biblical story
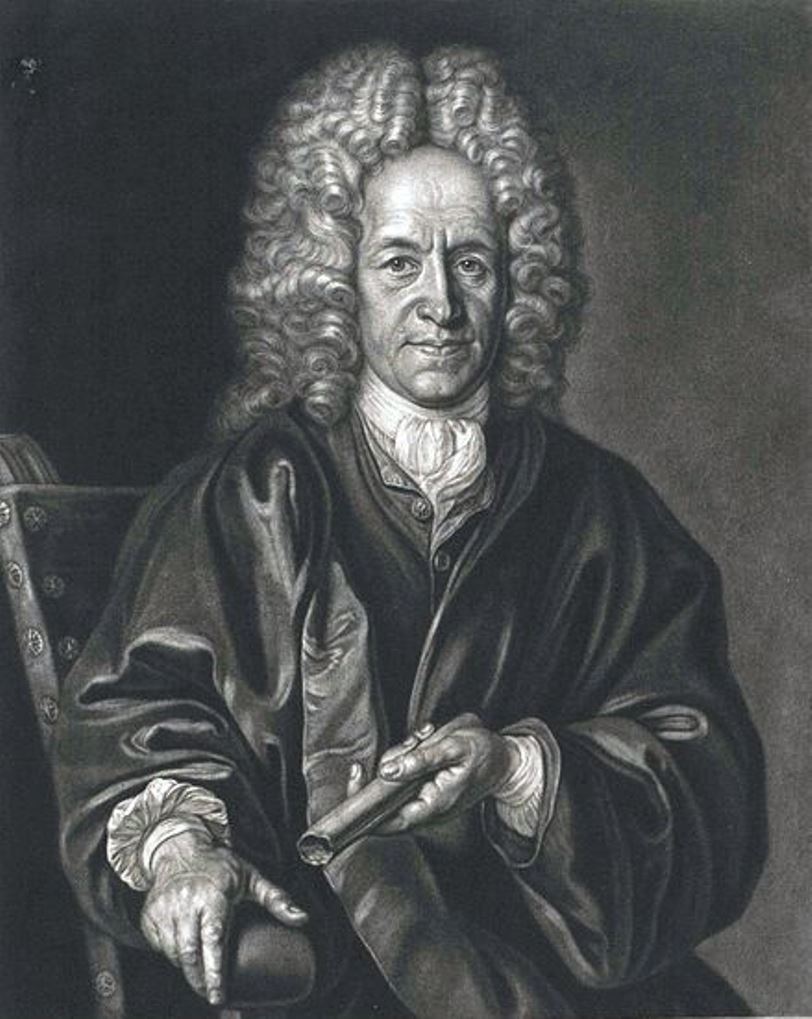

Christoph Weigel the Elder, full name Johann Christoph Weigel, was a German painter, engraver and publisher.
Weigel worked very successfully in the mezzotint technique. He was the first engraver to use a kind of machine for making backgrounds. He established his own printing house in Nuremberg in 1698, and worked closely with the imperial geographer and cartographer Johann Baptist Homann (1664-1724) to produce his maps. His younger brother Johann Christoph Weigel kept an art trade store in Nuremberg around the same time, and also quite successfully.
One of Weigel's most important works is the Ständebuch (Book of Classes) of 1698, which describes and illustrates with engravings more than two hundred trades and services, including mining.
