armorial &
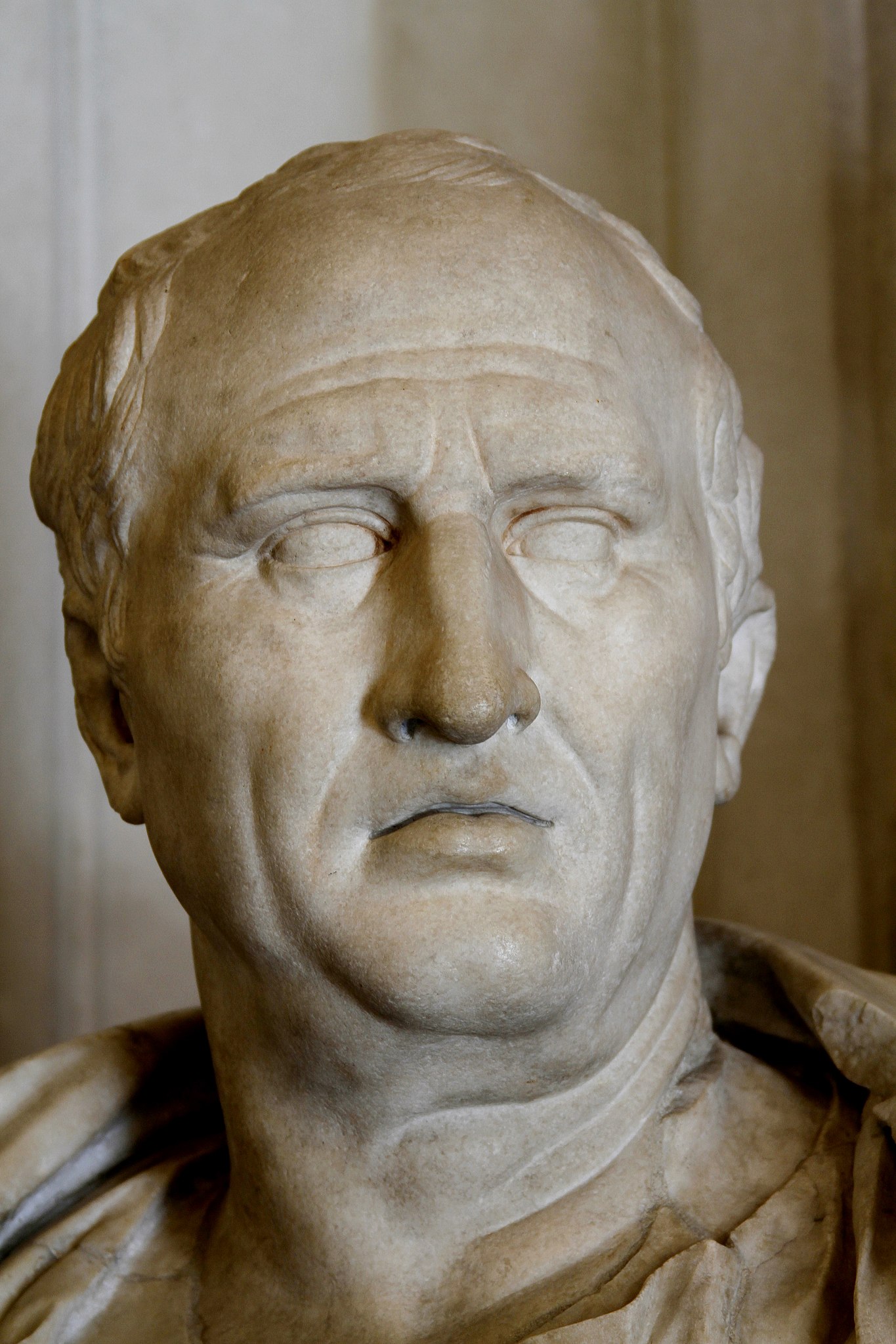

Marcus Tullius Cicero was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC.
His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocabulary with neologisms such as evidentia, humanitas, qualitas, quantitas, and essentia, distinguishing himself as a translator and philosopher.


