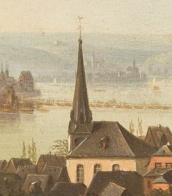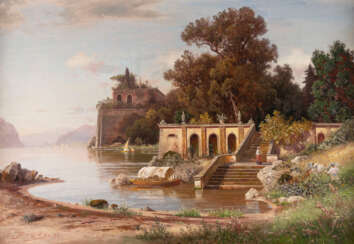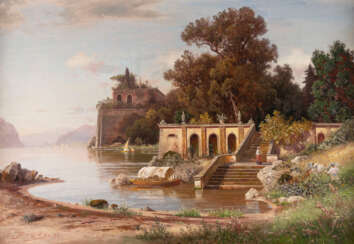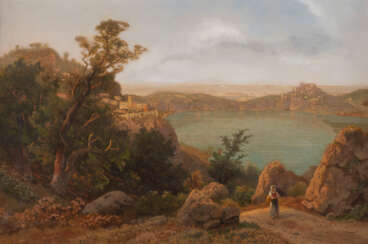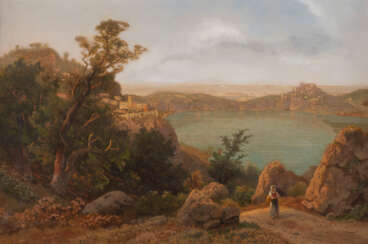carl gustav
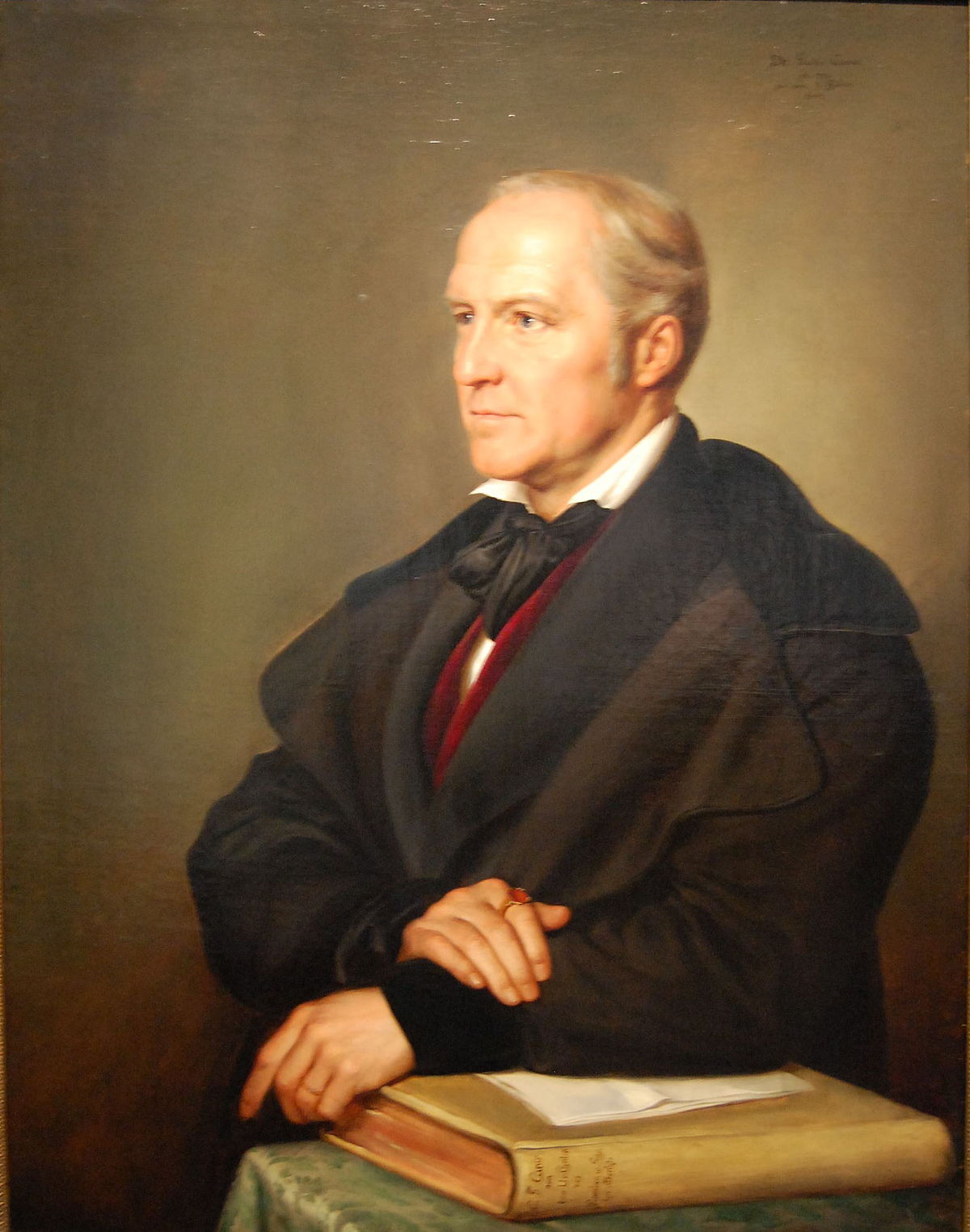

Carl Gustav Carus was a German painter of the first half of the 19th century. He is known as a landscape painter, as well as a scientist, physician (gynecologist, anatomist, pathologist, psychologist) and a major theorist of Romanticism in art.