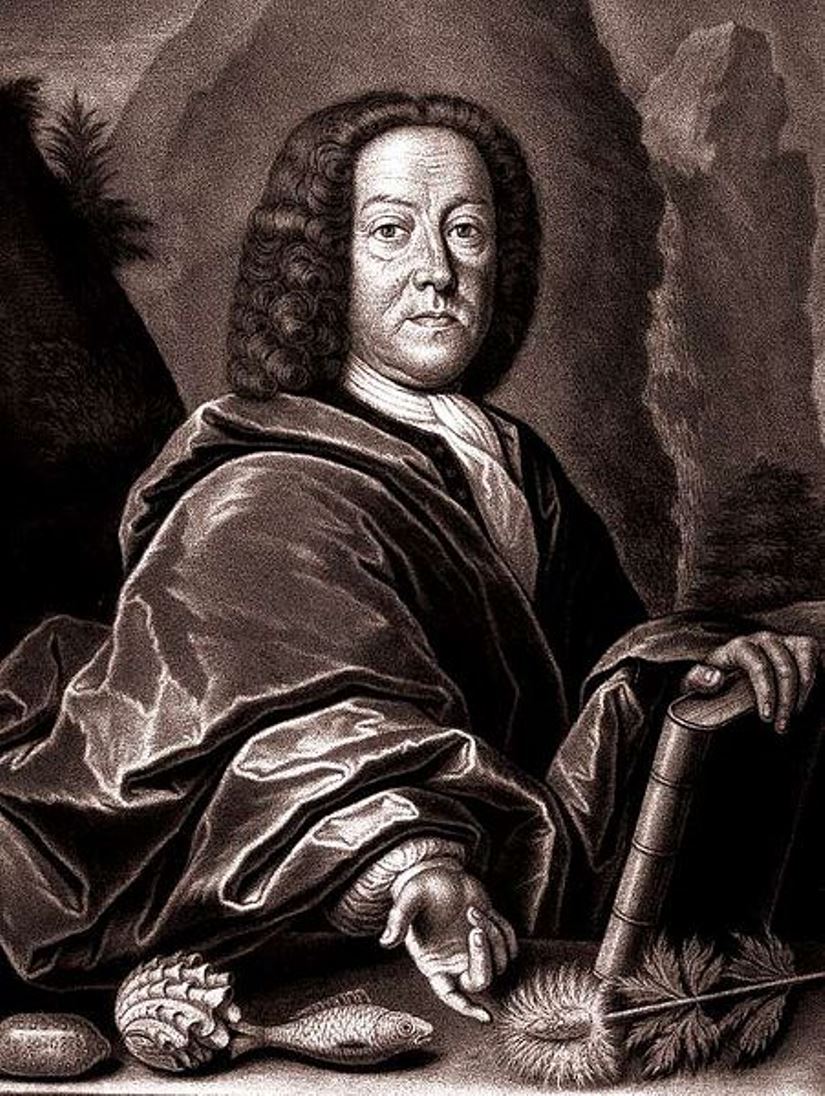


Johann Jakob Scheuchzer was a Swiss naturalist and geologist, paleontologist and fossil collector.
Scheuchzer studied at the University of Altdorf near Nuremberg, earned a doctorate in medicine at Utrecht University, and studied astronomy. He worked as a teacher, physician, and corresponded extensively with many scientists, writing several papers, including those on Swiss research, weather, geology, and fossils. Scheuchzer collected fossils during his extensive travels. And, as a proponent of diluvialism, he believed that all fossils and layers of the earth were formed by the Flood.
Between 1731 and 1735, Scheuchzer published a massive four-volume work called Physica Sacra, which is essentially a commentary on the Bible. It presented the facts of natural history along with passages of scripture. Thus Physcia Sacra attempted to reconcile the Bible with science.
This book is also called the "Copper Bible" because it contains over 750 magnificent color engravings on copper plates. These engravings are in themselves the pinnacle of engraving from the Baroque period. The illustrations depict scenes with biblical and scientific motifs. They were based on his own cabinet of natural history and other famous European cabinets of rare specimens. The engravings were produced by highly skilled engravers, including Georg Daniel Heumann and Johann August Corwin.
During his lifetime, Johann Jakob Scheuchzer wrote 34 scientific papers and many articles, and he was a member of the Royal Society.
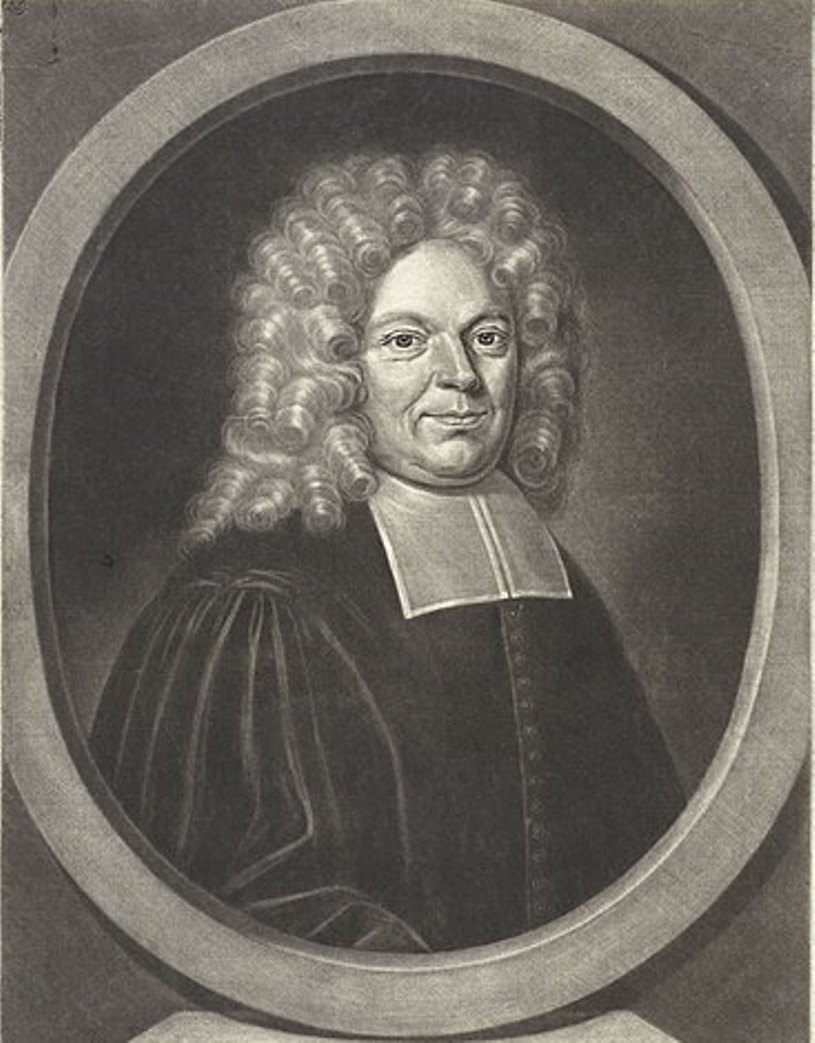


Jacques Basnage de Beauval was a French theologian and historian, diplomat and writer.
