madison remained active in public affairs. He edited his Journal of the Constitutional Convention, was co-chairman of the Virginia Constitutional Convention from 1829-1830, and chancellor of the University of Virginia from 1826-36. He was also Monroe's foreign policy advisor. Although Madison was a slave owner all his life, in the last years of his life he was active in the American Colonization Society, whose mission was to resettle slaves in Africa. James Madison died at the age of 85 in 1836.

Alexander Hamilton was an American politician and statesman, the founder of the American financial system.
A native of Great Britain, Hamilton arrived in continental America in late 1772 and enrolled at King's College in New York. He became captain of an artillery company in 1776 and fought in the battles of Kips Bay, White Plains, Trenton, and Princeton during the American War of Independence. For four years he served on George Washington's staff as adjutant with the rank of lieutenant colonel. And in 1782, Hamilton was chosen by New York as a delegate to the Confederate Congress.
Alexander Hamilton was also one of New York's delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. He was a passionate advocate of the Constitution and, along with future President James Madison and John Jay, contributed to the famous book The Federalist (1788), writing most of the essays for it. After George Washington was elected the nation's first president in 1789, he appointed Hamilton Secretary of the Treasury. As the first Secretary of the Treasury (1789-1795), Hamilton developed plans to finance the national debt, secure federal credit, encourage the expansion of manufacturing, and organize a federal bank. In 1801, Hamilton founded the New York Evening Post newspaper.
On July 11, 1804, Hamilton was mortally wounded in a duel with his personal and political rival, Vice President Aaron Burr. Today, Alexander Hamilton is revered as one of the founding fathers of the United States, he is known for his role in creating America's financial system, and his portrait is on the ten dollar bill.
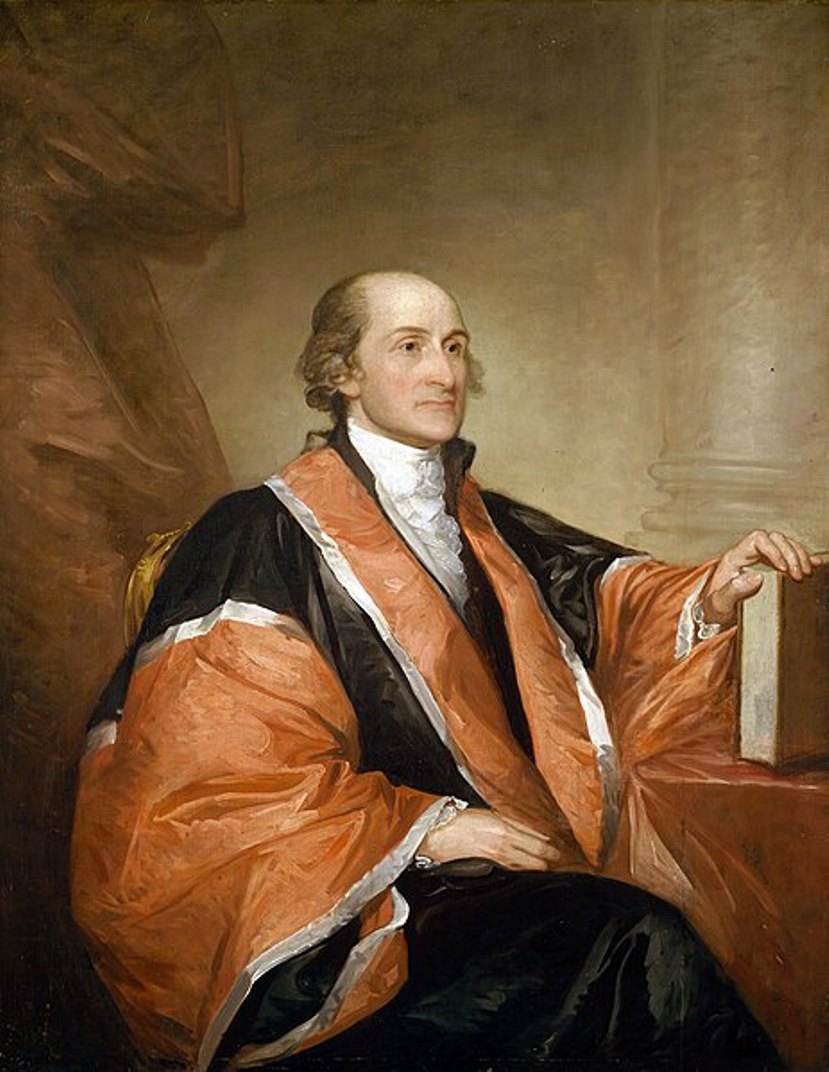

John Jay was an American lawyer and diplomat, statesman, and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Jay came from French Huguenots, after graduating from King's College (now Columbia University) he entered law school and was admitted to the bar in 1768. After the outbreak of hostilities in the spring of 1775, Jay continued to serve both in New York and in the Continental Congress, which elected him president in late 1778.
