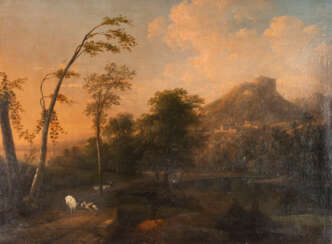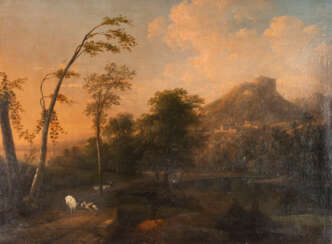myth
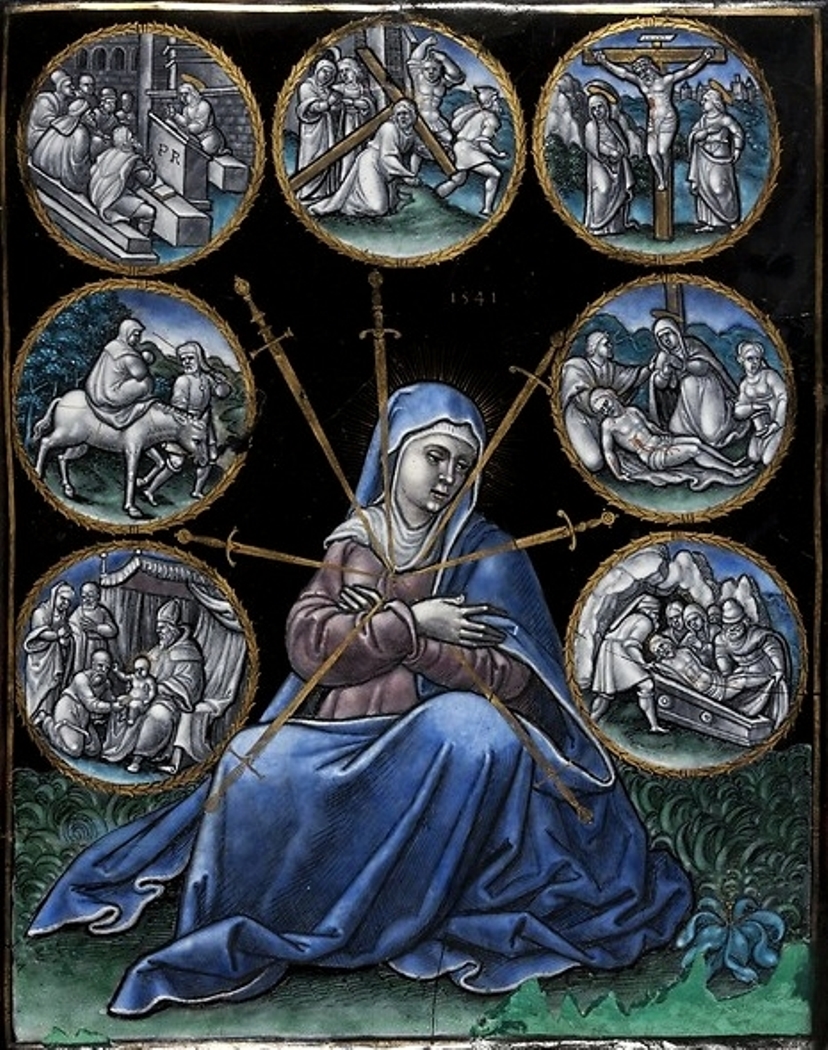

Pierre Reymond was a French painter and enameler.
Reymond ran a large workshop in Limoges, where one of his apprentices was Pierre Court. He specialized in tableware decorated with mythological scenes, including cups, plates, bowls and platters.
