cal. 1400

Giovanni di Ser Giovanni Guidi, more famously known as Scheggia, was an Italian painter whose contributions to the arts during the Renaissance period have carved him a distinct niche in art history. Born in Italy, Scheggia was a craftsman of narrative and decorative painting, specializing in altarpieces, cassone panels, and birth trays, which were popular in Florentine culture for their intricate storytelling and detailed artistry.
Scheggia is perhaps best known for his lively and detailed panels that graced the fronts of marriage chests, known as cassoni. These pieces were celebrated for their vivid depictions of allegorical and mythological scenes, showcasing Scheggia's skillful use of color and composition to bring tales to life. His work not only adorned the homes of the wealthy but also served as a testament to the rich cultural and artistic fervor of Renaissance Florence.
One of Scheggia's most notable works, the "Madonna of Humility with Angels," showcases his ability to blend divine and earthly realms in a harmonious composition that speaks volumes of his mastery over form and space. This, among other works by Scheggia, can be admired in museums across Italy, offering a glimpse into the vibrant Renaissance art scene.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Giovanni di Ser Giovanni Guidi represents an intriguing exploration into the less-trodden paths of Renaissance art. His paintings are a celebration of the era's innovative spirit, offering insights into the everyday lives, cultural practices, and artistic achievements of the time.
To delve deeper into the world of Renaissance art and uncover the gems of Giovanni di Ser Giovanni Guidi's legacy, signing up for updates is an essential step. This subscription ensures that enthusiasts and collectors are the first to know about new discoveries, exhibitions, and auction events related to Scheggia's work, providing exclusive opportunities to enrich their appreciation and collections of Renaissance art.


Johannes Busch was a major Dutch clergyman and reformed theologian.
As a monastic reformer and chronicler, the Augustinian canon of Windesheim, Johannes Busch is one of the most prominent figures of the Devotio moderna ("New Piety") movement in Catholicism. With his historiographical works Chronicle of the Monastery of Windesheim and Liber de reformatione monasteriorum he shaped the association of the Windesheim monastery and the late medieval observance movement.
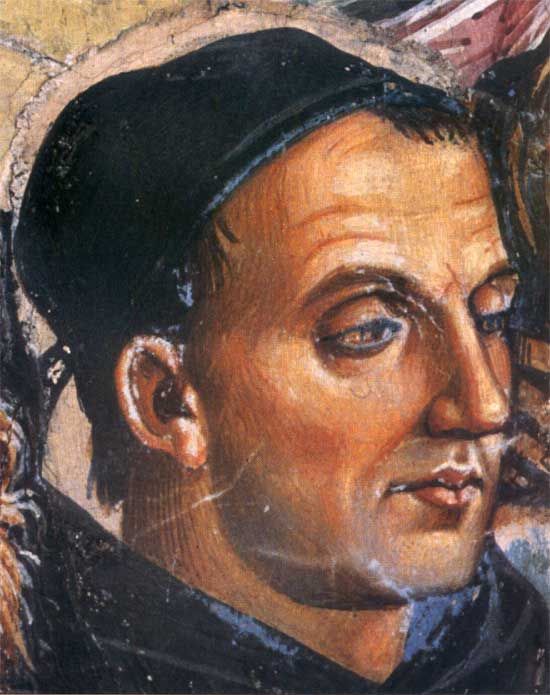


Fra Angelico, a name synonymous with the serenity and purity of Early Renaissance art, was a Dominican friar and Italian painter celebrated for his devout and luminous religious works. Born Guido di Pietro around 1395 in Vicchio, near Florence, he later became known as Fra Giovanni upon joining the Dominican order at Fiesole. His monastic life profoundly influenced his art, reflecting a deep spiritual commitment and a heavenly tranquility. Pope John Paul II recognized his sanctity by beatifying him in 1982, officially bestowing upon him the title "Blessed" and affirming his legacy as a bridge between heaven and earth through his art.
Fra Angelico's technical prowess and innovative approaches to composition and color set new standards in the art world. He was initially trained as an illuminator, which is evident in the delicate details and luminous quality of his works. His art was not confined by his religious duties; instead, his position allowed him to advance the Dominican order's mission through visually compelling narratives that spoke directly to the viewer's soul. His works, including altarpieces and frescoes, are revered for their serene religious attitude and classical influence, embodying the Early Renaissance spirit that sought to harmonize Christian themes with the natural world and human emotion.
Among his most notable contributions are the frescoes at the convent of San Marco in Florence, commissioned by Cosimo de' Medici. These works display Angelico's mastery over perspective and his ability to create a spiritual atmosphere that invites contemplation. The Annunciation, one of his most famous frescoes at San Marco, exemplifies his use of architectural space to frame the sacred narrative, integrating the divine with the everyday. His altarpieces, characterized by their detailed figures and harmonious compositions, were innovative in their unified presentation of sacred stories, moving away from the segmented Gothic style towards a more cohesive and immersive narrative experience.
Fra Angelico's influence extended beyond his lifetime, shaping the trajectory of Renaissance art through his integration of humanistic principles with devout Christian faith. His works are preserved in some of the world's most prestigious museums, including the Museo Diocesano in Cortona, the Uffizi Gallery, and the Museo del Convento di San Marco in Florence, continuing to inspire awe and reverence among viewers.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, the legacy of Fra Angelico offers a window into the soul of the Renaissance, where beauty and spirituality converge. To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to this pivotal artist, signing up for updates is a prudent step towards enriching one's collection with works that embody the zenith of religious and artistic expression in the Early Renaissance.