His father was a prominent lawyer and his grandfather and great-grandfather were pastors, Jacques studied theology and languages at the Academy of Saumur, then at Geneva and Sedan. In 1676, Jacques Basnage was appointed pastor at Rouen during the revocation of the Edict of Nantes, was forced to flee France for Holland, where he worked as a theologian, polemicist, historian, and diplomat in the service of the Grand Pensioner Hensius.
In 1717, on behalf of Holland, Basnage was sent to sign the treaty of the Triple Alliance (France, Holland, England). In the Annals of the United Provinces (1719-1726), compiled from the peace negotiations held at Münster, he displays breadth of vision, wisdom, and impartiality.
About 1719 Jacques Basnage was appointed historiographer of the Dutch states. He wrote several books on the Bible, the history of the Church, and the history of the Jewish people. Among the best known of these are his History of the Religion of the Protestant Denominations (1690), History of the Church of Jesus Christ to the Present Time (1699), written from Protestant positions, and History of the Jews (1706), as well as Jewish Antiquities, or Critical Notes on the Republic of the Jews (1713).
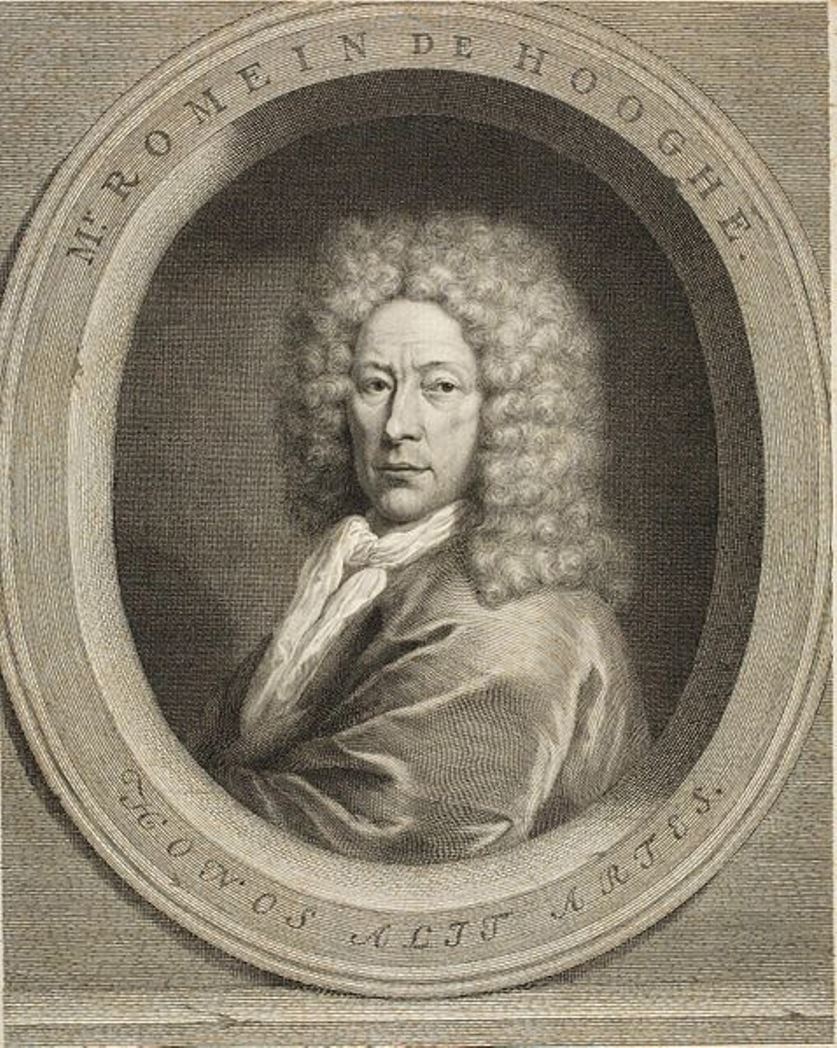

Romeyn de Hooghe was a Dutch painter, sculptor, engraver and caricaturist of the late Baroque period, writer and philosopher.