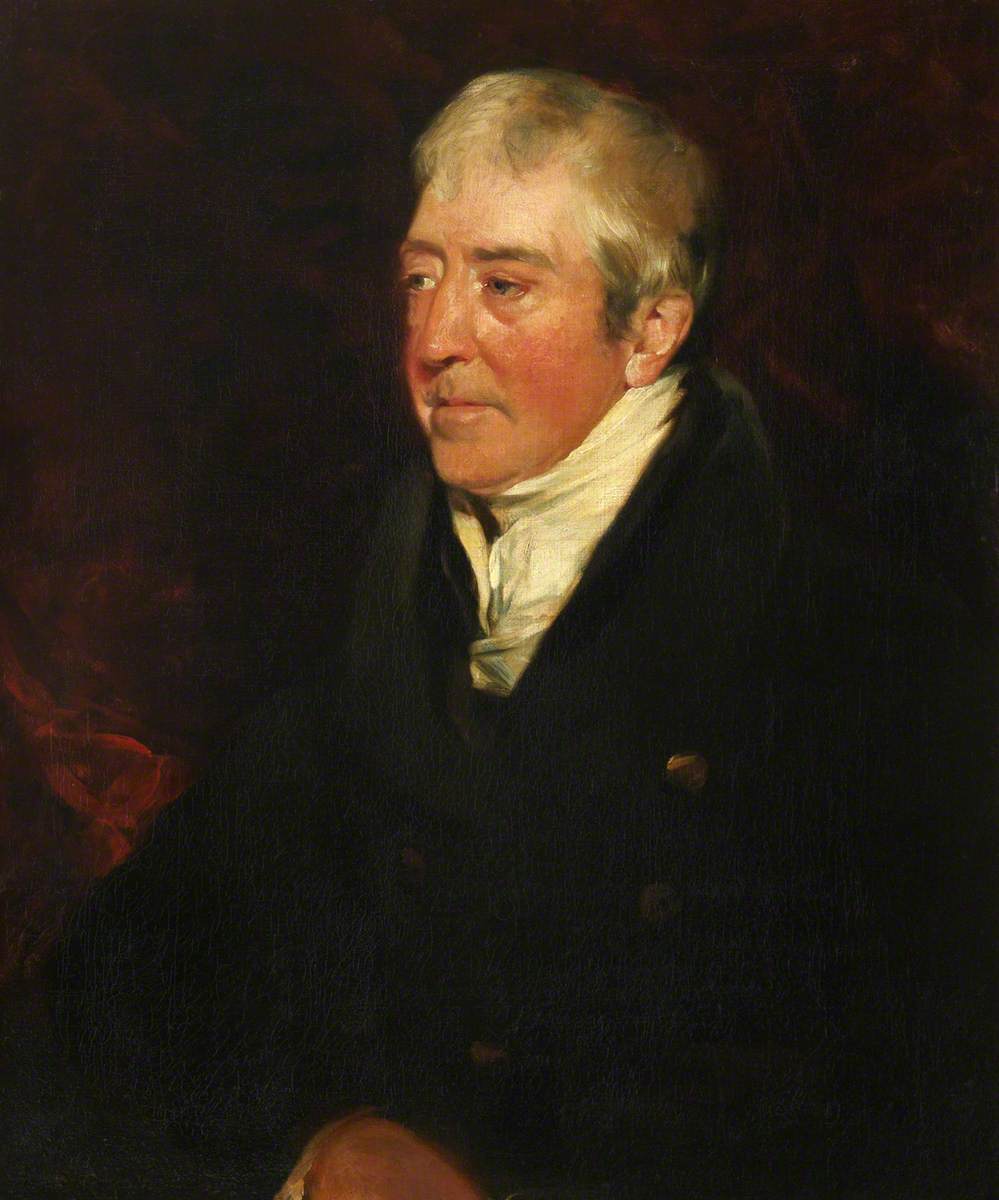


Alexander Nasmyth was a Scottish portrait and landscape painter, a pupil of Allan Ramsay. He also undertook several architectural commissions.
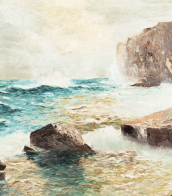

Alexander Nasmyth was a Scottish portrait and landscape painter, a pupil of Allan Ramsay. He also undertook several architectural commissions.
