astronomy & astrology

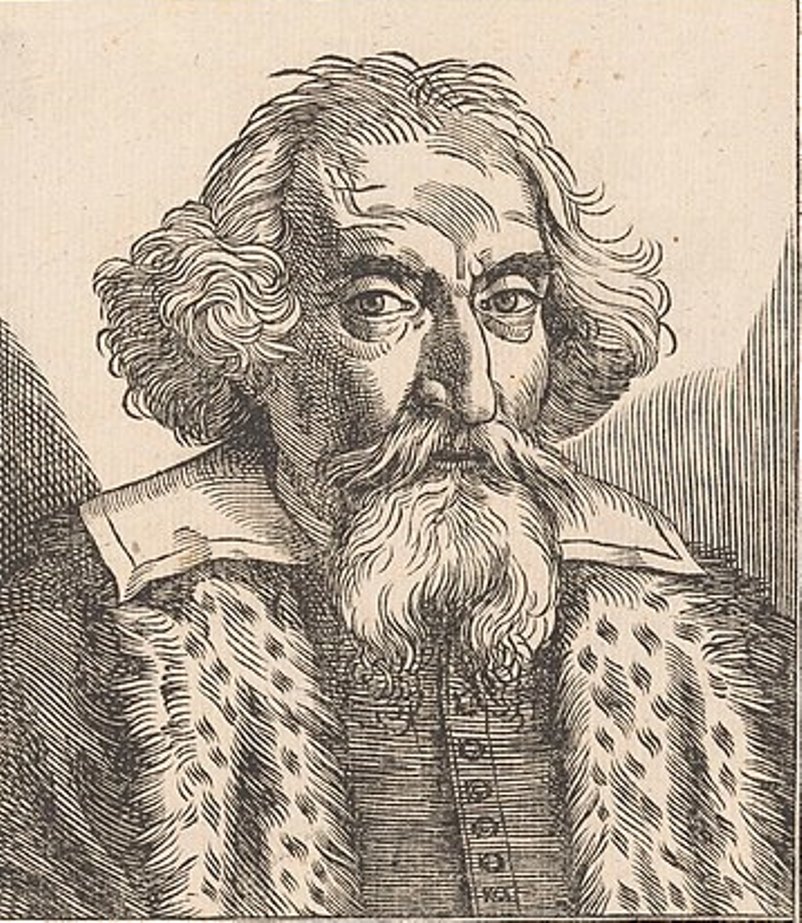
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.
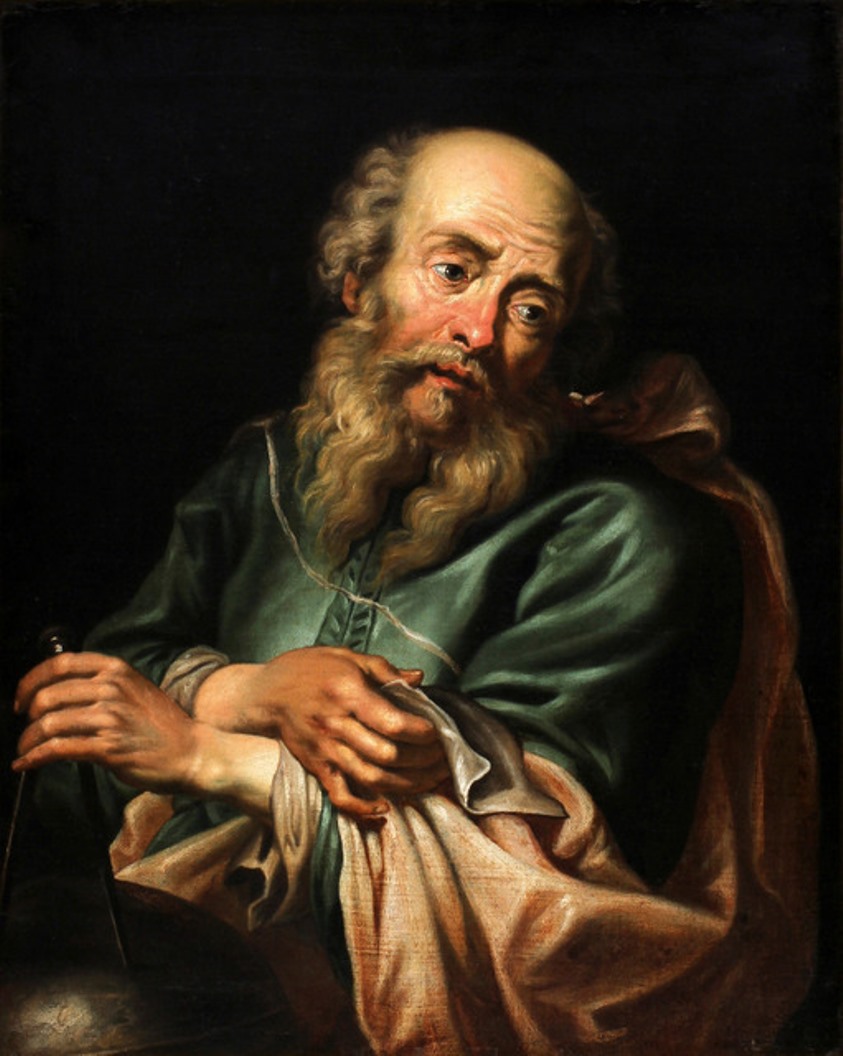