Carus created idyllic landscapes depicting moonlit nights, mountains, forests, Gothic architecture and ruins. In his work, according to critics, he combined a romantic view of nature with the classical ideal of beauty, understood the beautiful as a triad of God, nature and man. Noteworthy are his small-format, spontaneously created landscape sketches with images of clouds. The master is the author of "Nine Letters on Landscape Painting" - one of the main theoretical works that laid the foundations of the German Romantic school of painting.


Carl Gustav Carus was a German painter of the first half of the 19th century. He is known as a landscape painter, as well as a scientist, physician (gynecologist, anatomist, pathologist, psychologist) and a major theorist of Romanticism in art.
Carus created idyllic landscapes depicting moonlit nights, mountains, forests, Gothic architecture and ruins. In his work, according to critics, he combined a romantic view of nature with the classical ideal of beauty, understood the beautiful as a triad of God, nature and man. Noteworthy are his small-format, spontaneously created landscape sketches with images of clouds. The master is the author of "Nine Letters on Landscape Painting" - one of the main theoretical works that laid the foundations of the German Romantic school of painting.
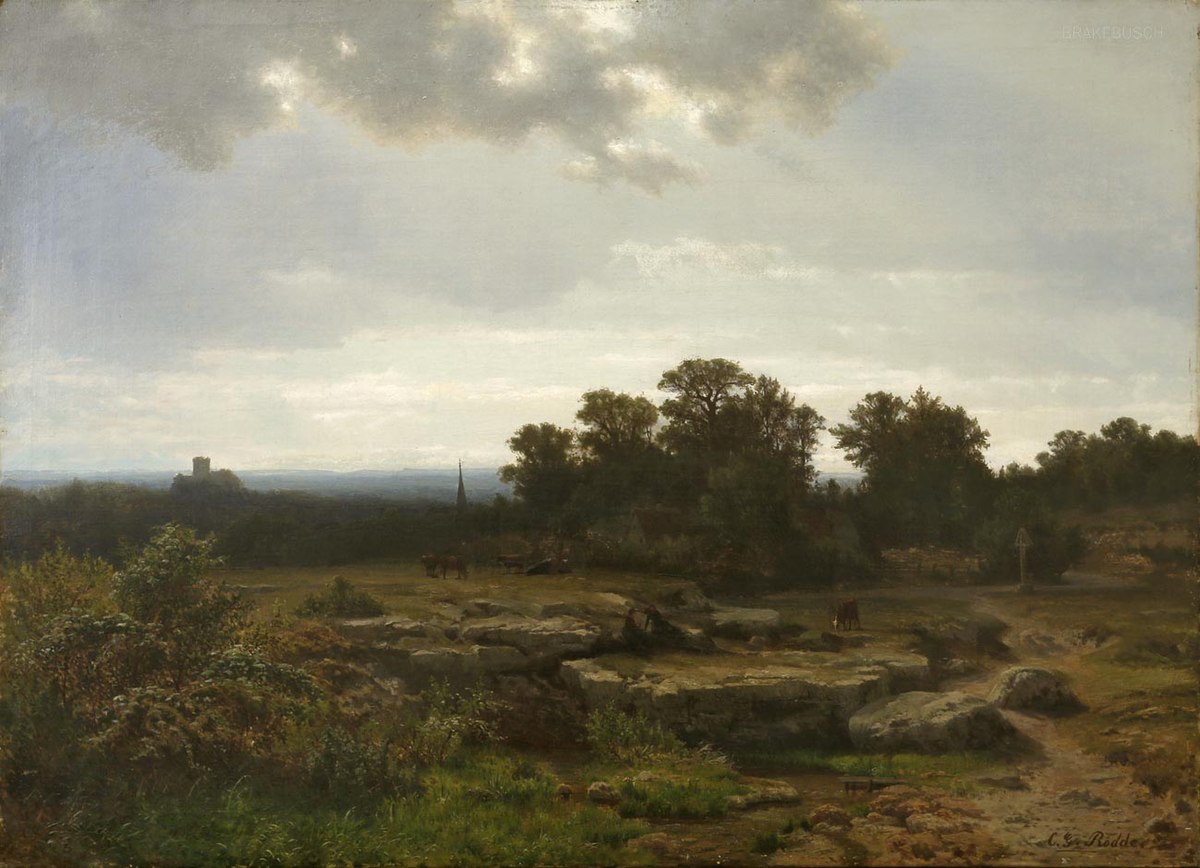


Carl Gustav Rodde was a German painter.
Rodde studied at the Düsseldorf Academy of Fine Arts under Johann Wilhelm Schirmer and Hans Fredrik Gude, and painted landscapes around Weimar, Danzig, Düsseldorf and Berlin, as well as Italian landscapes and vedutas.
Carl Gustav Rodde specialized in picturesque landscapes embodying an idealized vision of rural life. He adored the countryside and often preferred to depict picturesque vistas under the rays of the setting sun.
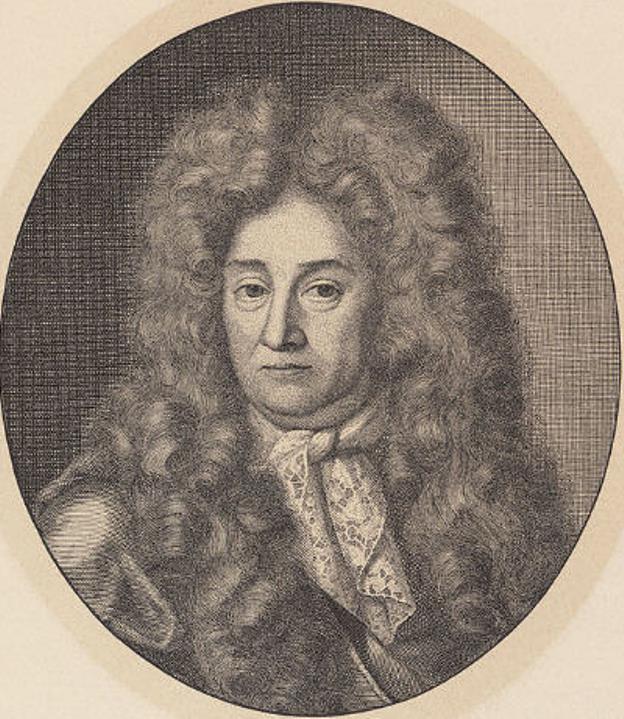




igmund Freud, born Sigismund Schlomo Freud, was an Austrian psychologist, psychiatrist and neurologist, the founder of psychoanalysis.
He graduated from the medical faculty of the University of Vienna, was engaged in self-education and numerous, cutting-edge for his time studies of the human psyche. The resulting psychoanalysis he created was both a theory of the human psyche, a therapy to alleviate its ills, and a tool for interpreting culture and society. Freud's psychoanalysis had a significant impact on psychology, medicine, sociology, anthropology, literature and art in the twentieth century.
Despite the sometimes harsh criticism of virtually all of his ideas and teachings, which continues almost a century after his death, Freud remains one of the most influential intellectual figures of our time.
