women's history & literature
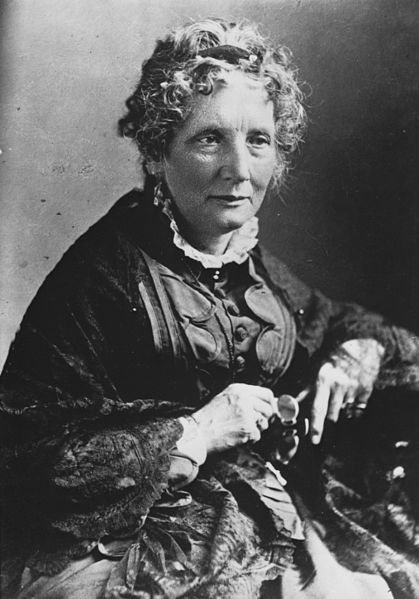


Harriet Beecher Stowe, full name Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe, was an American writer and poet, an activist for the eradication of slavery in the country.
Beecher Stowe is the author of the world-famous novel Uncle Tom's Cabin. Published first in a newspaper and first published as a book in 1852, it aroused widespread anger in the country and galvanized the fight against slavery in the southern United States. This novel was later reprinted many times in all languages of the world and has been screened more than once.
In her youth, Beecher Stowe received an academic education, wrote poetry, notes and essays on social topics. In addition to "The Shack", she wrote several other novels and was engaged in teaching.


Harriet Beecher Stowe, full name Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe, was an American writer and poet, an activist for the eradication of slavery in the country.
Beecher Stowe is the author of the world-famous novel Uncle Tom's Cabin. Published first in a newspaper and first published as a book in 1852, it aroused widespread anger in the country and galvanized the fight against slavery in the southern United States. This novel was later reprinted many times in all languages of the world and has been screened more than once.
In her youth, Beecher Stowe received an academic education, wrote poetry, notes and essays on social topics. In addition to "The Shack", she wrote several other novels and was engaged in teaching.


Hannah Webster Foster, born Hannah Webster, was an American writer.
Hannah received a good academic education for women and began writing political articles for Boston newspapers in the 1770s. In 1797, a sentimental novel she wrote, The Coquette, or the Story of Eliza Wharton, was published anonymously. The novel was based on a true story involving seduction, elopement, and a tragic death, and was a great success. The book was reprinted dozens of times, but it wasn't until the 1866 edition, many years after Foster's death, that the author's real name was placed on the title page for the first time.
