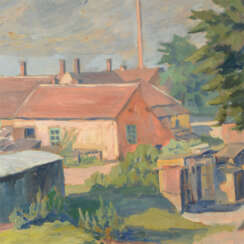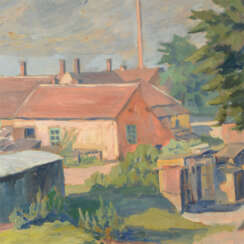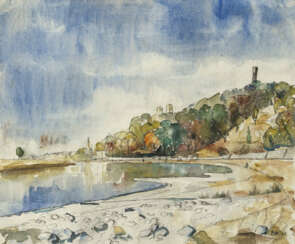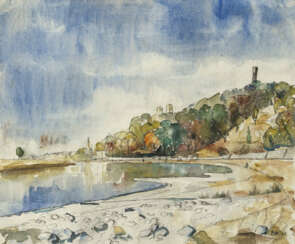бернхард кречмар (1889 - 1972)

Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
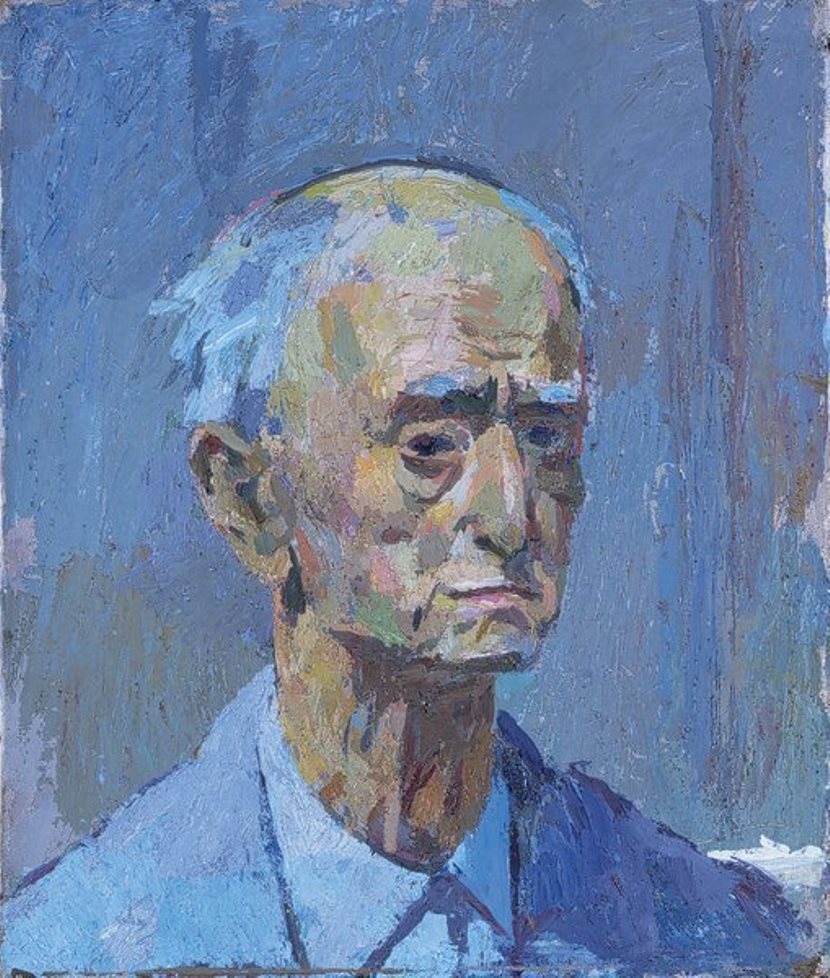
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.


Bernhard Kretzschmar was a German painter and graphic artist.
Kretzschmar studied at the Dresden Academy, in 1920 destroyed most of his work and began his career anew. In 1932 he co-founded the Dresden Secession, but later the Social Democrats banned him as a degenerate artist, and his paintings were removed from museums and galleries. Kretzschmar hated the Nazis and had to flee the country.
Like many artists of his generation, he dabbled in Expressionism, then switched to Verismo. He skillfully tried his hand at both Futurism and Impressionism. He painted on the themes of social poverty, as well as comically depicting the bourgeois way of life. In 1945, most of his works were destroyed in an air raid.
After World War II, social motifs receded into the background and Kretzschmar focused more on landscapes, more often in the suburban areas of Dresden. He also painted several self-portraits with somber, skeptical and ironic facial expressions during his lifetime, which provide a vivid characterization of the artist.
From 1946, Bernhard Kretzschmar worked as a professor at the University of Fine Arts in Dresden. In 1959 he received the National Prize of the GDR, and since 1969 he has been a corresponding member of the German Academy of Arts in East Berlin.