In the fall of 1779 he was appointed minister plenipotentiary to Spain, which had recently entered into an alliance with France against England. In May 1782 he traveled to Paris, where a treaty was concluded that formally ended the war with Great Britain in 1783. Before returning to America in July 1784, Jay was appointed secretary of foreign affairs.
In 1788, Jay actively advocated for the ratification of the U.S. Constitution by the state of New York. Together with future President James Madison and economist Alexander Hamilton, he participated in the creation of the famous book The Federalist (1788). Under the new Constitution, President Washington appointed John Jay Chief Justice of the United States in 1789, and in July 1795 he became Governor of New York. After completing his second term as governor in June 1801. Jay retired to his farm in Bedford, New York.


Alexander Hamilton was an American politician and statesman, the founder of the American financial system.
A native of Great Britain, Hamilton arrived in continental America in late 1772 and enrolled at King's College in New York. He became captain of an artillery company in 1776 and fought in the battles of Kips Bay, White Plains, Trenton, and Princeton during the American War of Independence. For four years he served on George Washington's staff as adjutant with the rank of lieutenant colonel. And in 1782, Hamilton was chosen by New York as a delegate to the Confederate Congress.
Alexander Hamilton was also one of New York's delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. He was a passionate advocate of the Constitution and, along with future President James Madison and John Jay, contributed to the famous book The Federalist (1788), writing most of the essays for it. After George Washington was elected the nation's first president in 1789, he appointed Hamilton Secretary of the Treasury. As the first Secretary of the Treasury (1789-1795), Hamilton developed plans to finance the national debt, secure federal credit, encourage the expansion of manufacturing, and organize a federal bank. In 1801, Hamilton founded the New York Evening Post newspaper.
On July 11, 1804, Hamilton was mortally wounded in a duel with his personal and political rival, Vice President Aaron Burr. Today, Alexander Hamilton is revered as one of the founding fathers of the United States, he is known for his role in creating America's financial system, and his portrait is on the ten dollar bill.


Alexander Vasilyevich Kuprin (Russian: Алекса́ндр Васи́льевич Купри́н) was a Russian painter and educator, renowned for his contribution to the "Jack of Diamonds" group and his profound influence on Soviet art. Born in Borisoglebsk, Voronezh region, in 1880, Kuprin's early life was steeped in the creative atmosphere provided by his family, moving to Voronezh in 1893. His educational journey through various art schools culminated at the Moscow School of Painting, Sculpture, and Architecture, where he was under the tutelage of Abram Arkhipov and Konstantin Korovin.
Kuprin's art evolved significantly over time. Initially inspired by French painting and Cézanne, his early works were marked by Cubist influences, characterized by a geometric simplification of forms. As one of the founding members of the Knave of Diamonds, he was at the forefront of avant-garde movements in Russia. However, his style underwent a transformation towards realism in the 1920s, influenced by his experiences in Nizhny Novgorod and later travels to Crimea. This period marked a departure from avant-garde to a focus on industrial landscapes and the natural beauty of the Crimean peninsula.