The Besançon illuminator was a French miniaturist painter from Besançon who worked in that city in the 1440s-1470s, decorating mainly the Books of Hours.
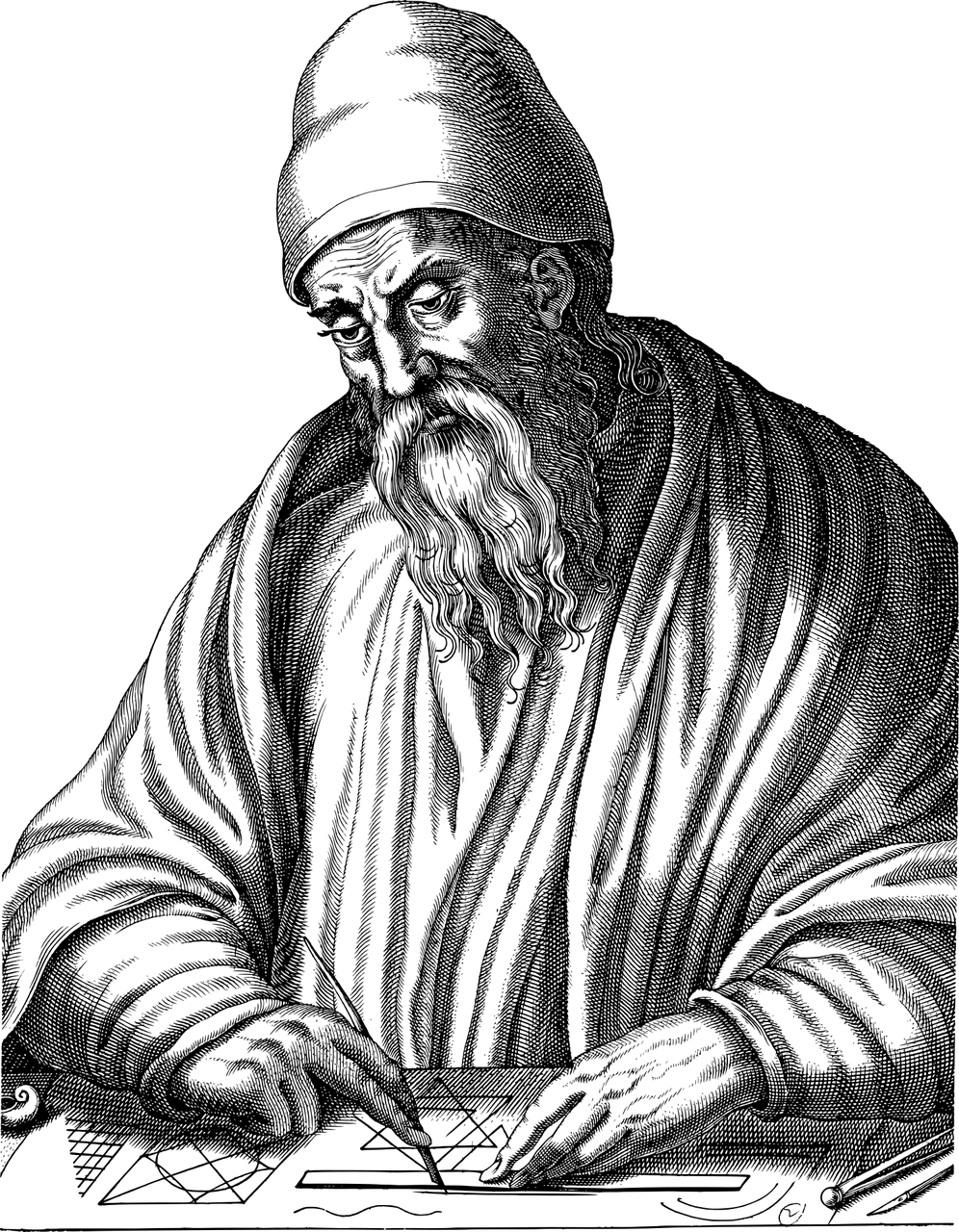


Euclid (Greek: Εὐκλείδης) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the Elements treatise, which established the foundations of geometry that largely dominated the field until the early 19th century. His system, now referred to as Euclidean geometry, involved new innovations in combination with a synthesis of theories from earlier Greek mathematicians, including Eudoxus of Cnidus, Hippocrates of Chios, Thales and Theaetetus. With Archimedes and Apollonius of Perga, Euclid is generally considered among the greatest mathematicians of antiquity, and one of the most influential in the history of mathematics.