Hooghe became famous for his political caricatures of King Louis XIV of France and propaganda pamphlets in support of William of Orange. He portrayed the war against the French monarch and his allies as a struggle between freedom and religious despotism.
Romeyn de Hooghe was a superb engraver and created over 3,500 engravings during his lifetime. His most important work is Hieroglyphica of Merkbeelden der oude volkeren (Hieroglyphics or Symbols of the Ancient Peoples), where he appeared not only as a consummate master of engraving, but also as a historian, talented writer and philosopher. This book has long been regarded in Europe as one of the most authoritative sources on classical mythology. It contains 64 engravings illustrating all stages of the narrative of myths, ancient cults and beliefs, and the interpretation of scripture, a guide to medieval Europe.
Romeyn de Hooghe also illustrated books and painted large panels. During his lifetime he was widely recognized as a painter and sculptor not only in his own country but also in other European countries.
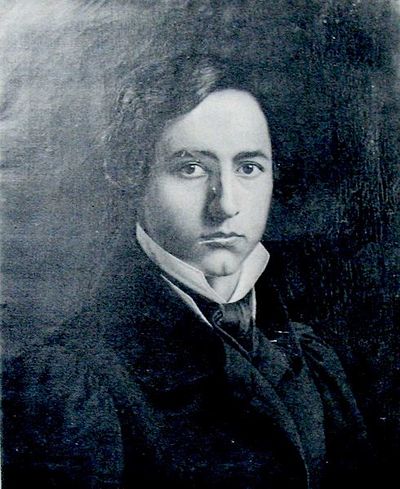


Franz Ittenbach was a German painter of the mid-nineteenth century. He is known as a historical and religious painter, associated with the Düsseldorf School of painting and considered one of the most important representatives of the Nazarenes.
Ittenbach created works mainly with religious subjects, which were characterized by simplicity of composition, nobility and correctness of drawing. Among his significant works are frescoes in various churches and altarpieces for temples. Ittenbach was a popular artist in court circles, a member of many European academies and the recipient of many medals and awards. He also painted portraits, although his main focus was on church art.
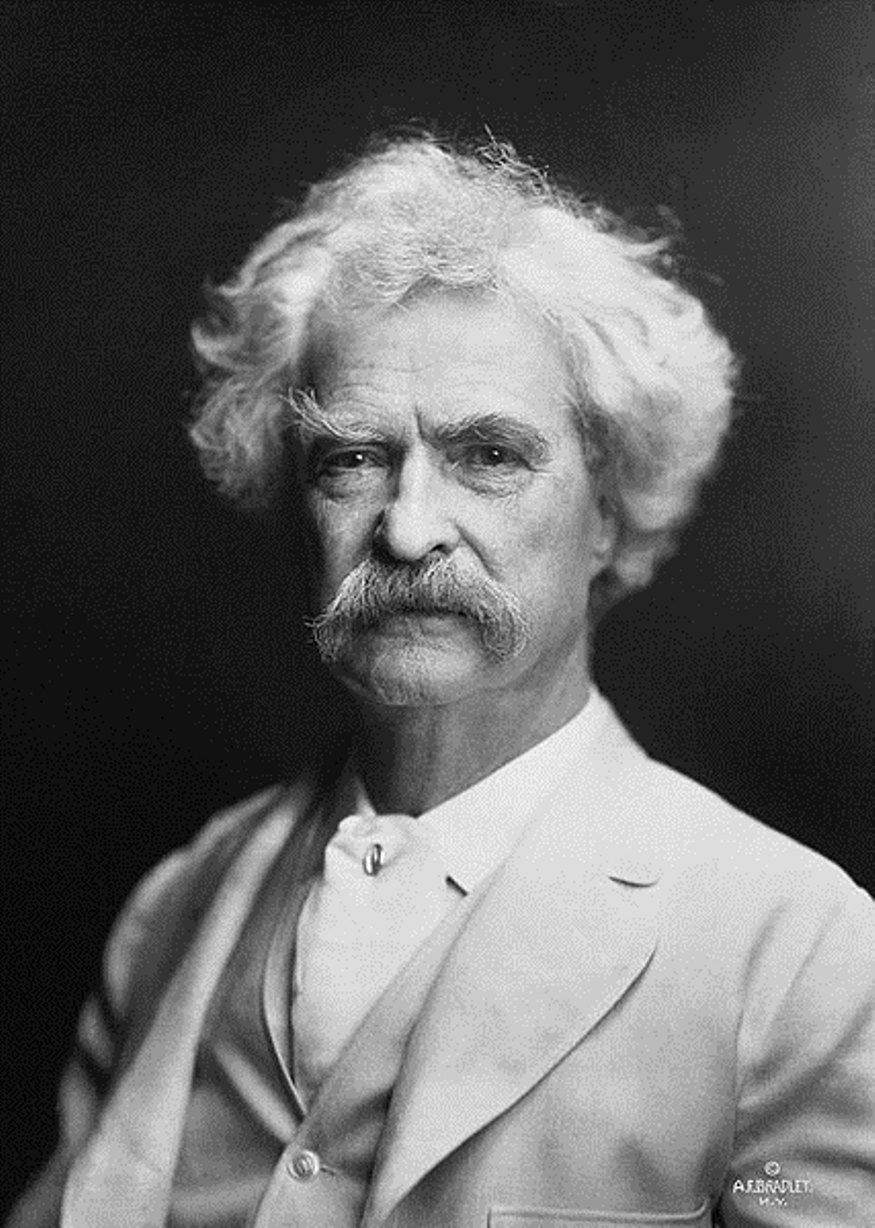
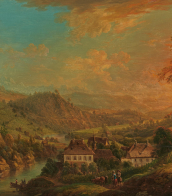

