fine press books
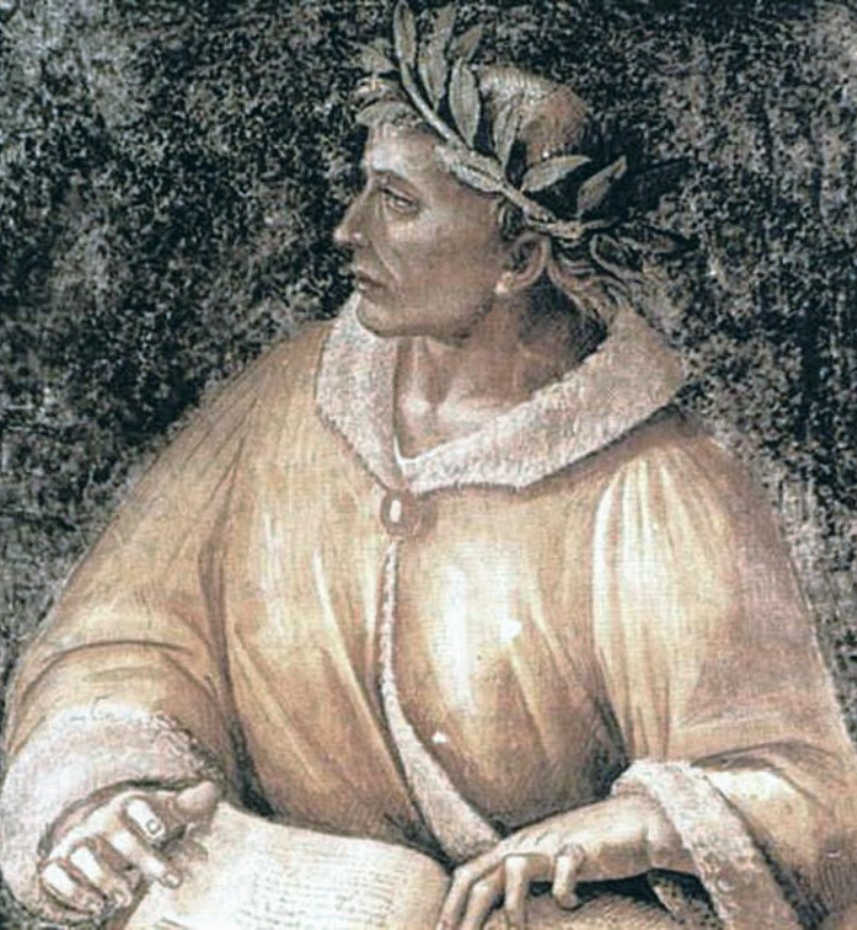

Publius Ovidius Naso, known as Ovidius (Ovid), was an ancient Roman poet who lived during the reign of Emperor Augustus.
Most of the information about the life and work of Ovid, scholars have drawn from his own works, as well as from the works of Seneca the Elder and Marcus Fabius Quintilianus. Ovid was from a fairly high class of "horsemen", studied rhetoric at the maestros of oratory of the ancient Roman Empire, and then went traveling, visiting Athens, Asia Minor and Sicily. As a young man, Ovid held minor public offices, was a member of the college of civil affairs, and served in an office that performed spiritual and secular duties at the state level.
However, Ovid was much more attracted to poetry, and he resigned and about 29-25 BC joined the circle of those chosen under the patronage of Marcus Valerius Messala Corvinus. After publishing Amores, a collection of love-erotic lyrics, around 15-16 BC, Ovid became one of Rome's most popular poets. He became famous for his works in the genre of elegy, as well as for his epic poem Metamorphoses (8 AD), which became one of the most important sources in the study of classical mythology.
For reasons unknown to us, in 8 A.D. Ovid was disgraced and exiled for the rest of his life to Tomes on the Black Sea, where he wrote his "Mournful Elegies" and a poem cycle entitled "Letters from Pontus". A contemporary of Virgil and Horace, Ovid was one of the three canonical representatives of Latin literature.