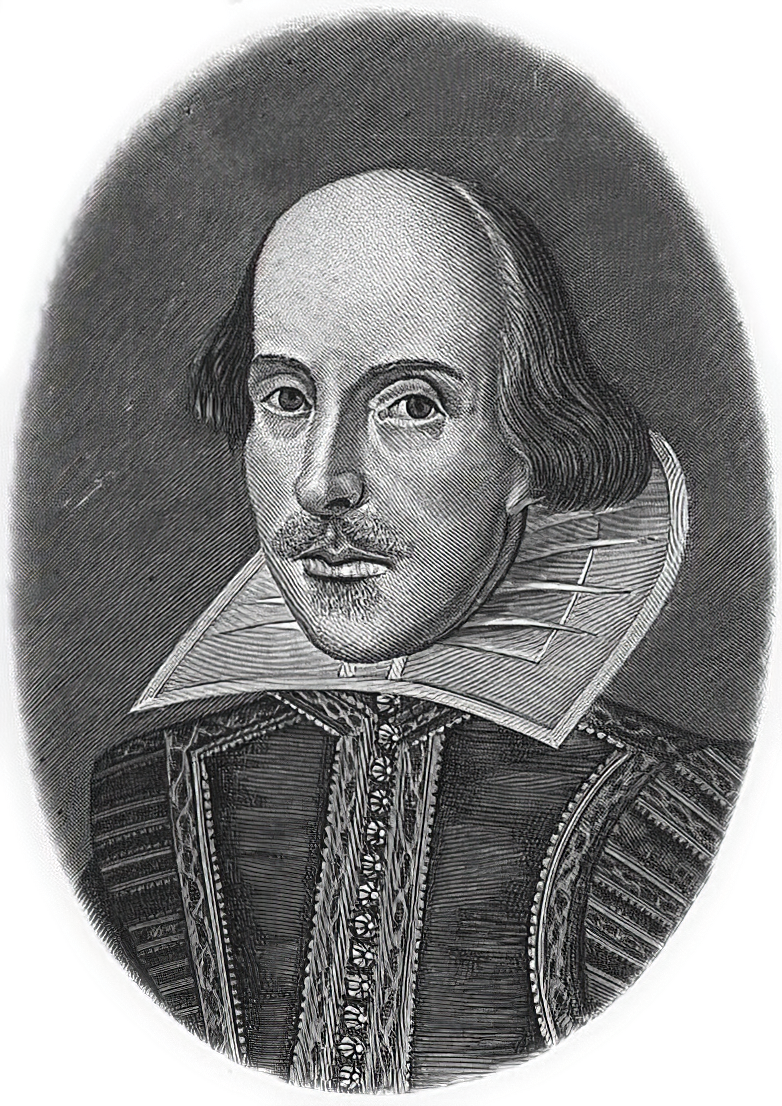


William Shakespeare was a British poet and playwright and writer.
William's father, John Shakespeare, was a merchant and official in Stratford. There are reports that he was a sailor for a time before joining a theater company in London. Beginning in the 1590s, Shakespeare began writing plays, and in 1593 he published a poem, Venus and Adonis, which became popular. He dedicated it to the Duke of Southampton, who was a philanthropist and patron of talent, and soon his business was booming.
From 1592 to 1600 Shakespeare wrote his dramas and romantic comedies "Richard III", "The Taming of the Shrew", "Romeo and Juliet", "A Midsummer Night's Dream" and "The Merchant of Venice", as well as the comedies "Much Ado About Nothing", "Twelfth Night" and the tragedy "Julius Caesar". The playwright's business was so successful that he even bought a large house in Stratford. In 1599, Shakespeare became one of the owners, playwright and actor of the new theater "Globe". In 1603 King James took Shakespeare's troupe under his direct patronage. In the mature period, the great playwright turned to tragedies, there were "Hamlet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth" and others.
