tell
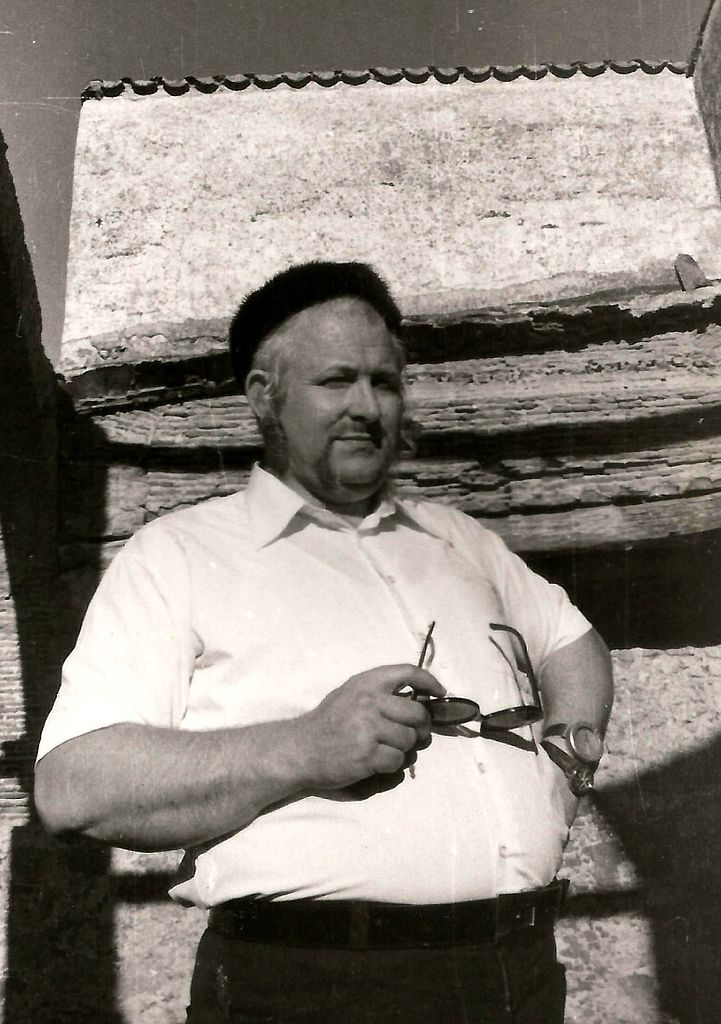

Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.
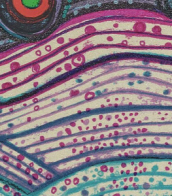

Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.
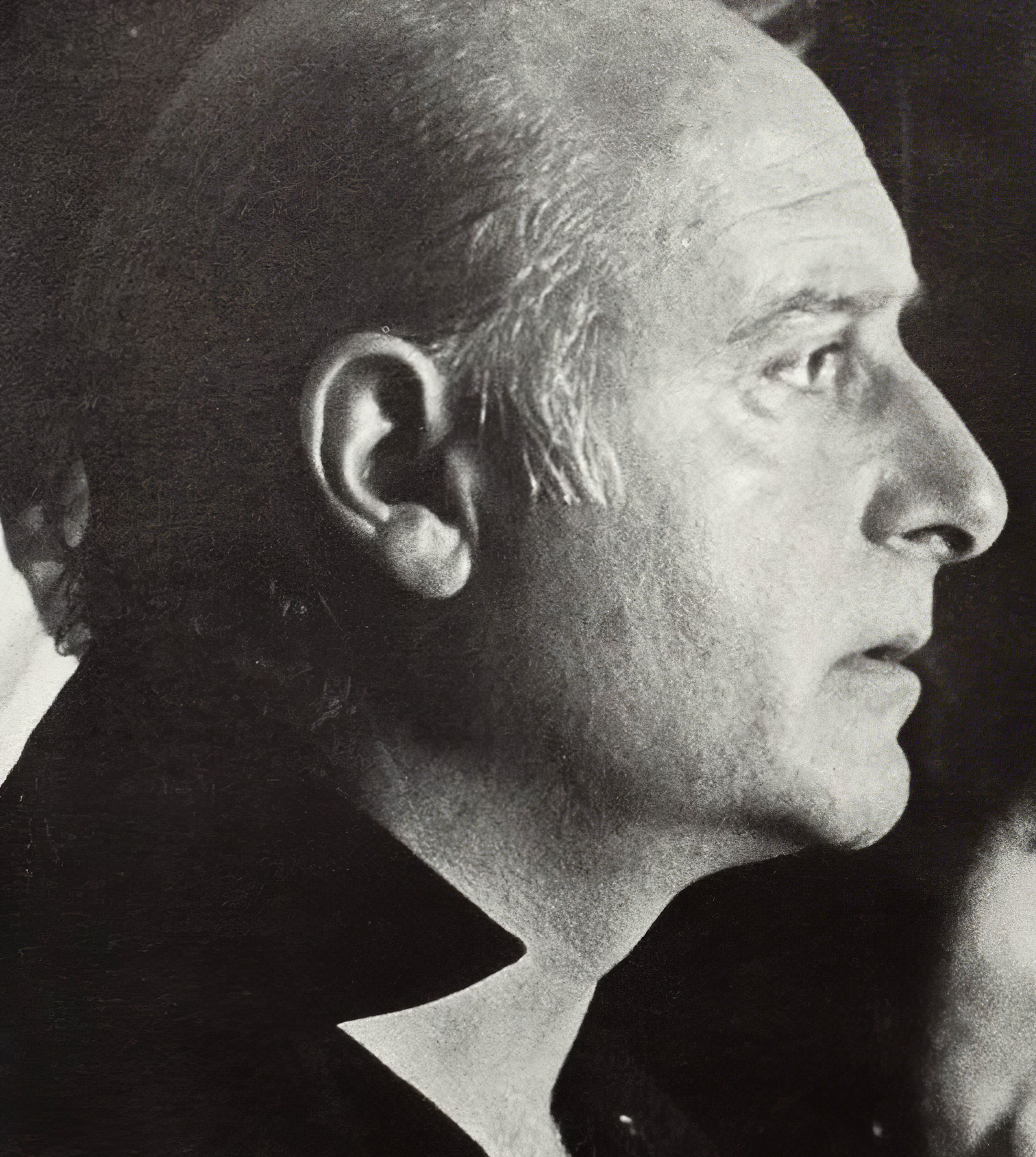


Domenico (Mimmo) Rotella was an Italian artist considered an important figure in post-war European art. Best known for his works of décollage and psychogeographics, made from torn advertising posters. He was associated to the Ultra-Lettrists an offshoot of Lettrism and later was a member of the Nouveau Réalisme, founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany.


Domenico (Mimmo) Rotella was an Italian artist considered an important figure in post-war European art. Best known for his works of décollage and psychogeographics, made from torn advertising posters. He was associated to the Ultra-Lettrists an offshoot of Lettrism and later was a member of the Nouveau Réalisme, founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany.


Domenico (Mimmo) Rotella was an Italian artist considered an important figure in post-war European art. Best known for his works of décollage and psychogeographics, made from torn advertising posters. He was associated to the Ultra-Lettrists an offshoot of Lettrism and later was a member of the Nouveau Réalisme, founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.


Wolf Vostell was a German artist who is considered a pioneer of video and installation art, and a key figure in the Fluxus movement. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Wuppertal and later at the École Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.
Vostell's art was heavily influenced by the horrors of World War II, and he often incorporated themes of violence and destruction in his work. He was interested in exploring the relationship between art and technology, and he experimented with new media such as television, video, and sound.
One of Vostell's most famous works is "Concrete Traffic," a 1970 installation in which he placed a Cadillac in a block of concrete. The piece was intended to comment on the impact of automobile culture on society and the environment.
Another notable work is "TV-Burying," a performance piece in which Vostell buried a television set in the ground, with only the screen visible. The work was a commentary on the pervasive influence of television on modern life.
Vostell's work has been exhibited extensively around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Venice Biennale, and the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris.