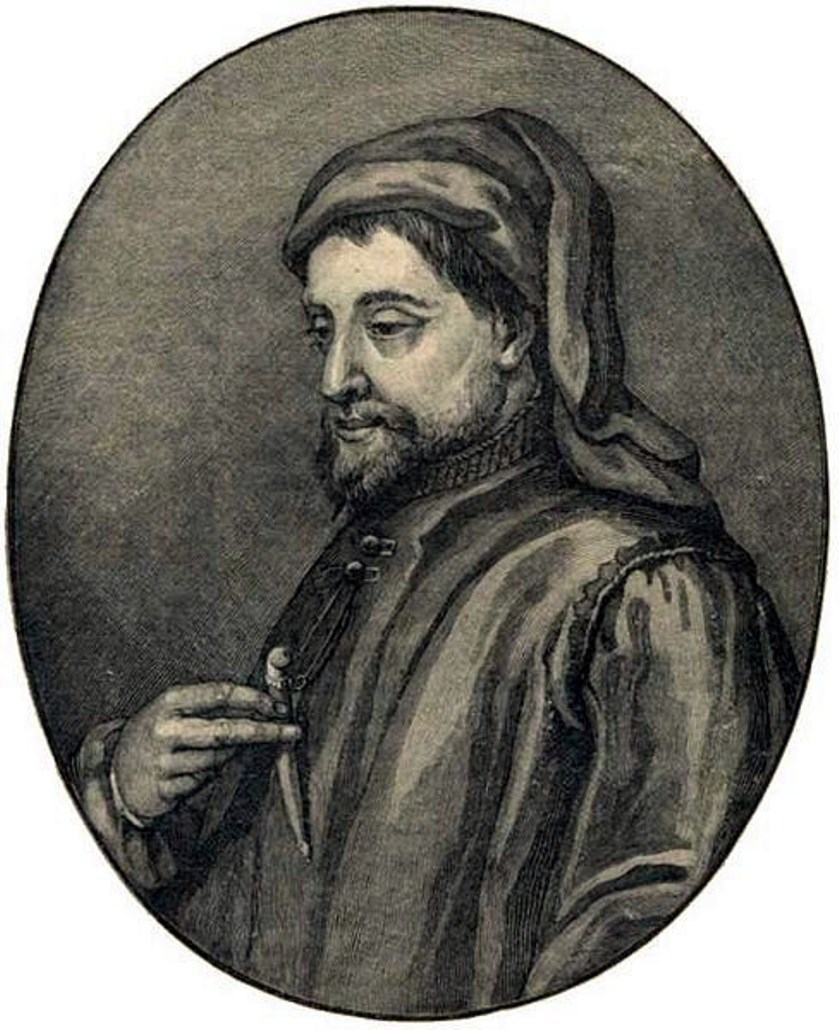


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.
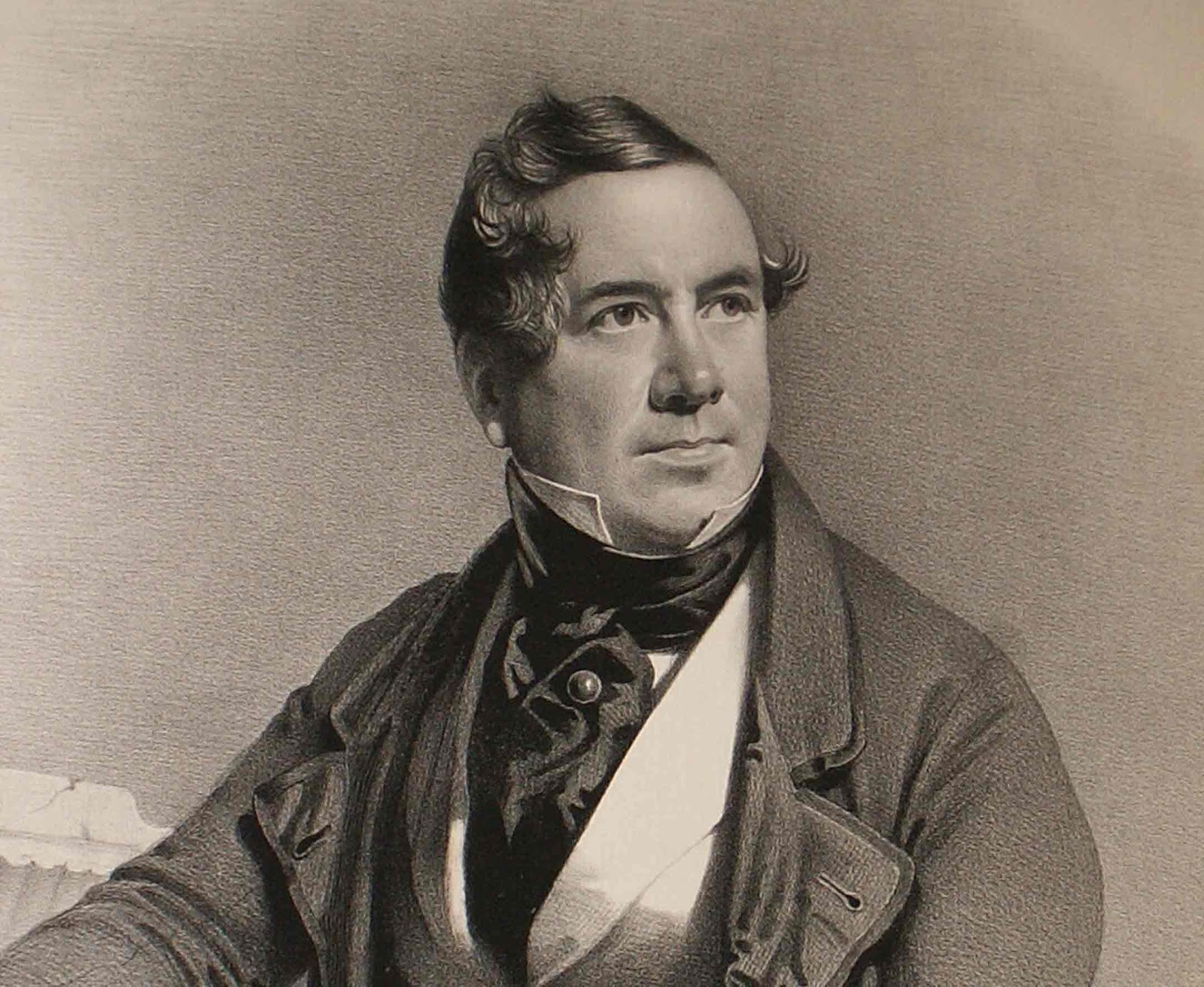






David Roberts was a Scottish painter and a member of the Royal Academy.
Since 1819, David Roberts worked as a scenographer in various theaters, where his creative potential was appreciated. Inspired by the positive feedback, some time later he seriously engaged in painting. After the first exhibition of works, held in 1824, the artist went on a trip. He visited several countries in Europe, where he created many drawings. In 1833, David Roberts continued to explore the world: he went to Spain, where he spent almost a year, also had time to visit Morocco, lived in Cairo for a