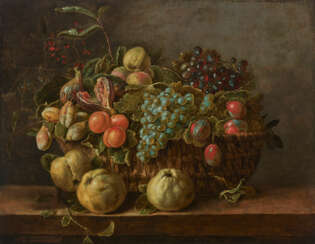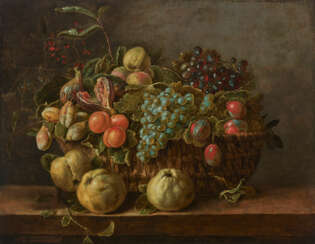belgium, antwerps

Jan Gossaert was a French-speaking painter from the Low Countries also known as Jan Mabuse (the name he adopted from his birthplace, Maubeuge) or Jennyn van Hennegouwe (Hainaut), as he called himself when he matriculated in the Guild of Saint Luke, at Antwerp, in 1503. He was one of the first painters of Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting to visit Italy and Rome, which he did in 1508–09, and a leader of the style known as Romanism, which brought elements of Italian Renaissance painting to the north, sometimes with a rather awkward effect. He achieved fame across at least northern Europe, and painted religious subjects, including large altarpieces, but also portraits and mythological subjects, including some nudity.


Adriaen van Utrecht was a Flemish painter known mainly for his sumptuous banquet still lifes, game and fruit still lifes, fruit garlands, market and kitchen scenes and depictions of live poultry in farmyards. His paintings, especially the hunting and game pieces, show the influence of Frans Snyders. The two artists are considered the main inventors of the genre of the pronkstillevens, i.e. still lifes that emphasized abundance by depicting a diversity of objects, fruits, flowers and dead game, often together with living people and animals. Van Utrecht also painted a number of flower still lifes. He was a regular collaborator with leading Antwerp painters who had been pupils or assistants of Peter Paul Rubens, such as Jacob Jordaens, David Teniers the Younger, Erasmus Quellinus II, Gerard Seghers, Theodoor Rombouts, Abraham van Diepenbeeck and Thomas Willeboirts Bosschaert.
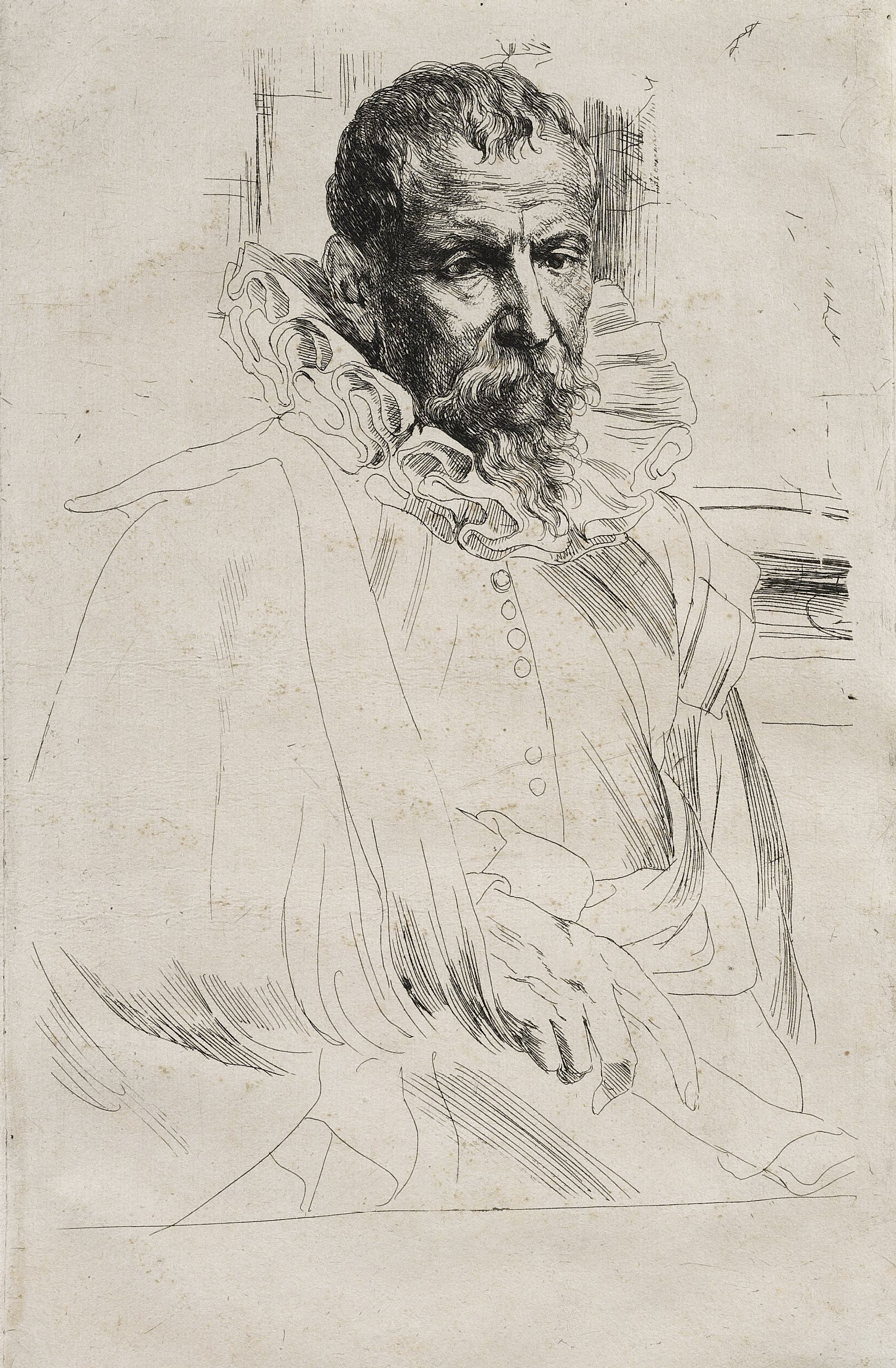


Pieter Brueghel the Younger was a Flemish artist celebrated for his detailed landscapes, religious themes, proverbs, and vibrant village scenes. Despite being the son of the illustrious Pieter Bruegel the Elder, Brueghel the Younger carved out his own niche in the art world, earning the moniker 'Hell Brueghel' for his dynamic scenes of fires and energetic copies of his father's peasant life portrayals.