Johannes Busch was a major Dutch clergyman and reformed theologian.
As a monastic reformer and chronicler, the Augustinian canon of Windesheim, Johannes Busch is one of the most prominent figures of the Devotio moderna ("New Piety") movement in Catholicism. With his historiographical works Chronicle of the Monastery of Windesheim and Liber de reformatione monasteriorum he shaped the association of the Windesheim monastery and the late medieval observance movement.


Bernhard Keil was a Danish Baroque painter.
He is considered a pupil of Rembrandt. Keil is known for his lively genre paintings depicting children, he also painted portraits and allegorical paintings.
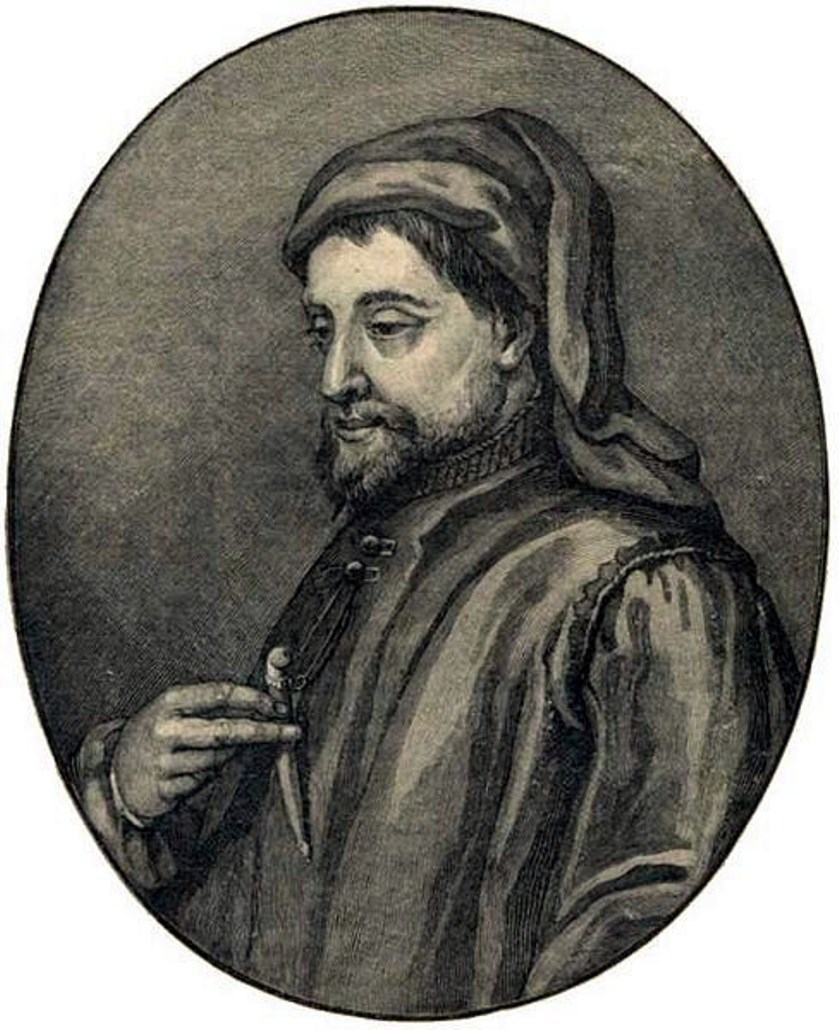