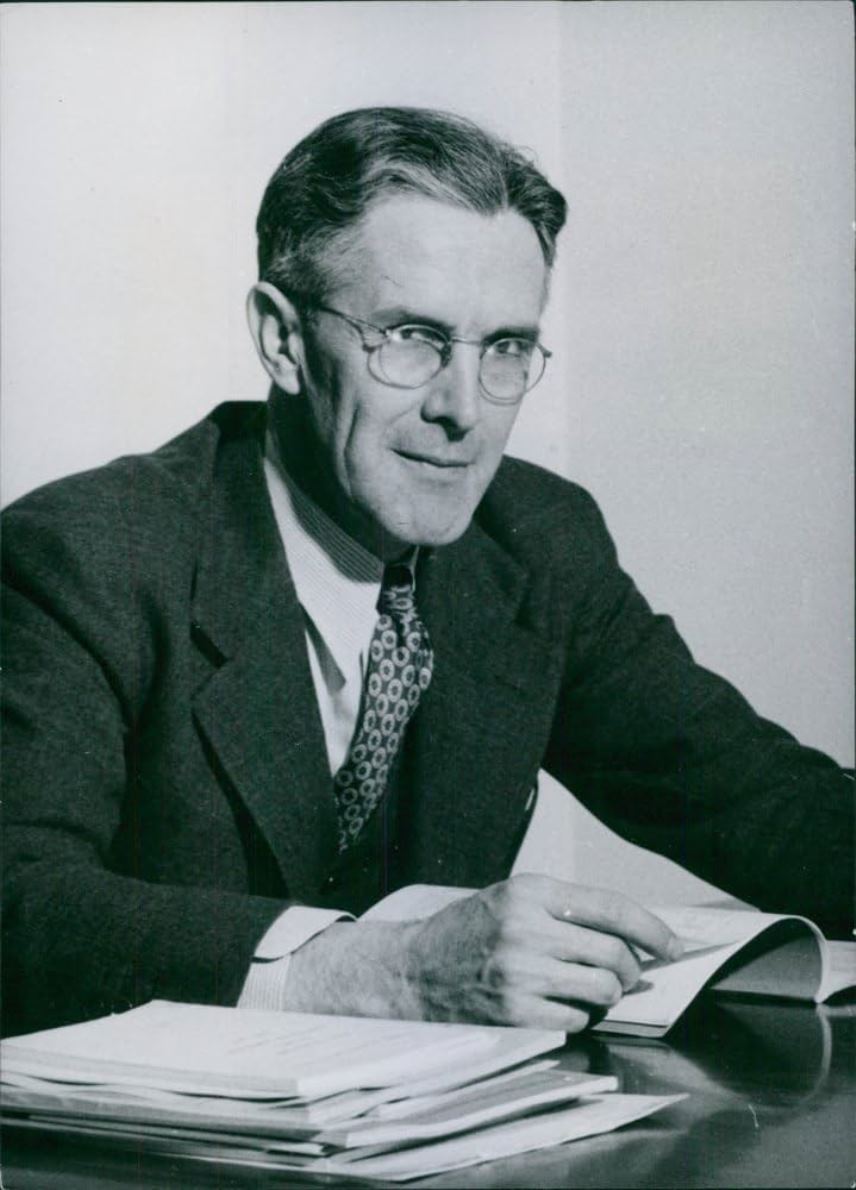


Henry DeWolf Smyth was an American scientist, nuclear physicist, and diplomat.
Smyth studied at Princeton and Cambridge Universities, taught in Princeton's physics department from 1924 to 1966, and chaired the department for many years. At first he investigated the ionization of gases, but from the mid-1930s he turned his attention to nuclear physics. During World War II, Smith was a member of the uranium section of the National Defense Research Committee. He also proposed electromagnetic techniques that were used to enrich the first samples of U-235 during the Manhattan Project. Smith worked as a consultant on this project from 1943 to 1945 and served as deputy director of the Metallurgical Laboratory at the University of Chicago.
