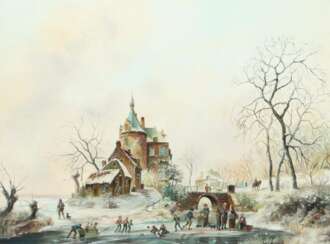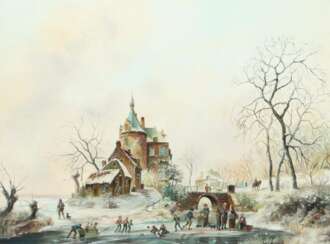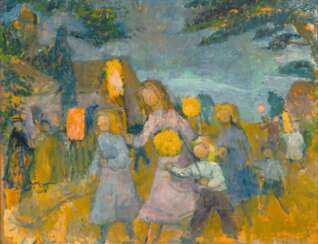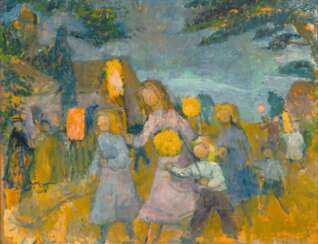kinder &
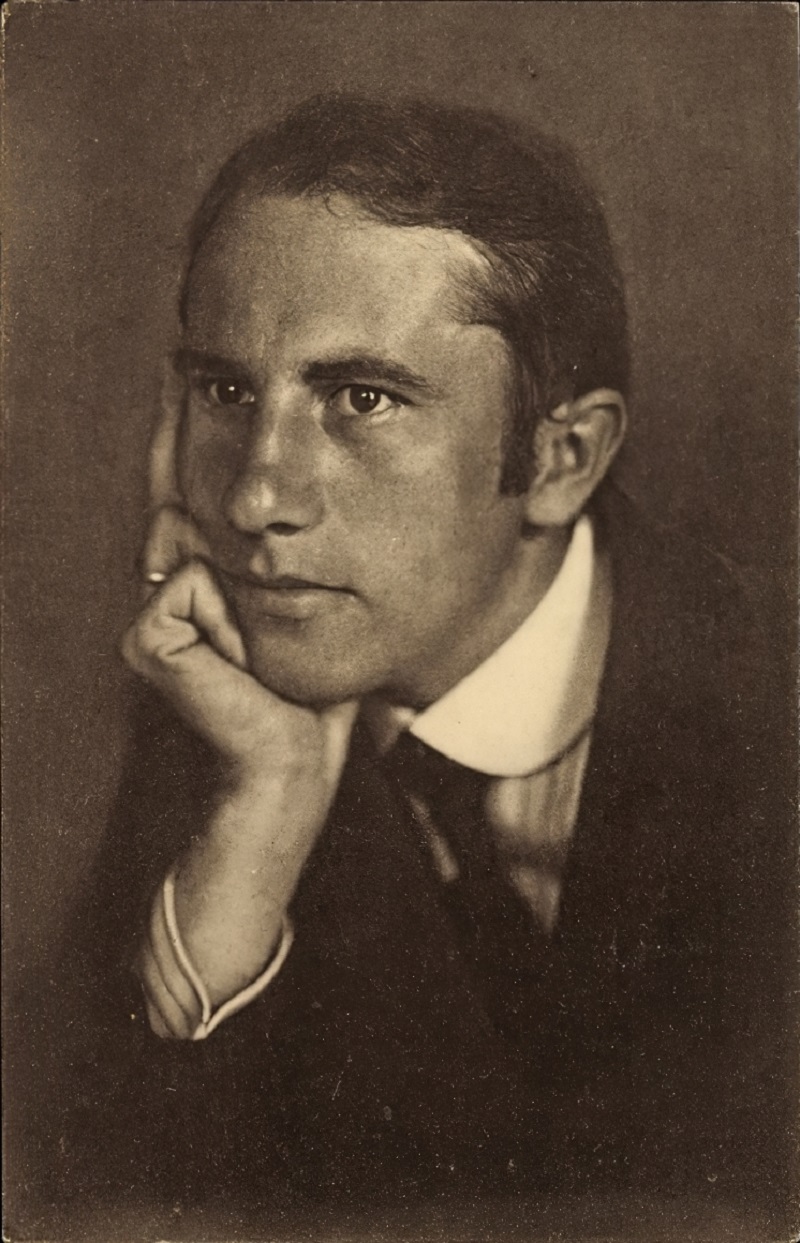