Brueghel the Younger's original creations, such as "The Village Lawyer," showcase his keen observation of village life, merging the energy and boldness of 17th-century style with his father's idiom. His work is characterized by its lively, picturesque depiction of peasants, albeit some critics argue they lack the subtlety and humanism of his father's creations. Despite this, Brueghel the Younger's legacy includes a significant number of original works and copies that were rediscovered in the 20th century, highlighting his contribution to the Flemish painting tradition.
His workshop was known for its prolific output, especially in producing copies of Bruegel the Elder's compositions, a testament to the enduring popularity and influence of the Bruegel family's artistic legacy. However, Brueghel the Younger also impressed with his unique compositions, contributing to the genre of still life and village scenes with a distinct style that resonated well into modern times.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Pieter Brueghel the Younger's works represent an important period in Flemish art, offering insights into the evolution of genre painting and the detailed portrayal of rural life. His paintings, held in esteemed collections worldwide, continue to be studied and admired for their vibrancy, narrative quality, and historical value.
To explore more about Pieter Brueghel the Younger and to stay updated on sales and auction events related to his work, signing up for specialized updates can offer exclusive insights into the world of this influential Flemish painter. This subscription ensures enthusiasts and collectors are well-informed about developments related to Brueghel the Younger's oeuvre, enhancing their appreciation and understanding of his artistic legacy.