In 1944, General Leslie Groves appointed Henry Smith to the Committee on Postwar Policy to propose a public policy for research and development of atomic energy after the war. He wrote the official public report on the bomb, which became known as the Smith Report and was widely distributed throughout the country.
After the war, Henry DeWolf Smith served as commissioner of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission and as the U.S. representative to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). In 1953, he was President Eisenhower's chief advisor on Ike's "Atoms for Peace" speech and received the Atoms for Peace Award in 1968.


Henry DeWolf Smyth was an American scientist, nuclear physicist, and diplomat.
Smyth studied at Princeton and Cambridge Universities, taught in Princeton's physics department from 1924 to 1966, and chaired the department for many years. At first he investigated the ionization of gases, but from the mid-1930s he turned his attention to nuclear physics. During World War II, Smith was a member of the uranium section of the National Defense Research Committee. He also proposed electromagnetic techniques that were used to enrich the first samples of U-235 during the Manhattan Project. Smith worked as a consultant on this project from 1943 to 1945 and served as deputy director of the Metallurgical Laboratory at the University of Chicago.
In 1944, General Leslie Groves appointed Henry Smith to the Committee on Postwar Policy to propose a public policy for research and development of atomic energy after the war. He wrote the official public report on the bomb, which became known as the Smith Report and was widely distributed throughout the country.
After the war, Henry DeWolf Smith served as commissioner of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission and as the U.S. representative to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). In 1953, he was President Eisenhower's chief advisor on Ike's "Atoms for Peace" speech and received the Atoms for Peace Award in 1968.


Henry DeWolf Smyth was an American scientist, nuclear physicist, and diplomat.
Smyth studied at Princeton and Cambridge Universities, taught in Princeton's physics department from 1924 to 1966, and chaired the department for many years. At first he investigated the ionization of gases, but from the mid-1930s he turned his attention to nuclear physics. During World War II, Smith was a member of the uranium section of the National Defense Research Committee. He also proposed electromagnetic techniques that were used to enrich the first samples of U-235 during the Manhattan Project. Smith worked as a consultant on this project from 1943 to 1945 and served as deputy director of the Metallurgical Laboratory at the University of Chicago.
In 1944, General Leslie Groves appointed Henry Smith to the Committee on Postwar Policy to propose a public policy for research and development of atomic energy after the war. He wrote the official public report on the bomb, which became known as the Smith Report and was widely distributed throughout the country.