Heinrich Mathias Ernst Campendonk was a painter and graphic designer born in Germany who became a naturalized Dutch citizen.
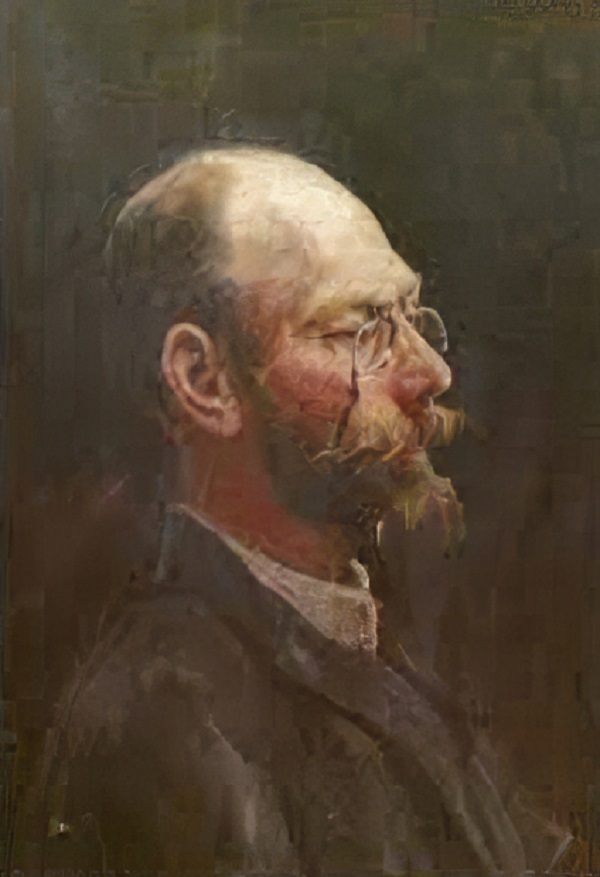


Gustav Kampmann was a German landscape painter and graphic artist. His work includes landscape paintings and lithographs, rarely with persons, sometimes with architectural elements. Kampmann has developed a personal, highly idiosyncratic style that impresses us with its openness, merely addressing motives, and spontaneous gesture. His works have a painterly freedom and a degree of abstraction that was not typical for that time.
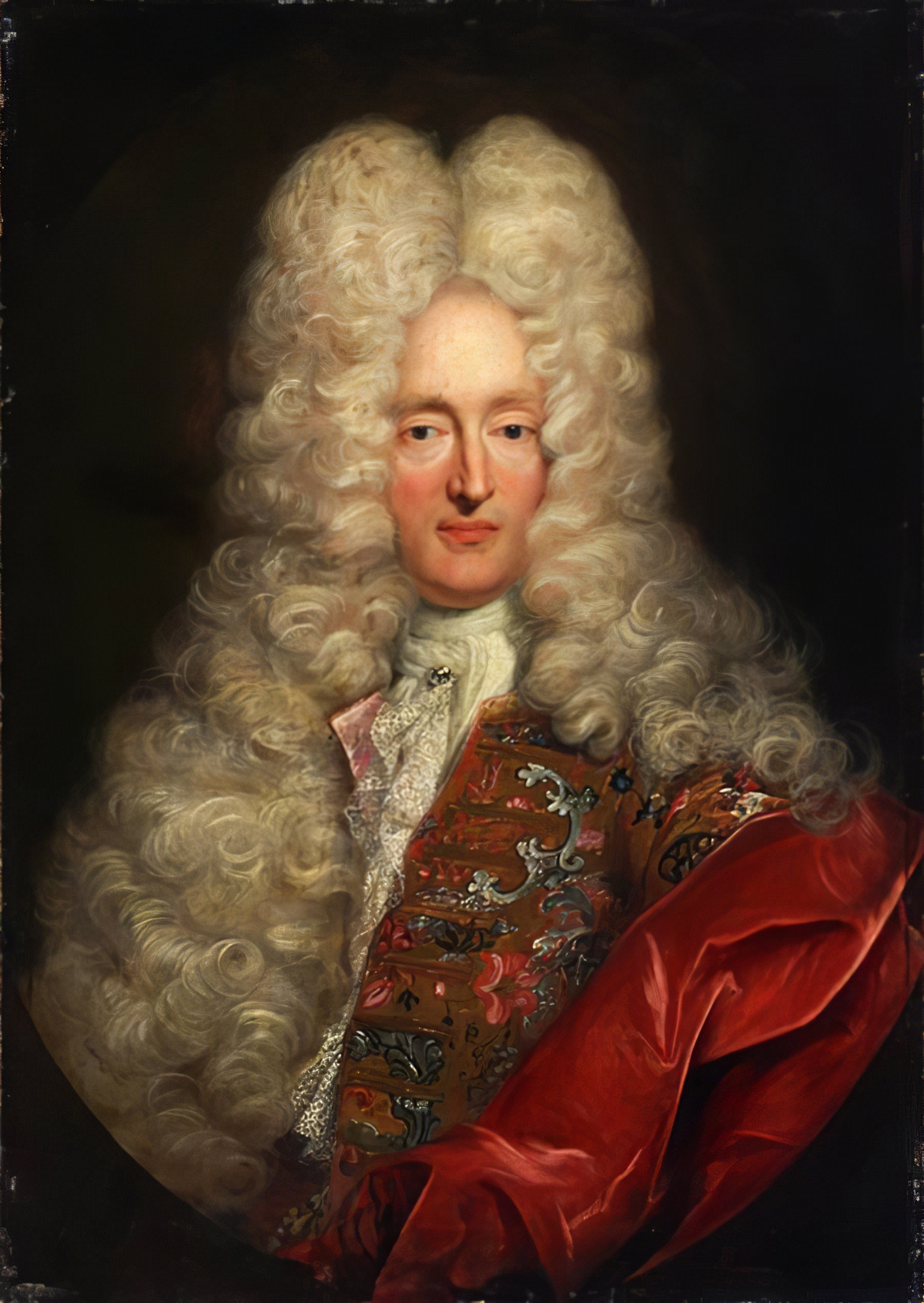