Mark Twain, real name Samuel Langhorne Clemens, was an American humanist writer, journalist, and social activist.
As a young man, Samuel worked in the printing press and in the gold mines, then went on a steamboat trip to Europe and the "Holy Land". His travel letters, full of vivid descriptions and ironic observations, were very well received by the public and were later revised into his first book, Innocents Abroad, published in 1869.
The pseudonym "Mark Twain" first appeared in 1863 under one of Samuel Clemens' short stories, and since then all his significant works have been signed by that name.
A talented storyteller, a peculiar humorist and moralist, Twain knew and loved his many diverse characters. His scandalizers and dreamers, caring aunts and ambitious politicians, grumpy widows and lying aristocrats, cunning but generous slaves, sentimental moralists, brave and naive children - all these types of American people Twain gave voice to thanks to his masterful command of colloquial language, slang and jargon. Twain wrote a lot and in a variety of genres: humor and satire, philosophical fiction and journalism and others, but he always stood on the position of humanist and democrat.
Mark Twain became world famous for his travel stories and adventure novels about his childhood, these are "The Adventures of Tom Sawyer" (1876) and "The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn" (1885). Twain is still one of America's, and indeed the world's, best and most beloved writers. His works have been and are still being published in many languages around the world.
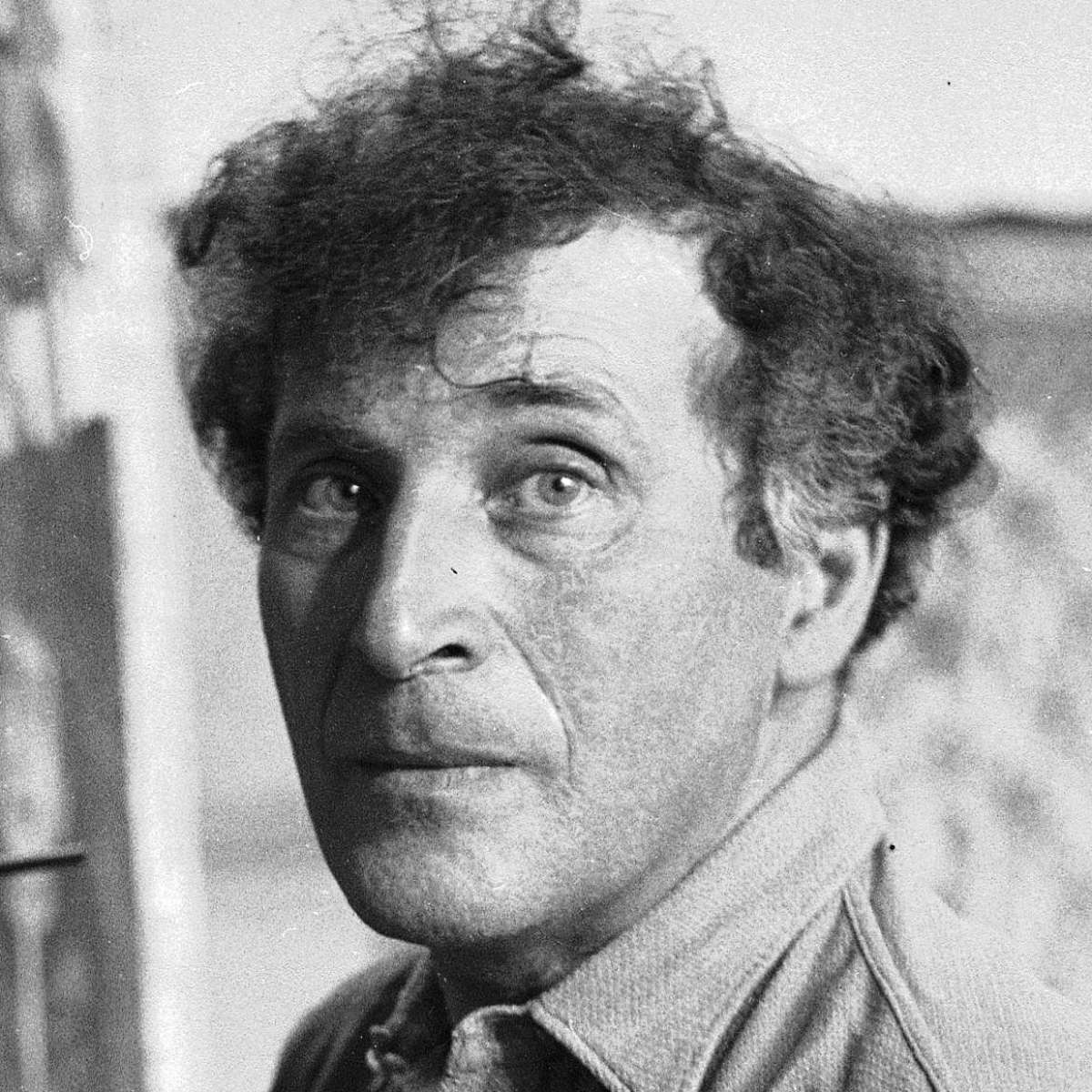


Marc Chagall (Russian: Марк Заха́рович Шага́л), born Moishe Shagal in 1887 near Vitebsk, Belarus (then part of the Russian Empire), was a Belarusian and French artist celebrated for his pivotal role in the avant-garde movement and his unique integration of Eastern European Jewish culture into modern art. His contributions spanned several artistic