options
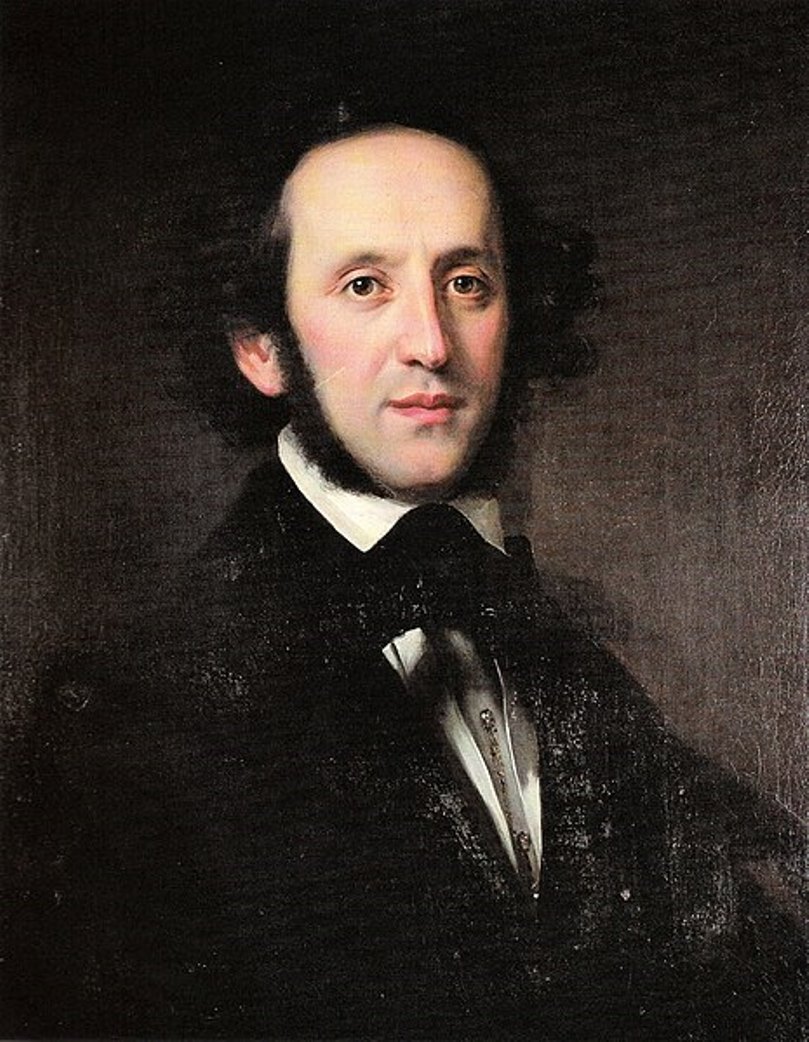











Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".
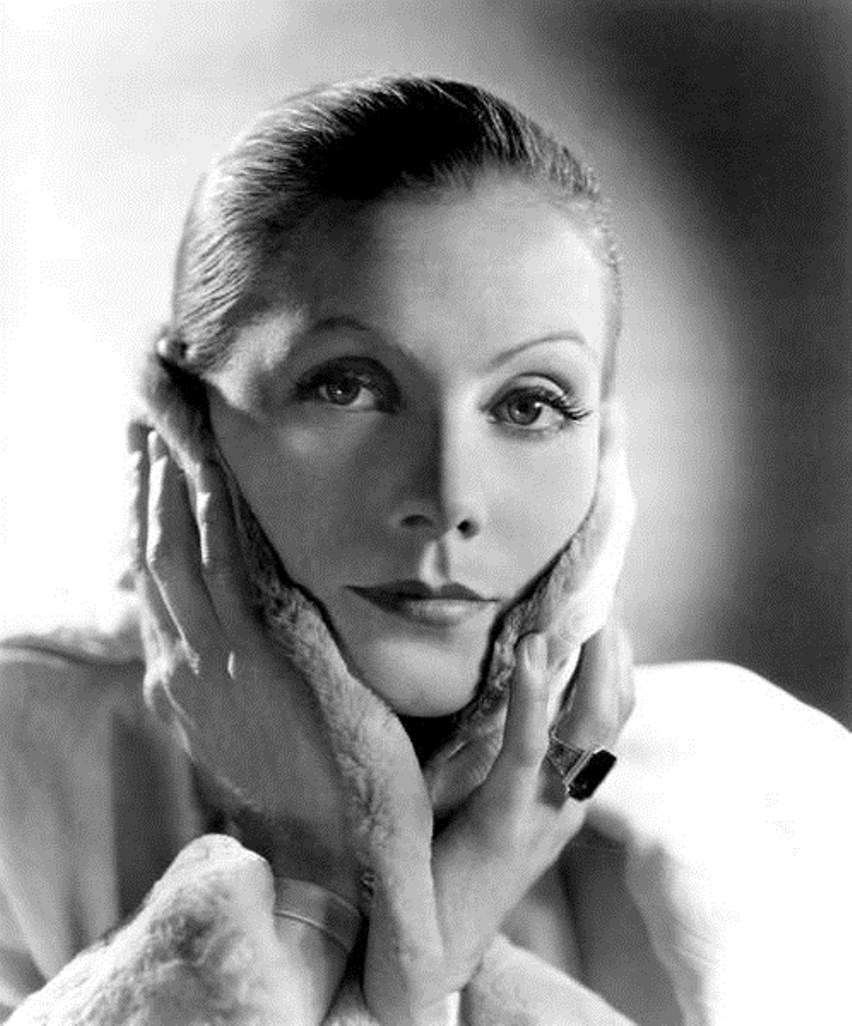


Greta Garbo, born Greta Lovisa Gustafsson, is a Swedish and American actress.
Greta was born into a poor family and early went to work - in a beauty salon, salesman, modeling for photos in local advertising magazines. And also studied at the drama school of the Royal Stockholm Drama Theater. The girl was noticed by agents, invited to a cameo in the movie "Peter the Tramp" and soon she became a star of silent movies in Sweden and Germany. In 1923, she changed her last name to Garbo. It was at this time that she caught the eye of Hollywood mogul Louis B. Mayer, who signed her to a one-year contract with MGM. Her first American film role was in Torrent (1926), followed by The Temptress (1926), which brought Garbo stardom.
Garbo was the highest paid actress of the pre-war era. Greta's talented and dramatic performance brought her worldwide fame and the title of one of the best actresses in Hollywood history. Anna Karenina and Mata Hari are two of the most significant roles of the actress. When the era of silent movies ended, a languid low voice with a slight hoarseness became a trademark of Garbo. For his contribution to the development of cinematography in 1954, Garbo was awarded an Oscar.
The life of Greta Garbo is still shrouded in mystery and myths. She was silent, preferred privacy and therefore was surrounded by an atmosphere of mystery. But under the outer facade of aloofness beat sensitive and passionate heart. Greta was a style icon of her time, she was imitated and envied by the stars of Hollywood.
After the outbreak of World War II in 1941, Greta Garbo never returned to the big movie, only sometimes playing occasional roles in small pictures. After the war, she returned to America and lived in seclusion in New York City for another 50 years. She did not give interviews, avoided reporters and went out on the street only when necessary and with dark glasses.