books about history
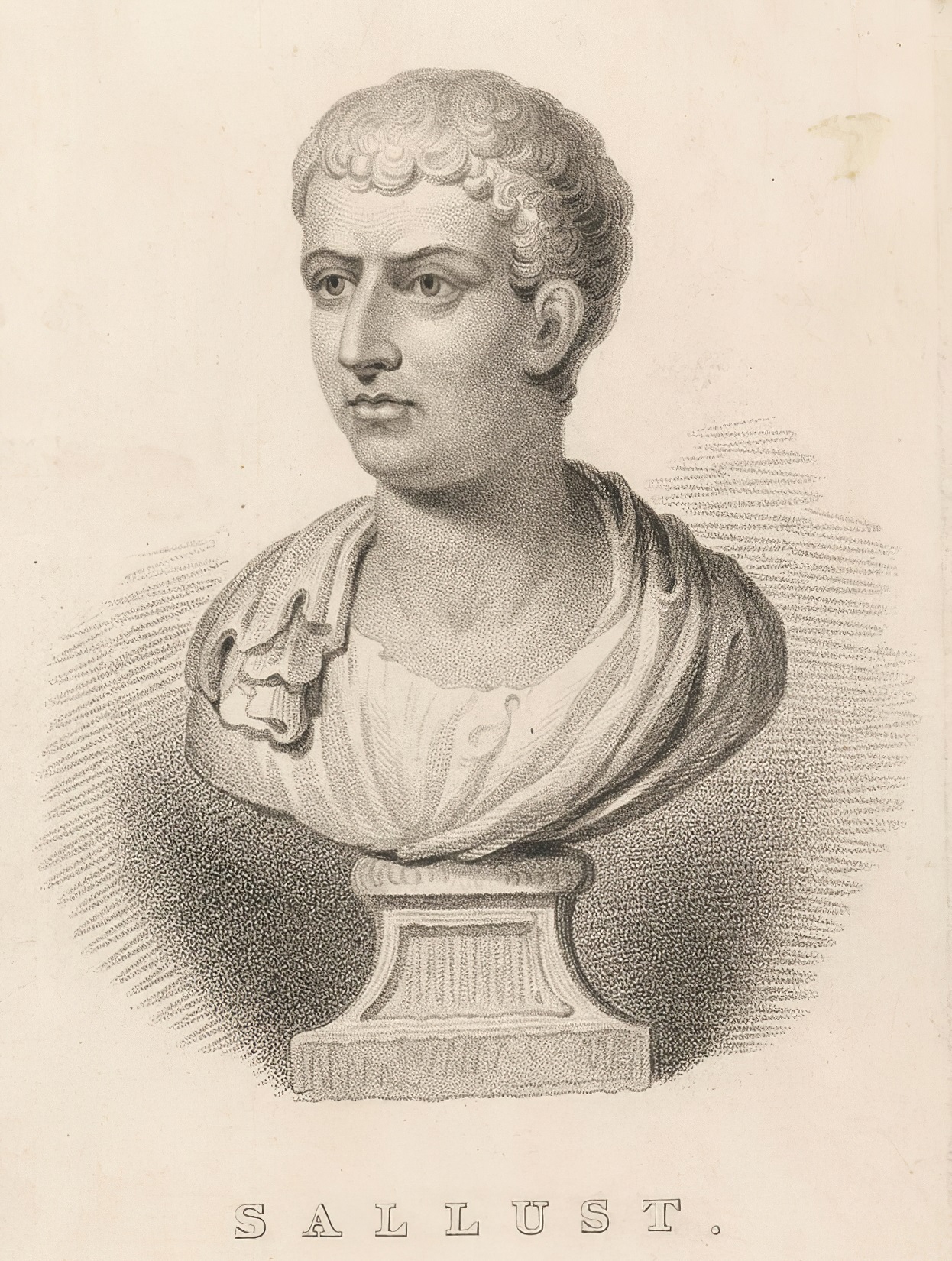



Sallust, or Gaius Sallustius Crispus, was an ancient Roman historian, a reformer of ancient historiography, who had a significant influence on Tacitus and other historians.