Hannah Foster's second book, The Boarding School, or Lessons of a Female Educator to her Female Educators (1798), was devoted to the subject of education.

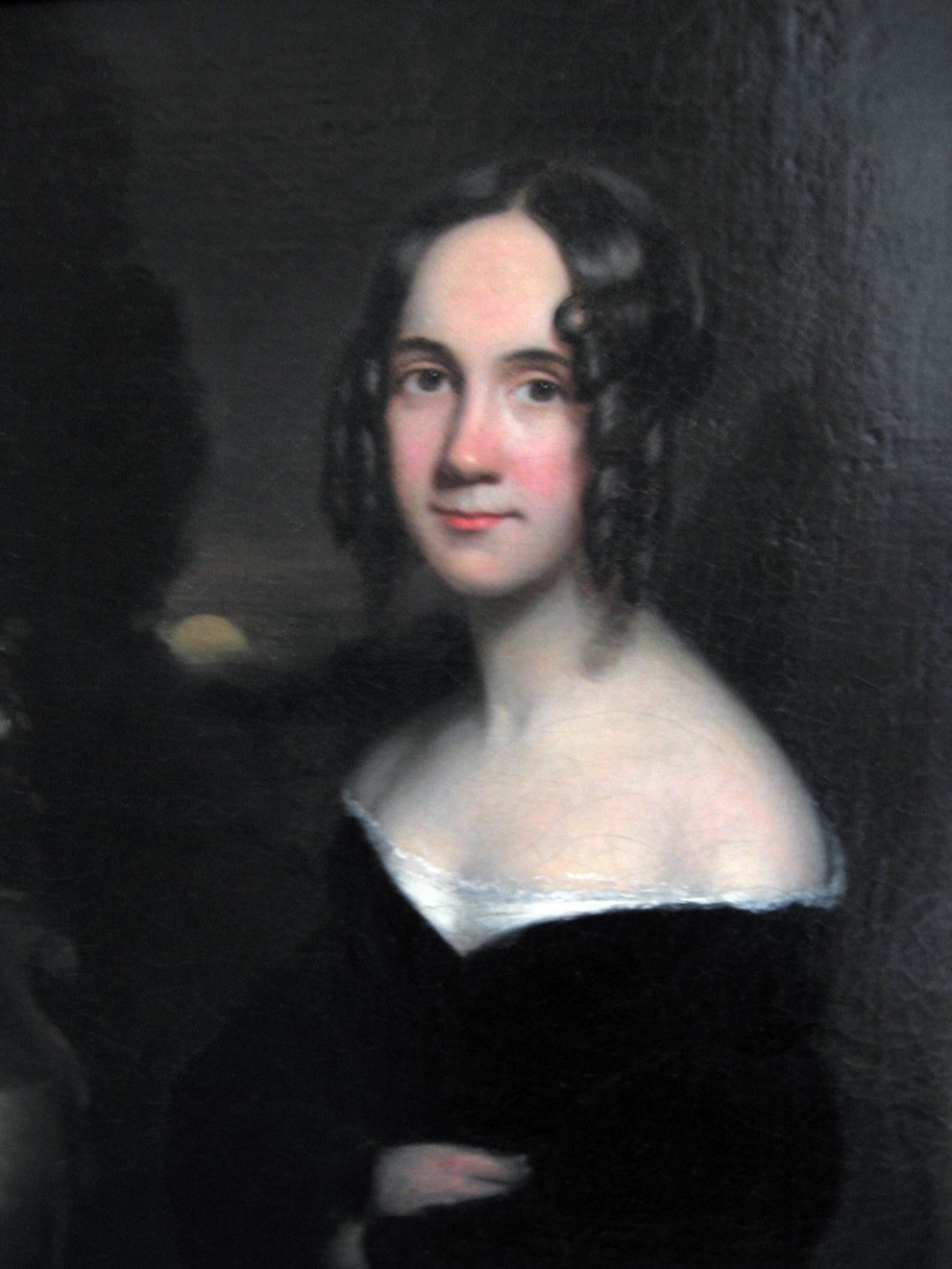
Sarah Josepha Buell Hale, born Sarah Josepha Buell, was an American writer, magazine editor, and civic activist.
Sarah Buell received a good home education and married David Hale in 1813, but, finding herself in financial difficulty after her husband's death, she turned to literary work in the 1820s. Her poems were published in local journals and in the collection The Genius of Oblivion (1823). Sarah also wrote several novels during her lifetime.
In 1828, she became editor of the new Boston edition of Ladies' Magazine (from 1834, American Ladies' Magazine). Hale herself wrote much of the wide variety of material for each issue-literary criticism, essays on American life, essays, and poetry, and she supported patriotic and humanitarian organizations, notably the Boston Ladies' Peace Society and the Sailors' Aid Society, which she founded in 1833. She was a lifelong advocate of women's education. During this period she also published Poems for Our Children (1830), containing her most famous work, Mary Had a Little Lamb.
In 1837, in Philadelphia, Hale became editor of Lady's Book, soon to be known as Godey's Lady's Book. During her years as editor, this publication became the most influential and circulating women's magazine published in the country at the time. Hale encouraged American writers: Edgar Allan Poe, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Harriet Beecher Stowe, and other women writers published in the magazine.
Hale's major accomplishment was Woman's Record; or, Sketches of Distinguished Women, published in 1853, 1869, and 1876. For this project, she produced some 36 volumes describing biographies of women, emphasizing their influence in history on social organization and literature.
Sarah Hale is considered one of the main organizers of the Thanksgiving holiday, and she helped shape the worldview of women of her time.
