english school

Howard While Skempton is a British composer, pianist and accordionist.
From 1967 Skempton studied in London with Cornelius Cardew, who helped him discover a musical language of great simplicity. Skempton and became known for the particular clarity of his musical language. He wrote over 300 works, many of which are miniatures for solo piano or accordion.
Skempton calls his works the "central nervous system" of his oeuvre. They include pieces for solo cello and guitar, Chamber Concerto for fifteen instruments, Concerto for Hardy Gurdy and Percussion, and others. Skempton's first major success came in 1991 with the premiere of his orchestral composition Lento. His orchestral and instrumental works have been recorded by the BBC Symphony Orchestra and the Bash Ensemble, among others.
In recent years Skempton has increasingly concentrated on vocal and choral music; his choral commissions include works for the BBC Singers and the Belfast Philharmonic Society. He is Professor Emeritus of Music at De Montfort University.

Richard Cosway was a leading English portrait painter of the Georgian and Regency era, noted for his miniatures.
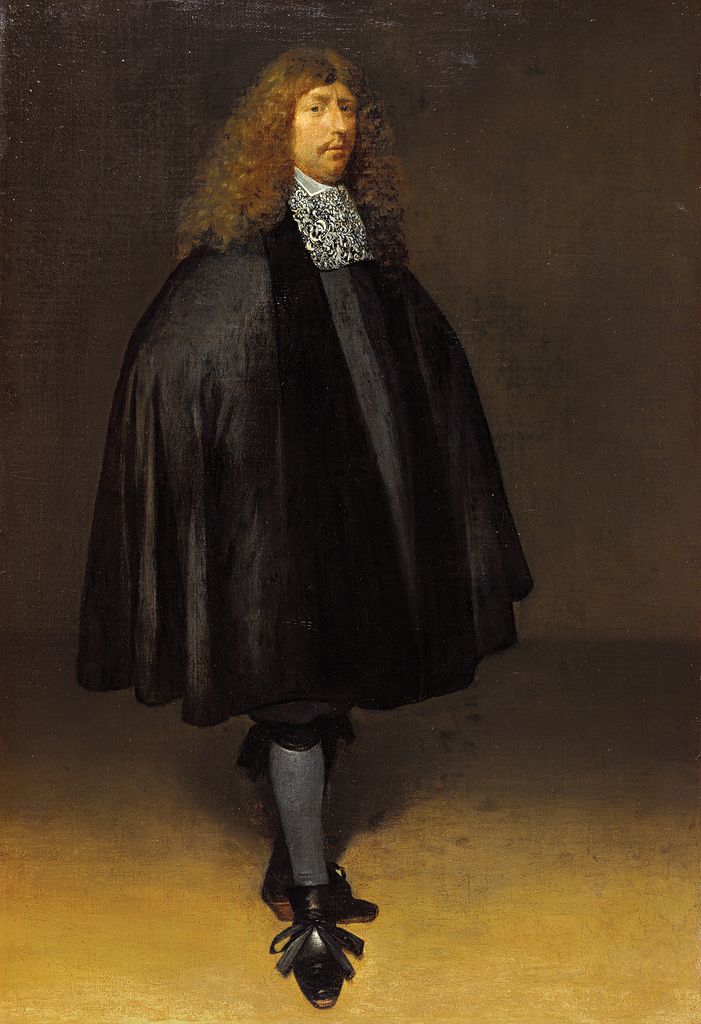


