john robins
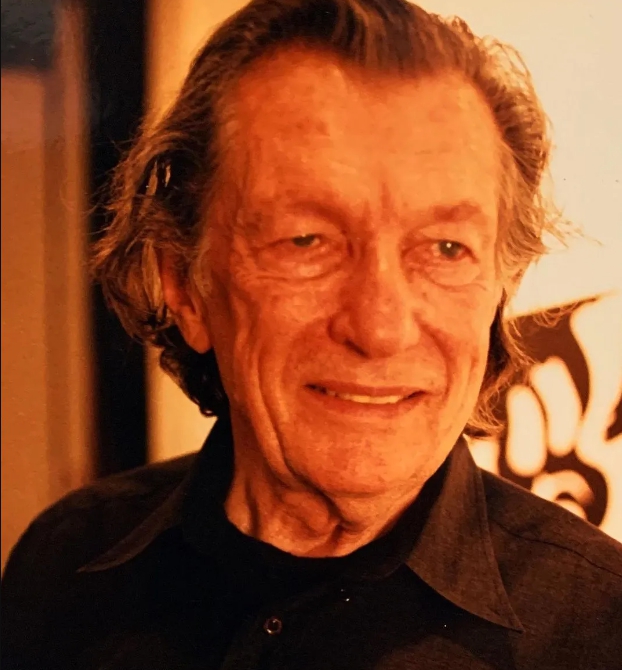


John Wesley was an American painter, known for idiosyncratic figurative works of eros and humor, rendered in a precise, hard-edged, deadpan style. Wesley's art largely remained true to artistic premises that he established in the 1960s: a comic-strip style of flat shapes, delicate black outline, a limited matte palette of saturated colors, and elegant, pared-down compositions. His characteristic subjects included cavorting nymphs, nudes, infants and animals, pastoral and historical scenes, and 1950s comic strip characters in humorously blasphemous, ambiguous scenarios of forbidden desire, rage or despair.
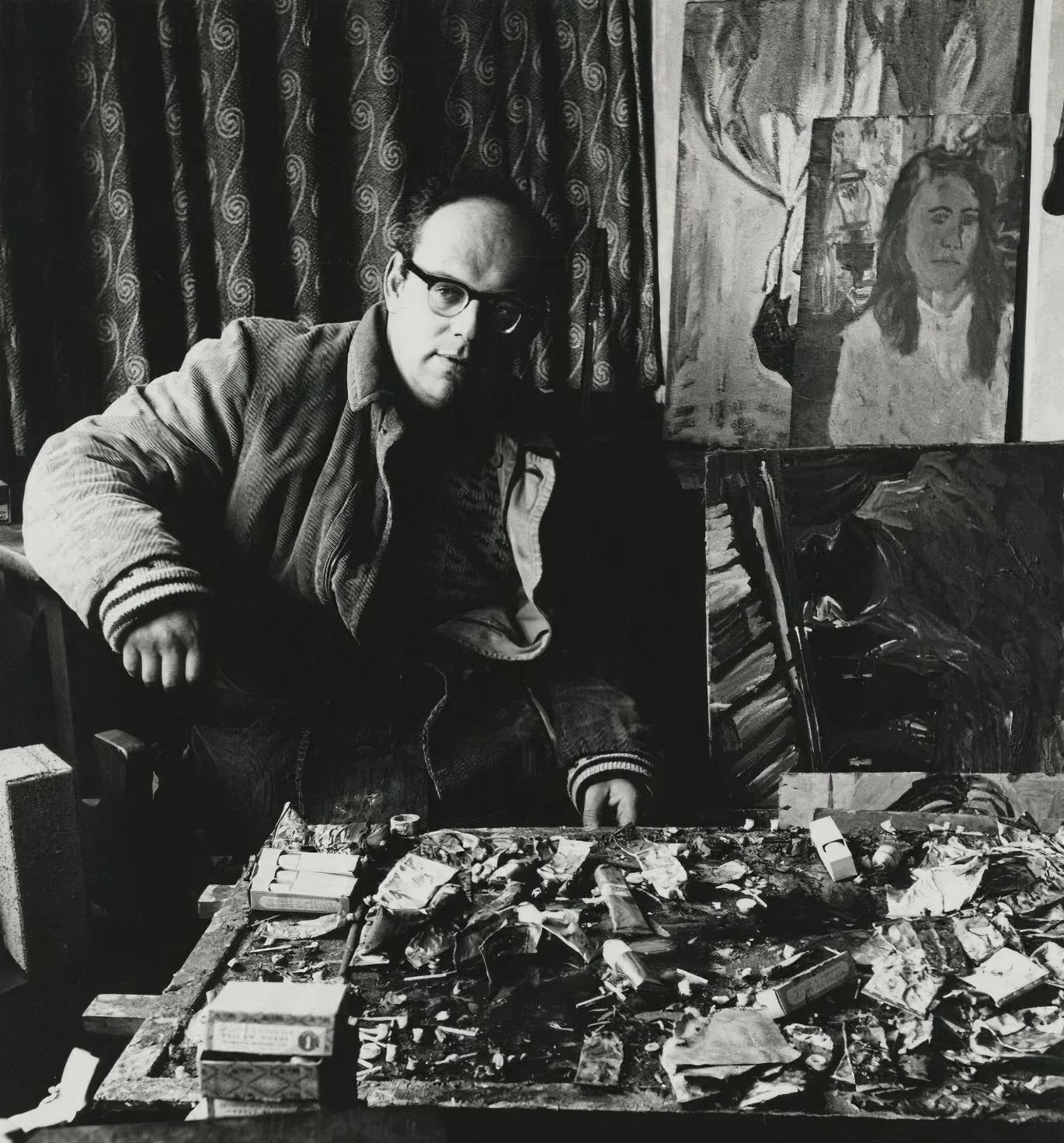