formats including painting, stained glass, stage sets, ceramics, tapestries, and fine art prints. Chagall's early modernist tendencies were enriched by his experiences across Saint Petersburg, Paris, and Berlin before World War I, leading to a distinctive style that melded Cubism, Symbolism, and Fauvism with his Jewish heritage.
Chagall's work is recognized for its emotional depth, often exploring themes of love, memory, and Jewish folklore through vibrant colors and dreamlike imagery. Notably, art critic Robert Hughes described him as "the quintessential Jewish artist of the twentieth century," a sentiment echoed by art historian Michael J. Lewis who regarded Chagall as a significant figure within European modernism and as the world's preeminent Jewish artist of his time.
Among Chagall's famed contributions are his stained-glass windows for the cathedrals of Reims and Metz, the UN, and the Jerusalem Windows in Israel. His monumental paintings include parts of the ceiling of the Paris Opéra and works that explore biblical themes, a hallmark of his oeuvre that underscores his enduring engagement with spiritual and religious motifs.
For art collectors and antiques experts, Chagall's works are notable not only for their artistic innovation but also for their rich cultural and historical significance. His art is housed in many prestigious museums worldwide, including the Marc Chagall National Museum in Nice, France, which focuses on his works inspired by religion and houses the series of paintings illustrating the biblical message.
For those interested in exploring Chagall's legacy and the vibrant intersection of culture, art, and history his work represents, signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Marc Chagall can provide invaluable insights and opportunities. This is an invitation to engage more deeply with the world of art and culture that Chagall so uniquely encapsulated in his work.