Gerard ter Borch was one of the leading masters of Dutch genre painting of the Golden Age. His realistic aesthetic was developed by the Delft masters Pieter de Hooch and Jan Vermeer.
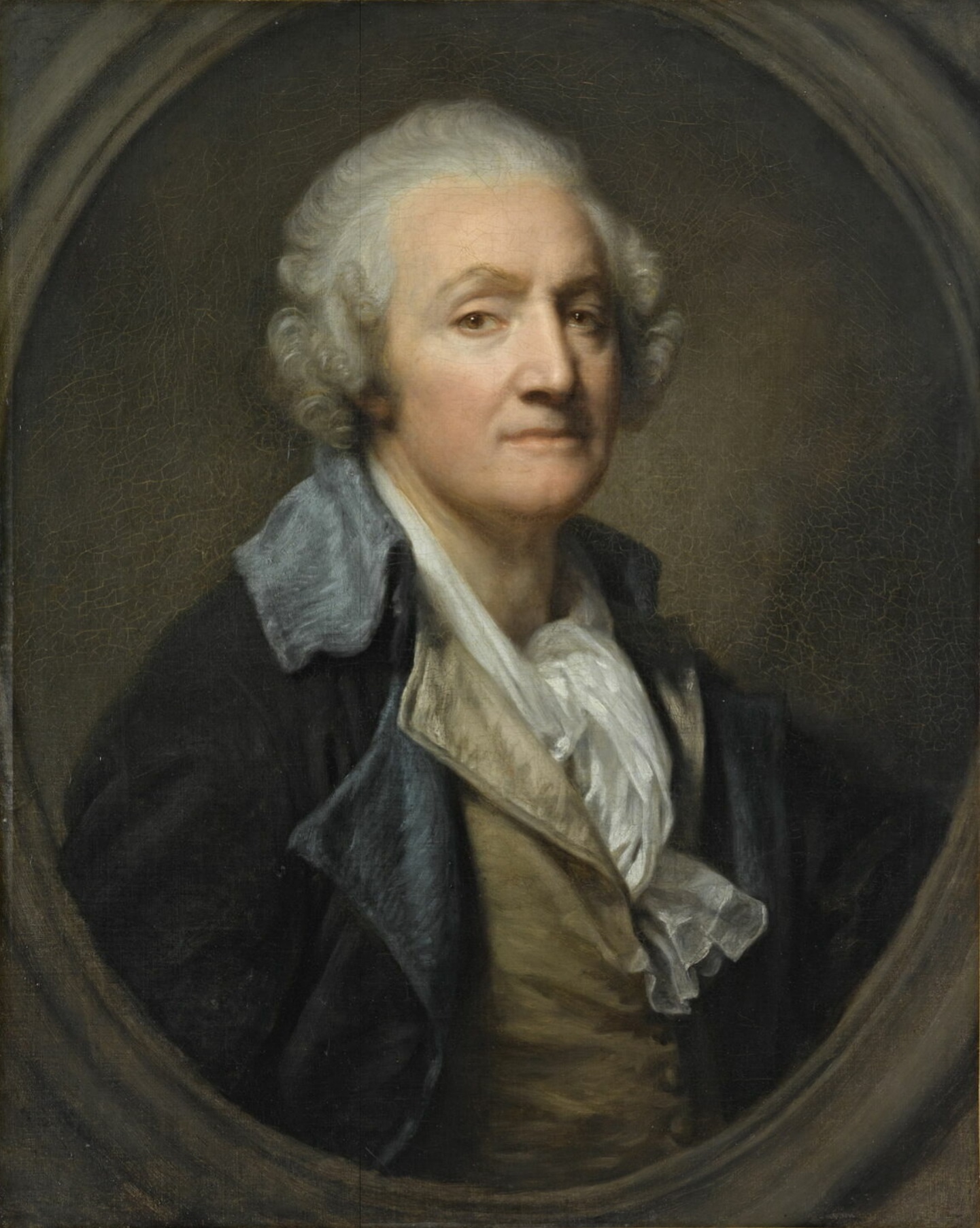