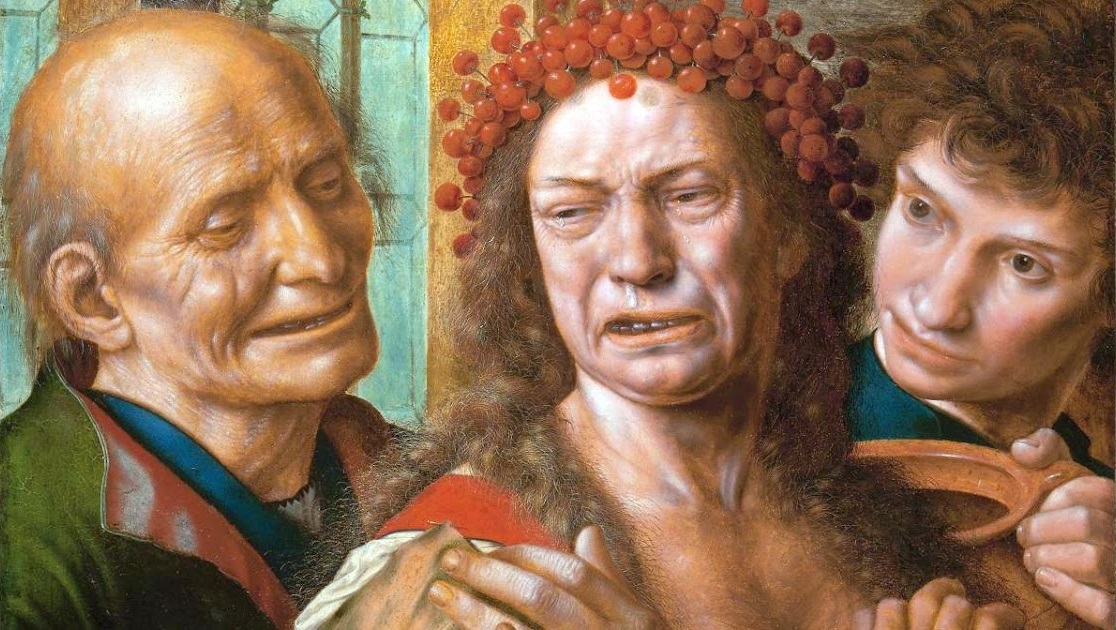


Jan van Hemessen was a leading Flemish Renaissance painter, belonging to the group of Italianizing Flemish painters called the Romanists, who were influenced by Italian Renaissance painting. Van Hemessen had visited Italy during the 1520s, and also Fontainebleau near Paris in the mid 1530s, where he was able to view the work of the colony of Italian artists known as the First School of Fontainebleau, who were working on the decorations for the Palace of Fontainebleau. Van Hemessen's works show his ability to interpret the Italian models into a new Flemish visual vocabulary.
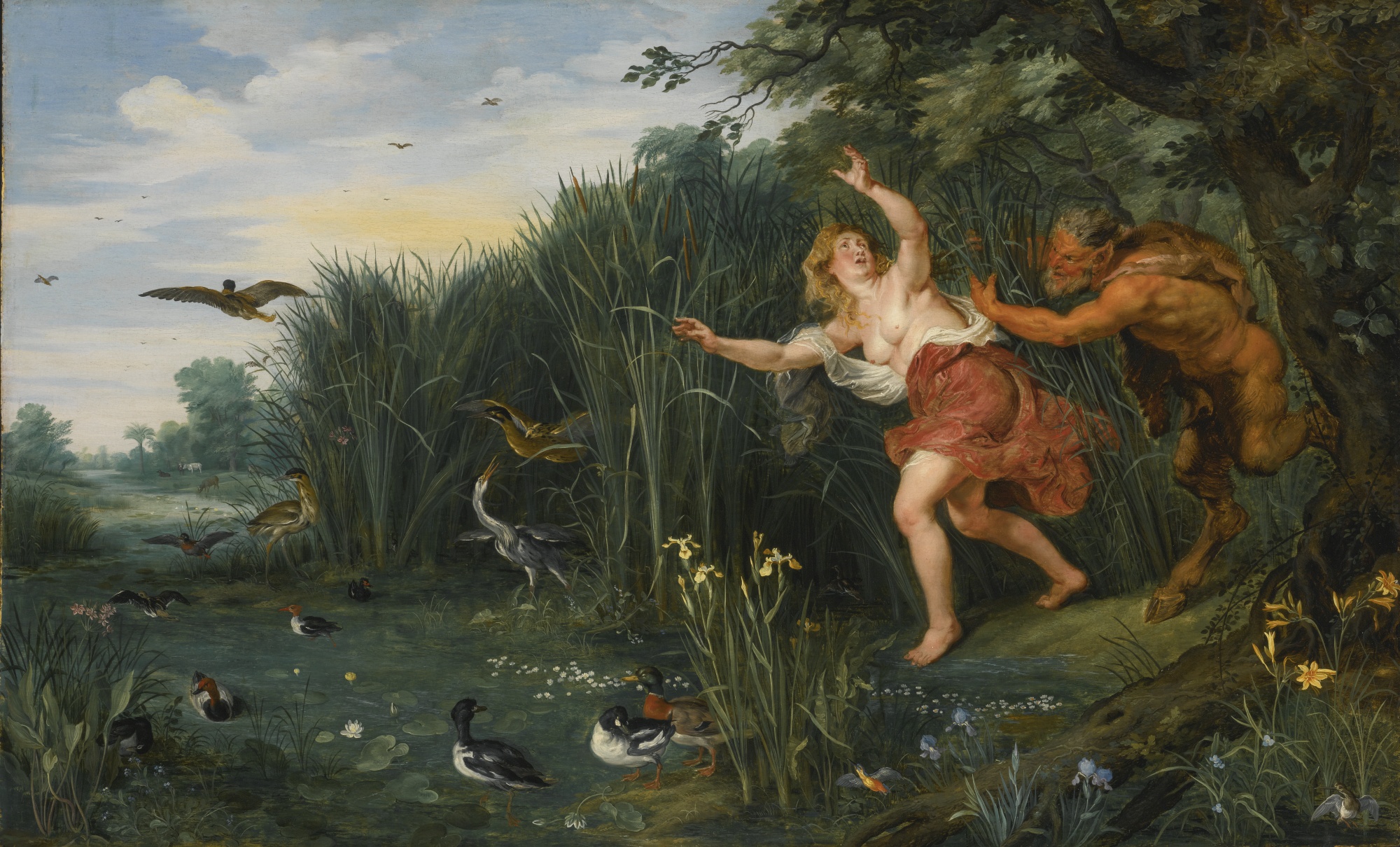


Jan Bruegel the Younger was a Flemish Baroque painter. He was the son of Jan Brueghel the Elder, and grandson of Pieter Bruegel the Elder, both prominent painters who contributed respectively to the development of Renaissance and Baroque painting in the Habsburg Netherlands. Taking over his father's workshop at an early age, he painted the same subjects as his father in a style which was similar to that of his father. He regularly collaborated with leading Flemish painters of his time.
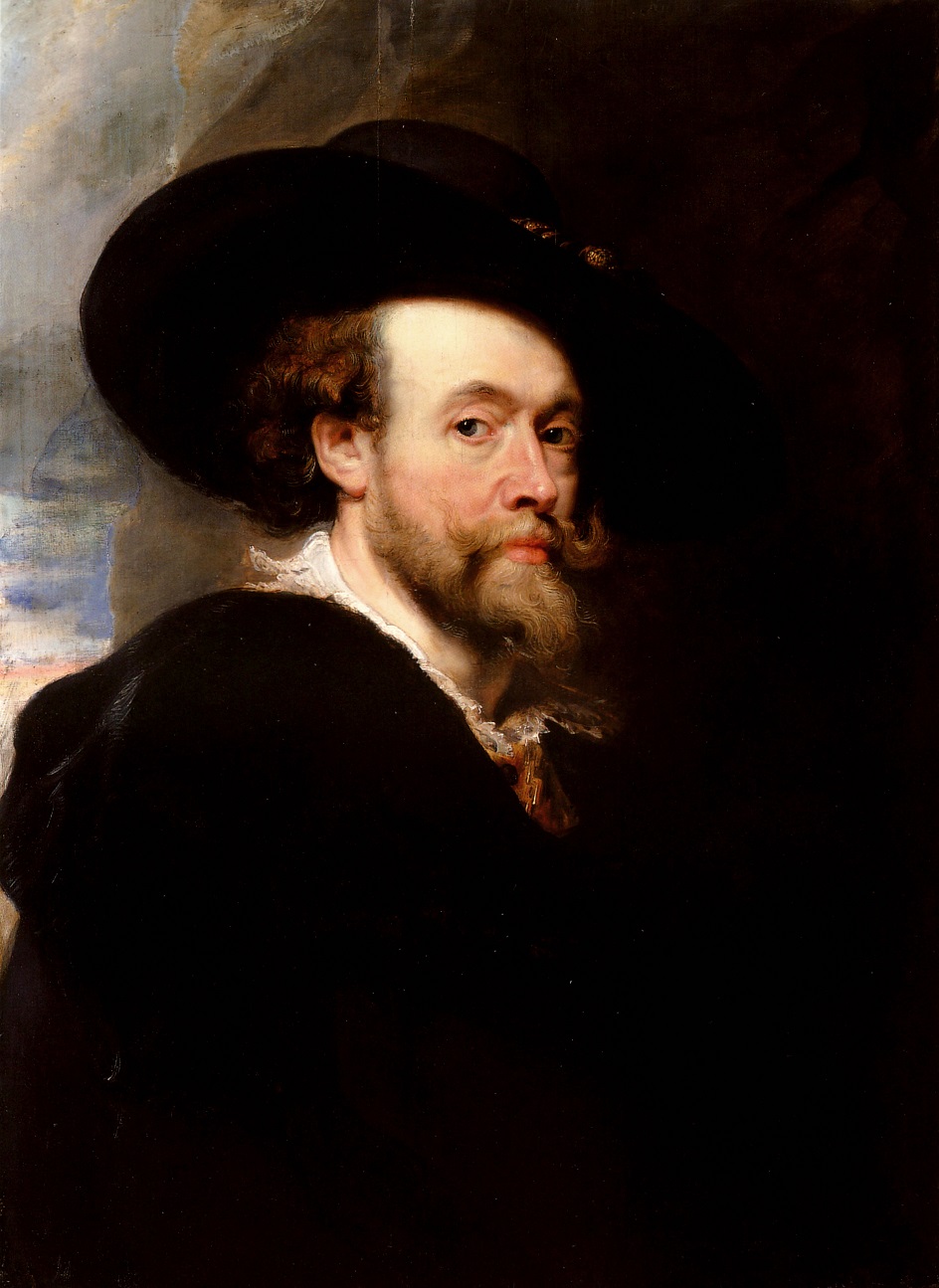