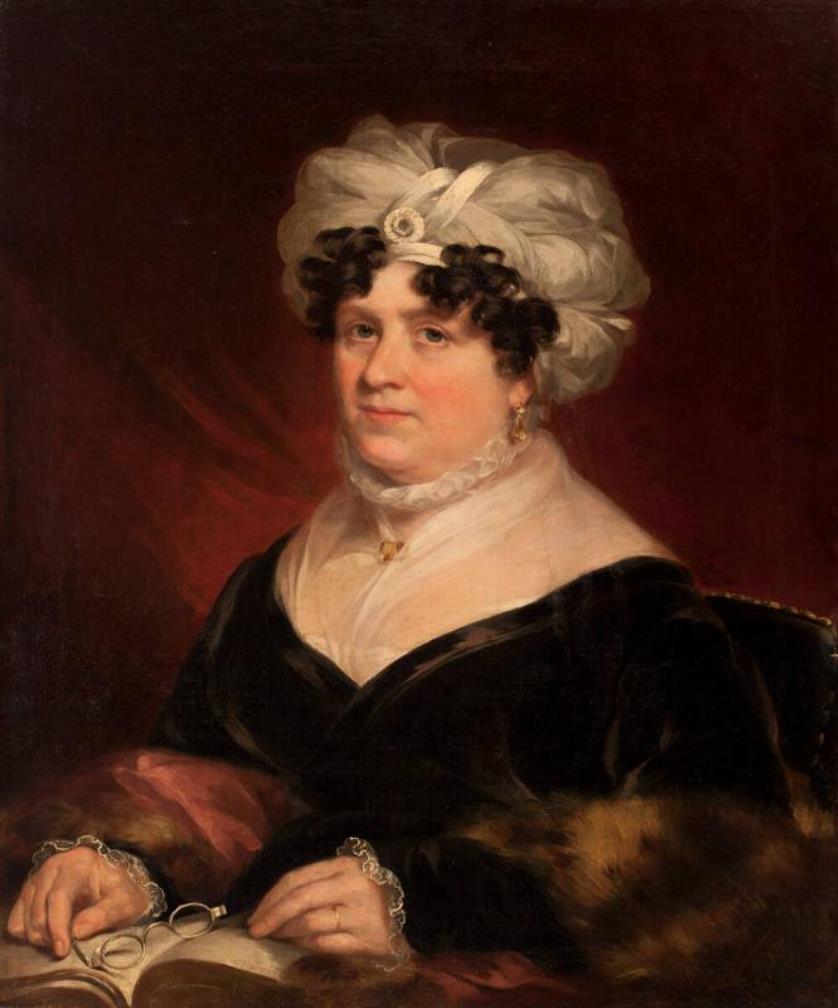


Susanna Rowson, née Haswell, was an American writer and poet, playwright, actress, and educator.
Susanna Haswell was the daughter of an officer in the Royal Navy. She published her first novel, Victoria, in 1786 and soon married businessman William Rowson. Susanna's greatest success was her first American bestseller, the novel Charlotte, A Tale of Truth (1791, in later editions under the title Charlotte Temple). This novel, a conventional sentimental story of seduction and remorse, was immensely popular and went through more than 200 editions.
In 1792 she became an actress and performed with her bankrupt husband in Scotland, as well as in Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Boston. In 1797, after retiring from the stage, Susanna opened the first "female academy" in Boston. Susanna Rowson also wrote many plays and musicals, and in doing so, helped to develop the performing arts in the United States. Later, she also edited the Boston Weekly Magazine, wrote geography and spelling textbooks, and moralizing manuals.
