15th&16th c.
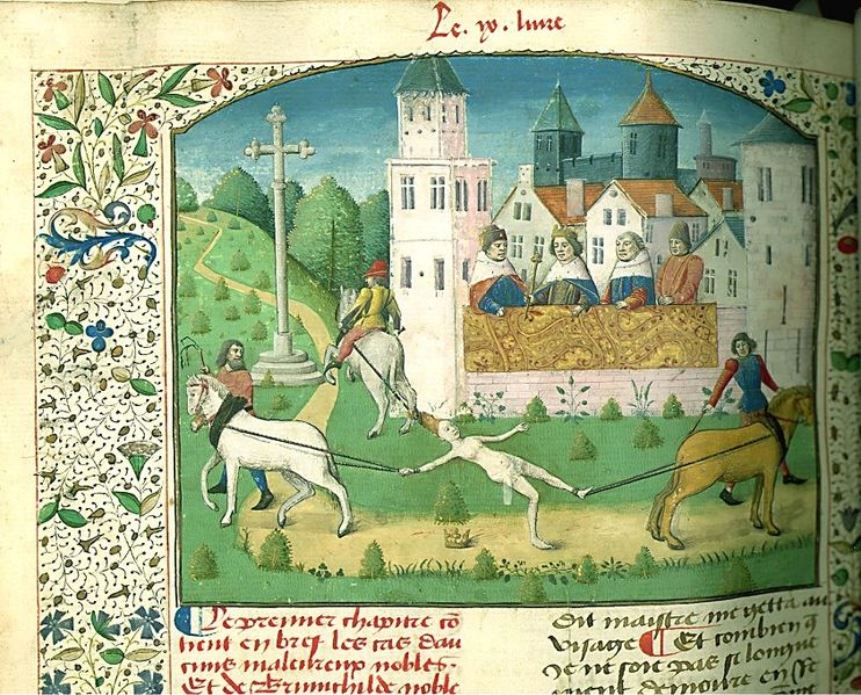


Maître François was a French illustrator who worked in Paris in the 1460s-1480s.
The identity of Maître François as an artist is first mentioned in a letter written by Robert Gauguin in 1473. Most of the prestigious commissions from the court and leading ecclesiastical figures of the time were carried out in François' studio. In Paris in the second half of the fifteenth century, one can trace the predominant style of illumination by the works of Master Jean Rolin, Maître François, and Master Jacques de Besançon. Bibliophiles close to the royal court encouraged the work of miniaturists through private commissions. In particular, Jacques d'Armagnac owned six manuscripts of Maitre Francois and his entourage.
Boccaccio's De casibus virorum illustrium was very popular in the 15th century, where the author retells the fates and downfalls of famous personalities from the Bible, antiquity and medieval history, ending with Boccaccio's own contemporaries in 14th-century Florence. For a long time this book was even more famous and successful than Boccaccio's Decameron. The text was translated into French in 1409 for Jean, Duke de Berry, by his secretary Laurent Premieffe. And the illustrations for the book were later created in the workshop of the then respected Maître François.
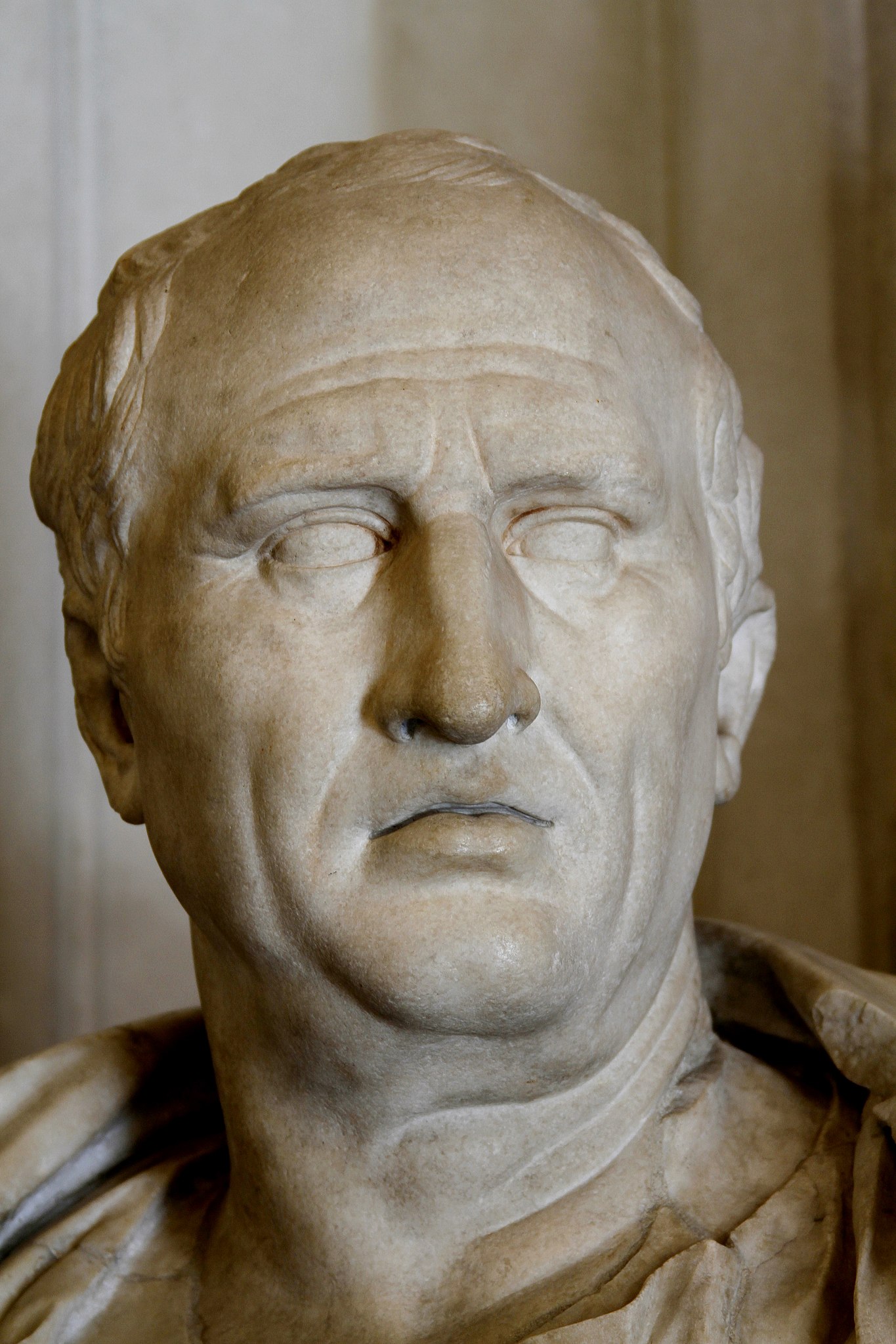