Jean-Baptiste Greuze was a French painter of portraits, genre scenes, and history painting.
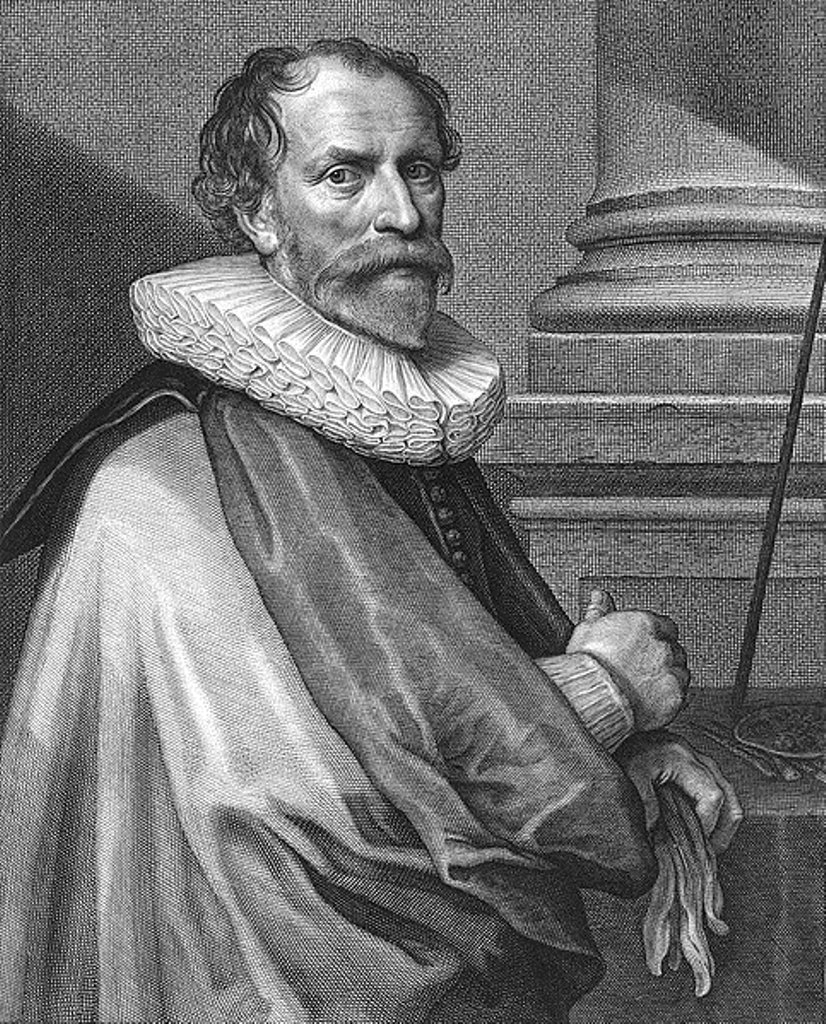


Michiel Jansz. van Mierevelt was a Dutch portrait painter of the Golden Age.
Michiel Jansz. van Mierevelt studied painting in Utrecht and soon became a recognized master of portraiture. He also painted on historical and mythological subjects.


James Butler was an American schoolteacher living in Pennsylvania and a writer.
He wrote the adventure novel about love and pirates Fortune's Foot-ball: or, the Adventures of Mercutio.
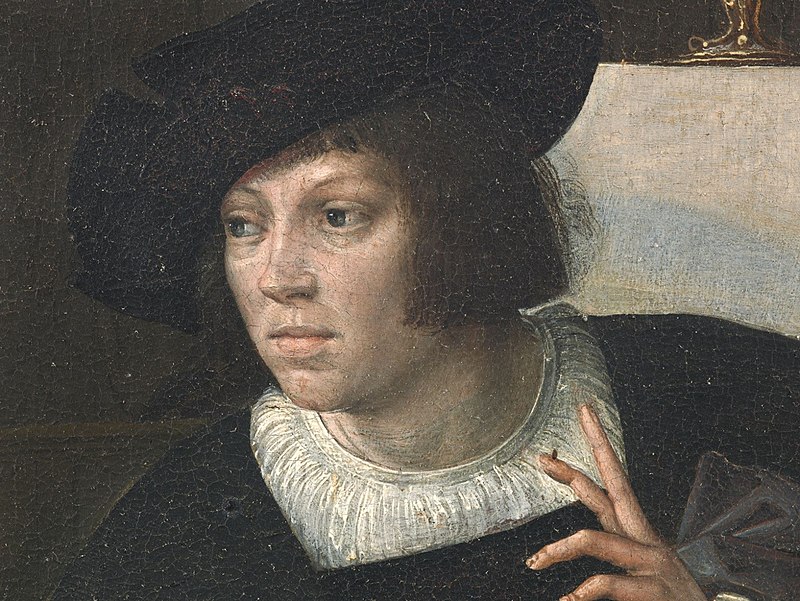