Sallust was one of the first Roman historians to introduce into historical works extended speeches of the main characters to better emphasise the peculiarities of their character and political orientation. He was also one of the first to cast a critical eye on the recent history of Rome. Minor passages of his main work, the Histories, have survived. More famous are two small historical monographs - "On the Conspiracy of Catiline" and "The Jugurthine War". The theoretical basis of the works of Sallust was the doctrine of moral decline, according to which the cause of the crisis of the Roman Republic was the departure from traditional virtues to the domination of ambition and greed.
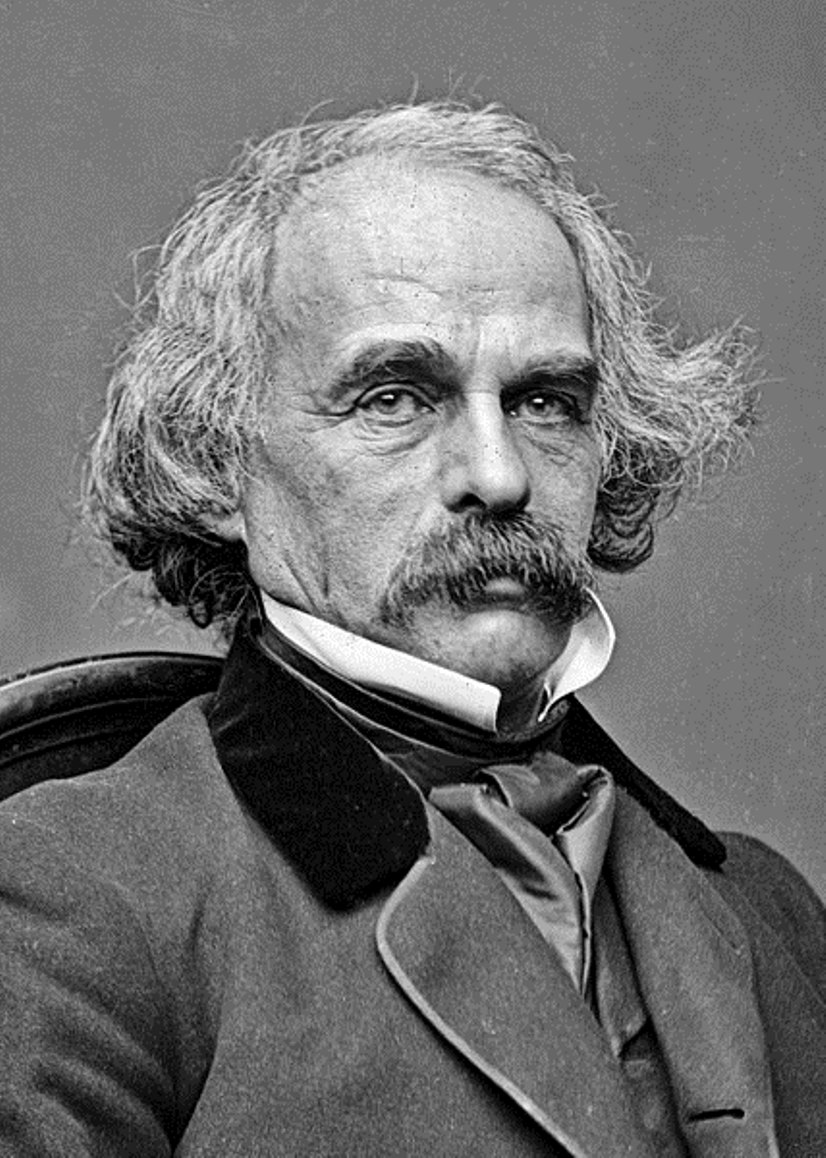

Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.