Although in the 19th century researchers had some doubts about the authorship of many of these works, William Shakespeare is considered the greatest English playwright, one of the best playwrights in the world. His plays have been translated into all major languages and to this day form the basis of the world theatrical repertoire, most of them have been screened many times. According to the Guinness Book of Records, Shakespeare remains the world's best-selling playwright, and his plays and poems have sold more than 4 billion copies in the nearly 400 years since his death.
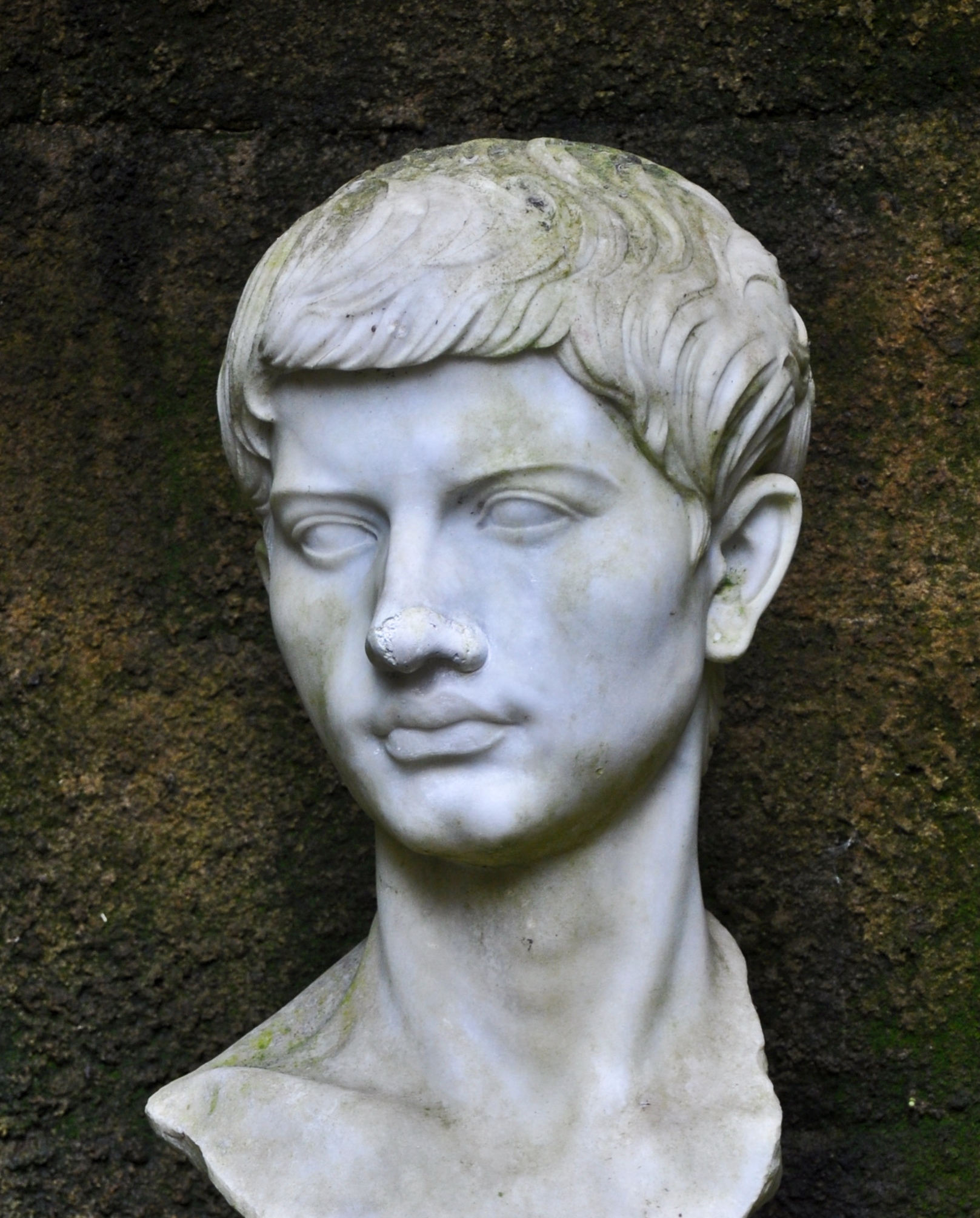


Publius Vergilius Maro, usually called Virgil or Vergil, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the Eclogues (or Bucolics), the Georgics, and the epic Aeneid. A number of minor poems, collected in the Appendix Vergiliana, were attributed to him in ancient times, but modern scholars consider his authorship of these poems as dubious.
