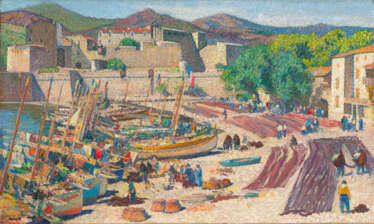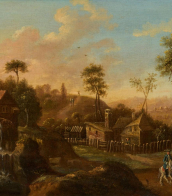architecture art
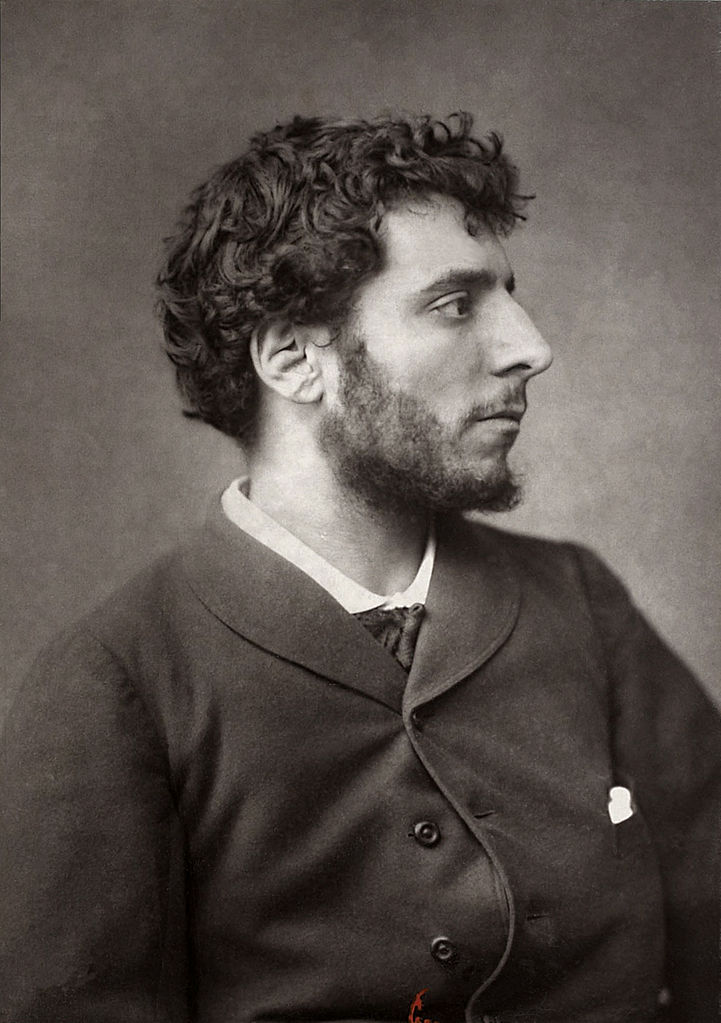

Henri-Jean Guillaume Martin was a French painter. Elected to the Académie des Beaux-Arts in 1917, he is known for his early 1920s work on the walls of the Salle de l'Assemblée générale, where the members of the Conseil d'État meet in the Palais-Royal in Paris. Other notable institutions that have featured his Post-Impressionist paintings in their halls through public procurement include the Élysée Palace, Sorbonne, Hôtel de Ville de Paris, Palais de Justice de Paris, as well as Capitole de Toulouse, although the Musée des Beaux-Arts de Bordeaux and Musée des Augustins also have sizeable public collections.