Frans van Stampart was a Flemish portrait painter, printmaker and publisher. The artist established a reputation as a portraitist of European rulers, aristocrats and higher clergy. He had an international career, which brought him to the court in Vienna where he worked as court painter of the Imperial court. He is also known as the co-publisher of two publications which depict the Imperial art collection in Vienna and for which he also made some of the engravings.


Heinrich Mathias Ernst Campendonk was a painter and graphic designer born in Germany who became a naturalized Dutch citizen.


Philippe de Champaigne was a French painter and engraver of Flemish origin, a major representative of the French Baroque school. He was one of the founders of the Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture in Paris. Champaigne created a very large number of portraits of the high nobility, as well as paintings on religious themes.


Philippe de Champaigne was a French painter and engraver of Flemish origin, a major representative of the French Baroque school. He was one of the founders of the Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture in Paris. Champaigne created a very large number of portraits of the high nobility, as well as paintings on religious themes.
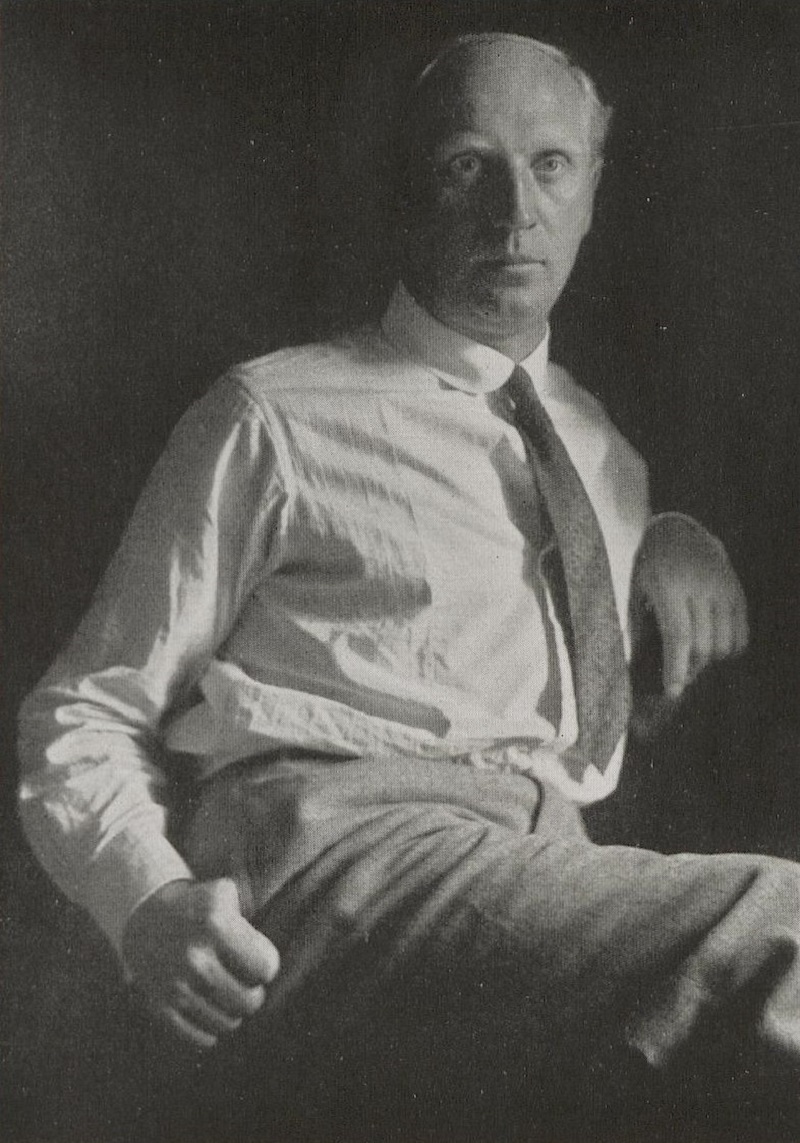


