style de sèvres

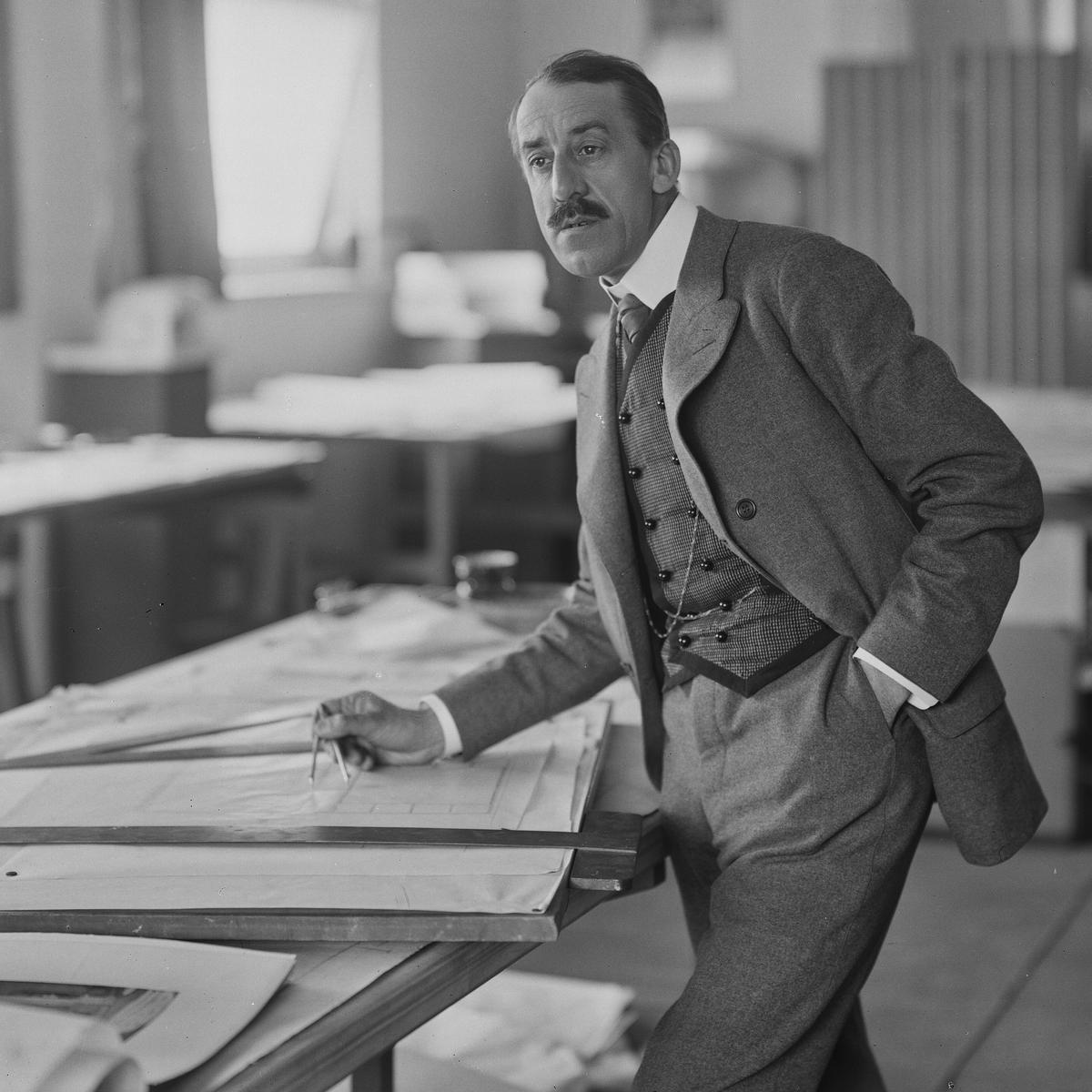
Paul Sérusier was a French Post-Impressionist painter and theorist, notable for his significant contributions to the art movement known as the Nabis. Born in Paris on November 9, 1864, Sérusier's work is characterized by its expressive use of color and pattern, inspired by the techniques of Paul Gauguin. He is best known for his exploration of color, sensation, and abstraction, particularly evident in works like "Le Talisman, the Aven River at the Bois d'Amour" (1888). This painting marks a departure from the Impressionists' more faithful representation of observed reality, focusing instead on translating sensations onto the canvas with vibrant brushstrokes and an emphasis on emotional expression over visual accuracy.
Sérusier's paintings often feature the landscapes and people of Brittany, notable for their contemplative mood achieved through firm contours and blocks of unmodulated color. His style evolved under the influence of Synthetism and Cloisonnism, favoring flattened forms and large swathes of color, as seen in "Farmhouse at le Pouldu" (1890). This approach reflects a decorative organization of objects, emphasizing the craft and execution of the scene.