Bernard van Orley was a versatile Flemish artist and representative of Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting, who was equally active as a designer of tapestries and, at the end of his life, stained glass. Although he never visited Italy, he belongs to the group of Italianizing Flemish painters called the Romanists, who were influenced by Italian Renaissance painting, in his case especially by Raphael.
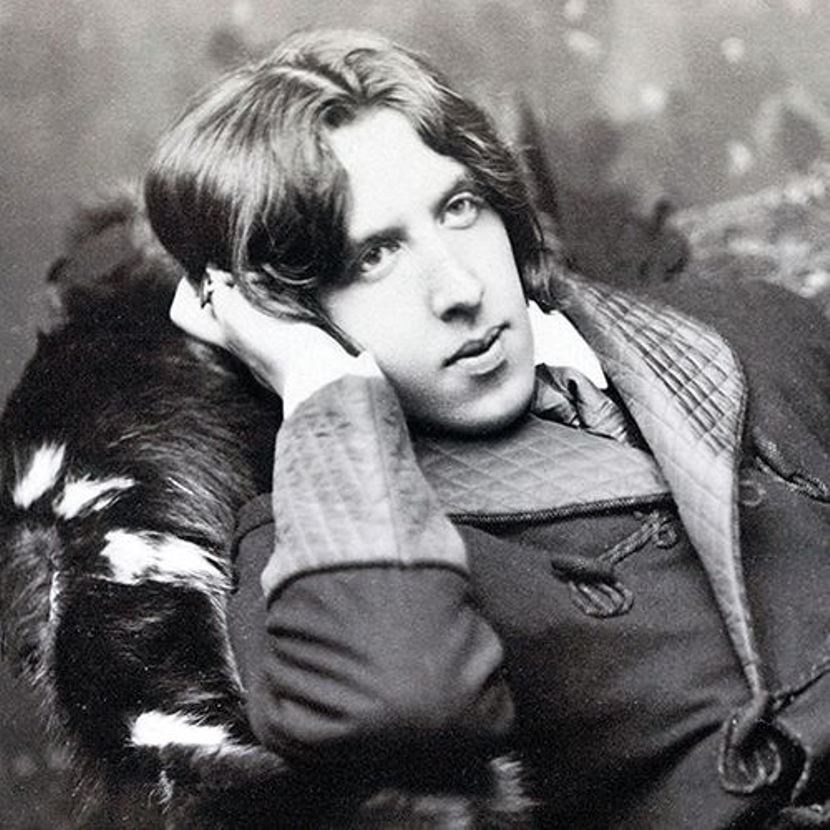





Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde - Irish writer, poet, philosopher and playwright, a bright representative of the literature of the Victorian period.
Oscar's parents were fond of literature and history, gave their son an excellent education. After graduating from Oxford University, Oscar moved to London, where he quickly entered the circle of secular society. His first book, a collection of poems, was published in 1881. Over the next year, the aspiring writer traveled across America with lectures on art. Then he traveled to France, where he met key figures of French literature of the time - Victor Hugo, Paul Verlaine, Emile Zola and others. Returning to his homeland, Oscar married, thanks to which his children's fairy tales appeared. His popularity grew rapidly, his work was favorably reviewed by Bernard Shaw.
Next, "The Crime of Lord Arthur Seville", "The Canterville Ghost", "The Sphinx without a riddle" were written. In 1890 Oscar Wilde wrote the novel "The Portrait of Dorian Gray", which was considered immoral in high society, but it brought the author the greatest fame. This novel is still considered a classic of world literature to this day. In the early 1890s Oscar Wilde wrote comedy plays "Lady Windermere's Fan", "A Woman Not Worth Watching", "An Ideal Husband" and "How Important It Is to Be Serious". In them, the author shows himself a master of witty dialog. During his life, Wilde wrote nine plays, one novel, many poems, stories and essays.
Bright and full life of a successful and talented writer ended when he met Lord Alfred Douglas. For this scandalous connection with the man, Oscar Wilde was sentenced to two years in prison. After leaving prison, he settled in France under an assumed name, abandoned by everyone. He wrote his last work, the autobiographical "Ballad of Reading Prison" two years before his death at the age of 46.


Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer, pianist, and conductor, one of the most famous and celebrated composers in world history.
Beethoven showed an aptitude for music at a very early age; from the age of four his father began to teach him. Beethoven's early works - piano sonatas and symphonies - were composed under the strong influence of the music of the great classical composers Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. As Beethoven matured, however, he began to experiment with new forms and harmonic sequences, and his music became more complex and emotionally charged.
Unfortunately, at the height of his talent, Beethoven began to gradually lose his hearing, to the point of complete deafness by the end of his life. Despite this, he continued to compose and conduct, using special devices to feel the vibrations of the music.
Beethoven's work is considered pivotal in classical music and is a bridge between the classical and Romantic eras. His works vividly express a wide range of emotions, from triumph and joy to sadness and despair. Beethoven was also one of the first composers to include soloists and chorus in his symphonies. Beethoven's best-known works include nine symphonies, 32 piano sonatas, 16 string quartets and the heroic opera Fidelio. These and many other works have cemented Beethoven's place in music history as one of the greatest composers of all time. His music continues to be played and studied by musicians and music lovers around the world.
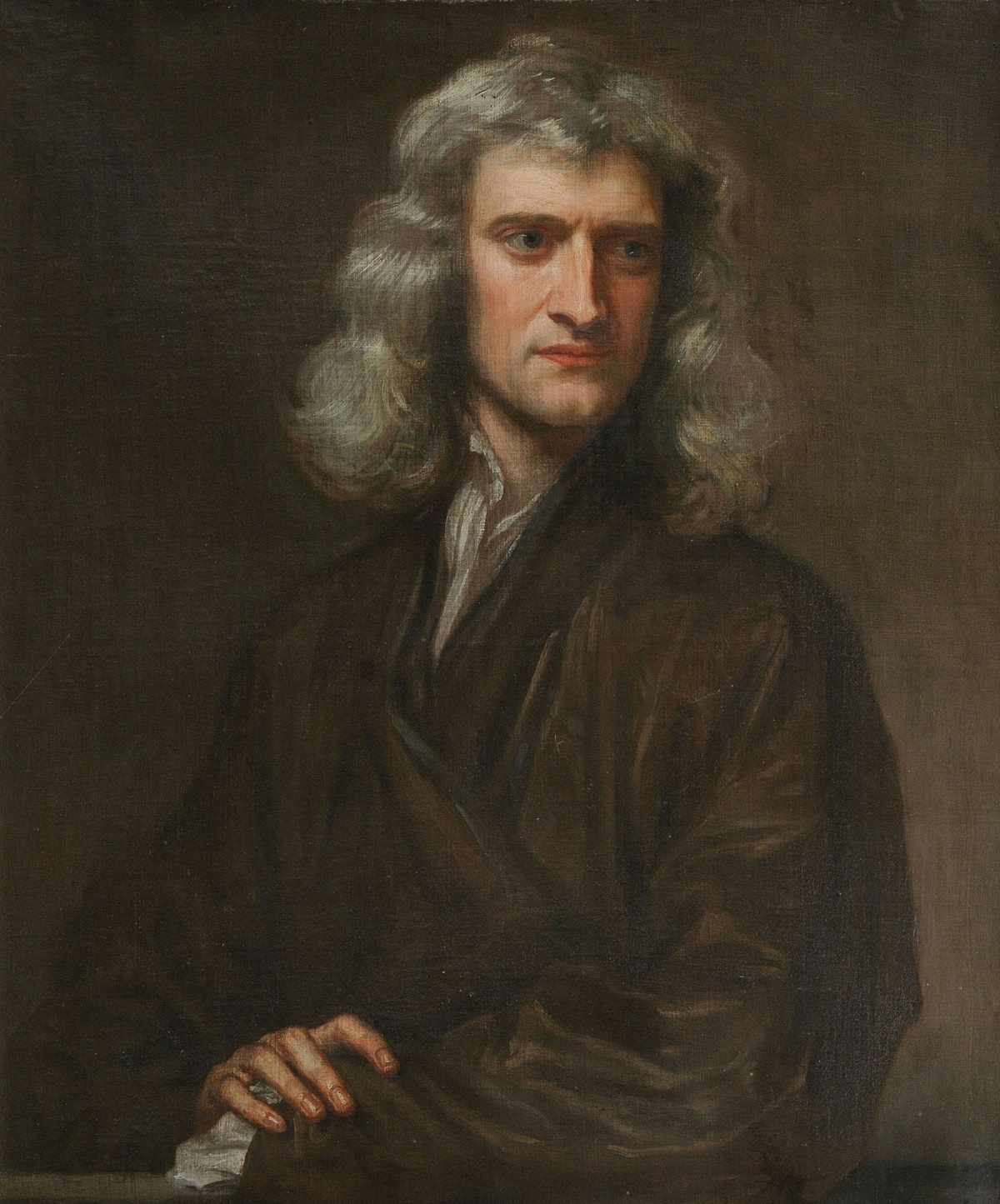