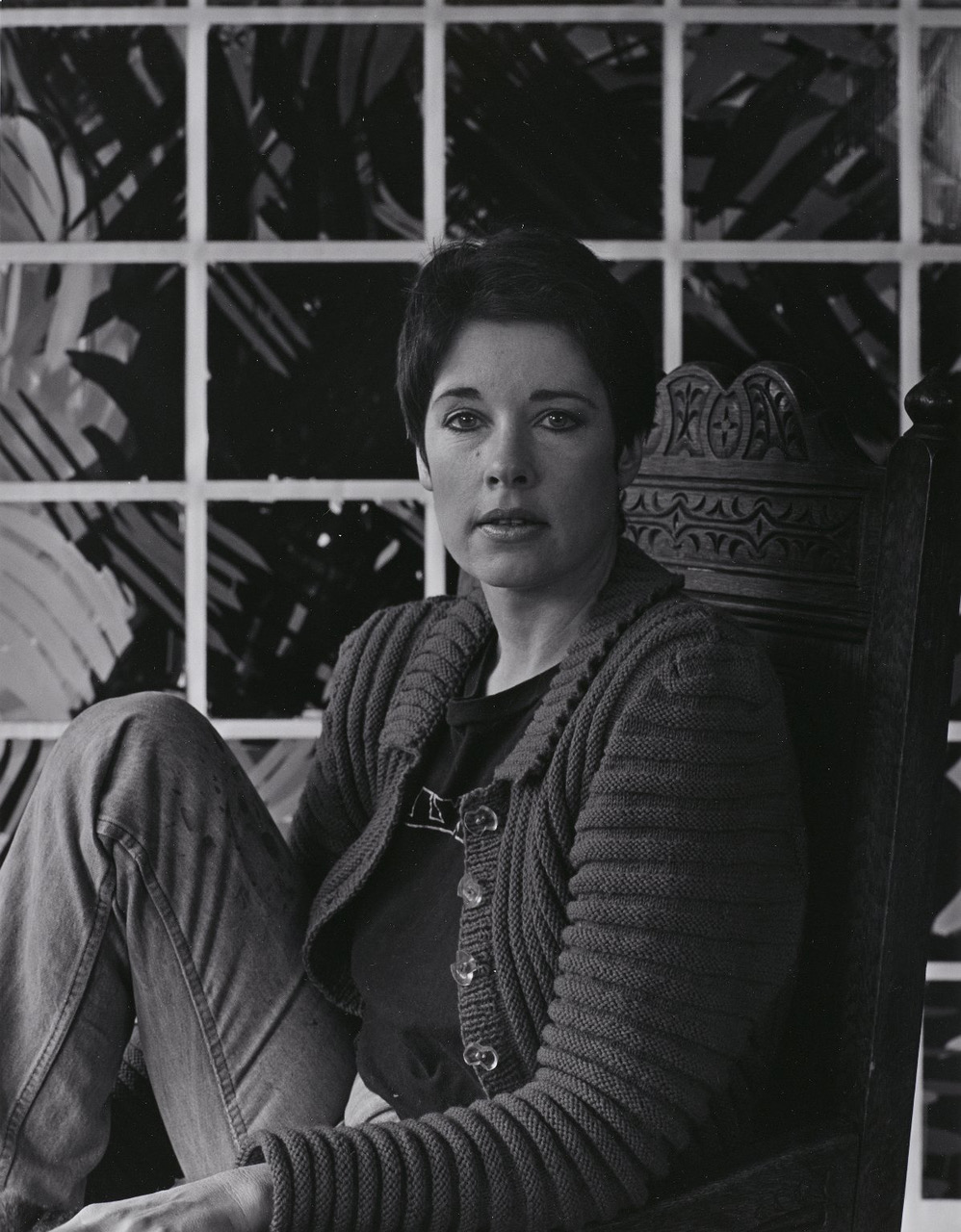


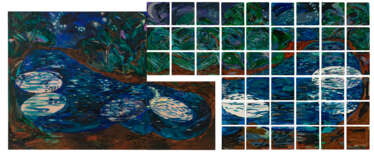
Jennifer Bartlett was an American artist. She was known for paintings and prints that combine the system-based aesthetic of conceptual art with the painterly approach of Neo-Expressionism. Many of her pieces were executed on small, square, enamel-coated steel plates that are combined in grid formations to create very large works.