Some of Sérusier's notable works are housed in prestigious museums such as the Musée d'Orsay in Paris, including "Portrait of Paul Ranson in Nabi Costume" (1890) and "Landscape" (1912). His legacy extends beyond his own artworks; he was a key figure in the formation of the Nabis movement, and his theoretical contributions have had a lasting impact on the art world.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Sérusier's work represents a unique blend of post-impressionist and symbolist styles, making his pieces highly valued both for their historical significance and their aesthetic appeal. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Paul Sérusier, sign up for our updates. This subscription service is exclusively focused on providing information related to Sérusier's work, ensuring you remain informed about opportunities to acquire pieces by this influential artist.



Roger de la Fresnaye was a French painter, a representative of Cubism in painting.
He studied at the Académie Julian in Paris and was fascinated by the art of Paul Cézanne. In his works Fresnaye synthesized lyrical color with geometric simplifications of Cubism.
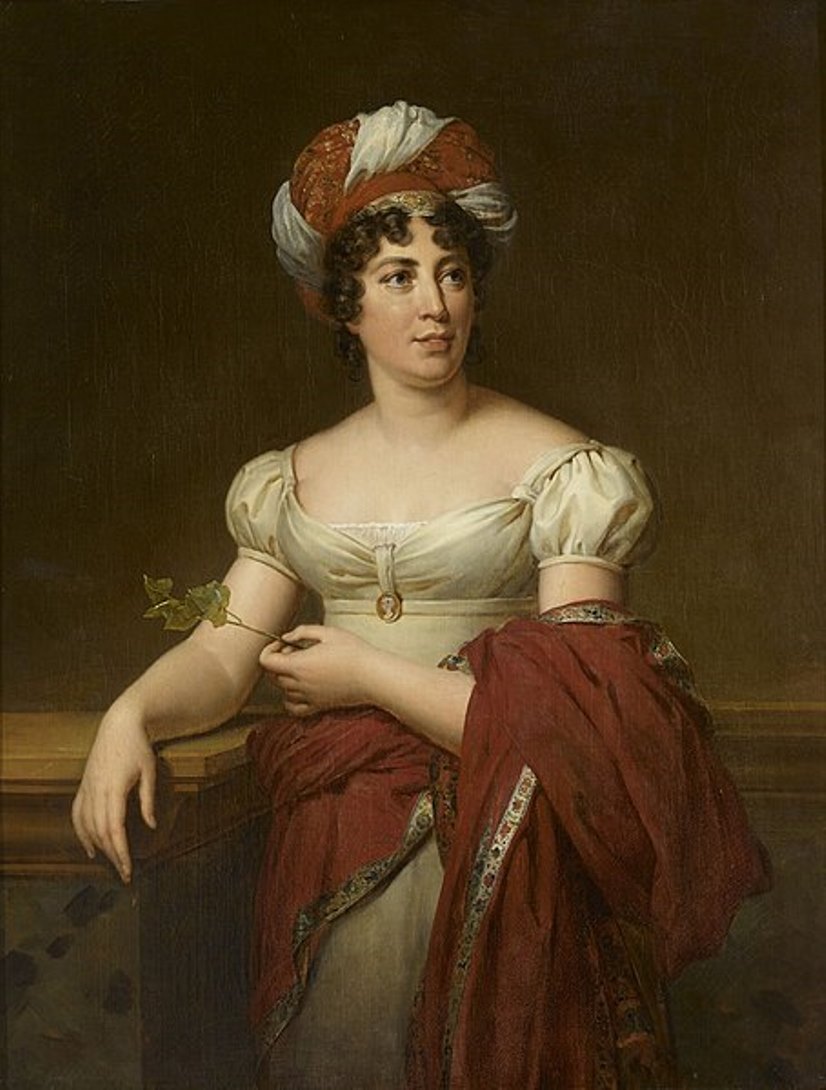


Anne-Louise-Germaine Necker, Baroness of Staël-Holstein, known as Madame de Staël, was a French writer, literary theorist, and publicist.
She was born into a Swiss family where her father was a banker and then finance minister to King Louis XVI, and her mother ran a brilliant literary and political salon in Paris where Voltaire, Diderot, and Hume frequented. Young Necker received a brilliant education, she absorbed the intellectual environment with great curiosity, becoming a witty and well-read conversationalist.
In 1786, she married the Swedish ambassador to Paris, Baron Eric de Staël-Holstein. It was a marriage of convenience, which ended in 1797 formal divorce.