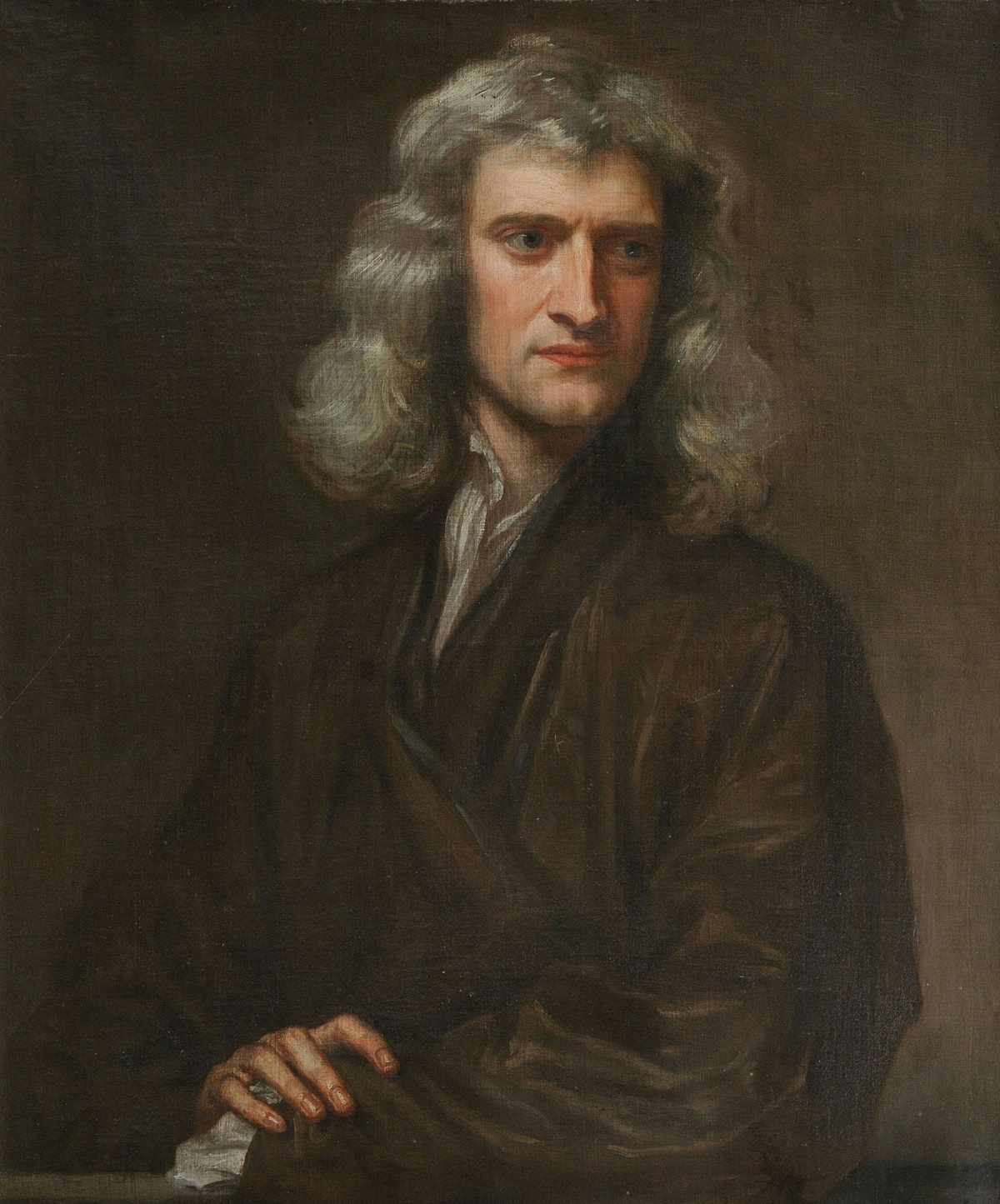


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.
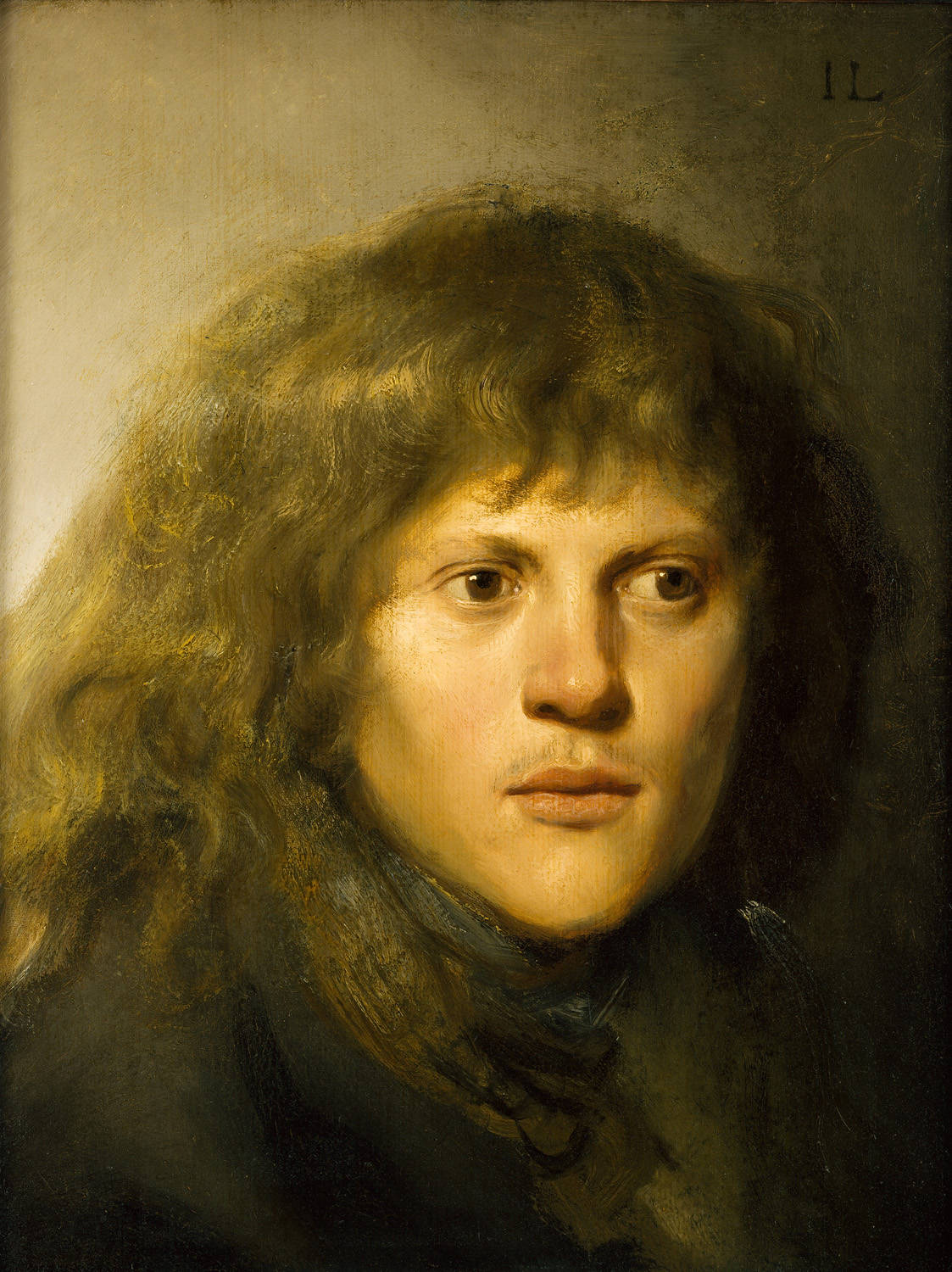


Jan Lievens was a Dutch painter, draughtsman, and engraver of the Golden Age and a member of the Guild of St. Luke in Antwerp.
It is known that while still very young, at the age of twelve, Lievens already created skillful paintings that amazed art lovers of Leiden. He was later friendly with Rembrandt, shared a studio with him, and painted in a similar style. Lievens was also a court painter in England and elsewhere.
Jan Leavens created genre scenes, landscapes, ceremonial portraits and sketches on various themes, as well as religious and allegorical images, which were already highly valued during his lifetime.


Hendrik van Cleve III was a Flemish painter, draughtsman and designer of prints. He is known for topographical views, including views of Rome and the Vatican, as well as imaginary landscapes. Traditionally, a large number of depictions of the construction of the Tower of Babel have been attributed to him but most of these are now attributed to anonymous Flemish painters, who are referred to as 'The Hendrik van Cleve III Group'.


Werner Rolewinck (Latin: Wernerus Rolewinkius) was a German chronicler, historian, and theologian.
Werner Rolewinck was a Cartesian monk. His best known and most important work is Fasciculus temporum, a history from the creation of the world to Pope Sixtus IV. Already during his lifetime this work was republished many times in Latin, French, Dutch, and German. Drawing on major Christian historiographical sources such as Orosius and Eusebius, Fasciculus presents the history of the world in the form of a genealogy, a traditional historiographical structure dating back to late antiquity.