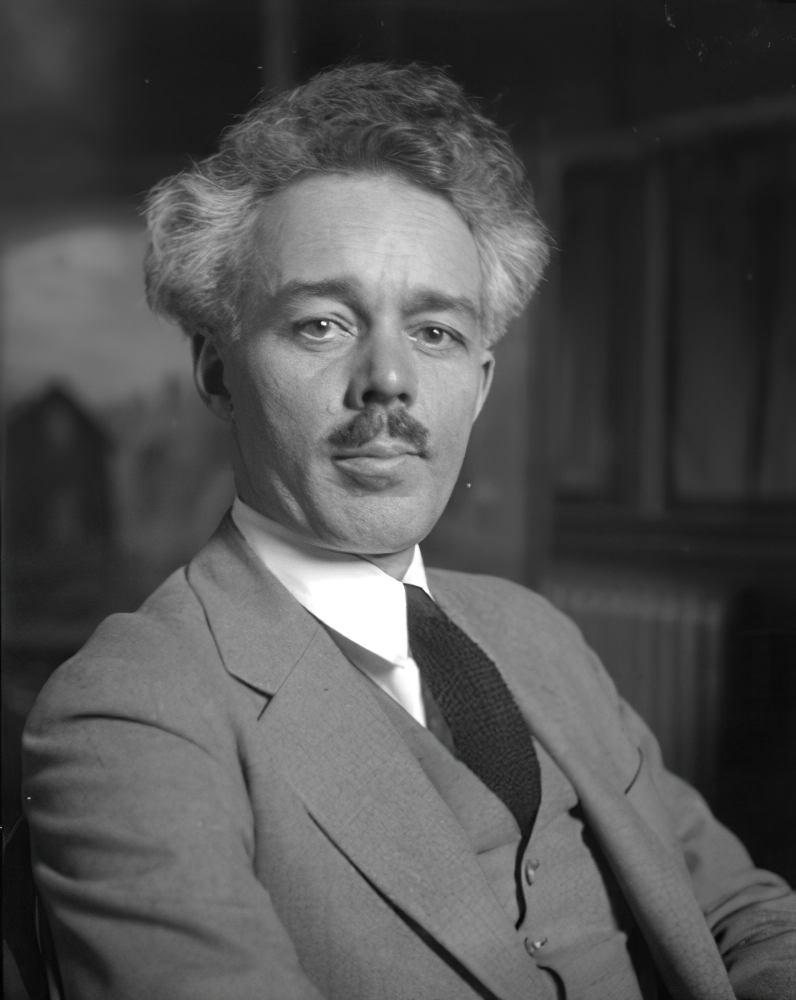


Lawren Stewart Harris was a Canadian painter, best known as a leading member of the Group of Seven. He played a key role as a catalyst in Canadian art and as a visionary in Canadian landscape art.
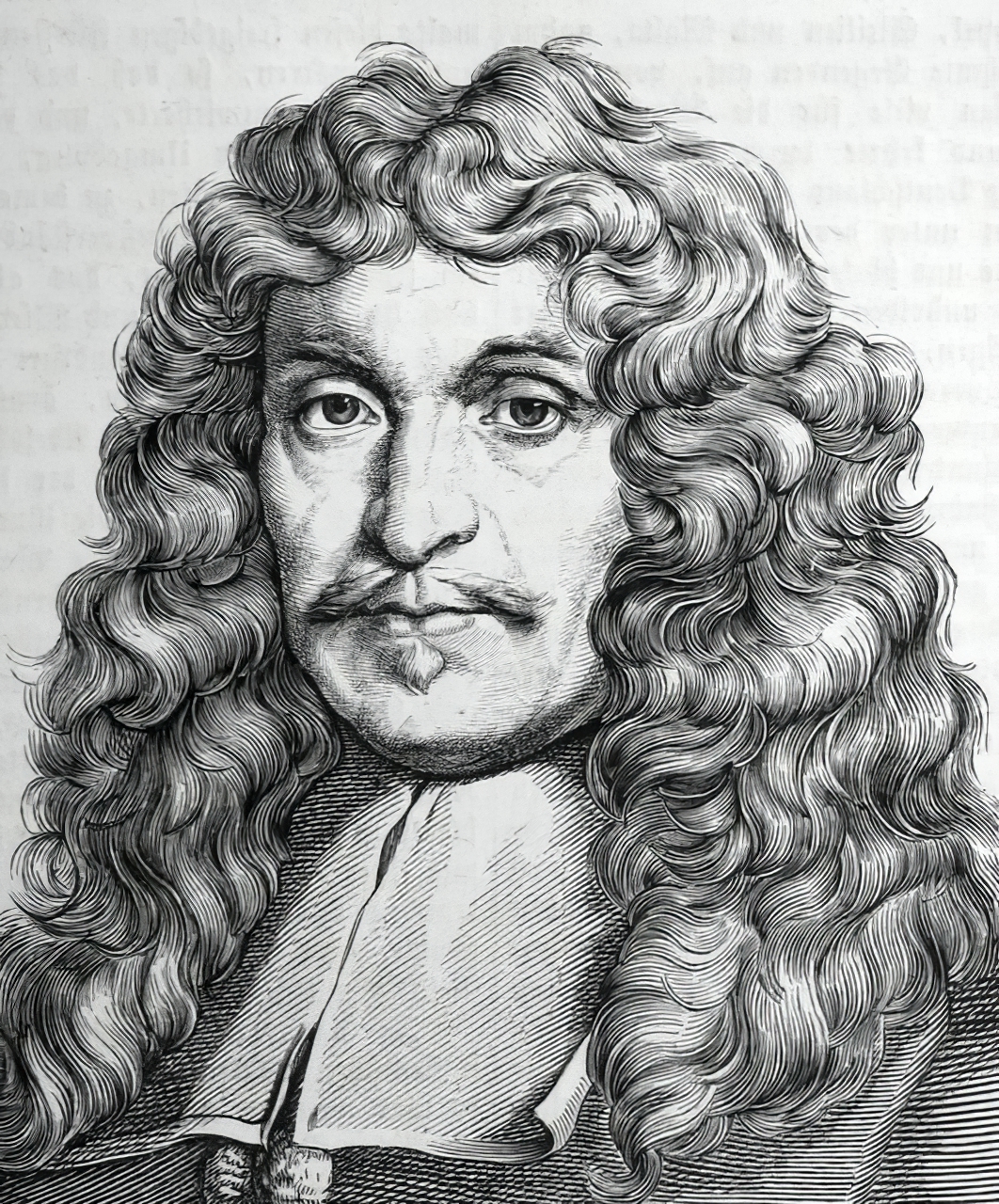


Joachim von Sandrart was a German Baroque art-historian and painter, active in Amsterdam during the Dutch Golden Age. He is most significant for his collection of biographies of Dutch and German artists the Teutsche Academie, published between 1675 and 1680.
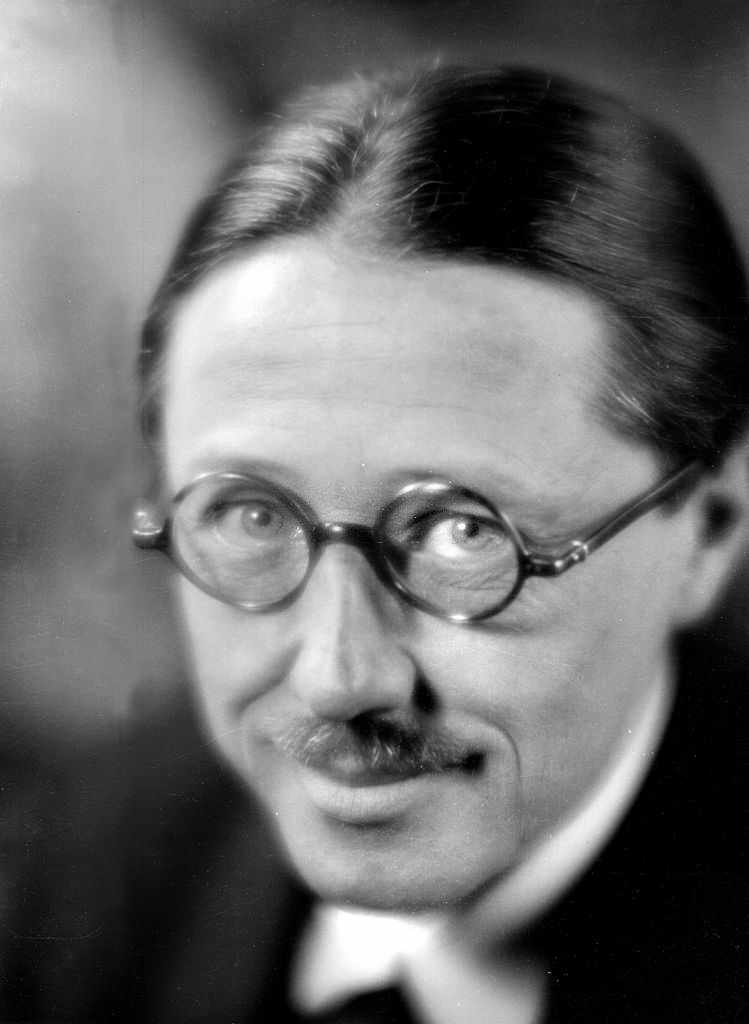

Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann, (sometimes called Jacques-Émile Ruhlmann), was a French