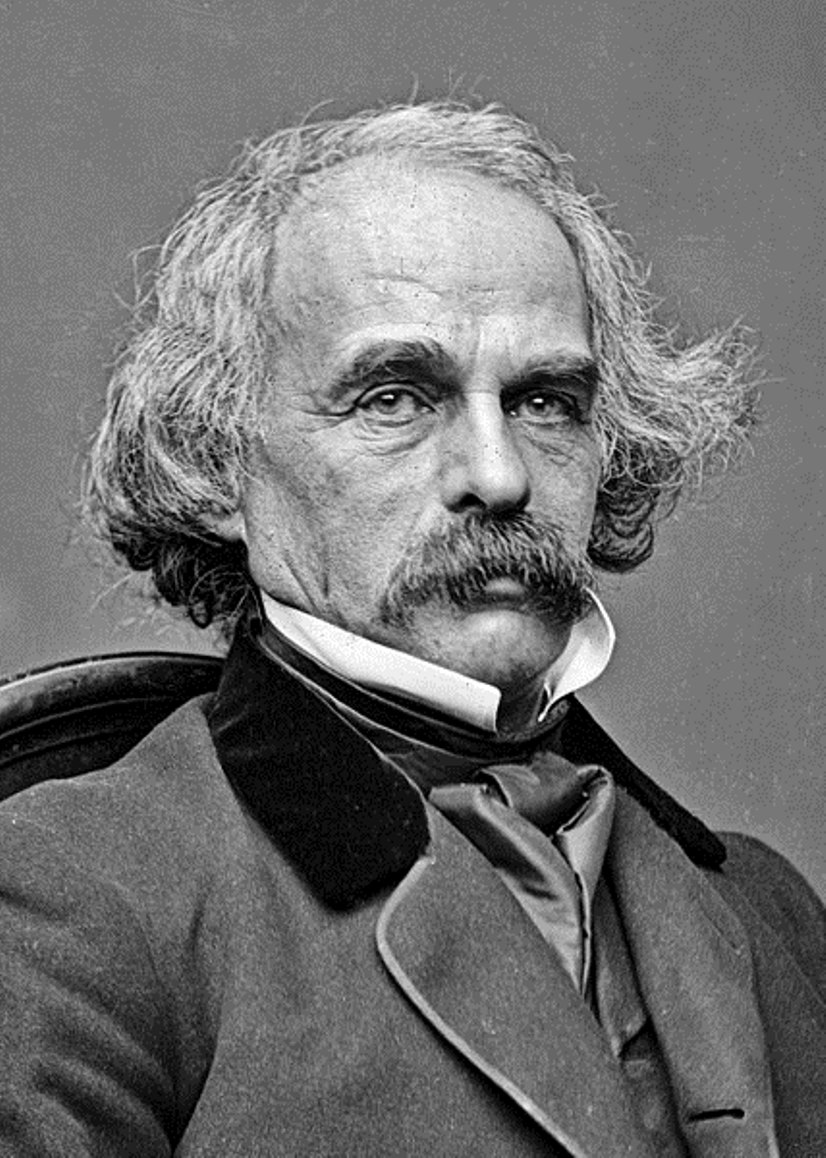


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.
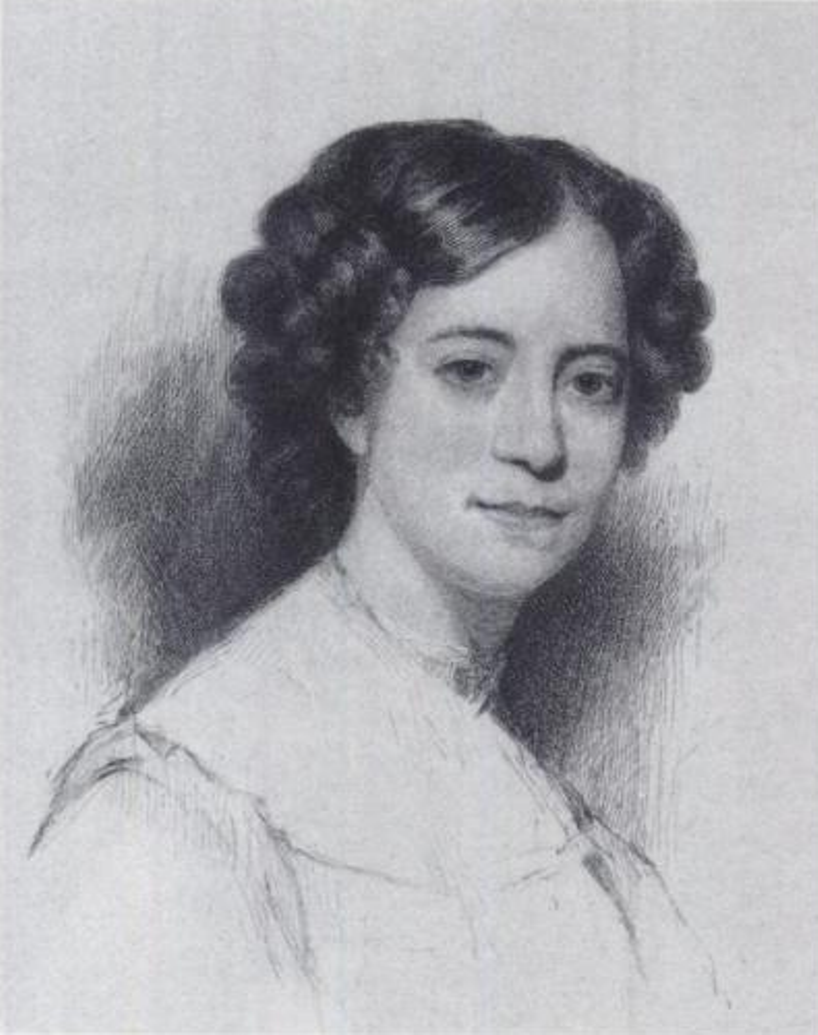

Sophia Amelia Hawthorne, née Peabody was an American artist and illustrator and writer.