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.
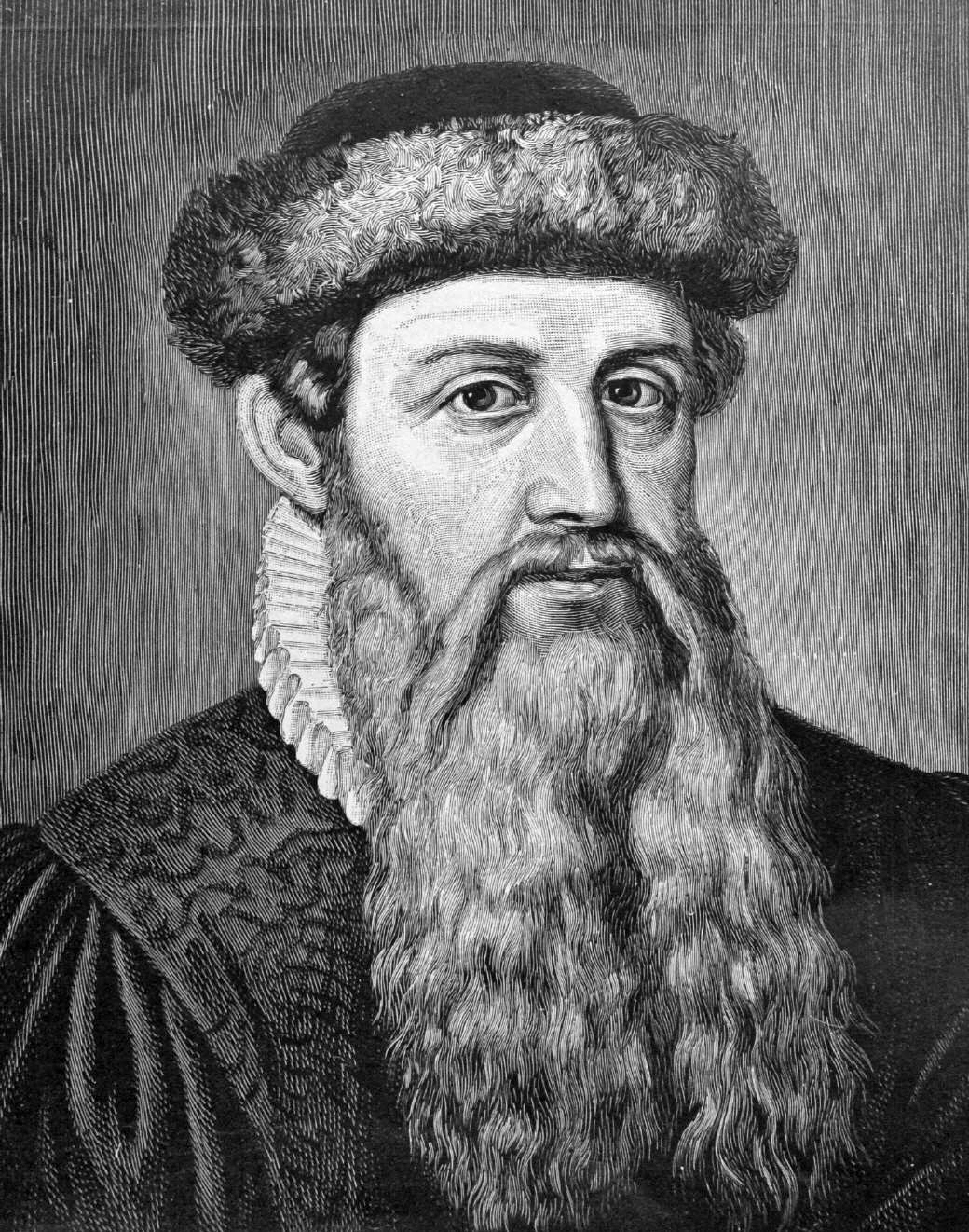


Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg was a German inventor and craftsman who introduced letterpress printing to Europe with his movable-type printing press. Though not the first of its kind, earlier designs were restricted to East Asia, and Gutenberg's version was the first to spread across the world. His work led to an information revolution and the unprecedented mass-spread of literature throughout Europe. It also had a direct impact on the development of the Renaissance, Reformation and humanist movement.
His many contributions to printing include the invention of a process for mass-producing movable type; the use of oil-based ink for printing books; adjustable molds; mechanical movable type; and the use of a wooden printing press similar to the agricultural screw presses of the period. Gutenberg's method for making type is traditionally considered to have included a type metal alloy and a hand mould for casting type. The alloy was a mixture of lead, tin, and antimony that melted at a relatively low temperature for faster and more economical casting, cast well, and created a durable type. His major work, the Gutenberg Bible, was the first printed version of the Bible and has been acclaimed for its high aesthetic and technical quality.


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.












![[BUSCH, Johannes (1399/1400-after 1475)]](/assets/image/picture_2944660/8eb08/3af5961a08f66311d195db6df32ee3231689112800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[BUSCH, Johannes (1399/1400-after 1475)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2944660/8eb08/3af5961a08f66311d195db6df32ee3231689112800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)































































