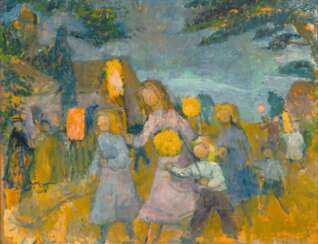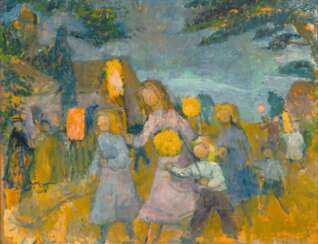oppel

Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.


Lisel Oppel, actually Anna Amalie Elisabeth Oppel, was a German painter and ceramist who remains to this day one of the most memorable members of the Worpswede artist colony. From 1917 she studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Richard Riemerschmid and Hermann Gröber.
Liesel Oppel painted simple paintings with great joy and colourfulness; mainly portraits, people at work and on holidays, less often pure landscapes. One of Oppel's special pictorial themes was children's pastimes in the countryside, in which she adopted and extended the motifs of the early Worpswede artists. Most of her work was created in the 1950s. She continued her expressive painting style.