Virgil's work has had wide and deep influence on Western literature, most notably Dante's Divine Comedy, in which Virgil appears as the author's guide through Hell and Purgatory.
Virgil has been traditionally ranked as one of Rome's greatest poets. His Aeneid is also considered a national epic of ancient Rome, a title held since composition.

Francis Picabia, born Francis-Marie Martinez de Picabia, was a French avant-garde painter, poet, and typographist, whose work is celebrated for its diversity and innovation. His journey through various art movements, including Impressionism, Cubism, Dadaism, and Surrealism, showcases his refusal to be confined by any one style. Picabia's art is known for its eclectic nature, often blending mechanical elements with organic forms, thereby challenging traditional perceptions of art and beauty.
Picabia's significant contribution to the art world lies not just in his varied artistic output but also in his philosophical approach to creation. He believed in the freedom of expression, often using his art to critique societal norms and the art establishment itself. This rebellious spirit made him a pivotal figure in the Dada movement, where his works were celebrated for their irony and disdain for conventional art values.
Among his notable works, "Amorous Parade" and "I See Again in Memory My Dear Udnie" stand out, housed in prestigious institutions like the Museum of Modern Art in New York. These pieces exemplify Picabia's mastery over blending different elements of art movements, creating works that remain influential to this day. His legacy is not just in the pieces he created but also in his attitude towards art, encouraging future generations to challenge and redefine the boundaries of creativity.