After the war, Henry DeWolf Smith served as commissioner of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission and as the U.S. representative to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). In 1953, he was President Eisenhower's chief advisor on Ike's "Atoms for Peace" speech and received the Atoms for Peace Award in 1968.
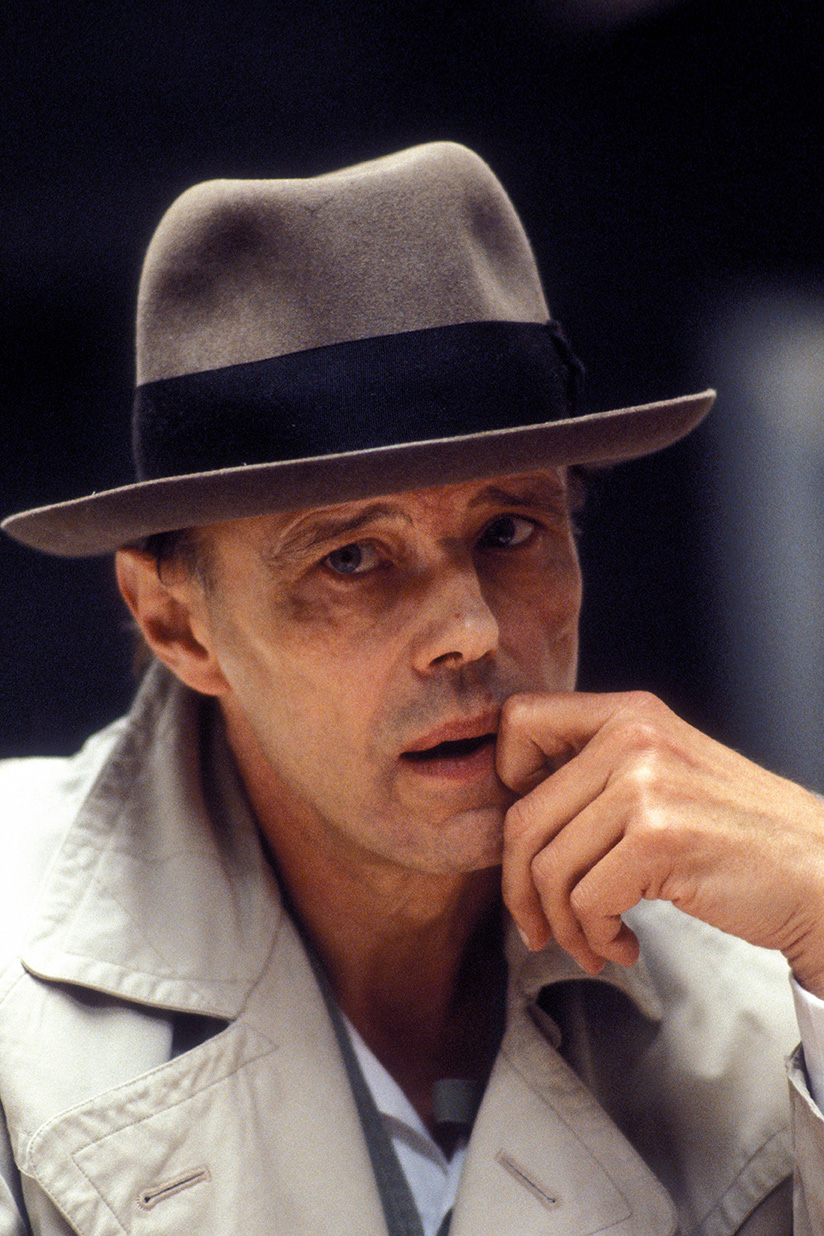




Joseph Heinrich Beuys was a German artist, renowned for his significant contributions to the realms of sculpture, painting, and installation art, which have left a lasting impact on the culture and art world. His work transcended traditional boundaries, merging art with social theory and politics, thus redefining the role of the artist in society. Beuys's unique approach to materials, incorporating substances like fat and felt, symbolized healing and insulation, reflecting his broader philosophical and ecological concerns.
Beuys's art was deeply influenced by his experiences during World War II and his academic background in natural sciences and sculpture. His concept of "social sculpture" proposed that art could transform society, emphasizing creativity as a fundamental component of human existence. This vision led him to use his performances, or "actions," as a medium to communicate his ideas, making him a pivotal figure in the Fluxus movement. Notable works such as "How to Explain Pictures to a Dead Hare" and "7000 Oaks" exemplify his innovative use of performance and environmental art to engage and challenge the public.
His legacy is preserved in major museums and galleries worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Modern in London. These institutions house key pieces that exemplify Beuys's diverse artistic output, from his early drawings and sculptures to his later installations and public interventions. His influence extends beyond the art world, impacting environmental activism and educational reform, underscoring his belief in the transformative power of art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Joseph Heinrich Beuys remains a figure of immense interest, not only for his groundbreaking artworks but also for his profound impact on contemporary art theory and practice. To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Beuys, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription ensures you are always in the loop regarding opportunities to engage with the enduring legacy of one of the most influential artists of the 20th century.


Joseph Heinrich Beuys was a German artist, renowned for his significant contributions to the realms of sculpture, painting, and installation art, which have left a lasting impact on the culture and art world. His work transcended traditional boundaries, merging art with social theory and politics, thus redefining the role of the artist in society. Beuys's unique approach to materials, incorporating substances like fat and felt, symbolized healing and insulation, reflecting his broader philosophical and ecological concerns.
