антонио валлизнери i (1661 - 1730)

Antonio Vallisneri the Elder was an Italian naturalist, physician and geologist, collector, and member of the Royal Society of London.
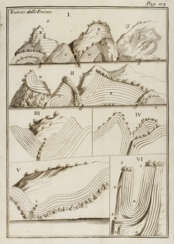
He studied in Bologna, Venice, Padua and Parma and headed the chair first of practical medicine and then of theoretical medicine at the University of Padua. In addition to medicine, Vallisneri conducted important research in the natural sciences. In particular, in the field of geology, he is credited with recognizing the organic nature of fossils unrelated to the Great Flood, which contributed to the end of centuries-old disputes. His observations on the water cycle, thermal waters and some mines in the Apennines were also important.
Vallisneri was interested in all branches of the natural sciences, collecting numerous collections of animals, minerals, and other natural objects during his lifetime. The scientist compiled a brief catalog of his collection, which was published in 1733 by his son, Antonio Vallisneri, Jr. The Vallisneri Museum included naturalistic finds, anatomical preparations, medical and scientific instruments, antiques, and exotics from various cultures and eras as well as geographical origins. In 1734, his son donated this museum to the University of Padua, initiating the creation of a general museum for the university.
Antonio Vallisneri Jr. followed in his father's footsteps and for many years held the position of professor of natural history at the University of Padua. He devoted his life to collecting and processing his father's writings and tidying up his library, which contained about a thousand volumes. These were donated to the University Library in Padua.


Antonio Vallisneri the Elder was an Italian naturalist, physician and geologist, collector, and member of the Royal Society of London.
He studied in Bologna, Venice, Padua and Parma and headed the chair first of practical medicine and then of theoretical medicine at the University of Padua. In addition to medicine, Vallisneri conducted important research in the natural sciences. In particular, in the field of geology, he is credited with recognizing the organic nature of fossils unrelated to the Great Flood, which contributed to the end of centuries-old disputes. His observations on the water cycle, thermal waters and some mines in the Apennines were also important.
Vallisneri was interested in all branches of the natural sciences, collecting numerous collections of animals, minerals, and other natural objects during his lifetime. The scientist compiled a brief catalog of his collection, which was published in 1733 by his son, Antonio Vallisneri, Jr. The Vallisneri Museum included naturalistic finds, anatomical preparations, medical and scientific instruments, antiques, and exotics from various cultures and eras as well as geographical origins. In 1734, his son donated this museum to the University of Padua, initiating the creation of a general museum for the university.
Antonio Vallisneri Jr. followed in his father's footsteps and for many years held the position of professor of natural history at the University of Padua. He devoted his life to collecting and processing his father's writings and tidying up his library, which contained about a thousand volumes. These were donated to the University Library in Padua.