wonderful world
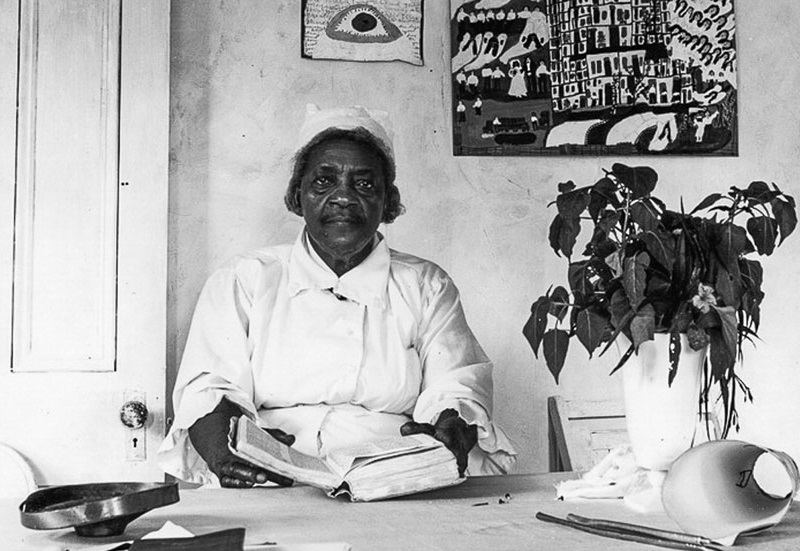

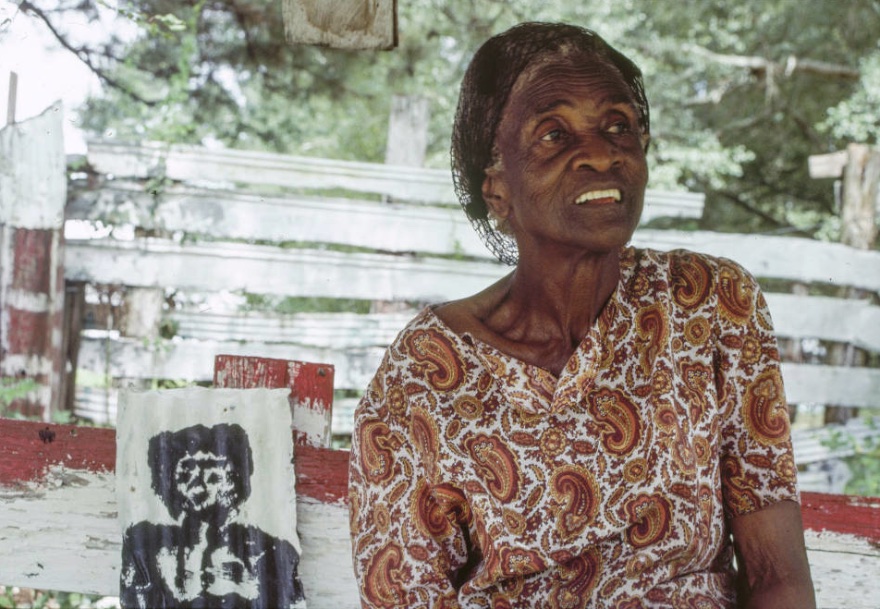
Sister Gertrude Morgan was a self-taught African-American artist, musician, poet and preacher. Sister Morgan achieved critical acclaim during her lifetime for her folk art paintings. Her work has been included in many groundbreaking exhibitions of visionary and folk art from the 1970s onwards.
Similar to other self-taught artists, Sister Morgan used simple forms to depict the human figure. Her works are characterized by their lack of the use of formal techniques such as perspective and definition of light and shadow, giving them a flat, two dimensional quality. She painted and drew using acrylics, tempera, ballpoint pen, watercolors, crayon, colored and lead pencils and felt tip markers. Using inexpensive materials she had at hand, Sister Morgan painted on paper, toilet rolls, plastic pitchers, paper megaphones, scrap wood, lampshades, paper fans and styrofoam trays. The fact that she was self-taught, coupled with her choice of materials as well as her style and subject matter have led her to be characterized as a naive, folk, visionary, vernacular and outsider artist.