Frank Philip Stella, an American icon in the realms of painting, sculpture, and printmaking, has left an indelible mark on the art world with his pioneering work in minimalism and post-painterly abstraction. Born on May 12, 1936, in Malden, Massachusetts, Stella's artistic journey commenced with his studies in painting at Phillips Academy, Andover, and history at Princeton University. His move to New York City in 1958 heralded the start of an illustrious career that would see him challenge and redefine artistic boundaries.
Stella's work is celebrated for its innovative approach to form, color, and composition. His early endeavors in the late 1950s showcased black paintings characterized by bands of bare canvas, which played a pivotal role in emphasizing the flatness of the picture plane. This deliberate artificiality in his work garnered considerable attention and positioned him at the forefront of Post-Painterly Abstraction, a movement that reacted against the emotive excesses of Abstract Expressionism.
Throughout his career, Stella continued to push the limits of abstraction. His vocabulary expanded to include vibrant and dynamic assemblages that projected out from the wall, utilizing a variety of materials from steel to plastic. This evolution of his style is not only a testament to his ingenuity but also his influence on contemporary art. Notable works that exemplify his groundbreaking approach include "Grajau I," "Harran II," and "Eskimo Curlew," among others, which can be found in prestigious collections such as The Glass House and the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum.
For art collectors and enthusiasts alike, Stella's oeuvre offers a captivating exploration into the possibilities of abstract art. His continued relevance and the profound impact of his work on both his peers and successive generations of artists underscore his status as a seminal figure in modern art.
Stay updated on new discoveries, sales, and auction events related to Frank Philip Stella by signing up for our newsletter. This subscription is your gateway to the latest in the world of Frank Stella, ensuring you never miss an opportunity to engage with the works of this monumental artist.


Domenico (Mimmo) Rotella was an Italian artist considered an important figure in post-war European art. Best known for his works of décollage and psychogeographics, made from torn advertising posters. He was associated to the Ultra-Lettrists an offshoot of Lettrism and later was a member of the Nouveau Réalisme, founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany.
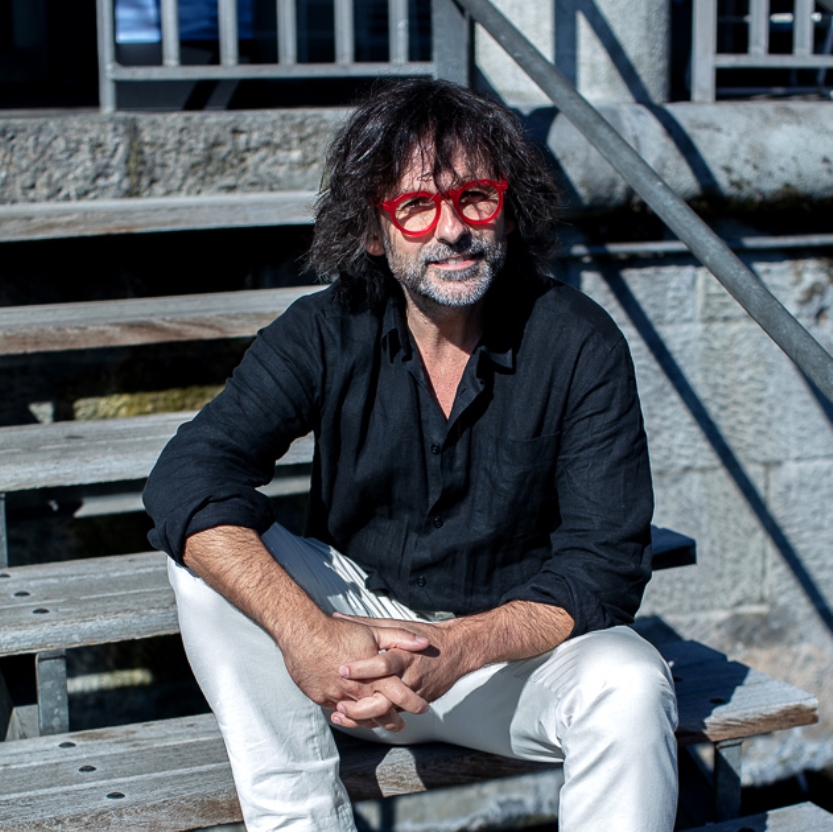