long time and made sketches everywhere. Subsequently, his works were published in various magazines, and the author gained fame as a talented illustrator. In 1841, the artist became a member of the Royal Academy.
In the 1840s, an album with his works was published, thanks to these publications, David Roberts became the most famous painter of the Victorian era. The artist also skillfully depicted monuments of architecture. David Roberts' paintings are striking in their photographic accuracy, and he is still considered one of the best architectural painters in his homeland.
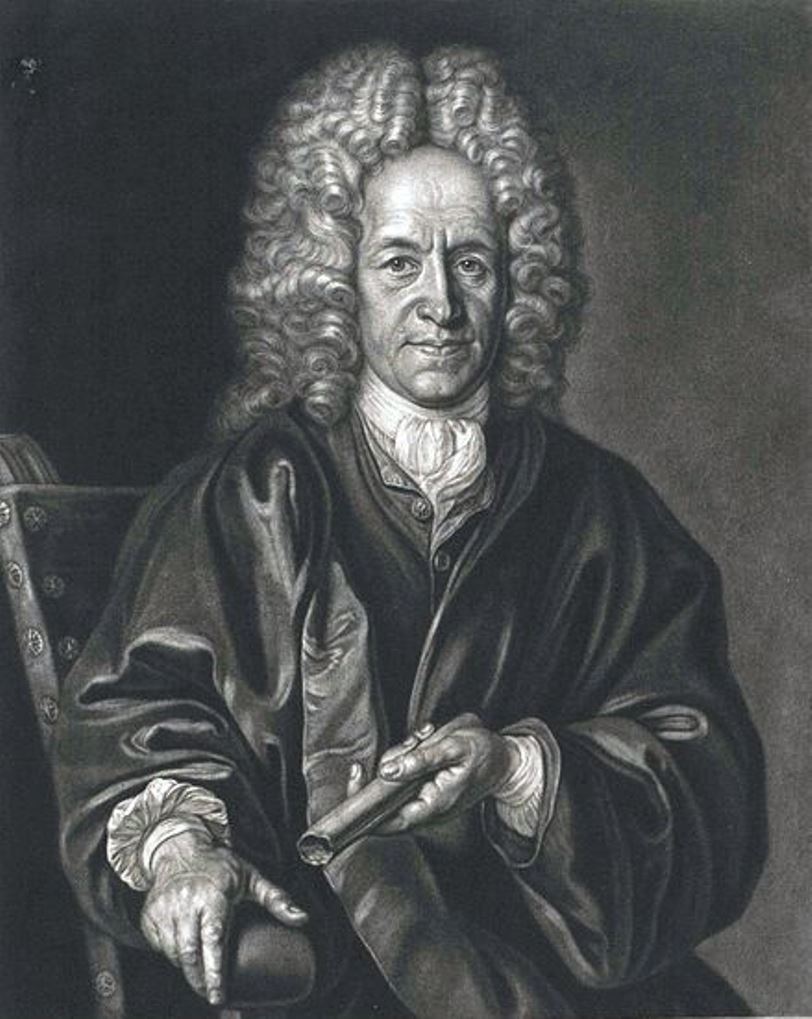


Christoph Weigel the Elder, full name Johann Christoph Weigel, was a German painter, engraver and publisher.