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Picabia's works represent not only significant artistic achievements but also valuable insights into the evolution of modern art. To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Francis Picabia, sign up for updates. This subscription is an essential resource for enthusiasts looking to enrich their collections with pieces from one of the most innovative artists of the 20th century.
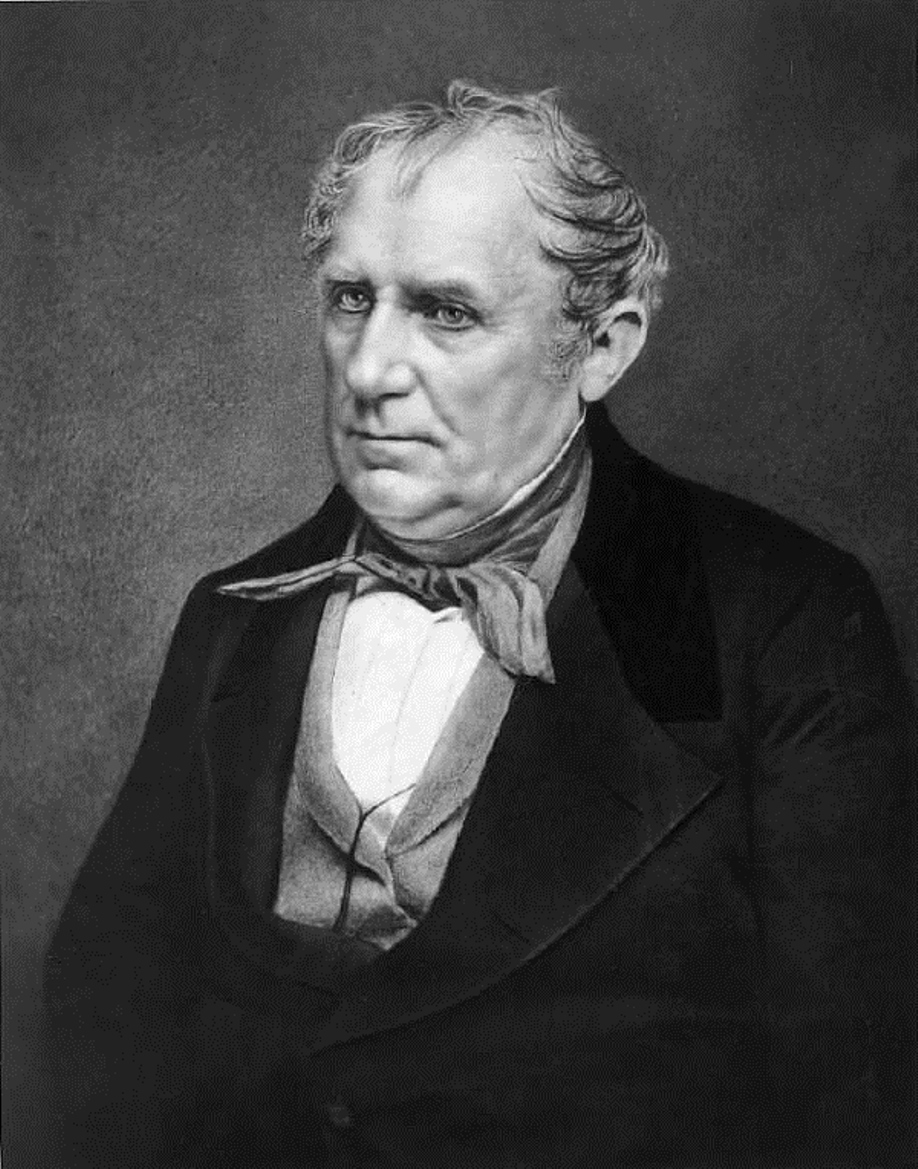


James Fenimore Cooper is an American writer and the founder of the Western genre.
Cooper is the first major American novelist, he wrote a whole series of novels from American life: "The Pioneers" (1823), "The Last of the Mohicans" (1826), "The Prairie" (1827), "The Pathfinder" (1840), "The Beastmaster, or the First Warpath" (1841). The author fascinatingly and vividly describes how Europeans waged wars among themselves on the American continent, involving Indian tribes in these strife. All of these works were a huge success in 19th century Europe and are still being reprinted today.
At the height of his popularity, Cooper spent seven years in Europe, and then returned to the United States, where he wrote works on military-historical and maritime themes until his advanced old age. Among them are "The Pilot, or Maritime History" (1823), "The Red Corsair" (1827).




Master of the Rouen Échevinage was a French artist, one of the leading 15th-century Rouen illustrators, named after the magnificent manuscripts he painted for the Bibliothèque des Echevins in Rouen. He was active between the 1450s and 1480s.