John Randall Bratby was an English painter who founded the kitchen sink realism style of art that was influential in the late 1950s. He made portraits of his family and celebrities. His works were seen in television and film. Bratby was also a writer.


John Randall Bratby was an English painter who founded the kitchen sink realism style of art that was influential in the late 1950s. He made portraits of his family and celebrities. His works were seen in television and film. Bratby was also a writer.
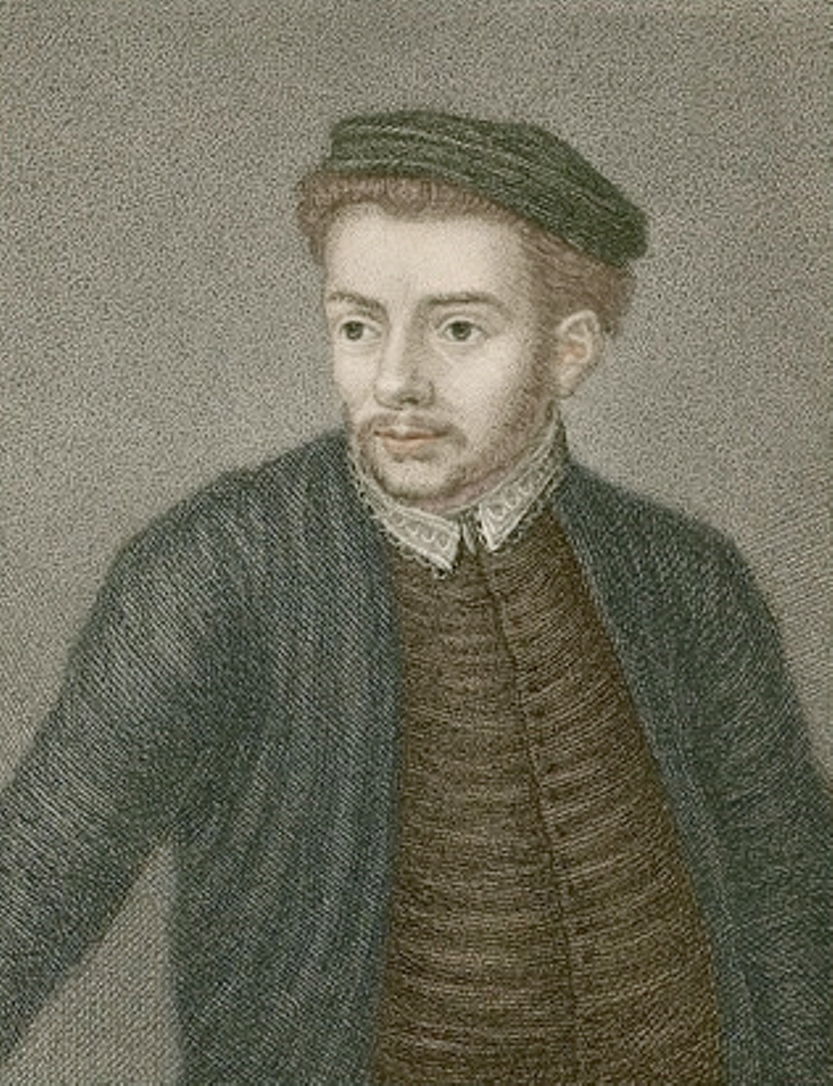