Peter Paul Rubens was a distinguished Flemish Baroque painter, renowned for his dynamic, vibrant, and sensuous paintings. Born on June 28, 1577, in Siegen, Westphalia, Germany, Rubens' family moved back to Antwerp in the Spanish Netherlands (now Belgium) after his father's death. He was raised in his mother’s Roman Catholic faith and received a classical education. He began his artistic training in 1591 and later traveled to Italy, where he was profoundly influenced by Renaissance masters like Titian, Tintoretto, and Veronese. This experience significantly shaped his artistic style.
Rubens' art is celebrated for its emphasis on movement, color, and sensuality. He was particularly skilled in depicting religious and mythological scenes, portraits, and landscapes. Some of his notable works include "The Descent from the Cross" and "The Raising of the Cross," which are prime examples of Baroque religious art, showcasing his unique style that blended influences from Italian Renaissance and his own innovations.
Rubens was not just a painter but also a diplomat, serving at various European courts. He was knighted by both Philip IV of Spain and Charles I of England. His diplomatic missions often intertwined with his artistic endeavors, as seen during his travels to Spain and Italy. In addition to painting, he was involved in designing tapestries, prints, and book title-pages. He ran a large workshop in Antwerp, producing works that were popular with nobility and art collectors across Europe. His studio was in his home, the Rubenshuis, now a museum.
His influence extended to his students, notably Anthony van Dyck, and his collaborative works with other artists like Jan Brueghel the Elder. Rubens' work continued to be celebrated for its vitality and influence on the Baroque style, making him one of the most influential artists of his time.
For those interested in the work and life of Peter Paul Rubens, many of his works can be found in museums and galleries worldwide, including the National Gallery in London, which houses several of his paintings like "A View of Het Steen in the Early Morning" and "Minerva protects Pax from Mars ('Peace and War')".
To stay updated on new product sales, auction events, and more related to Peter Paul Rubens, sign up for our updates. We provide essential information tailored for collectors and experts in art and antiques, focusing on the magnificent work of Rubens and his enduring legacy in the world of art.