Madame de Staël became known not only for her stunning and versatile works, but also for her enormous influence on the intellectual climate of that 19th century. During her lifetime she was known as a novelist, but she became much more famous as a political philosopher, literary critic, and theorist of Romanticism. Madame de Staël was an implacable opponent of Napoleon I and traveled around Europe for a decade during his reign from 1803. In 1810, the writer published one of her most famous and influential works, On Germany. She returned to Paris in 1814, after the fall of Napoleon, and wrote "Reflections on the Principal Events of the French Revolution."
In her travels, Madame de Staël met many politicians, artists and writers and was known for her cosmopolitanism and feminism. Madame de Staël epitomized the European culture of her time, combining ideas from neoclassicism to romanticism in her glittering salon for leading intellectuals.
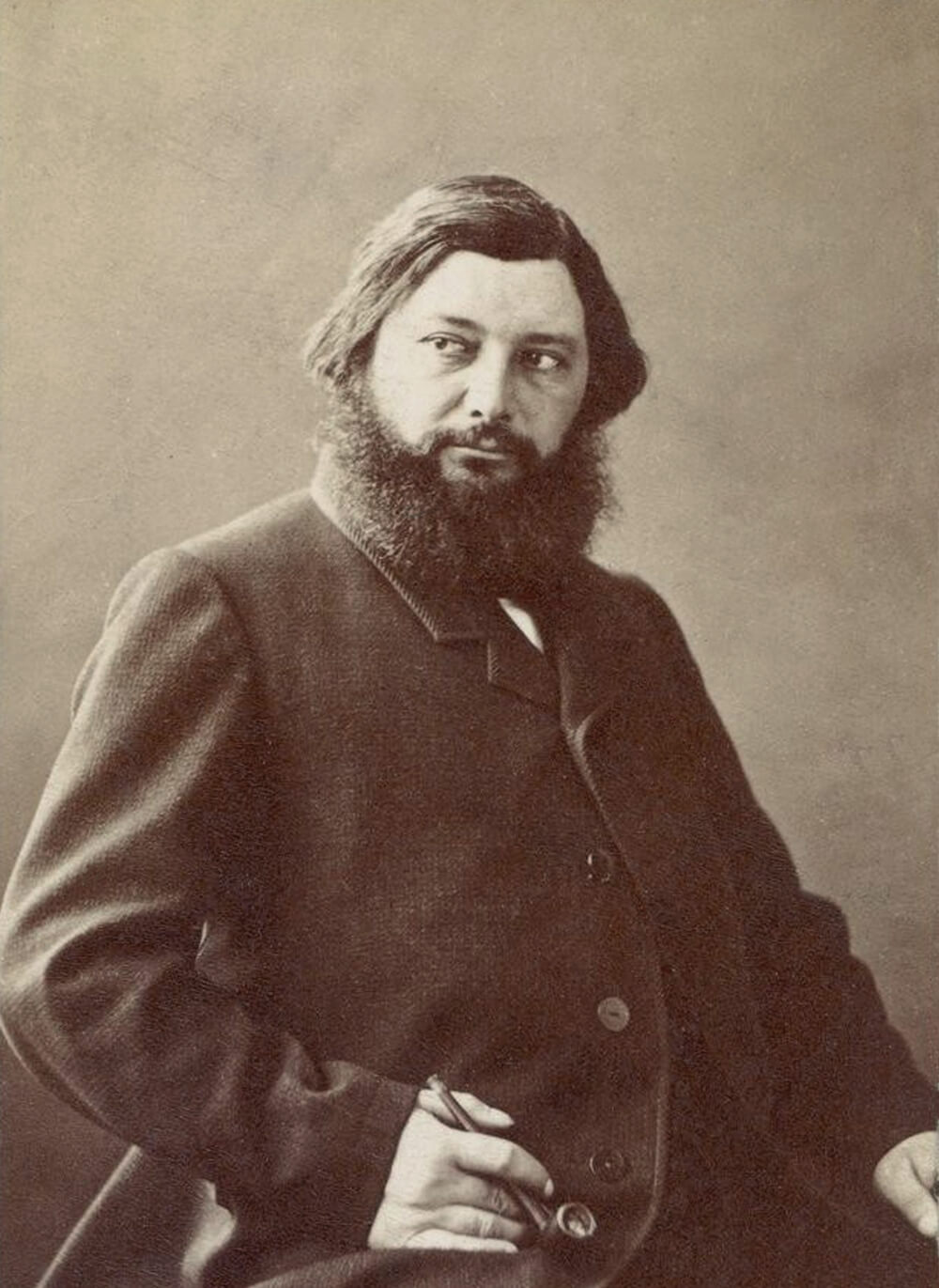




Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and the Romanticism of the previous generation of visual artists. His independence set an example that was important to later artists, such as the Impressionists and the Cubists. Courbet occupies an important place in 19th-century French painting as an innovator and as an artist willing to make bold social statements through his work.