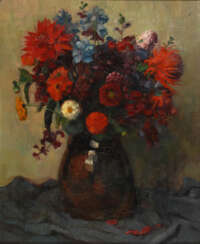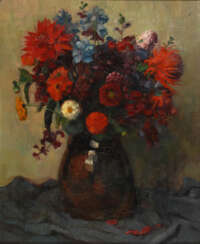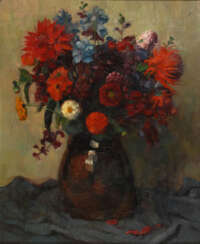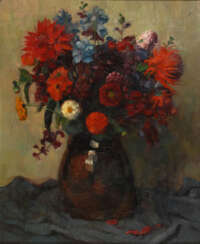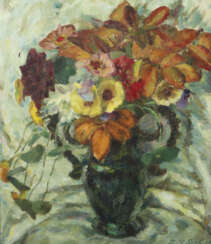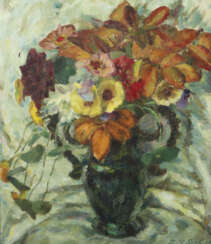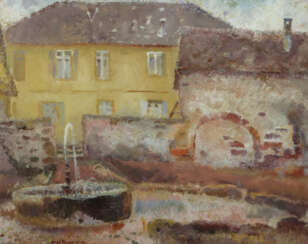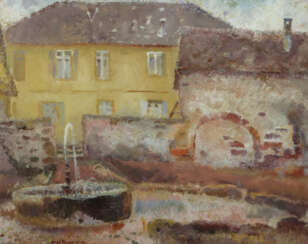558 Items by auctions and galleries:
franz heinrich
Lot 2001 Gref, Franz Heinrich Stühlingen/Baden 1872 - 1957 Weilimdorf
Franz Heinrich Gref (1872 - 1957)  Auktion 83: Antiquitäten & Moderne Kunst
Auktion 83: Antiquitäten & Moderne Kunst 

Franz Heinrich Gref
14.12.1872 - 17.09.1957

Yves Siebers Auktionen GmbH
Auktion 83: Antiquitäten & Moderne Kunst
Date: 23.03.2023 10:30 UTC +01:00
Number of lots in the catalog: 1067