John Skelton was an English poet and writer of the Tudor period.
He was educated at the University of Cambridge, followed by degrees in rhetoric at Oxford, in the Netherlands, and at Cambridge. He was also a translator of ancient Greek and Roman authors. In 1488 Skelton was appointed court poet to Henry VII and then tutor to the Duke of York (later Henry VIII). In 1498 he took holy orders.
Skelton was known as a poet and satirist on both political and religious subjects. His best-known works include the moralizing play Magnyficence (1516), the humorous poem The Tunning of Elinor Rumming (1520), and numerous satirical poems in which he ridiculed both secular and ecclesiastical authorities. His reputation was confirmed by Erasmus of Rotterdam himself, who spoke highly flatteringly of Skelton.


Paul Gauguin, a French artist born in Paris in 1848, is renowned for his significant contributions to Post-Impressionism, Primitivism, and Synthetism. Gauguin's art is distinguished by his experimental use of color and style, which set him apart from the traditional Impressionist movement.
Gauguin's early life was marked by a period in Peru, which influenced his artistic perspective. Initially, he pursued a career in stockbroking but soon turned to art, driven by financial necessity and a growing passion. His artistic journey began under the mentorship of Impressionist artist Camille Pissarro and through exposure to the works of other avant-garde artists.
The hallmark of Gauguin's work is his exploration of non-Western cultures, particularly during his time in Tahiti and the Marquesas Islands. This period saw the creation of some of his most famous works, including "Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?" His paintings from this era, characterized by vivid colors and Symbolist themes, reflect a fusion of cultural influences and his quest for a "primitive" expression of spiritual and emotional states.
Despite his innovative style, Gauguin struggled with financial difficulties and health issues throughout his life. His work received little recognition during his lifetime, but posthumously, he gained acclaim for influencing modern artists like Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse.
Today, Gauguin's works are celebrated in galleries and museums worldwide for their unique blend of cultural influences and artistic innovation. His enduring legacy is a testament to his unique vision and the profound impact he had on the art world.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques, stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Paul Gauguin. Sign up now for exclusive updates and immerse yourself in the world of this visionary artist.
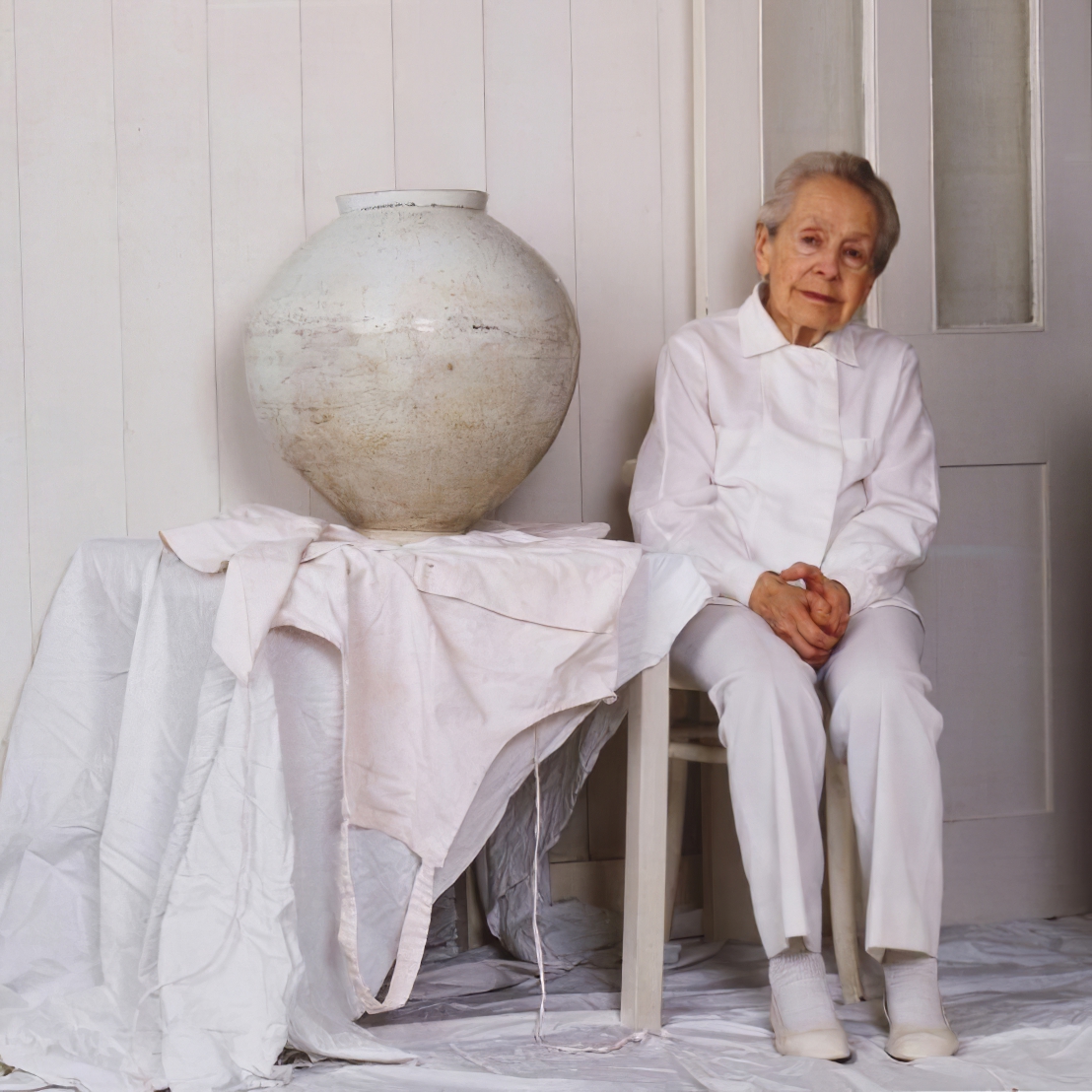