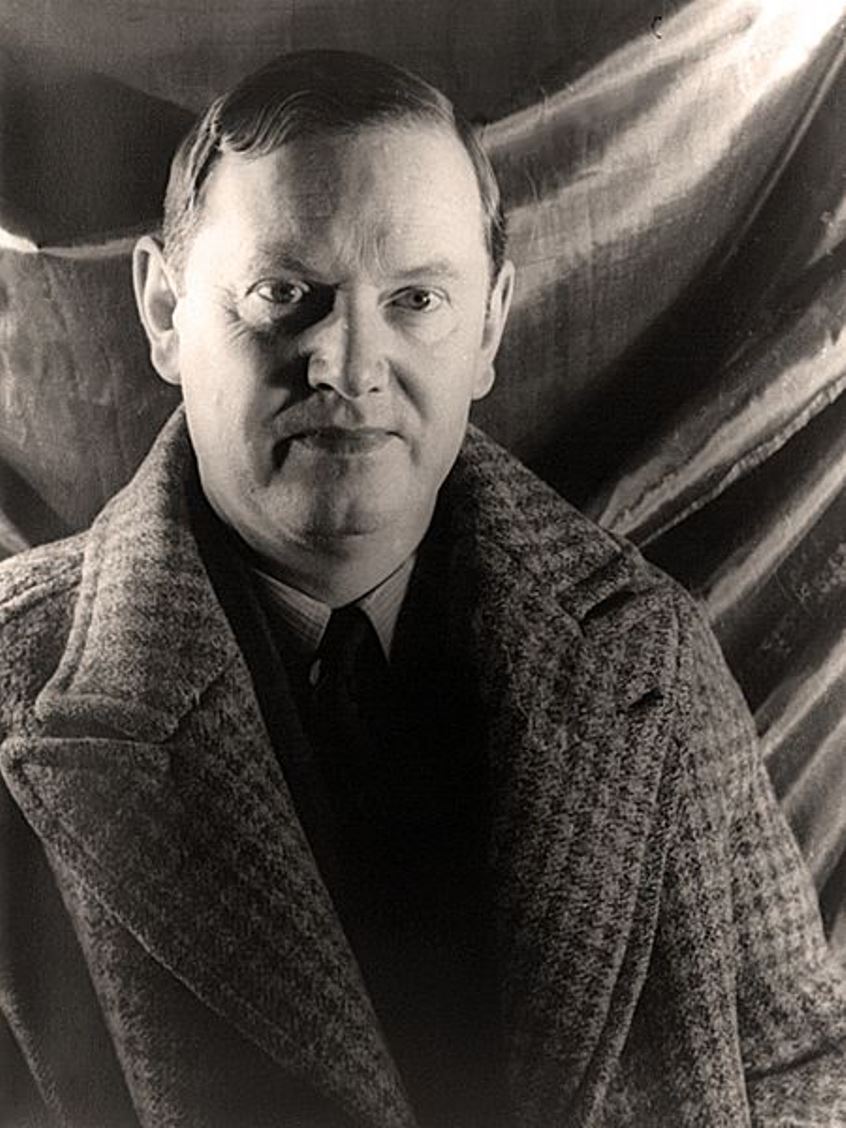


Evelyn Waugh, full name Arthur Evelyn St. John Waugh, was a British satirical writer, travel writer and historian.
Evelyn Waugh studied at Lancing College in Sussex and at Hertford College in Oxford. He then began traveling and writing, soon earning a reputation as a witty satirist. He visited Ethiopia and the Belgian Congo, and traveled to South America. His works are almost always based on personal experience; notable among the early ones are Decline and Fall (1928), Nasty Bodies (1930), Black Mischief (1932), and others.
During World War II, Evelyn Waugh served in the Royal Marines and the Royal Horse Guards. Written at this time, the novel "Return to Brideshead" (1945) is about an aristocratic English Roman Catholic family. In the trilogy "Men in Arms" (1952), "Officers and Gentlemen" (1955) and "Unconditional Surrender" (1961), the author conducted a serious analysis of the events of World War II, as an eternal struggle between good and evil, civilization and barbarism. Later on these works were filmed television series.
Evelyn Waugh also left a significant trace in journalism and literary criticism, he is considered one of the finest stylists in English prose of the XX century.