His significant works, often reflecting his fascination with the interplay of light, shadow, and form, are held in high esteem, with notable pieces like "Still Life With Blue Tray" and "The Beasal’skaia Valley" housed in the Tret’iakov Gallery. Kuprin's commitment to education saw him teaching at various institutions, including the Moscow textile Institute and the Moscow Higher Art and Industrial School, influencing generations of artists.
Alexander Vasilyevich Kuprin's legacy is not only in the beauty he captured on canvas but also in the minds he shaped through his teaching. His works, a testament to the evolution of Russian art through turbulent times, continue to inspire and captivate.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques can find a deeper appreciation for Kuprin's work by exploring his contributions to the Russian avant-garde and his influence on Soviet art aesthetics. For those interested in staying updated on sales and auction events related to Alexander Vasilyevich Kuprin, signing up for updates is highly recommended. This subscription will provide exclusive insights into the availability of his works, ensuring enthusiasts don't miss the opportunity to own a piece of Russian art history.
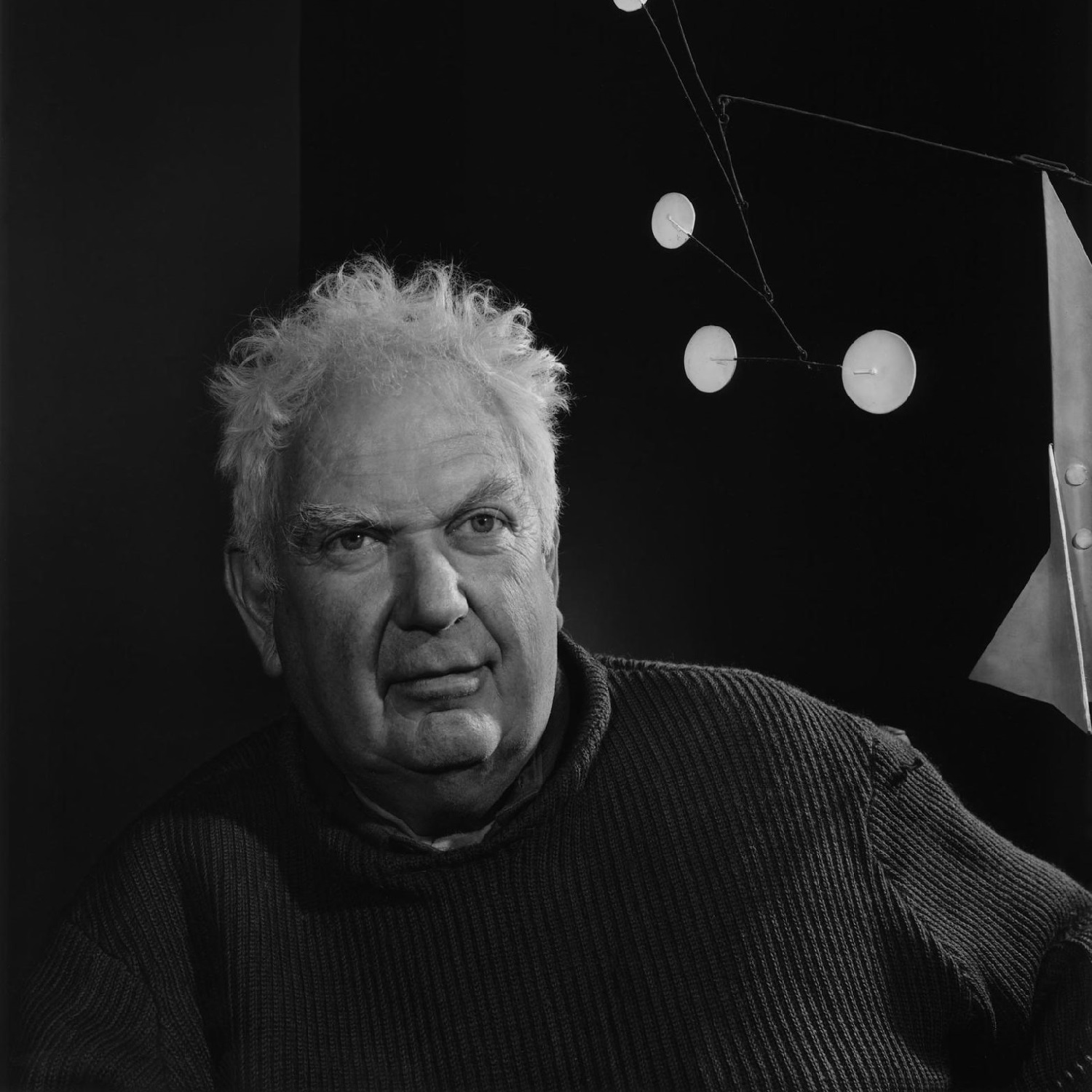


Alexander Calder was an American artist celebrated for his revolutionary contributions to modern sculpture, including his invention of the mobile. Born into a family of artists on July 22, 1898, in Lawnton, Pennsylvania, and passing away on November 11, 1976, in New York, Calder harnessed his background in mechanical engineering to create kinetic sculptures that moved with air currents, alongside his monumental stationary sculptures known as "stabiles".