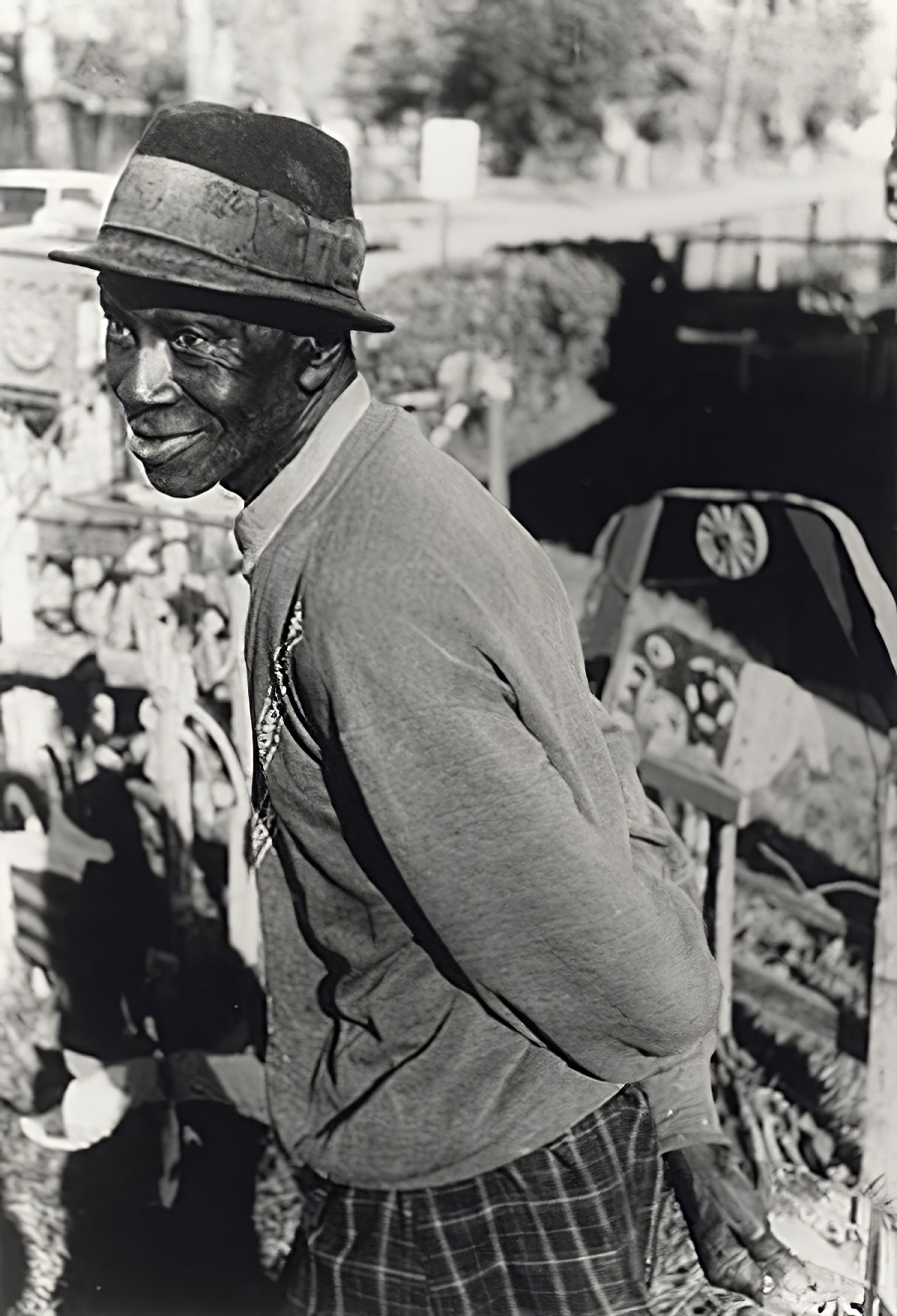

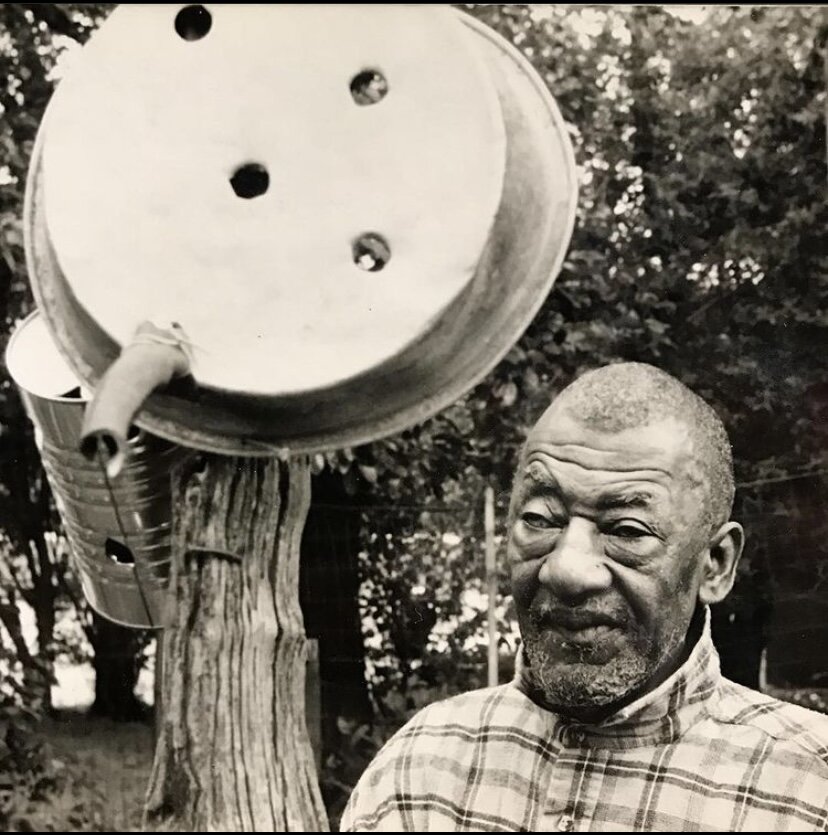
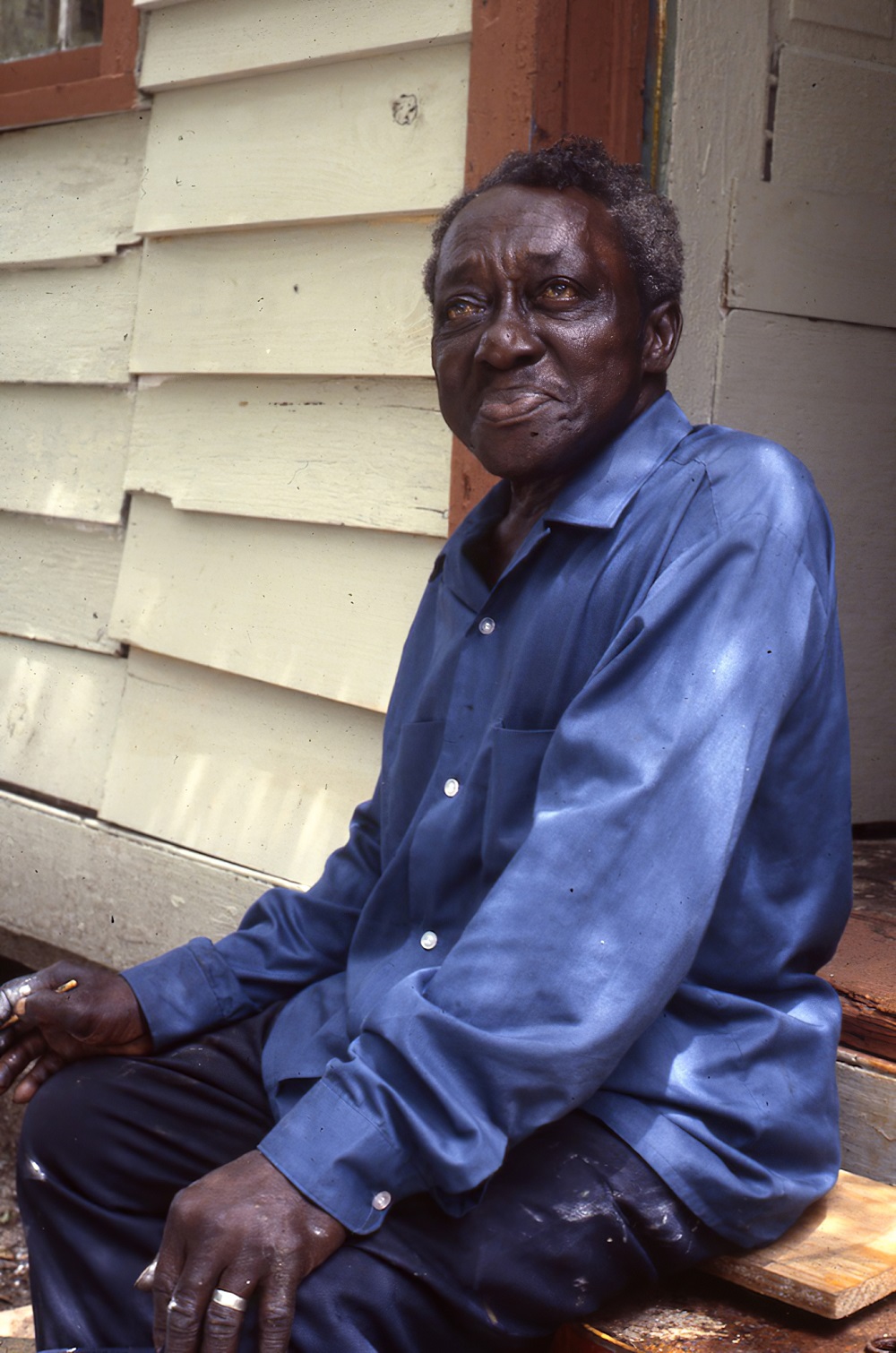
David Butler was an African American sculptor and painter from Good Hope, Louisiana. His style is epitomized by kinetic sculptures made from recycled tin or wood, which he embellished with saturated colors and geometric patterns. His work is now in the permanent collections of the Smithsonian American Art Museum, the American Folk Art Museum, and the Philadelphia Museum of Art.


Sister Gertrude Morgan was a self-taught African-American artist, musician, poet and preacher. Sister Morgan achieved critical acclaim during her lifetime for her folk art paintings. Her work has been included in many groundbreaking exhibitions of visionary and folk art from the 1970s onwards.
Similar to other self-taught artists, Sister Morgan used simple forms to depict the human figure. Her works are characterized by their lack of the use of formal techniques such as perspective and definition of light and shadow, giving them a flat, two dimensional quality. She painted and drew using acrylics, tempera, ballpoint pen, watercolors, crayon, colored and lead pencils and felt tip markers. Using inexpensive materials she had at hand, Sister Morgan painted on paper, toilet rolls, plastic pitchers, paper megaphones, scrap wood, lampshades, paper fans and styrofoam trays. The fact that she was self-taught, coupled with her choice of materials as well as her style and subject matter have led her to be characterized as a naive, folk, visionary, vernacular and outsider artist.


David Butler was an African American sculptor and painter from Good Hope, Louisiana. His style is epitomized by kinetic sculptures made from recycled tin or wood, which he embellished with saturated colors and geometric patterns. His work is now in the permanent collections of the Smithsonian American Art Museum, the American Folk Art Museum, and the Philadelphia Museum of Art.