Marcus Tullius Cicero was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC.
His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocabulary with neologisms such as evidentia, humanitas, qualitas, quantitas, and essentia, distinguishing himself as a translator and philosopher.


Marcus Tullius Cicero was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC.
His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocabulary with neologisms such as evidentia, humanitas, qualitas, quantitas, and essentia, distinguishing himself as a translator and philosopher.



Francesco Petrarca was an Italian poet, the founder of European humanism, and one of the greatest figures of the Italian Proto-Renaissance.
Petrarca studied at the University of Montpellier, then at the University of Bologna, in 1330 entered the service of Cardinal Giovanni Colonna as a chaplain. Then he made various pilgrimages, in 1353 settled in Milan at the court of Archbishop Giovanni Visconti, and carried out important diplomatic missions. Petrarca spent the last years of his life in the village of Arquà near Padua.
Since 1337 Petrarca began to write literary works: these were historical poems in Latin and lyric poems in Italian. In 1327 Francesco saw Laura for the first time, undivided love for which was the main source of his poetry. Laura was for him an object of adoration and pure platonic love. Despite the fact that they saw each other only a few times and were not really acquainted, Petrarca carried this feeling through his life.
Passionate about ancient culture, Petrarch deciphered and commented on the manuscripts of Cicero, Quintilian and others. He opposed medieval scholasticism interest in the earthly purpose of man, argued that the nobility of man depends not on the nobility of origin, but on his virtue. Petrarca highly valued the mind and creative abilities of man, and these humanistic ideas found vivid expression in his lyrics, revealing the inner world of man. Petrarca's work laid the foundation for the formation of Italian humanism. He also dreamed of the unification of Italy, the revival of the former greatness of Rome.
Francesco Petrarca had one of the richest libraries of his time, where ancient Roman writers, poets, historians, philosophers were represented. He was one of the brightest representatives of the culture of the Renaissance. Petrarca's works are characterized by perfection of form and musicality of verse, which played a significant role in the development of European poetry. Among his works are the poem "Africa" about the Second Punic War in Latin, allegorical pastoral eclogues "Bucolics" (1346/1357), a book of songs "My Italy", "Noble Spirit", sonnets, etc.

![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


















![[PS. PLINY or SEXTUS AURELIUS VICTOR (c.320-390), here attributed to SUETONIUS (c.69-c.122)]](/assets/image/picture_2279392/a798a/95cf59293202b19a9dc4a52962fc9d1c1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[PS. PLINY or SEXTUS AURELIUS VICTOR (c.320-390), here attributed to SUETONIUS (c.69-c.122)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2279392/a798a/95cf59293202b19a9dc4a52962fc9d1c1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)



























![[Otto F Ege (1888-1951)]](/assets/image/picture_1224251/d61d4/2b91d3cddec40f58a9c6819b11b58c111607468400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Otto F Ege (1888-1951)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1224251/d61d4/2b91d3cddec40f58a9c6819b11b58c111607468400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)

