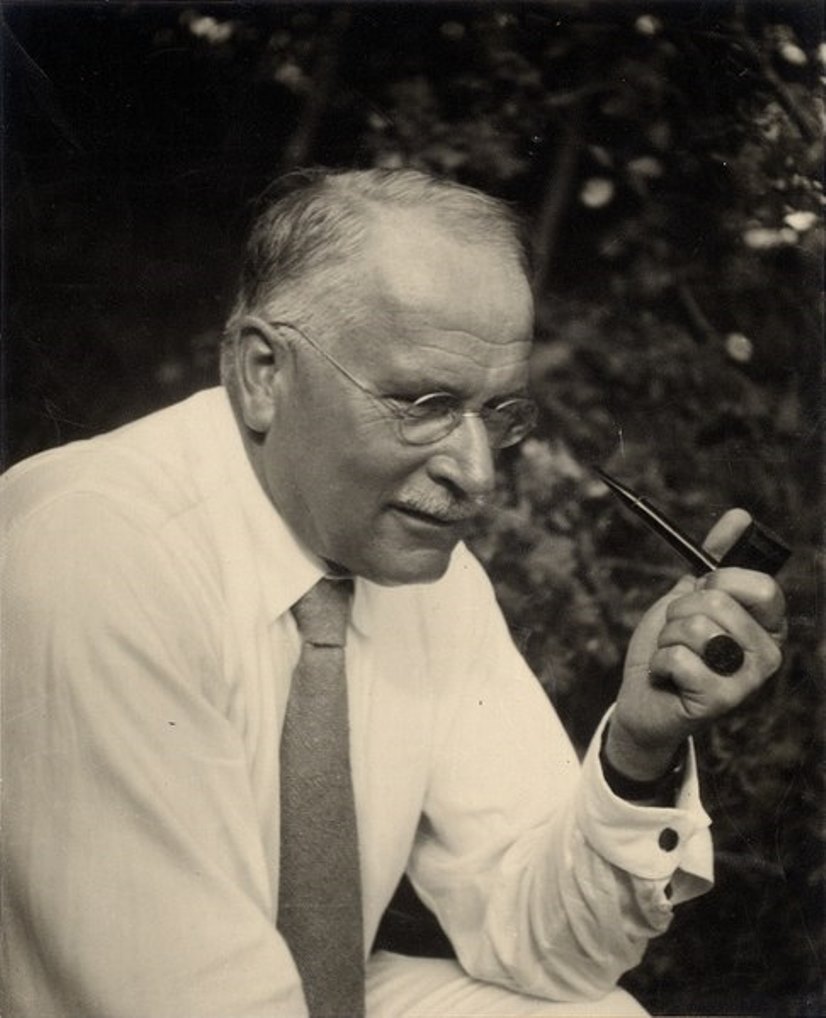


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychologist and psychiatrist, professor, and the founder of analytical psychology.
He studied at the University of Zurich and conducted many studies in scientific psychology and psychiatry. From 1907 to 1912, Jung was a close associate of Sigmund Freud, but later they had serious disagreements and parted ways.
Carl Jung proposed and developed the concepts of extraverted and introverted personality, archetypes and the collective unconscious. He introduced the term "collective unconscious" as a part of the mind containing memories and impulses of which the individual is unaware, common to humanity as a whole and deriving from inherited brain structure. It differs from the personal unconscious, which arises from the experience of the individual. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains archetypes, or universal primordial images and ideas.
Historical research helped Jung pioneer psychotherapy for middle-aged and elderly people, especially those who felt their lives had lost meaning. He helped them appreciate the place of their lives in the sequence of history. Jung devoted many years of his life to developing his ideas, especially those concerning the relationship between psychology and religion. His work had a significant impact on psychiatry and the study of religion, literature, and related fields.


Carl Gustav Rodde was a German painter.
Rodde studied at the Düsseldorf Academy of Fine Arts under Johann Wilhelm Schirmer and Hans Fredrik Gude, and painted landscapes around Weimar, Danzig, Düsseldorf and Berlin, as well as Italian landscapes and vedutas.
Carl Gustav Rodde specialized in picturesque landscapes embodying an idealized vision of rural life. He adored the countryside and often preferred to depict picturesque vistas under the rays of the setting sun.