Weigel worked very successfully in the mezzotint technique. He was the first engraver to use a kind of machine for making backgrounds. He established his own printing house in Nuremberg in 1698, and worked closely with the imperial geographer and cartographer Johann Baptist Homann (1664-1724) to produce his maps. His younger brother Johann Christoph Weigel kept an art trade store in Nuremberg around the same time, and also quite successfully.
One of Weigel's most important works is the Ständebuch (Book of Classes) of 1698, which describes and illustrates with engravings more than two hundred trades and services, including mining.
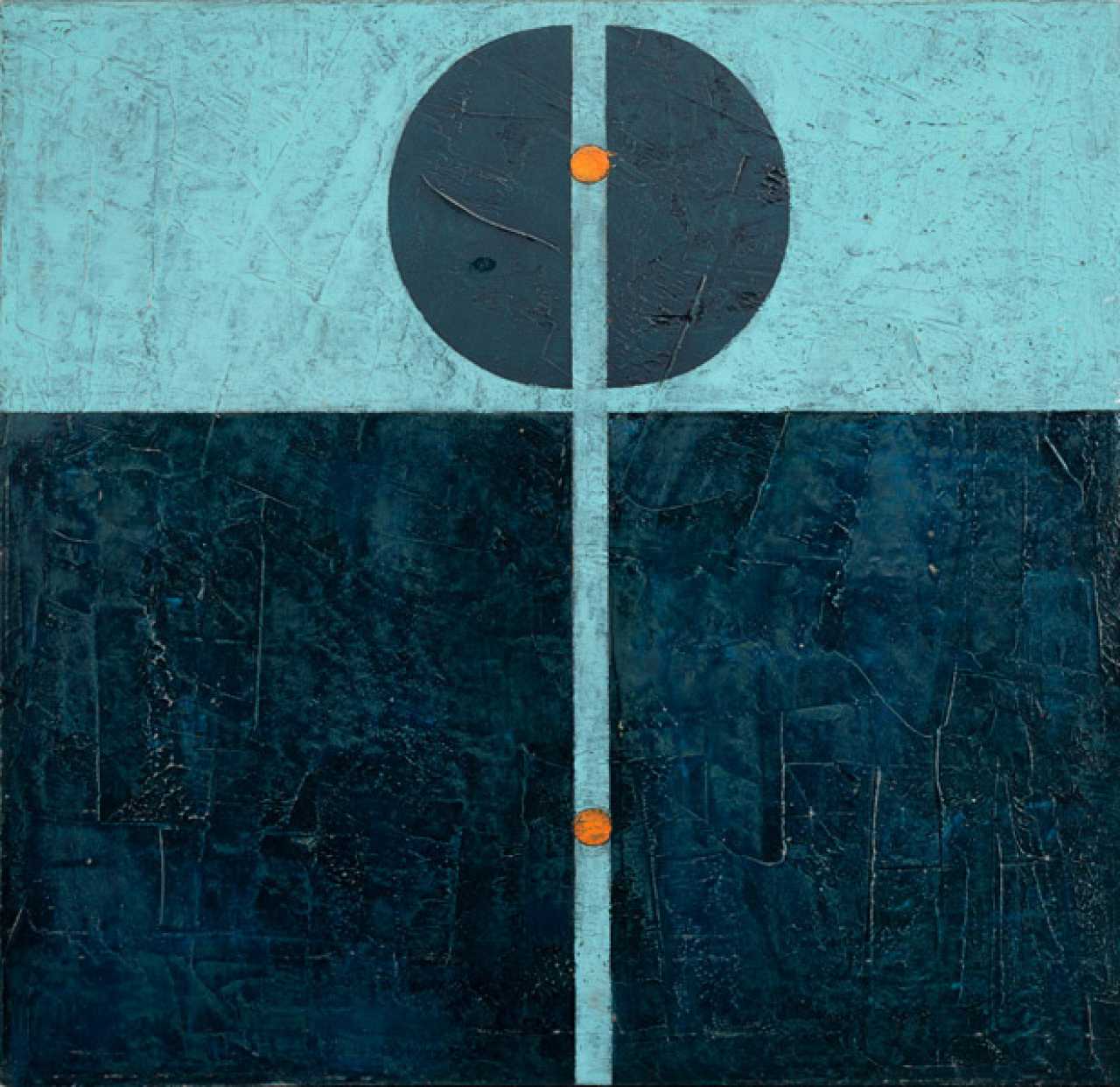




Robert Salomon Gessner is a Swiss abstractionist artist and graphic designer.