furniture designer and interior decorator, who was one of the most important figures in the Art Deco movement. His furniture featured sleek designs, expensive and exotic materials and extremely fine craftsmanship, and became a symbol of the luxury and modernity of Art Deco. It also produced a reaction from other designers and architects, such as Le Corbusier, who called for simpler, functional furniture.
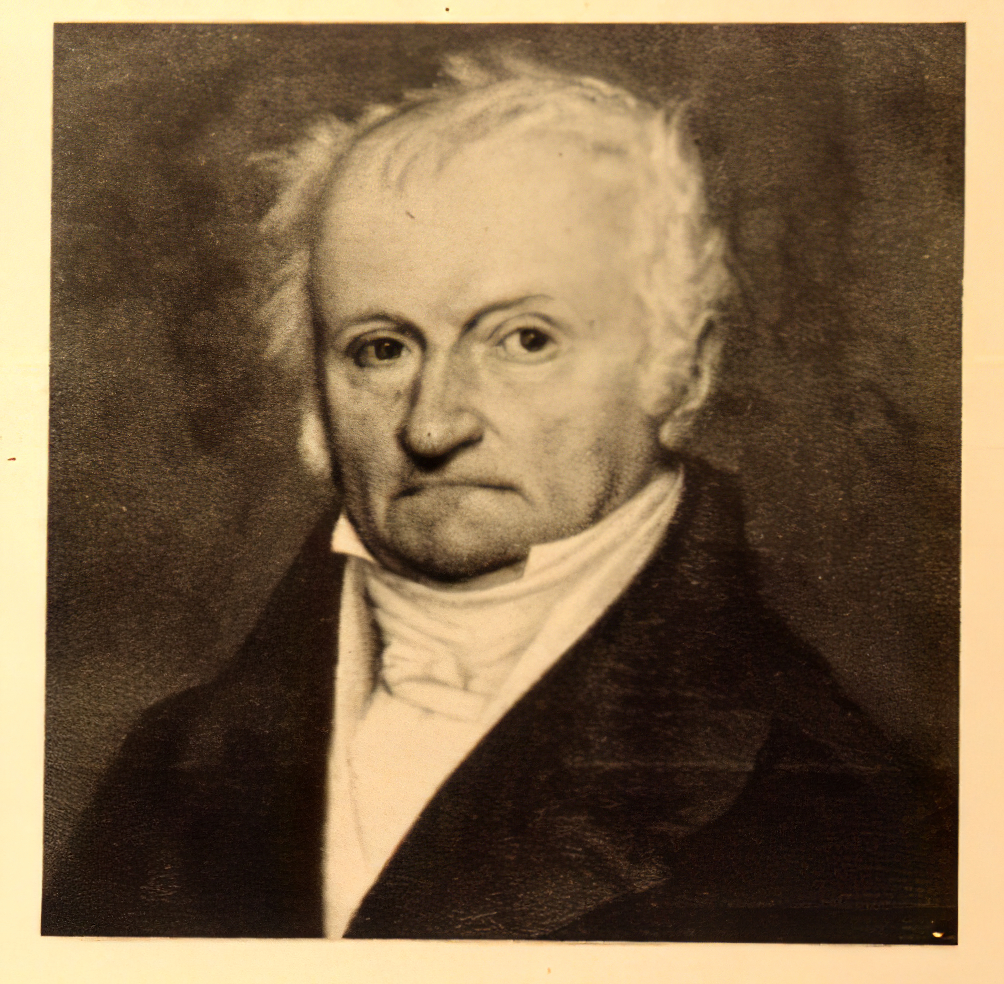
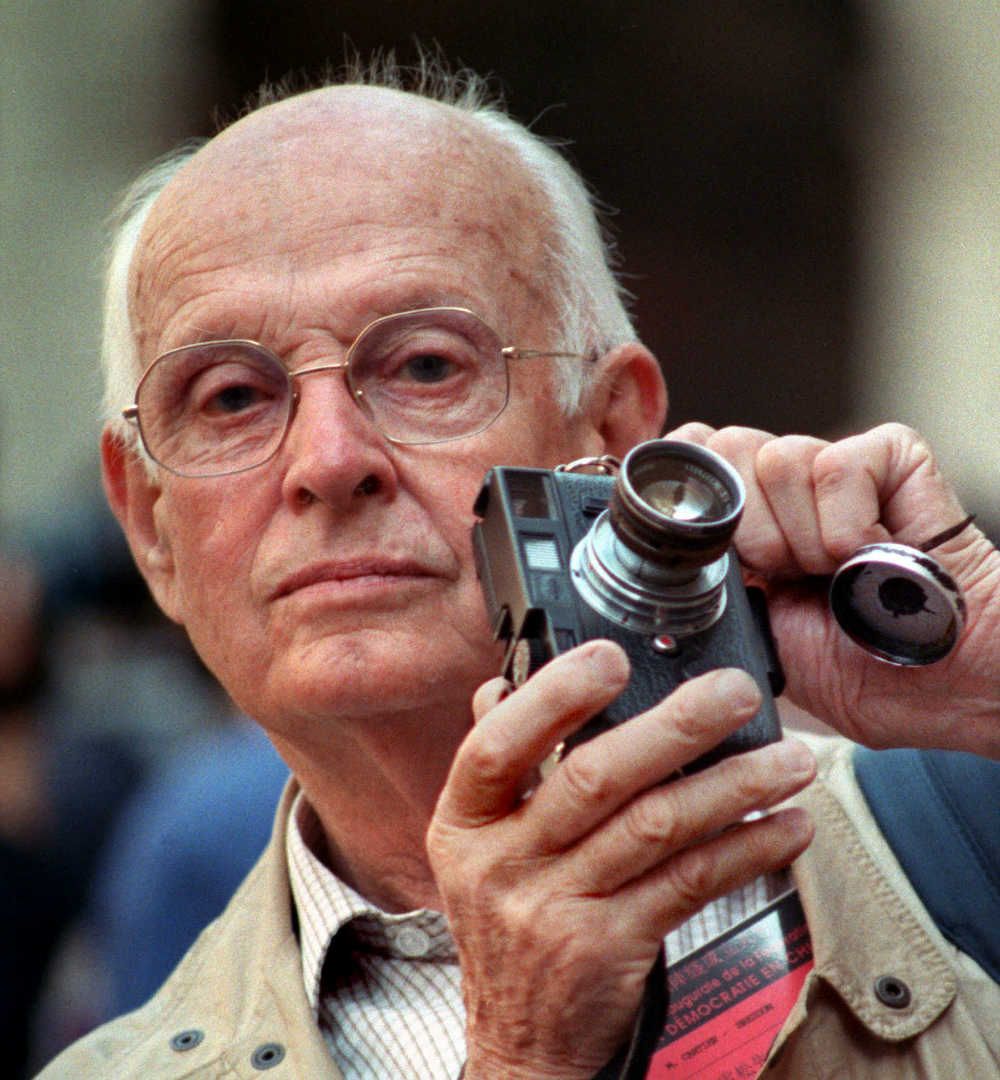




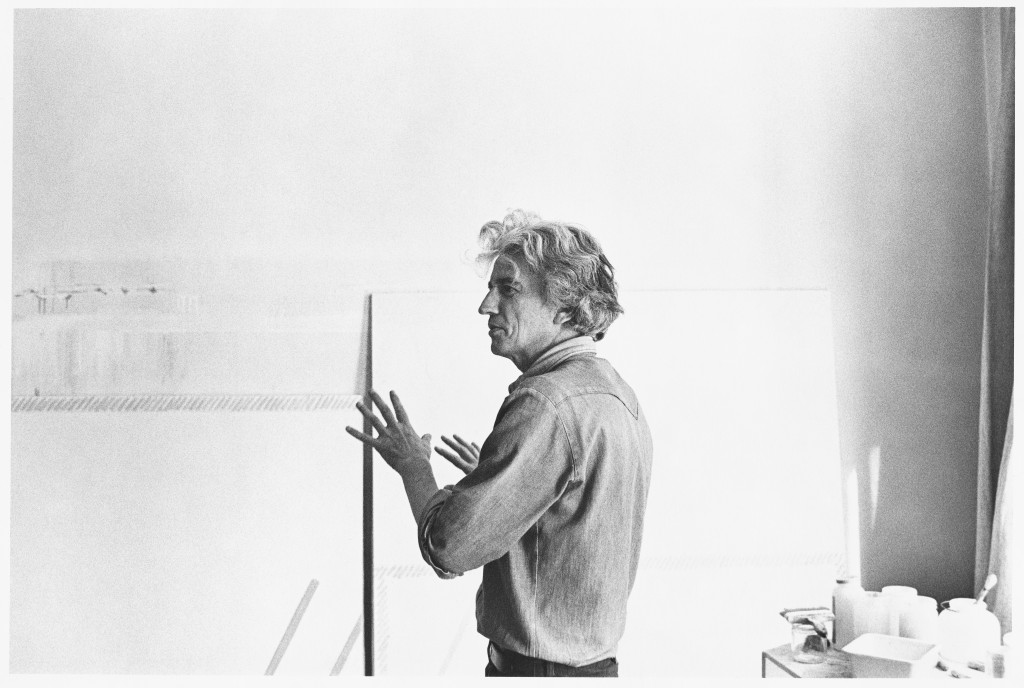
Henri Cartier-Bresson was a French artist renowned for his groundbreaking work in photography, particularly in the realms of photojournalism and street photography. Born