Niclas Castello, real name Norbert Zerbs, is a German painter and sculptor, representative of Pop Art.
Niclas studied art in Germany, Paris and New York. In the 1990s in West Berlin he discovered street art, which became the basis of his career. He is known for a series of sculptures titled "Kiss Sculptures" and the works "Cube Painting-Sculpture". Castello also uses an unusual technique to capture the moment the work emerges: at the end of the realization, the artist takes the piece and compresses it to place it in a box.
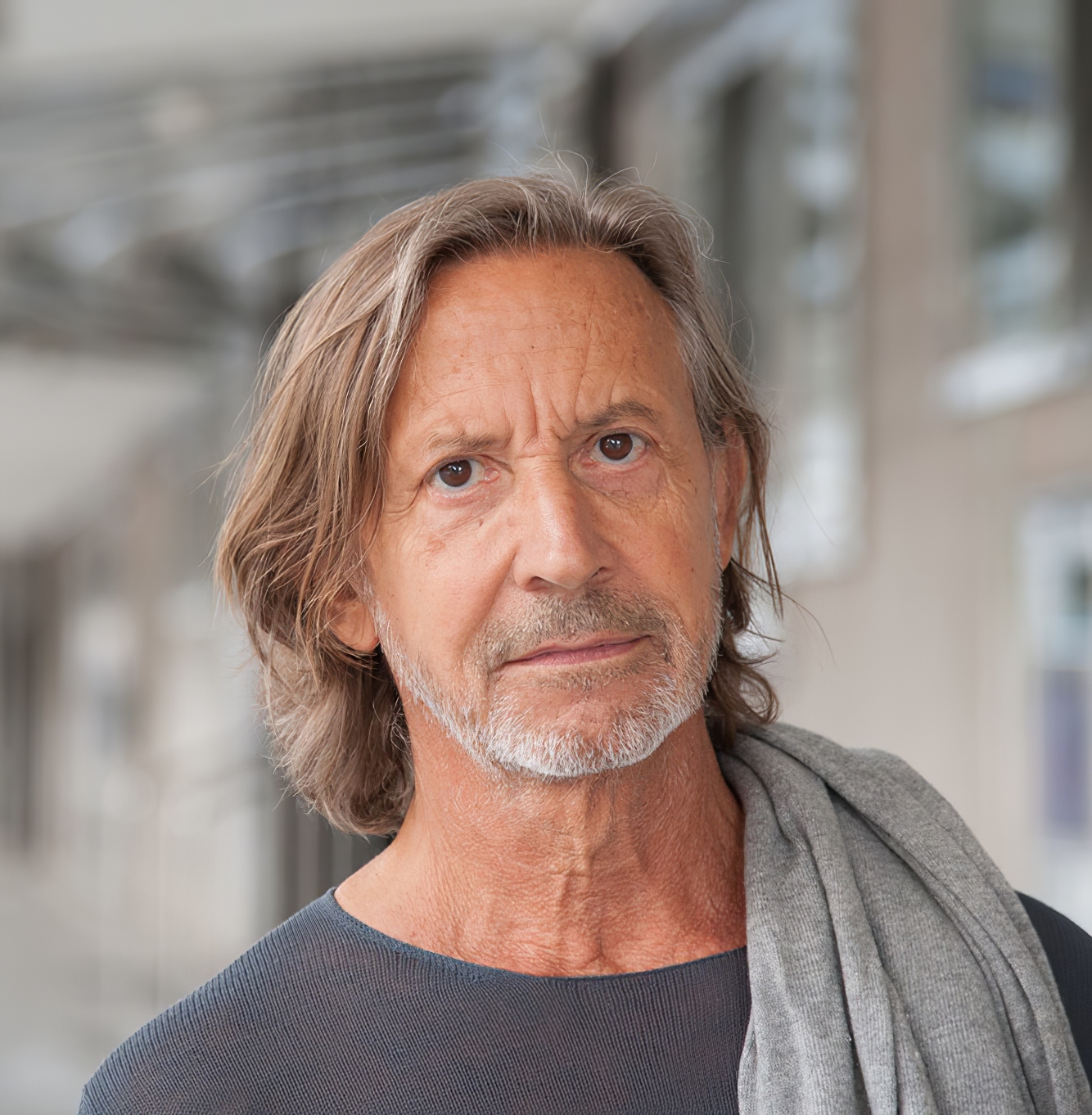


Luciano Castelli is a Swiss painter, graphic artist, photographer, sculptor and musician.