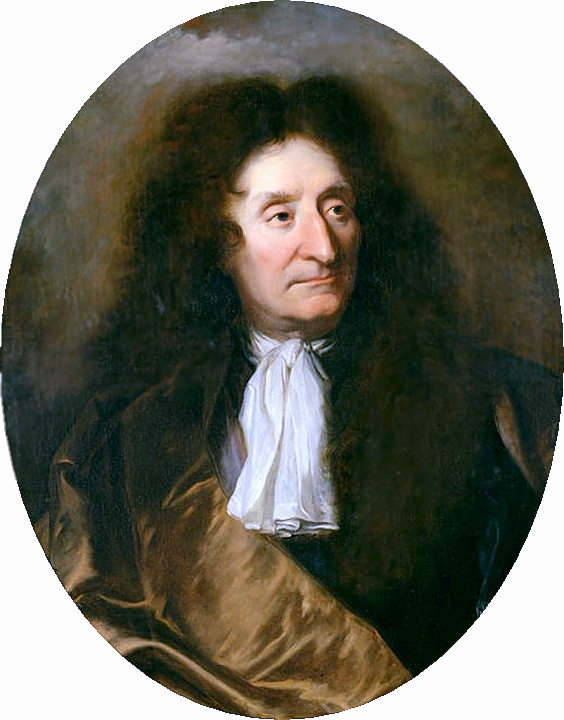
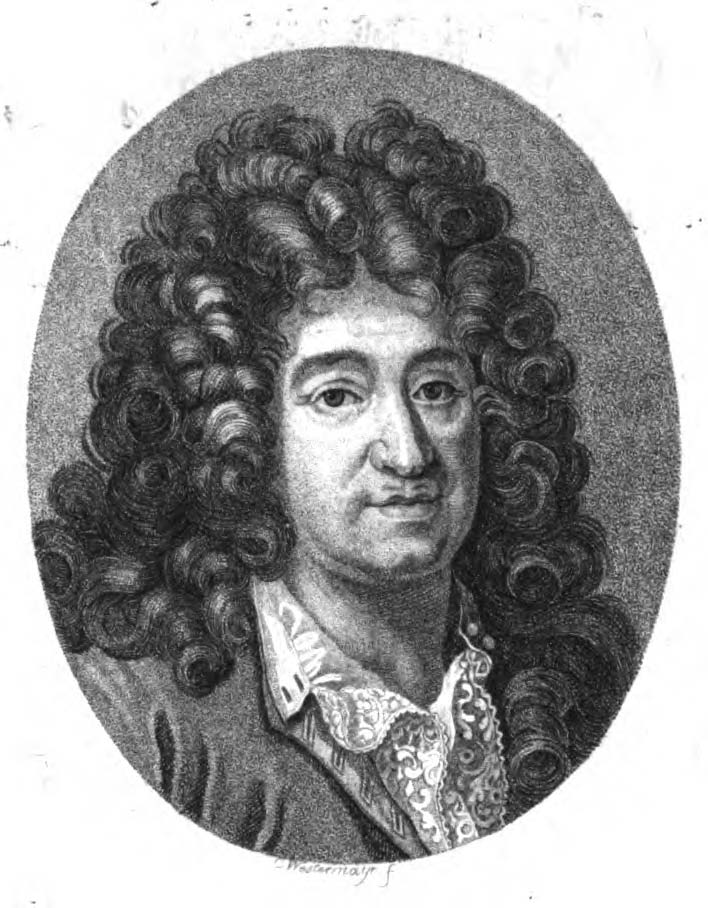








Nicolas Sanson the Elder (Nicolas Sanson d’Abbeville) was a French cartographer who served under two kings in matters of geography. He has been called the "father of French cartography." He gave lessons in geography both to Louis XIII and to Louis XIV. Active from 1627, Sanson issued his first map of importance, the "Postes de France". After publishing several general atlases himself he became the associate of Pierre Mariette, a publisher of prints. He died in Paris on 7 July 1667. Two younger sons succeeded him as geographers to the king. Sanson's maps were used as a model by his son, Guillaume, and, at least initially, by Duval, his nephew, in his 1664 folio map and 1660 atlas minor map. In 1692 Hubert Jaillot collected Sanson's maps in an Atlas nouveau.