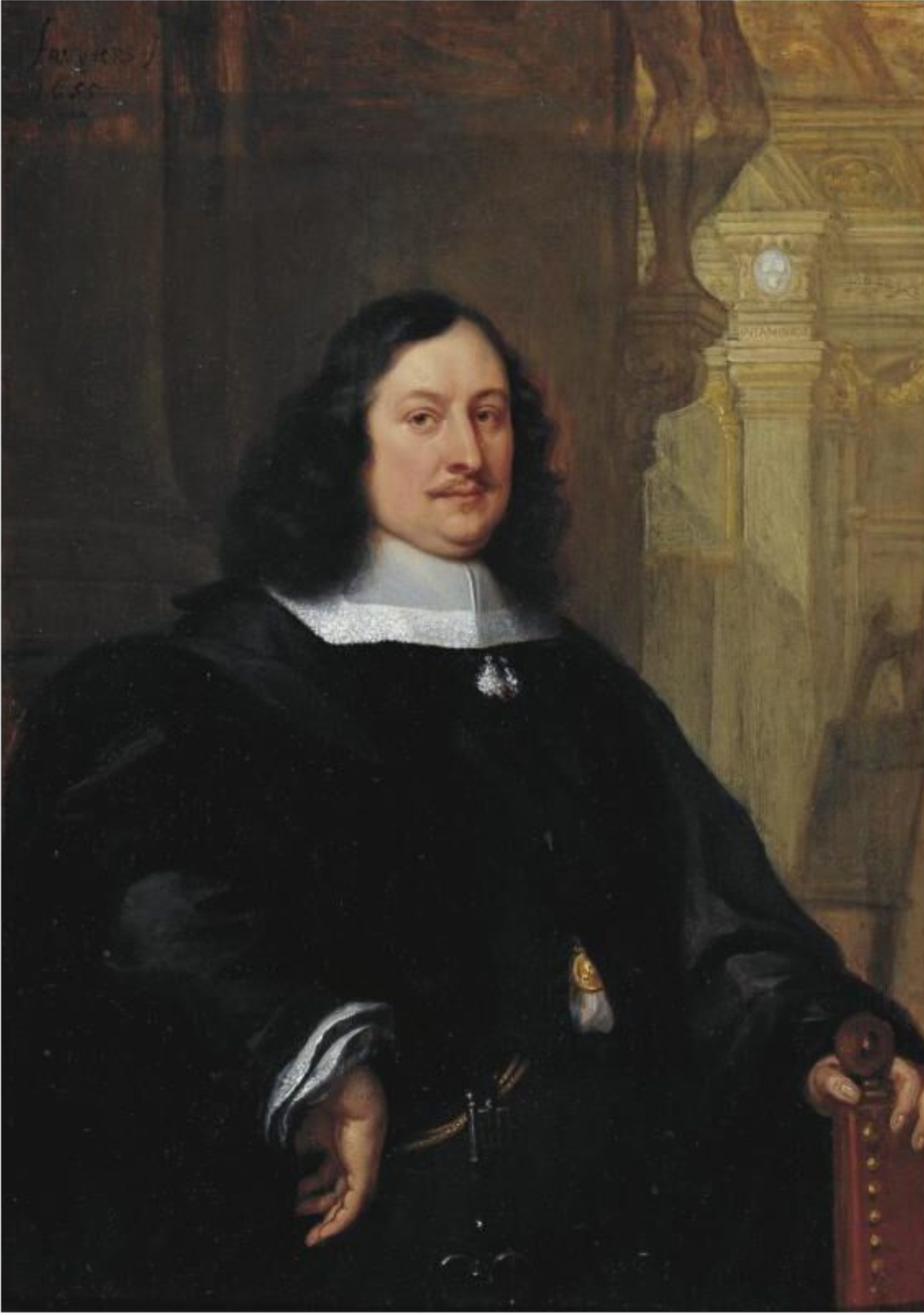


David Teniers the Younger was a Flemish Baroque painter, printmaker, draughtsman, miniaturist painter, staffage painter, copyist and art curator. He was an extremely versatile artist known for his prolific output. He was an innovator in a wide range of genres such as history painting, genre painting, landscape painting, portrait and still life. He is now best remembered as the leading Flemish genre painter of his day. Teniers is particularly known for developing the peasant genre, the tavern scene, pictures of collections and scenes with alchemists and physicians.
He was court painter and the curator of the collection of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm, the art-loving Governor General of the Habsburg Netherlands. He created a printed catalogue of the collections of the Archduke. He was the founder of the Antwerp Academy, where young artists were trained to draw and sculpt in the hope of reviving Flemish art after its decline following the death of the leading Flemish artists Rubens and Anthony van Dyck in the early 1640s. He influenced the next generation of Northern genre painters as well as French Rococo painters such as Antoine Watteau.