Another famous work by Rolewink is a description of the manners and customs of his homeland entitled De laude veteris Saxsoniæ nunc Westphaliæ dictæ.


Elizabeth I was Queen of England and Ireland from 1558 to 1603 and was the last monarch of the Tudor dynasty.
Elizabeth was the daughter of Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn, his second wife, who was executed when Elizabeth was two years old. Her youth was full of uncertainties, and her chances for the throne seemed very slim. Against all odds, however, Elizabeth inherited the throne after the death of her half-sister in November 1558. She was very well educated, fluent in five languages, intelligent, determined, and shrewd.
Above all, Elizabeth was committed to maintaining peace and stability in England. Her 45-year reign is considered one of the most glorious in English history, a path of triumph and success. Under her rule a secure Anglican church was established. Elizabeth's reign was marked by many bold discoveries, and the arts flourished as well.
Elizabeth chose never to marry. She used her prospects of marriage as a political tool in foreign and domestic politics. However, the "virgin queen" was presented as a selfless woman who sacrificed personal happiness for the good of the nation.





























































![[ELIZABETH I (1533-1603)].](/assets/image/picture_2945045/ddfad/e62990c18d4c8bf371d8ca34cc48a1481689112800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[ELIZABETH I (1533-1603)].](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2945045/ddfad/e62990c18d4c8bf371d8ca34cc48a1481689112800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)