Luciano Castelli is a Swiss painter, graphic artist, photographer, sculptor and musician.
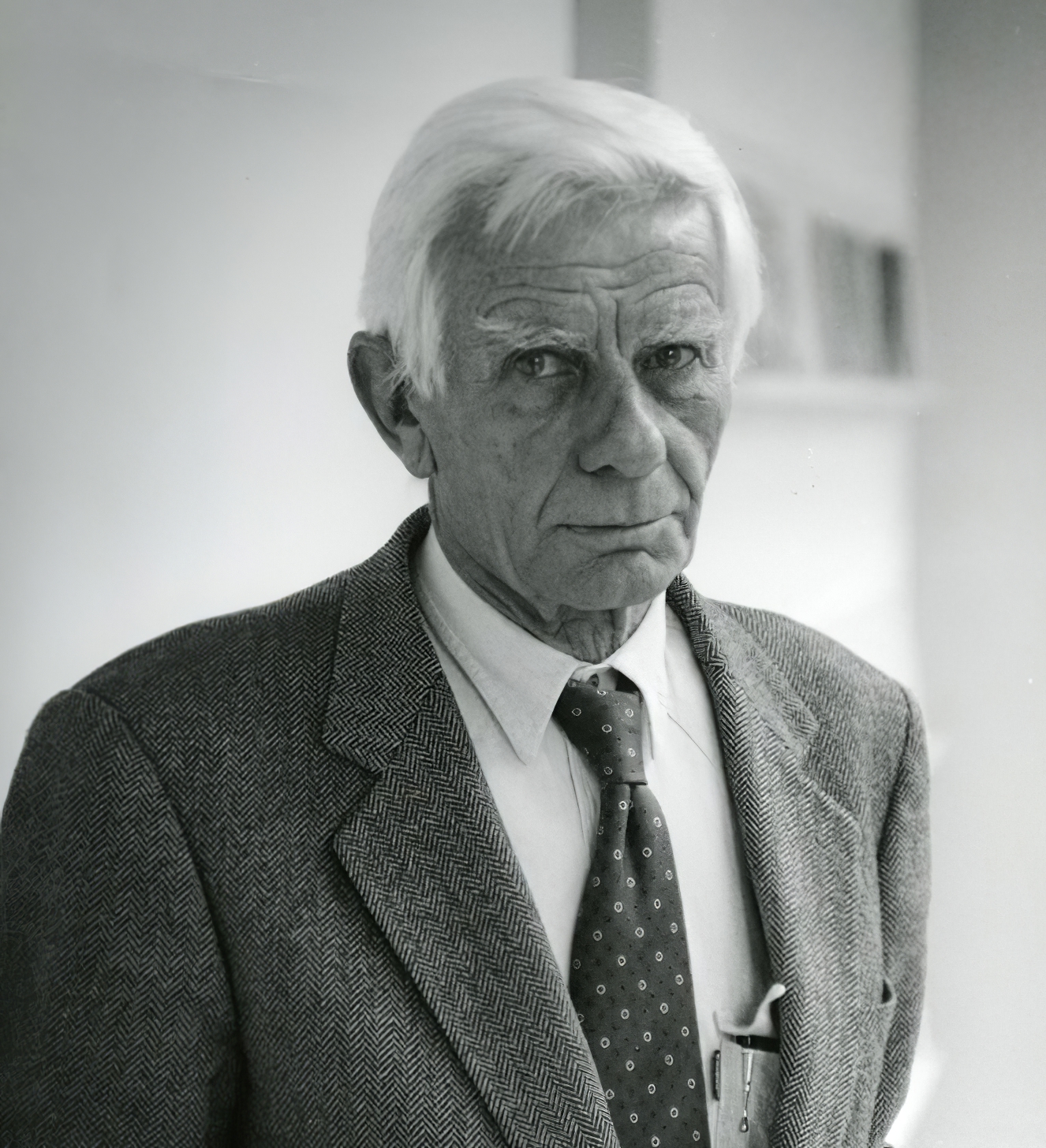


Enrico Castellani was an Italian artist. He was active in Italy from the early 1960s, and associated with Piero Manzoni and Vincenzo Agnetti. Castellani is known for his "paintings of light". He studied at the Ecole Nationale Superieure in Belgium, then settled in Milan. Castellani collaborated with artists such as Getulio Alviani, Piero Manzoni, and others. In 2010 he received the Praemium Imperiale for painting.