Theo Champion was a German painter. His work was part of the painting event in the art competition at the 1928 Summer Olympics.
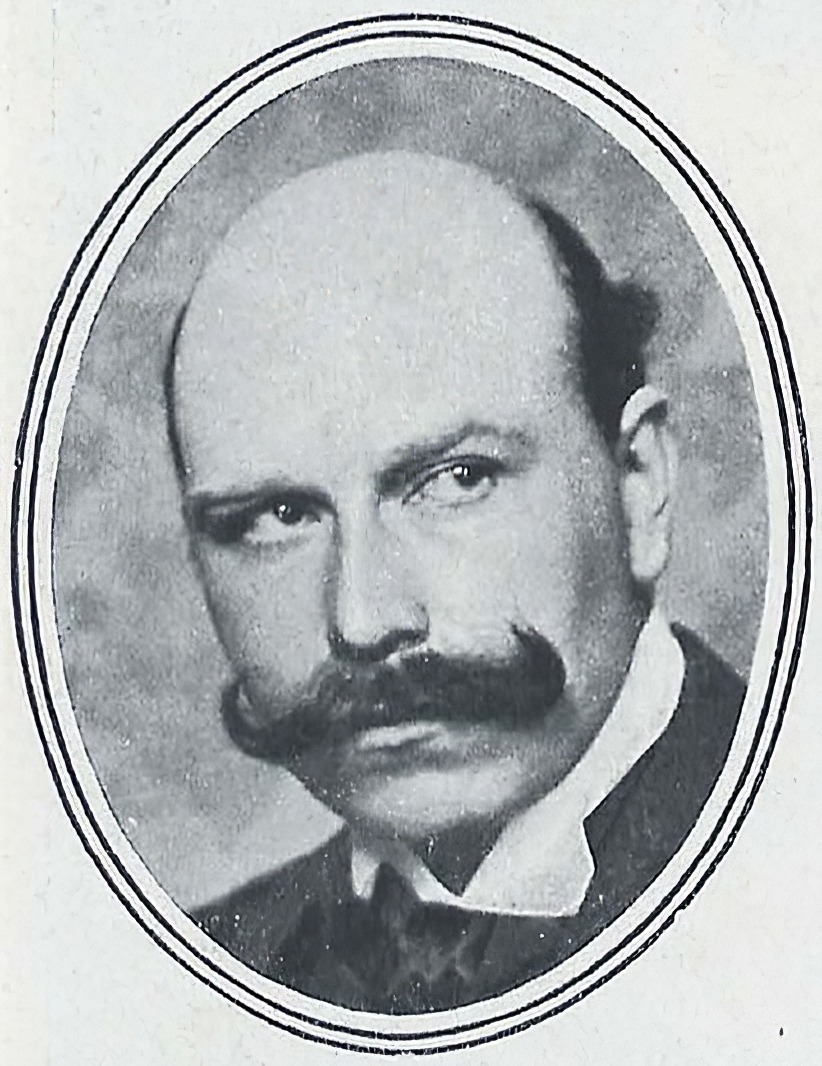


Arthur Kampf was a German painter. He was associated with the Düsseldorf school of painting.
Kampf's work is most strongly associated with the genre of traditional history painting, though throughout his lifetime he explored styles influenced by Impressionism and Art Nouveau. He was also celebrated for large scale portrait work and in particular children's portraiture. Kampf also worked extensively as an illustrator, contributing drawings to volumes by Shakespeare (1925), R. Herzog, History of Prussia (1913) and J.W. Goethe, Faust (1925). Kampf's artwork post World War II largely focused on religious themes.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.

Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.