Beuys's art was deeply influenced by his experiences during World War II and his academic background in natural sciences and sculpture. His concept of "social sculpture" proposed that art could transform society, emphasizing creativity as a fundamental component of human existence. This vision led him to use his performances, or "actions," as a medium to communicate his ideas, making him a pivotal figure in the Fluxus movement. Notable works such as "How to Explain Pictures to a Dead Hare" and "7000 Oaks" exemplify his innovative use of performance and environmental art to engage and challenge the public.
His legacy is preserved in major museums and galleries worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Modern in London. These institutions house key pieces that exemplify Beuys's diverse artistic output, from his early drawings and sculptures to his later installations and public interventions. His influence extends beyond the art world, impacting environmental activism and educational reform, underscoring his belief in the transformative power of art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Joseph Heinrich Beuys remains a figure of immense interest, not only for his groundbreaking artworks but also for his profound impact on contemporary art theory and practice. To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Beuys, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription ensures you are always in the loop regarding opportunities to engage with the enduring legacy of one of the most influential artists of the 20th century.


Joseph Heinrich Beuys was a German artist, renowned for his significant contributions to the realms of sculpture, painting, and installation art, which have left a lasting impact on the culture and art world. His work transcended traditional boundaries, merging art with social theory and politics, thus redefining the role of the artist in society. Beuys's unique approach to materials, incorporating substances like fat and felt, symbolized healing and insulation, reflecting his broader philosophical and ecological concerns.
Beuys's art was deeply influenced by his experiences during World War II and his academic background in natural sciences and sculpture. His concept of "social sculpture" proposed that art could transform society, emphasizing creativity as a fundamental component of human existence. This vision led him to use his performances, or "actions," as a medium to communicate his ideas, making him a pivotal figure in the Fluxus movement. Notable works such as "How to Explain Pictures to a Dead Hare" and "7000 Oaks" exemplify his innovative use of performance and environmental art to engage and challenge the public.
His legacy is preserved in major museums and galleries worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Modern in London. These institutions house key pieces that exemplify Beuys's diverse artistic output, from his early drawings and sculptures to his later installations and public interventions. His influence extends beyond the art world, impacting environmental activism and educational reform, underscoring his belief in the transformative power of art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Joseph Heinrich Beuys remains a figure of immense interest, not only for his groundbreaking artworks but also for his profound impact on contemporary art theory and practice. To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Beuys, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription ensures you are always in the loop regarding opportunities to engage with the enduring legacy of one of the most influential artists of the 20th century.


Joseph Heinrich Beuys was a German artist, renowned for his significant contributions to the realms of sculpture, painting, and installation art, which have left a lasting impact on the culture and art world. His work transcended traditional boundaries, merging art with social theory and politics, thus redefining the role of the artist in society. Beuys's unique approach to materials, incorporating substances like fat and felt, symbolized healing and insulation, reflecting his broader philosophical and ecological concerns.
Beuys's art was deeply influenced by his experiences during World War II and his academic background in natural sciences and sculpture. His concept of "social sculpture" proposed that art could transform society, emphasizing creativity as a fundamental component of human existence. This vision led him to use his performances, or "actions," as a medium to communicate his ideas, making him a pivotal figure in the Fluxus movement. Notable works such as "How to Explain Pictures to a Dead Hare" and "7000 Oaks" exemplify his innovative use of performance and environmental art to engage and challenge the public.
His legacy is preserved in major museums and galleries worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate Modern in London. These institutions house key pieces that exemplify Beuys's diverse artistic output, from his early drawings and sculptures to his later installations and public interventions. His influence extends beyond the art world, impacting environmental activism and educational reform, underscoring his belief in the transformative power of art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Joseph Heinrich Beuys remains a figure of immense interest, not only for his groundbreaking artworks but also for his profound impact on contemporary art theory and practice. To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Beuys, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription ensures you are always in the loop regarding opportunities to engage with the enduring legacy of one of the most influential artists of the 20th century.