Enrico Castellani was an Italian artist. He was active in Italy from the early 1960s, and associated with Piero Manzoni and Vincenzo Agnetti. Castellani is known for his "paintings of light". He studied at the Ecole Nationale Superieure in Belgium, then settled in Milan. Castellani collaborated with artists such as Getulio Alviani, Piero Manzoni, and others. In 2010 he received the Praemium Imperiale for painting.


Enrico Castellani was an Italian artist. He was active in Italy from the early 1960s, and associated with Piero Manzoni and Vincenzo Agnetti. Castellani is known for his "paintings of light". He studied at the Ecole Nationale Superieure in Belgium, then settled in Milan. Castellani collaborated with artists such as Getulio Alviani, Piero Manzoni, and others. In 2010 he received the Praemium Imperiale for painting.


Domenico (Mimmo) Rotella was an Italian artist considered an important figure in post-war European art. Best known for his works of décollage and psychogeographics, made from torn advertising posters. He was associated to the Ultra-Lettrists an offshoot of Lettrism and later was a member of the Nouveau Réalisme, founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany.


Enrico Castellani was an Italian artist. He was active in Italy from the early 1960s, and associated with Piero Manzoni and Vincenzo Agnetti. Castellani is known for his "paintings of light". He studied at the Ecole Nationale Superieure in Belgium, then settled in Milan. Castellani collaborated with artists such as Getulio Alviani, Piero Manzoni, and others. In 2010 he received the Praemium Imperiale for painting.

Frank Philip Stella, an American icon in the realms of painting, sculpture, and printmaking, has left an indelible mark on the art world with his pioneering work in minimalism and post-painterly abstraction. Born on May 12, 1936, in Malden, Massachusetts, Stella's artistic journey commenced with his studies in painting at Phillips Academy, Andover, and history at Princeton University. His move to New York City in 1958 heralded the start of an illustrious career that would see him challenge and redefine artistic boundaries.
Stella's work is celebrated for its innovative approach to form, color, and composition. His early endeavors in the late 1950s showcased black paintings characterized by bands of bare canvas, which played a pivotal role in emphasizing the flatness of the picture plane. This deliberate artificiality in his work garnered considerable attention and positioned him at the forefront of Post-Painterly Abstraction, a movement that reacted against the emotive excesses of Abstract Expressionism.
Throughout his career, Stella continued to push the limits of abstraction. His vocabulary expanded to include vibrant and dynamic assemblages that projected out from the wall, utilizing a variety of materials from steel to plastic. This evolution of his style is not only a testament to his ingenuity but also his influence on contemporary art. Notable works that exemplify his groundbreaking approach include "Grajau I," "Harran II," and "Eskimo Curlew," among others, which can be found in prestigious collections such as The Glass House and the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum.
For art collectors and enthusiasts alike, Stella's oeuvre offers a captivating exploration into the possibilities of abstract art. His continued relevance and the profound impact of his work on both his peers and successive generations of artists underscore his status as a seminal figure in modern art.
Stay updated on new discoveries, sales, and auction events related to Frank Philip Stella by signing up for our newsletter. This subscription is your gateway to the latest in the world of Frank Stella, ensuring you never miss an opportunity to engage with the works of this monumental artist.

Domenico (Mimmo) Rotella was an Italian artist considered an important figure in post-war European art. Best known for his works of décollage and psychogeographics, made from torn advertising posters. He was associated to the Ultra-Lettrists an offshoot of Lettrism and later was a member of the Nouveau Réalisme, founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany.


Enrico Castellani was an Italian artist. He was active in Italy from the early 1960s, and associated with Piero Manzoni and Vincenzo Agnetti. Castellani is known for his "paintings of light". He studied at the Ecole Nationale Superieure in Belgium, then settled in Milan. Castellani collaborated with artists such as Getulio Alviani, Piero Manzoni, and others. In 2010 he received the Praemium Imperiale for painting.