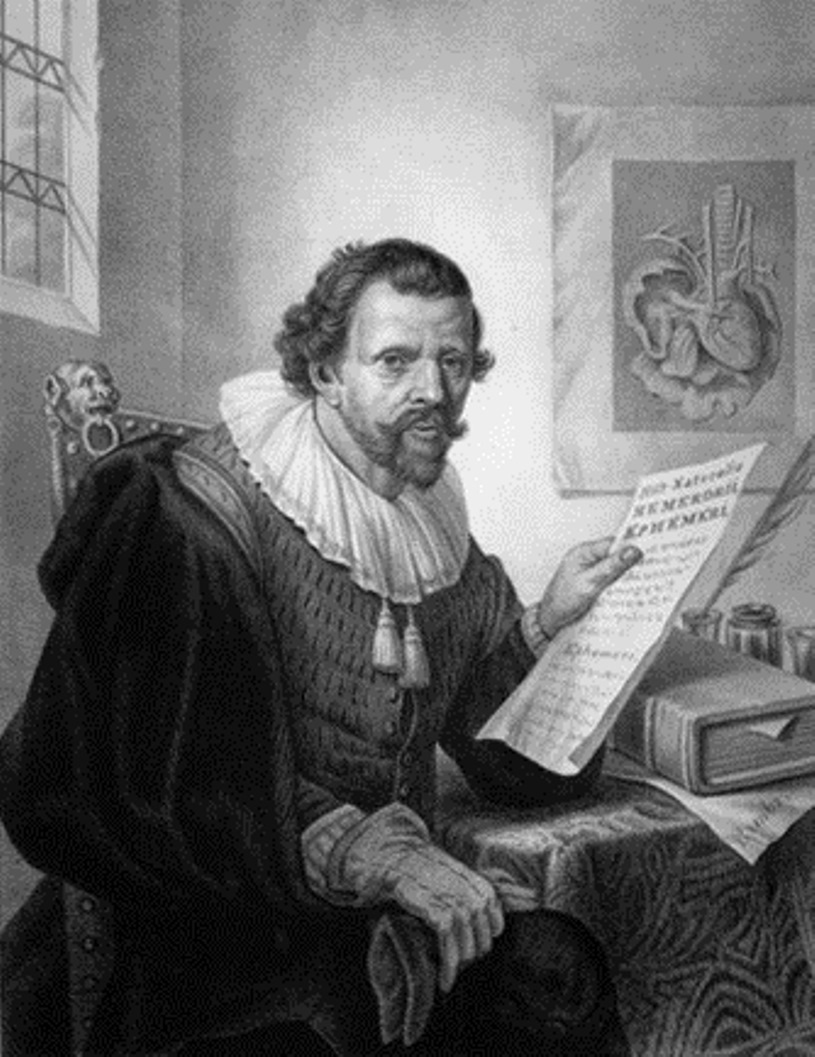


Jan Swammerdam was a Dutch naturalist and biologist, anatomist and microscopist.
Swammerdam graduated from the Faculty of Medicine at Leiden University, then studied in Paris, earning a doctorate in medicine, and devoted himself exclusively to microscopic research. He used a single-lens microscope to study insect anatomy, and accurately described and illustrated the life history and anatomy of many species. His observations of their development allowed him to divide insects into four major divisions according to the degree and type of metamorphosis. His greatest contribution to biology was to understand insect development and to demonstrate that the same organism persists through different stages.
Jan Swammerdam wrote a voluminous work entitled A General History of Insects (1669) and The Bible of Nature (1737-1738), one of the finest collections of microscopic observations ever published. Considered the most accurate of the classical microscopists, he was the first to observe and describe erythrocytes in 1658.
Swammerdam was also a recognized anatomist: in 1670 he was granted the privilege of dissecting human bodies in Amsterdam, which at the time required a special license available only to a limited number of researchers. He developed a new dissection technique and also designed several new instruments.


Jan Swammerdam was a Dutch naturalist and biologist, anatomist and microscopist.
Swammerdam graduated from the Faculty of Medicine at Leiden University, then studied in Paris, earning a doctorate in medicine, and devoted himself exclusively to microscopic research. He used a single-lens microscope to study insect anatomy, and accurately described and illustrated the life history and anatomy of many species. His observations of their development allowed him to divide insects into four major divisions according to the degree and type of metamorphosis. His greatest contribution to biology was to understand insect development and to demonstrate that the same organism persists through different stages.
Jan Swammerdam wrote a voluminous work entitled A General History of Insects (1669) and The Bible of Nature (1737-1738), one of the finest collections of microscopic observations ever published. Considered the most accurate of the classical microscopists, he was the first to observe and describe erythrocytes in 1658.
Swammerdam was also a recognized anatomist: in 1670 he was granted the privilege of dissecting human bodies in Amsterdam, which at the time required a special license available only to a limited number of researchers. He developed a new dissection technique and also designed several new instruments.