on August 22, 1908, in Chanteloup, France, Cartier-Bresson's early artistic endeavors were in painting, which he began studying at the age of five. His transition to photography was marked by his adoption of a 35mm Leica camera in 1931, a tool that became synonymous with his work.
Henri Cartier-Bresson's photography is celebrated for its unique blend of spontaneity and composition, capturing moments that reveal deeper truths about their subjects. His theory of "the decisive moment" – that is, capturing an event that is ephemeral and spontaneous, yet significant – has had a profound influence on the field of photography. His work has been exhibited in prestigious venues such as the Museum of Modern Art in New York and is held in high esteem in art collections worldwide.
In addition to his personal achievements, Henri Cartier-Bresson was a co-founder of Magnum Photos in 1947, a cooperative agency for worldwide photographers that significantly influenced photojournalism. Later in his career, Cartier-Bresson returned to painting and drawing, demonstrating his lifelong commitment to the arts.
For art collectors and experts, Henri Cartier-Bresson's work offers a pivotal exploration of 20th-century photography, blending artistic vision with the unguarded moments of life. His influence extends beyond his images, shaping the way we perceive and engage with visual narratives.
To explore more about Henri Cartier-Bresson's influential career and works, and to stay updated on exhibitions or sales featuring his photography, you might consider subscribing to updates from art institutions or galleries that frequently showcase his work.


Henri Cartier-Bresson was a French artist renowned for his groundbreaking work in photography, particularly in the realms of photojournalism and street photography. Born on August 22, 1908, in Chanteloup, France, Cartier-Bresson's early artistic endeavors were in painting, which he began studying at the age of five. His transition to photography was marked by his adoption of a 35mm Leica camera in 1931, a tool that became synonymous with his work.