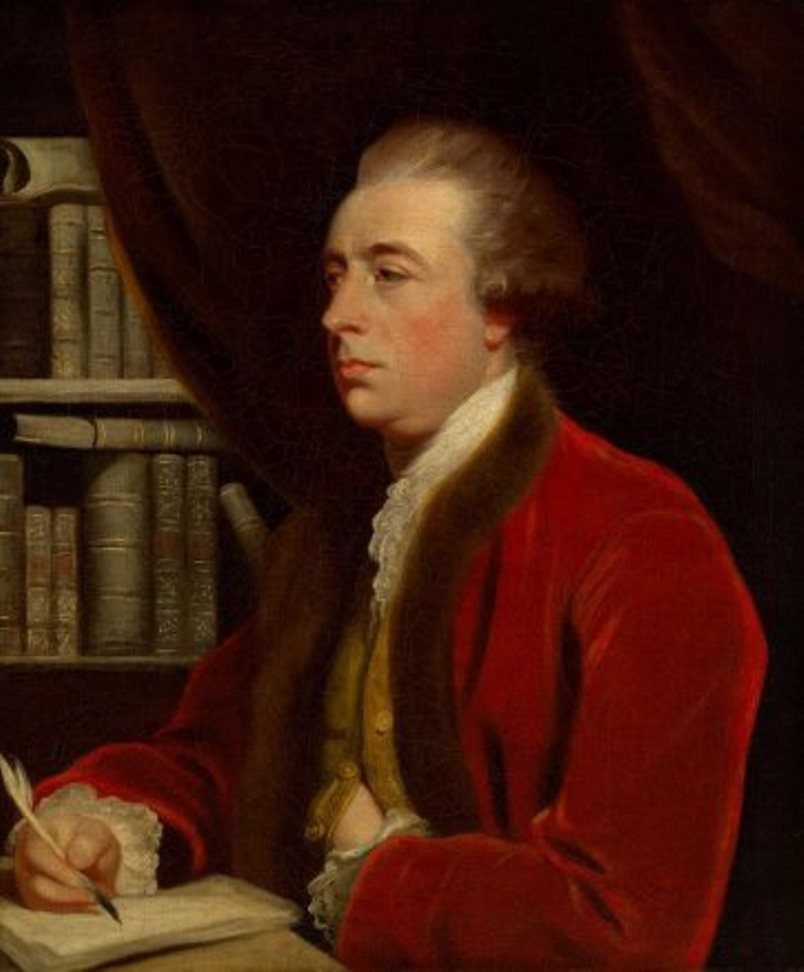

John Hawkesworth was a British writer, playwright and book editor.
In collaboration with Samuel Johnson, Hawkesworth founded the periodical The Adventurer. He wrote poems and articles for this publication and for the Gentleman's Magazine, and edited the works of Swift (1754-1755). Hawksworth adapted several literary works for the theater and also composed various original dramatic works himself.
John Hawksworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to compile An Account of Voyages made in the Southern Hemisphere (1773), devoted mainly to the exploratory voyages of Captain James Cook.



Euclid (Greek: Εὐκλείδης) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the Elements treatise, which established the foundations of geometry that largely dominated the field until the early 19th century. His system, now referred to as Euclidean geometry, involved new innovations in combination with a synthesis of theories from earlier Greek mathematicians, including Eudoxus of Cnidus, Hippocrates of Chios, Thales and Theaetetus. With Archimedes and Apollonius of Perga, Euclid is generally considered among the greatest mathematicians of antiquity, and one of the most influential in the history of mathematics.













































![[VIEILH DE VARENNES, Raymond-Augustin (fl. c. 1790) Jean-Michel MOREAU (1741–1814)]](/assets/image/picture_2943505/fd768/abf0e404e7daa93bfaeacc83883ab1631689199200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[VIEILH DE VARENNES, Raymond-Augustin (fl. c. 1790) Jean-Michel MOREAU (1741–1814)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2943505/fd768/abf0e404e7daa93bfaeacc83883ab1631689199200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![McIAN, [Robert] R. (1803 – 1856) and James LOGAN (1797–1872)](/assets/image/picture_2943586/c610b/bc8a381ac624c9318364d86e25534b151689199200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![McIAN, [Robert] R. (1803 – 1856) and James LOGAN (1797–1872)](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2943586/c610b/bc8a381ac624c9318364d86e25534b151689199200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)








![[VIEILH DE VARENNES, Raymond-Augustin (fl. c. 1790) Jean-Michel MOREAU (1741–1814)]](/assets/image/picture_3615552/96cab/d9a9a9b26b2aad77d2e293aeae2975f41702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[VIEILH DE VARENNES, Raymond-Augustin (fl. c. 1790) Jean-Michel MOREAU (1741–1814)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3615552/96cab/d9a9a9b26b2aad77d2e293aeae2975f41702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)