decimal









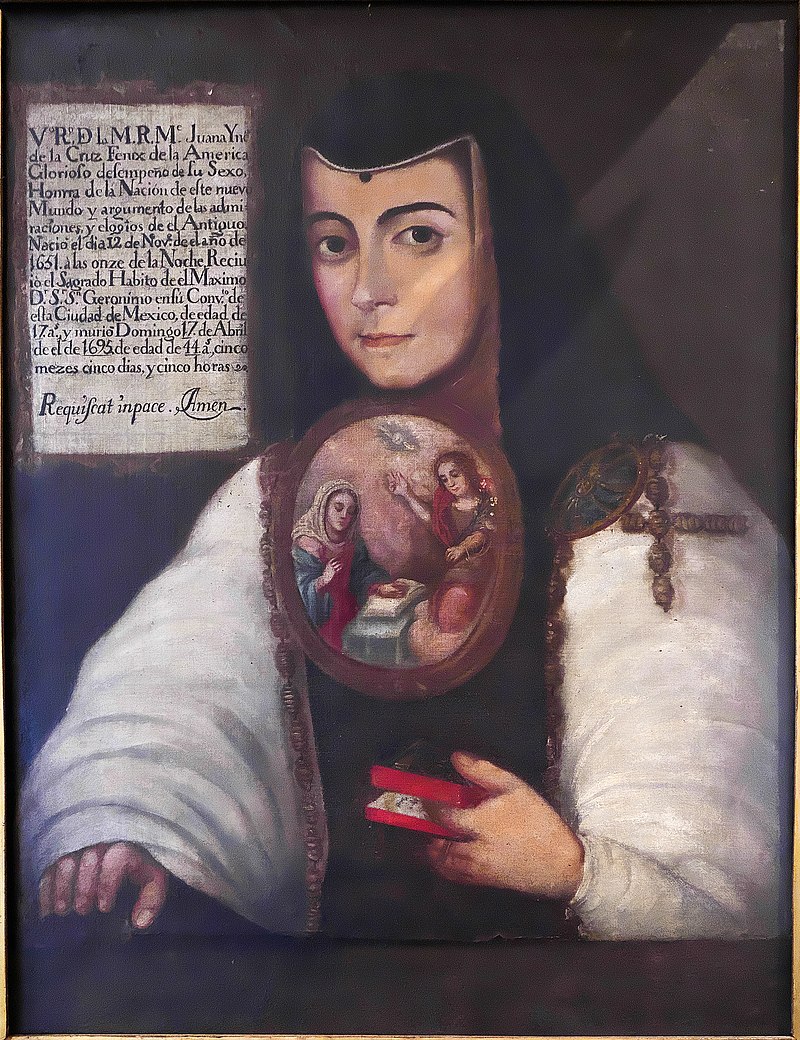
Juana Inés de la Cruz or Juana of Asbaje, real name Juana Inés de Asbaje Ramírez de Santillananota, was a Mexican poet, scholar, and writer of the Latin American colonial period and the Spanish Baroque, and a Jerónimo nun.
Juana Ramírez was born into a poor family (Spanish father and Creole mother) and from an early age showed a burning thirst for knowledge and giftedness, but as a woman she was almost entirely self-taught. By her teens, she had already learned Greek logic and taught Latin to young children. She also learned Nahuatl, an Aztec language spoken in Central Mexico, and wrote several short poems in the language. At the age of 16, the girl was introduced to the court, and her intelligence impressed even Viceroy Antonio Sebastian de Toledo, Marquis de Mancera, and in 1664 he invited her to serve as maid of honor.
In 1669, at the age of 21, she took her tonsure at the Convent of Santa Paula of the Hieronymite Order in Mexico City, where she remained a recluse for the rest of her life. In the convent, Sister Juana enjoyed exceptional freedom: she continued to socialize with scholars and senior members of the court, amassed one of the largest private libraries in the New World, as well as a collection of musical and scientific instruments. Her plays in verse, poetry, and compositions for state and religious festivals were frequently and successfully performed at the palace.
Sister Juana was an outstanding representative of Spain's Golden Age: she was the last significant writer of the Latin American Baroque and the first great exponent of colonial Mexican culture. Sister Juana wrote sonnets, romances, and ballads, drawing on a vast store of classical, biblical, philosophical, and mythological sources. She also composed moral, satirical, and religious texts, as well as many poems praising courtiers, but she also defended women's right to education.
At the end of her life, due to pressure from religious dogmatists, Sister Juana had to sell her extensive library of some 4,000 volumes and return to strict reclusiveness. In 1695, the plague struck the convent and, while caring for her sisters, Juana died of the disease at about the age of forty-four.
Today, Juana Inés de la Cruz is a national icon of Mexico and Mexican identity as a prominent writer of the Spanish-American colonial period. The former convent where she lived is a center of higher education, and her image adorns Mexican currency.




Johann Hartmann Beyer was a German physician, mathematician and statesman.
He earned a master's degree in liberal arts at the University of Strasbourg, and then graduated from the University of Tübingen with a doctorate in medicine. In 1588 Beyer returned to his native Frankfurt and began working as a physician; a year later he was appointed Physicus ordinarius - his duties included overseeing the city's health care and pharmacy system.
In 1614 Beyer took up the position of senior burgomaster of Frankfurt, but during the Fetmilch Rebellion he became involved in conflict, was forced to resign and returned to science.
He had the richest library of scientific books, numbering about 2500 volumes, wrote scientific works on astronomy and mathematics, engaged in medical activity, having invented the famous Frankfurt pills. Beyer carried on a lively correspondence with scientists, including mathematician Johannes Kepler, dealing with decimal fractions. Beyer bequeathed his rich inheritance to the city and to charity.


Tomasino da Vimercate was an Italian miniaturist. He worked in Milan from 1390 to 1415.