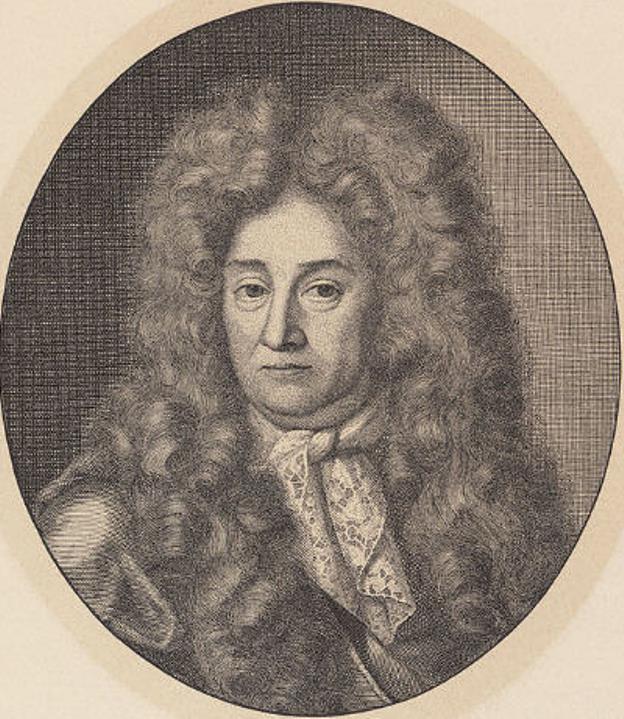
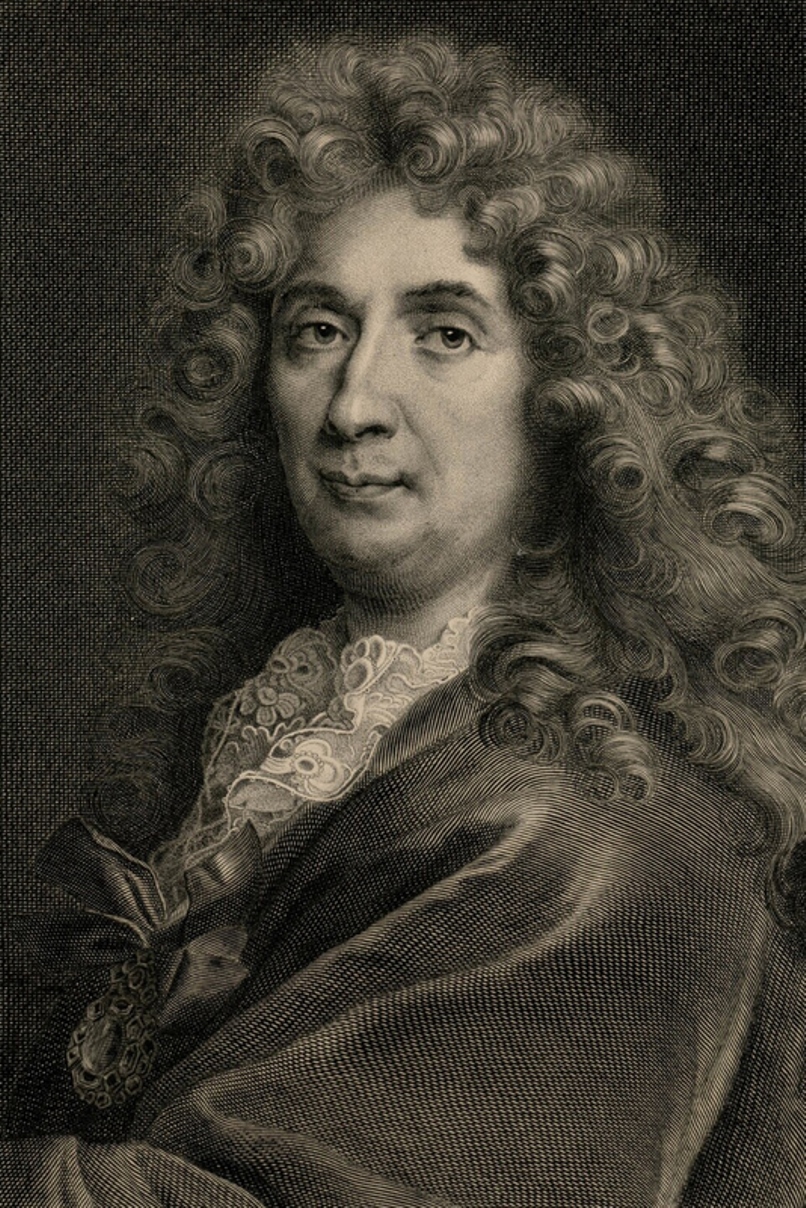






Charles Le Brun was a French painter, draftsman and chief decorator of the Palace of Versailles.