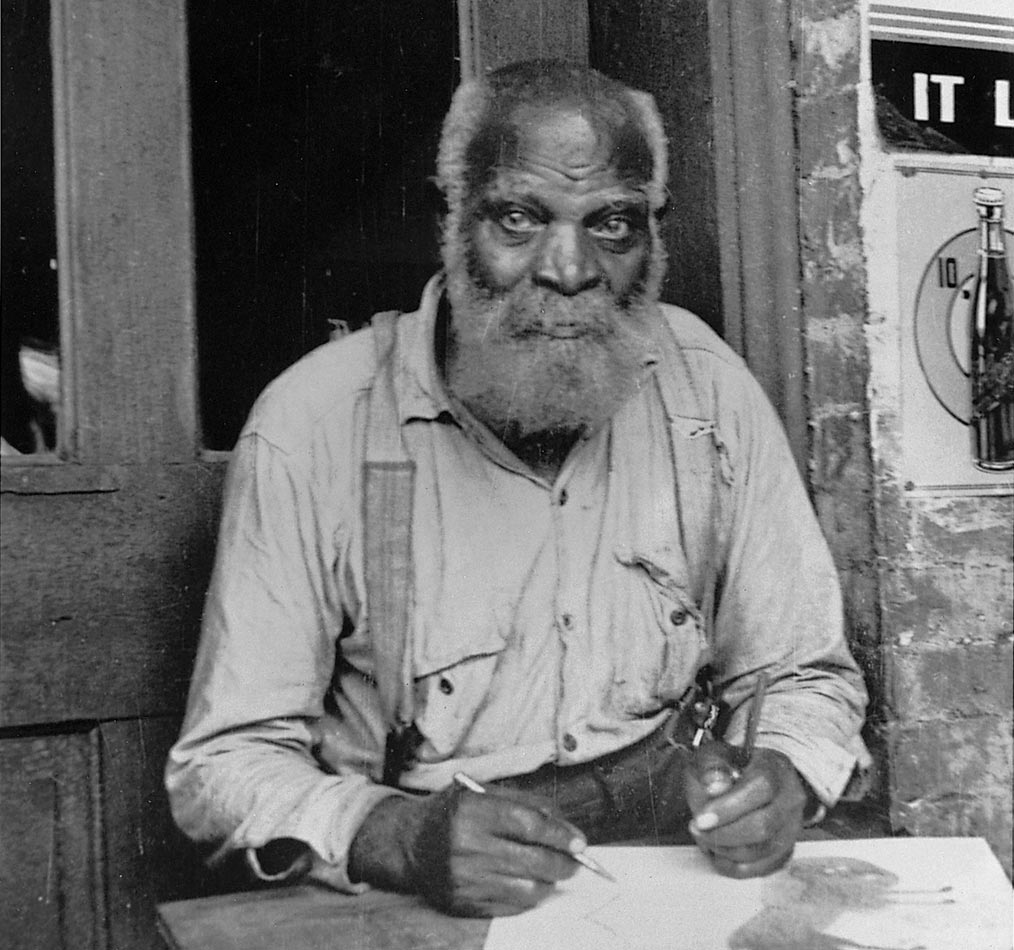
Thomas "Sam" Doyle was an African-American artist from Saint Helena Island, South Carolina. His colorful paintings on sheet metal and wood recorded the history and people of St. Helena’s Gullah community.
Doyle's paintings and sculptures are held in the permanent collections of American Folk Art Museum, the High Museum of Art, the Smithsonian American Art Museum, the Gibbes Museum of Art and the Los Angeles County Museum of Art and Penn Center (Penn School on St. Helena Island).


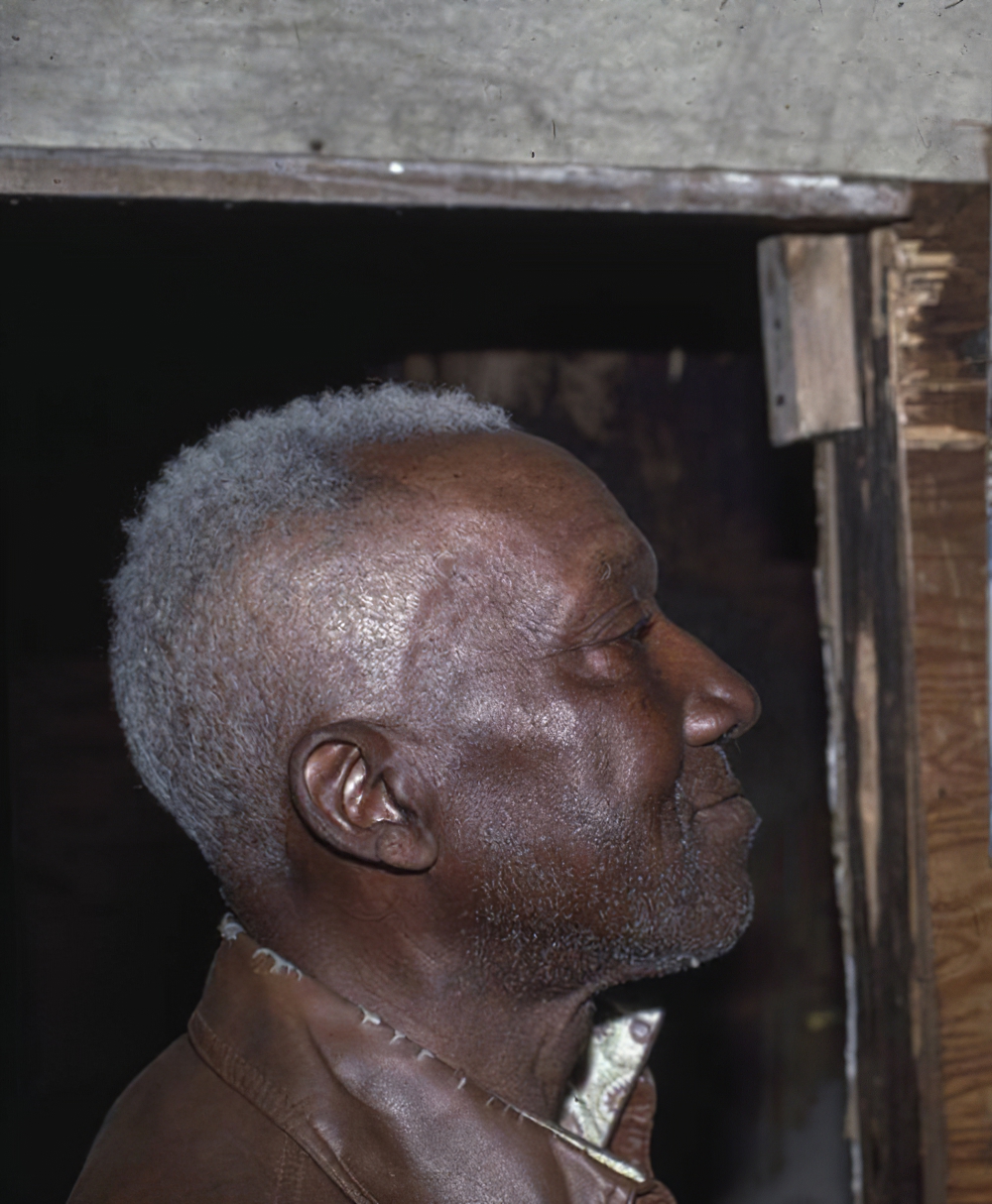
William Traylor was an African-American self-taught artist from Lowndes County, Alabama. Born into slavery, Traylor spent the majority of his life after emancipation as a sharecropper. It was only after 1939, following his move to Montgomery, Alabama, that Traylor began to draw. At the age of 85, he took up a pencil and a scrap of cardboard to document his recollections and observations. From 1939 to 1942, while working on the sidewalks of Montgomery, he produced nearly 1 500 pieces of art.
While Traylor received his first public exhibition in 1940, it was not until 30 years after his death that his work finally began to receive broader attention, in the late 1970s. Recent acceptance of Traylor as a significant figure of American folk and modern art has been founded on the efforts of Charles Shannon, as well as the evolving tastes of the art world. Shannon, who first encountered Traylor's work in 1940, brought Traylor to the attention of the larger art world. Traylor now holds a central position in the fields of "self-taught" and modern art.


Elijah Pierce was a 20th-century wood carver. Pierce was the youngest in his family born from a former slave on a farm in Baldwyn. He began carving at a young age using a pocket knife. He first started carving animals because of his prior life of growing up on a farm. Pierce was honored with the National Heritage Fellowship for his art and influence in the woodcarving community in 1982.


David Butler was an African American sculptor and painter from Good Hope, Louisiana. His style is epitomized by kinetic sculptures made from recycled tin or wood, which he embellished with saturated colors and geometric patterns. His work is now in the permanent collections of the Smithsonian American Art Museum, the American Folk Art Museum, and the Philadelphia Museum of Art.


John Bunion (J. B.) Murray was an abstract expressionist painter from Glascock County, GA. His work has been shown among folk art exhibitions and is included at the American Folk Art Museum and the Smithsonian American Art Museum, and has been featured in many museum exhibitions, including "Self-Taught Genius" at AFAM and "When the Stars Begin to Fall" at the Studio Museum. His work is best known for its codified use of colors and improvised script, called "spirit script," which could only be translated by the artist.

































