Galileo Galilei was an Italian naturalist, physicist, mechanic, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician.
Using his own improved telescopes, Galileo Galilei observed the movements of the Moon, Earth's satellites, and the stars, making several breakthrough discoveries in astronomy. He was the first to see craters on the Moon, discovered sunspots and the rings of Saturn, and traced the phases of Venus. Galileo was a consistent and convinced supporter of the teachings of Copernicus and the heliocentric system of the world, for which he was subjected to the trial of the Inquisition.
Galileo is considered the founder of experimental and theoretical physics. He is also one of the founders of the principle of relativity in classical mechanics. Overall, the scientist had such a significant impact on the science of his time that he cannot be overemphasized.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Galileo Galilei was an Italian naturalist, physicist, mechanic, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician.
Using his own improved telescopes, Galileo Galilei observed the movements of the Moon, Earth's satellites, and the stars, making several breakthrough discoveries in astronomy. He was the first to see craters on the Moon, discovered sunspots and the rings of Saturn, and traced the phases of Venus. Galileo was a consistent and convinced supporter of the teachings of Copernicus and the heliocentric system of the world, for which he was subjected to the trial of the Inquisition.
Galileo is considered the founder of experimental and theoretical physics. He is also one of the founders of the principle of relativity in classical mechanics. Overall, the scientist had such a significant impact on the science of his time that he cannot be overemphasized.



Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Galileo Galilei was an Italian naturalist, physicist, mechanic, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician.
Using his own improved telescopes, Galileo Galilei observed the movements of the Moon, Earth's satellites, and the stars, making several breakthrough discoveries in astronomy. He was the first to see craters on the Moon, discovered sunspots and the rings of Saturn, and traced the phases of Venus. Galileo was a consistent and convinced supporter of the teachings of Copernicus and the heliocentric system of the world, for which he was subjected to the trial of the Inquisition.
Galileo is considered the founder of experimental and theoretical physics. He is also one of the founders of the principle of relativity in classical mechanics. Overall, the scientist had such a significant impact on the science of his time that he cannot be overemphasized.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits.
Kepler created the three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did seminal work in optics and geometry, calculated the most accurate astronomical tables, and made many inventions and discoveries in physics on which further scientific discoveries by advanced scientists were based.