Charles came from an educated and respected family, trained in painting in Italy and very soon his talents were appreciated in the highest circles of France. In 1660 Le Brun painted "The Family of Darius before Alexander", which brought him the reputation of a brilliant French painter, and in 1664 he received the position of the first painter of the king. Thereafter he received more and more commissions and more honors.
From 1662 Le Brun controlled all the artistic projects of the royal court. In the Palace of Versailles, Lebrun created beautiful decorations: the Ambassadors' Staircase, the Hall of Mirrors, the Peace Room and the War Room. In each of his designs, he emphasized the king's achievements. He was also responsible for the decoration of the State Apartments, which was entrusted to the greatest artists of the time, who worked from his drawings. Le Brun also designed most of the statues in the park at Versailles. This enormous work cemented his reputation as a true seventeenth-century genius, as well as one of the founders, ideologues, and chief representatives of the classicist "grand style" of King Louis XIV's era.
In 1648 Le Brun became a founding member of the Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture, and in 1663 - the manager of the Manufacture of tapestries.
Charles Le Brun was not only the creator of the "grand style", but also contributed to the rebirth of classicism into academism.
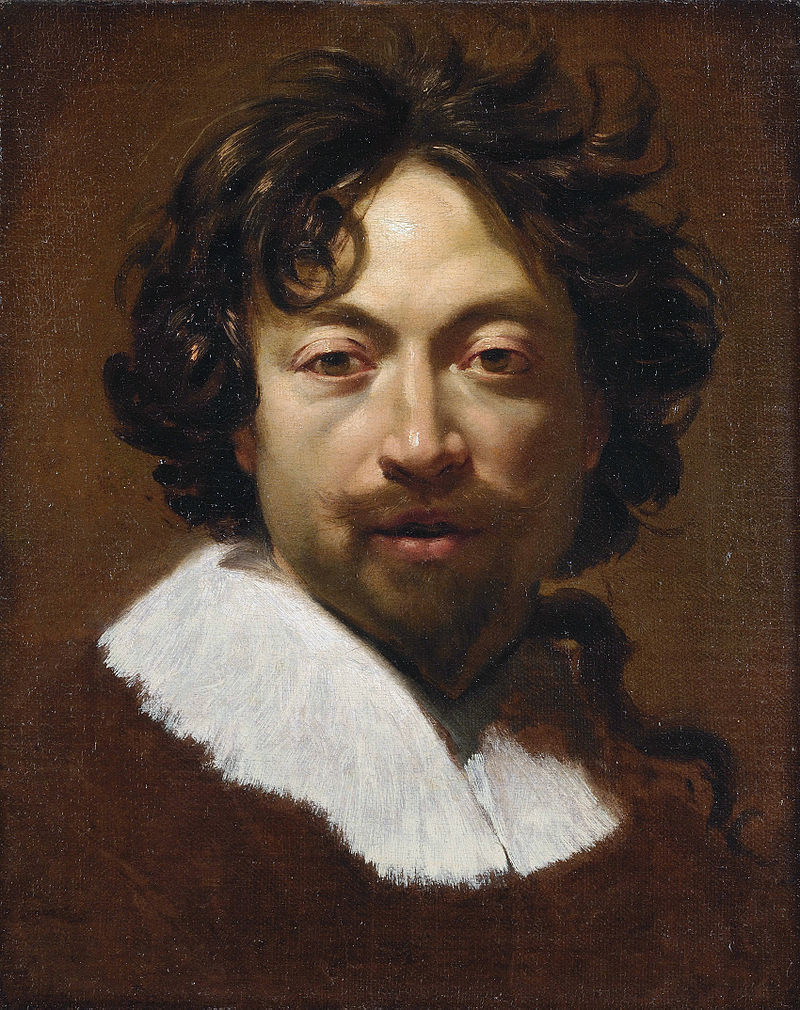


Simon Vouet was a French painter who studied and rose to prominence in Italy before being summoned by Louis XIII to serve as Premier peintre du Roi in France. He and his studio of artists created religious and mythological paintings, portraits, frescoes, tapestries, and massive decorative schemes for the king and for wealthy patrons, including Richelieu. During this time, "Vouet was indisputably the leading artist in Paris," and was immensely influential in introducing the Italian Baroque style of painting to France. He was also "without doubt one of the outstanding seventeenth-century draughtsmen, equal to Annibale Carracci and Lanfranco."

