Lucie Rie was an Austrian-born British studio potter.
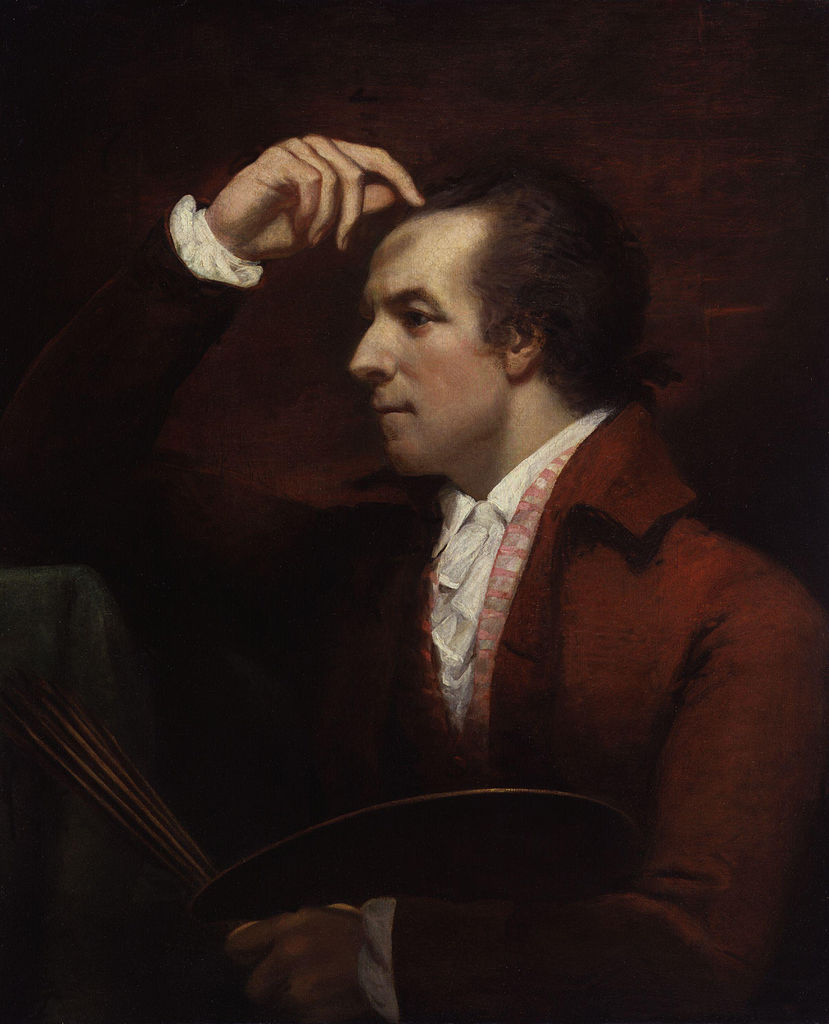


James Northcote was a British painter.