Sophia Peabody is the wife of writer Nathaniel Hawthorne. Before her marriage, she was already an accomplished artist; during her life she also published articles, her diaries, and some of Nathaniel's notebooks, which she edited and published after his death.


Susanna Rowson, née Haswell, was an American writer and poet, playwright, actress, and educator.
Susanna Haswell was the daughter of an officer in the Royal Navy. She published her first novel, Victoria, in 1786 and soon married businessman William Rowson. Susanna's greatest success was her first American bestseller, the novel Charlotte, A Tale of Truth (1791, in later editions under the title Charlotte Temple). This novel, a conventional sentimental story of seduction and remorse, was immensely popular and went through more than 200 editions.
In 1792 she became an actress and performed with her bankrupt husband in Scotland, as well as in Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Boston. In 1797, after retiring from the stage, Susanna opened the first "female academy" in Boston. Susanna Rowson also wrote many plays and musicals, and in doing so, helped to develop the performing arts in the United States. Later, she also edited the Boston Weekly Magazine, wrote geography and spelling textbooks, and moralizing manuals.
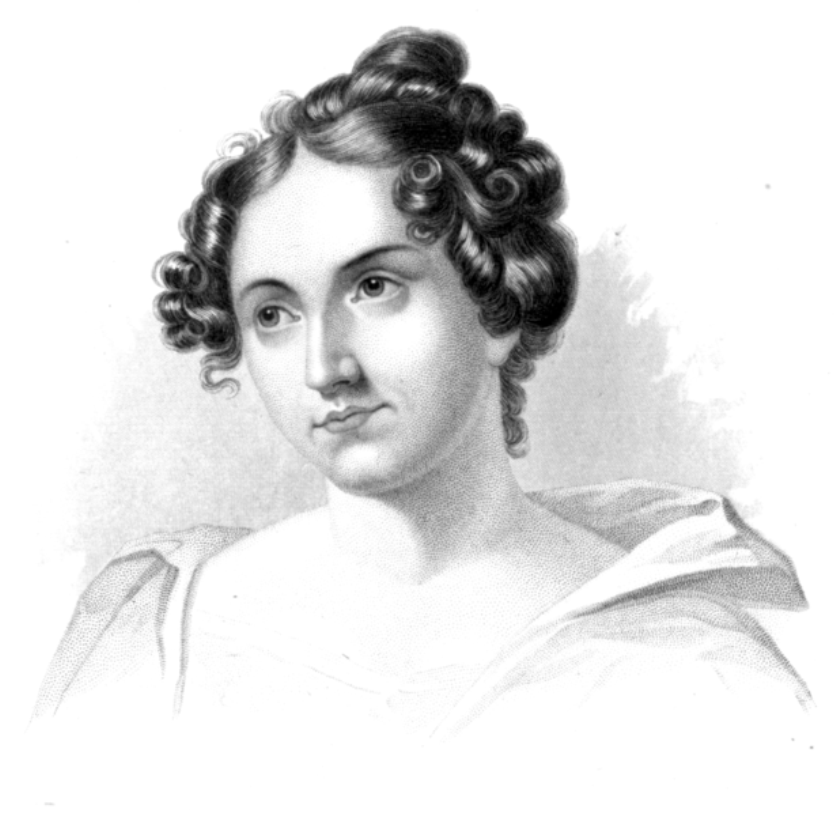


Catharine Maria Sedgwick was a successful American novelist writer of the first half of the 19th century.