Henri Cartier-Bresson's photography is celebrated for its unique blend of spontaneity and composition, capturing moments that reveal deeper truths about their subjects. His theory of "the decisive moment" – that is, capturing an event that is ephemeral and spontaneous, yet significant – has had a profound influence on the field of photography. His work has been exhibited in prestigious venues such as the Museum of Modern Art in New York and is held in high esteem in art collections worldwide.
In addition to his personal achievements, Henri Cartier-Bresson was a co-founder of Magnum Photos in 1947, a cooperative agency for worldwide photographers that significantly influenced photojournalism. Later in his career, Cartier-Bresson returned to painting and drawing, demonstrating his lifelong commitment to the arts.
For art collectors and experts, Henri Cartier-Bresson's work offers a pivotal exploration of 20th-century photography, blending artistic vision with the unguarded moments of life. His influence extends beyond his images, shaping the way we perceive and engage with visual narratives.
To explore more about Henri Cartier-Bresson's influential career and works, and to stay updated on exhibitions or sales featuring his photography, you might consider subscribing to updates from art institutions or galleries that frequently showcase his work.
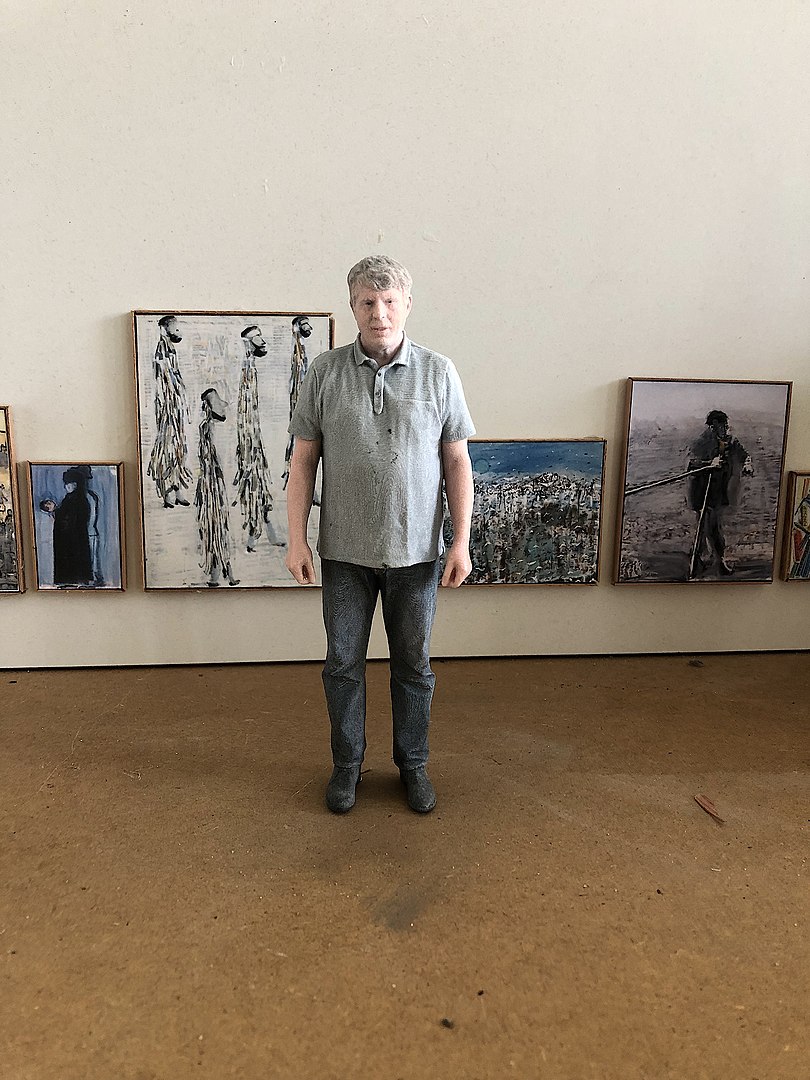


Thomas Hartmann is a German painter. He taught at the Nuremberg Art Academy until his retirement in 2018.
Thomas Hartmann is one of the most influential German painters of recent decades.