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.

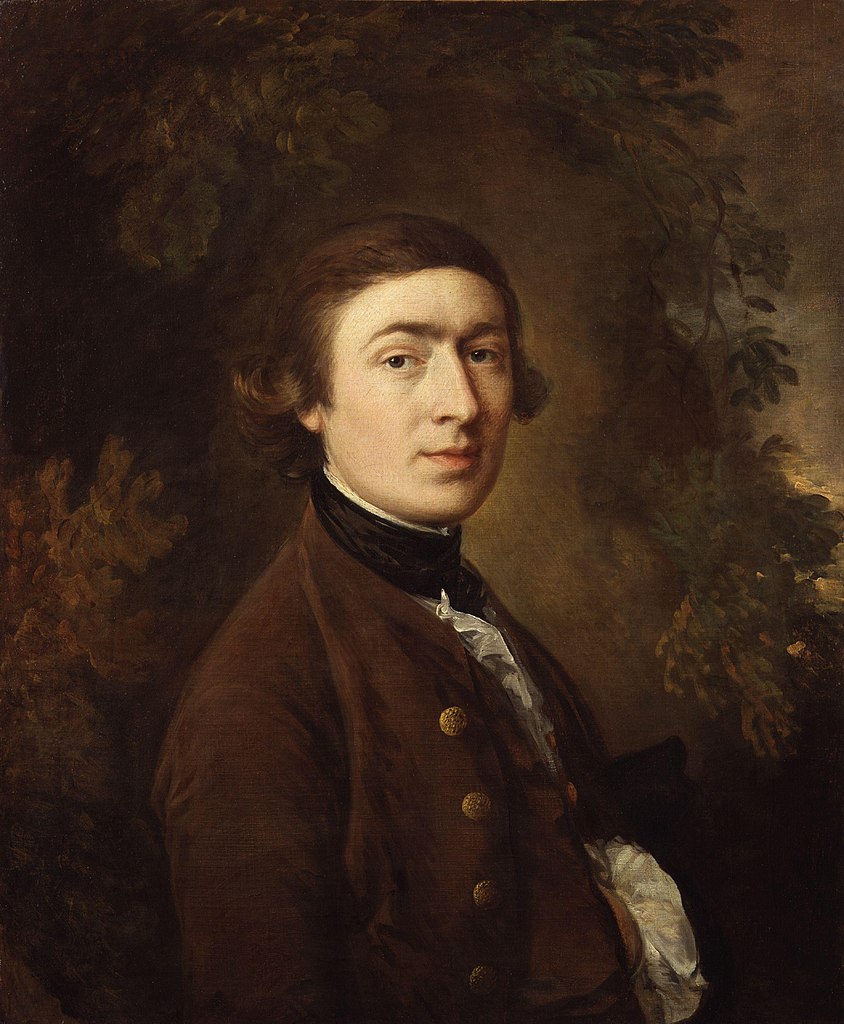
Thomas Gainsborough was an English painter, renowned for his mastery in both portraiture and landscape art, active during the 18th century. Born in Sudbury, Suffolk, Gainsborough displayed early artistic talent, which led him to London to study art seriously. He is often celebrated for his fluid and expressive brushwork and his innovative approach to portrait and landscape painting. Gainsborough was notably influenced by Dutch landscape paintings and the Rococo style, which is evident in his delicate and evocative use of color and light.
Thomas Gainsborough's career gained significant momentum when he moved to Bath, where he attracted a fashionable clientele. This period was marked by his creation of portraits that seamlessly integrated the sitters into lush, idyllic landscapes. Despite his success with portraits, Gainsborough preferred painting landscapes, often expressing a desire to escape the demands of portrait commissions to focus on these scenic representations.
Some of his most famous works include "The Blue Boy" and "Mr. and Mrs. Andrews." "The Blue Boy" is particularly noted for its vibrant blue costume and has been a hallmark of Gainsborough's style in capturing the personality and elegance of the youth. His works are held in high esteem and are part of collections across major museums globally, such as the National Gallery, Tate Britain, and the Huntington Library, to name a few.
For those interested in exploring Thomas Gainsborough's contributions to art, his paintings offer a glimpse into the social fabric and the natural beauty of 18th-century England, making him a pivotal figure in the English school of painting. His ability to convey character and atmosphere in his portraits and landscapes alike ensures his continued relevance and admiration in the art world today.
If you are keen on updates related to Thomas Gainsborough's art pieces, sales, and auctions, consider signing up for specialized newsletters or alerts that focus on his works and their presence in modern collections and sales events.






































![[WILDE, Oscar (1854-1900)]](/assets/image/picture_4084566/95c2b/lahwoc3u4qf9a2monehopf8hrdgtqqfscop5zvi2iyvpfee2ozgaz9zixwfubjc1719907174jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[WILDE, Oscar (1854-1900)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4084566/95c2b/lahwoc3u4qf9a2monehopf8hrdgtqqfscop5zvi2iyvpfee2ozgaz9zixwfubjc1719907174jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)














![[NEWTON, Isaac (1642-1727)] – Nathaniel HAWES (d. 1700)](/assets/image/picture_2279770/a4540/yuinyqzhzesrjjrkhx5cgen4dyqa2yovnhi1oqpdrbjtx7ouvxvrk4gf4ex2lhuq1656671033jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[NEWTON, Isaac (1642-1727)] – Nathaniel HAWES (d. 1700)](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2279770/a4540/yuinyqzhzesrjjrkhx5cgen4dyqa2yovnhi1oqpdrbjtx7ouvxvrk4gf4ex2lhuq1656671033jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)

