![Georg Matthaeus Seutter | Atlas Novus, Vienna, 1730 [but slightly later], fine hand-coloured maps](/assets/image/picture_3553109/b1d41/yspc3vopast5vu1ma0lzreqghwaerqt2ucnaizrgmcay5fqdbkpu7zhjkjno7l1d1699098514jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Georg Matthaeus Seutter | Atlas Novus, Vienna, 1730 [but slightly later], fine hand-coloured maps](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3553109/b1d41/yspc3vopast5vu1ma0lzreqghwaerqt2ucnaizrgmcay5fqdbkpu7zhjkjno7l1d1699098514jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)




![Bible, German | [Weimar Elector’s Bible], 1768, finely bound by Johann Georg Dachau](/assets/image/picture_3530780/76ab9/nvwdvs4jdjiwgyrzawmys1hf-bfbodud9bfclkbyoclb1qikahsbn9dr7iivta6o1698927154jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Bible, German | [Weimar Elector’s Bible], 1768, finely bound by Johann Georg Dachau](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3530780/76ab9/nvwdvs4jdjiwgyrzawmys1hf-bfbodud9bfclkbyoclb1qikahsbn9dr7iivta6o1698927154jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)




![Johann Wilhelm Weinmann | [Phytanthoza iconographia, Dutch edition], Amsterdam, 1736-1748, fine engraved and mezzotint plates, printed in colours and finished by hand](/assets/image/picture_3553150/3e7db/g2yw3bupouens3hdnhlq-noaoh-o2sqjso298iyjisgoiz0hhf44foapd1rd4p1699101121jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Johann Wilhelm Weinmann | [Phytanthoza iconographia, Dutch edition], Amsterdam, 1736-1748, fine engraved and mezzotint plates, printed in colours and finished by hand](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3553150/3e7db/g2yw3bupouens3hdnhlq-noaoh-o2sqjso298iyjisgoiz0hhf44foapd1rd4p1699101121jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Jean-Baptiste Audebert | Histoire naturelle des singes. Paris, 1797-[1800], in the original parts, fine illustrations of primates](/assets/image/picture_3530743/97533/zll8szmoumzsdx86feof1b4xnhwzoiihymos91lyuesaxchvije5vgcl7ima5r1698925527jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Jean-Baptiste Audebert | Histoire naturelle des singes. Paris, 1797-[1800], in the original parts, fine illustrations of primates](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3530743/97533/zll8szmoumzsdx86feof1b4xnhwzoiihymos91lyuesaxchvije5vgcl7ima5r1698925527jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)











![Daniel Giraud Elliot | A monograph of the bucerotidae, or family of the hornbills. New York, [1876]-1882, fine plates by Keulemans](/assets/image/picture_3530945/0858a/rrsdrxzxxhbxpvqrwotocjaf3ttuqp2mkmdjuujntklnggbkietevtohrlsuahd1698994172jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Daniel Giraud Elliot | A monograph of the bucerotidae, or family of the hornbills. New York, [1876]-1882, fine plates by Keulemans](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3530945/0858a/rrsdrxzxxhbxpvqrwotocjaf3ttuqp2mkmdjuujntklnggbkietevtohrlsuahd1698994172jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


![Thomas Pennant | The British zoology. London, [1761]-1766, fine coloured plates](/assets/image/picture_3553052/cf9ca/5vmcpiiefschwxfd644hmmxujwr-inwgmjwdqtkchu1wuxzb45ec2hhjerbwp1699094282jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Thomas Pennant | The British zoology. London, [1761]-1766, fine coloured plates](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3553052/cf9ca/5vmcpiiefschwxfd644hmmxujwr-inwgmjwdqtkchu1wuxzb45ec2hhjerbwp1699094282jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)