Calder's early life was marked by his creation of toys and various objects, showcasing his inherent talent and creativity from a young age. Despite initially pursuing a career in mechanical engineering, Calder's true calling in the arts was undeniable. He moved to New York City, where he enrolled at the Art Students League, laying the groundwork for his iconic artistic style. In 1926, Calder relocated to Paris, which became a pivotal moment in his career, leading to the creation of "Calder's Circus," a whimsical assembly of wire figures that gained him entry into the avant-garde art circles of Europe.
Throughout the 1930s and beyond, Calder's work evolved from figurative painting to abstract sculptures that brought motion into the realm of art, a transition influenced by his visit to Piet Mondrian's studio. His innovative mobiles and stabiles were celebrated for their ingenuity and aesthetic appeal, earning Calder international recognition and numerous accolades. Among his well-known public commissions are the .125 mobile for John F. Kennedy Airport and the monumental red-painted steel stabile, "Flamingo," for the Federal Center Plaza in Chicago.
Calder's legacy extends far beyond his sculptures; his work encompassed painting, printmaking, jewelry design, and even set and costume design for theatre productions. His influence on modern art is profound, inspiring future generations of artists to explore the kinetic possibilities of sculpture.
For art enthusiasts and collectors interested in Alexander Calder's groundbreaking work, staying informed about upcoming sales and auctions is essential. Sign up for updates to never miss an opportunity to own a piece by this influential American sculptor, highlighting his unique contributions to the art world.
























![[Введенский, А.И. Избранное]. Vvedenskij, A.I. Izbrannoe / A.I. Vvedenskij; Herausgegeben und eingeleitet von Wolfgang Kasack.](/assets/image/picture_4222130/24a66/uie08a0ernnknemxx9wfjicvg0s-7i8tcqwqr3q0ks9iv285wp8uw-3c79pf-t3s1727387160jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Введенский, А.И. Избранное]. Vvedenskij, A.I. Izbrannoe / A.I. Vvedenskij; Herausgegeben und eingeleitet von Wolfgang Kasack.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4222130/24a66/uie08a0ernnknemxx9wfjicvg0s-7i8tcqwqr3q0ks9iv285wp8uw-3c79pf-t3s1727387160jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Экз. из биб-ки Феликса Юсупова]. Гейрот, А.Ф. Описание Петергофа. [1501—1868]: I. Исторический очерк Петергофа. II. Путеводитель по Петергофу / А. Гейрот.](/assets/image/picture_2303596/10604/efbctbqmtsosohjjuzt5hobwwywhrwhxr8n4riunbxpcboecur9aza1ks2xzcmvq1659663050jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Экз. из биб-ки Феликса Юсупова]. Гейрот, А.Ф. Описание Петергофа. [1501—1868]: I. Исторический очерк Петергофа. II. Путеводитель по Петергофу / А. Гейрот.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2303596/10604/efbctbqmtsosohjjuzt5hobwwywhrwhxr8n4riunbxpcboecur9aza1ks2xzcmvq1659663050jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)




