Domenico (Mimmo) Rotella was an Italian artist considered an important figure in post-war European art. Best known for his works of décollage and psychogeographics, made from torn advertising posters. He was associated to the Ultra-Lettrists an offshoot of Lettrism and later was a member of the Nouveau Réalisme, founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany.
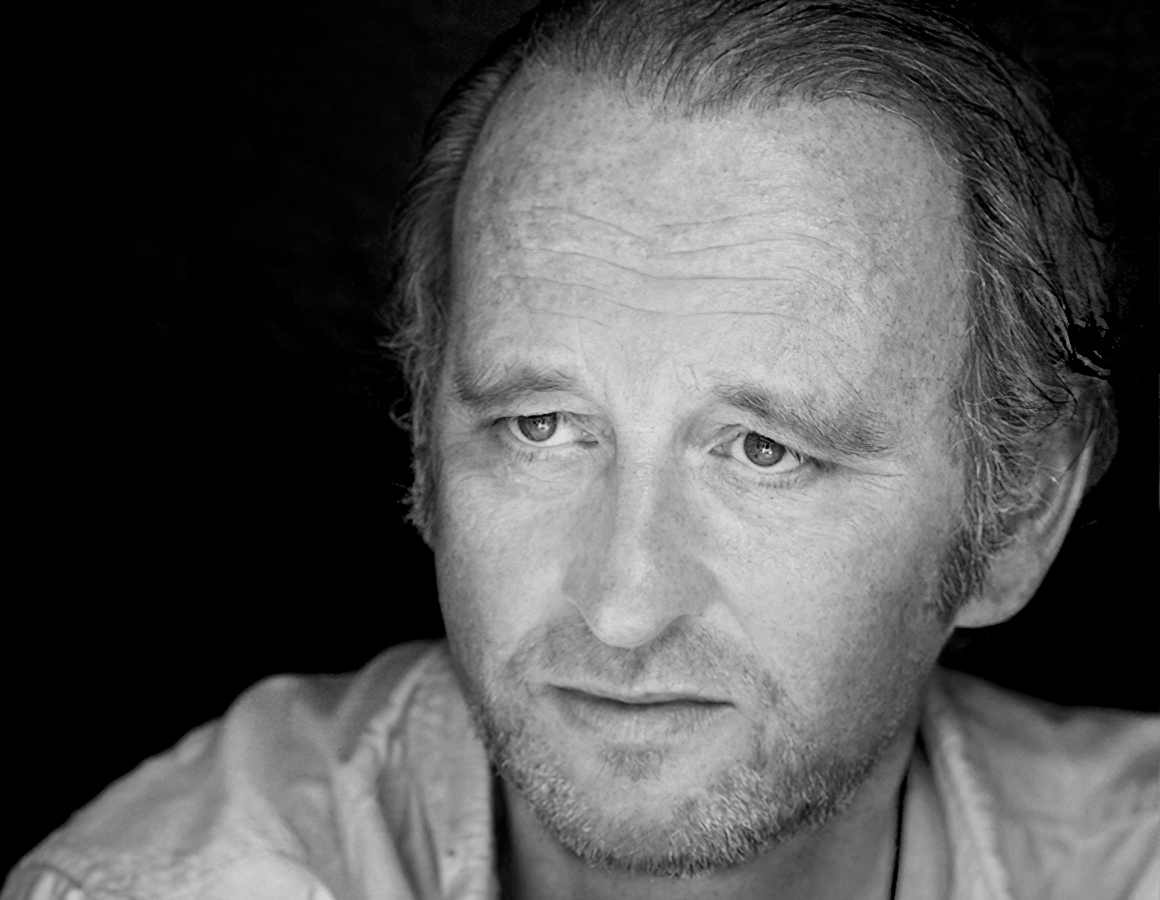


Giovanni Castell is a German visual artist and graphic designer. Known for his digital paintings, he lives and works in Hamburg, Germany.


Giovanni Castell is a German visual artist and graphic designer. Known for his digital paintings, he lives and works in Hamburg, Germany.






























