Fortunio Liceti (Latin: Fortunius Licetus) was an Italian physician, natural philosopher, writer and educator.
Liceti studied philosophy and medicine at the University of Bologna and earned doctorates in these disciplines. He taught logic and philosophy at the University of Pisa, and became professor of philosophy at the University of Padua and the University of Bologna. At the University of Padua, Liceti became friends with Galileo Galilei.
Liceti's inquisitive mind was interested in a wide range of subjects: from genetics and reproduction to gems and animals. In general, Fortunio Liceti was a very industrious and prolific scientist: he published a book each year, writing more than seventy works on a wide range of subjects, including the human soul, reproduction, and birth defects.
In 1616, Liceti wrote and published the first edition of De monstruorum causis, natura et differentiis (On the Causes, Nature, and Differences of Monsters), a chronologically ordered catalog of monsters from antiquity to the seventeenth century. Among these monsters were infants with congenital malformations. Liceti was one of the first scholars to attempt to systematically categorize birth defects according to their causes, including numerous causes not related to the supernatural. This topic interested the scientist greatly and he returned to it several times during his life, supplementing it with illustrations, among other things. From 1640 to 1650. Liceti also wrote and published seven different volumes in which he answered questions from famous people on a wide variety of medical topics.
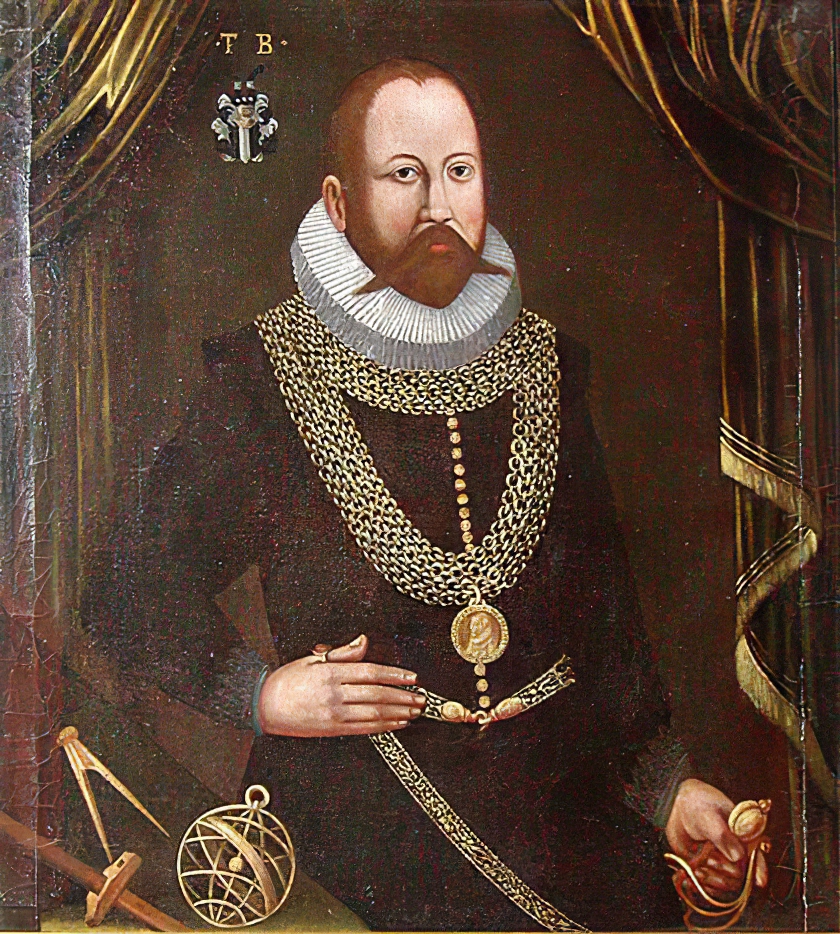


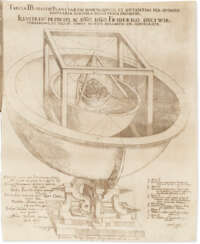
Tycho Brahe, born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, more commonly called Tycho, was a prominent Danish astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist of the Renaissance.
As a young man he traveled extensively throughout Europe, studying in Wittenberg, Rostock, Basel, and Augsburg and acquiring mathematical and astronomical instruments. In 1572 Tycho unexpectedly even for himself discovered a new star in Cassiopeia, and the publication of this turned the young Dane into an astronomer of European reputation. For further astronomical research he established an observatory and gathered around him modern progressive scientists.
Besides practicing astronomy, Tycho was an artist, scientist, and craftsman, and everything he undertook or surrounded himself with had to be innovative and beautiful. He even founded a printing house to produce and bind his manuscripts in his own way, and he perfected sanitary ware for convenience. His development of astronomical instruments and his work in measuring and fixing the positions of the stars laid a solid foundation for future discoveries.
Tycho's observations - the most accurate possible before the invention of the telescope - included a comprehensive study of the solar system and the precise positions of more than 777 fixed stars. What Tycho accomplished using only his simple instruments and intellect remains a remarkable achievement of the Renaissance.









![[GALILEO GALILEI (1564-1642) and Girolamo SPINELLI (c.1580-1647)]](/assets/image/picture_4734998/a317b/b78ba02793ea9f7c89bc2421c803edfc1752012000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[GALILEO GALILEI (1564-1642) and Girolamo SPINELLI (c.1580-1647)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4734998/a317b/b78ba02793ea9f7c89bc2421c803edfc1752012000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)










![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)




![Cosmographia [and] Ephemerides](/assets/image/picture_4401461/eea10/04f6588683753b2366796b34a2d6c8041736866800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Cosmographia [and] Ephemerides](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4401461/eea10/04f6588683753b2366796b34a2d6c8041736866800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)











![FARGHANI, Ahmad Ibn Muhammad al- (c.800-870) [ALFRAGANUS]](/assets/image/picture_2585488/b2dc2/1738f671edb1755923d3628b40f4dd701670972400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![FARGHANI, Ahmad Ibn Muhammad al- (c.800-870) [ALFRAGANUS]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2585488/b2dc2/1738f671edb1755923d3628b40f4dd701670972400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)