Catharine was the daughter of Theodore Sedgwick, a lawyer, congressman and later senator and state supreme court justice. She was one of the most prolific and respected American novelists of the period, writing six novels, eight works for children, two biographies, and more than 100 short prose stories. The famous writer Edgar Allan Poe reviewed her work quite favorably.
Sedgwick wrote the novels Redwood (1824), Hope Leslie (1827), Clarence (1830), and The Linwoods (1835), her last novel, "Married or Single?" was published in 1857. Her works in particular raise questions about the relationship between nurture and management, and the key role of women in shaping the emerging nation.
Catherine Sedgwick was also active in the New York Women's Prison Association from its inception in 1854 until her death.
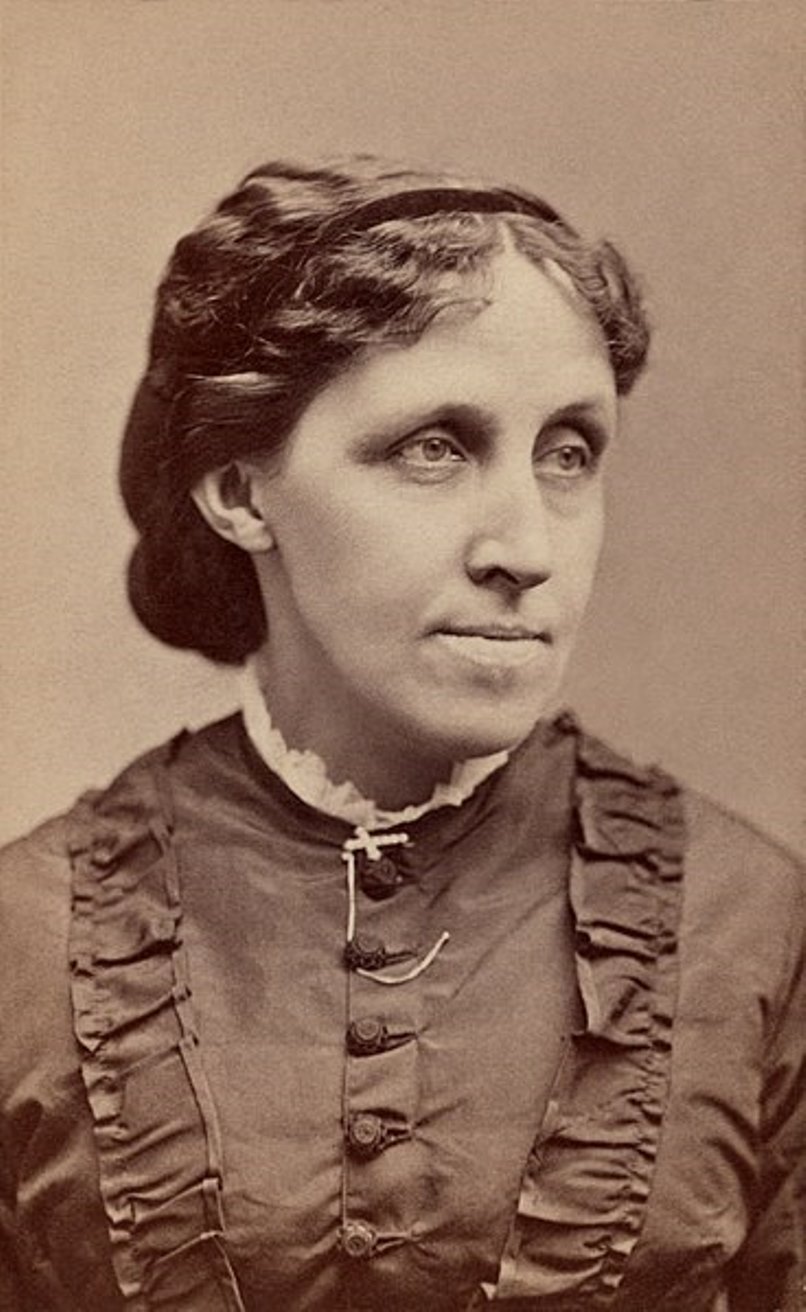


Louisa May Alcott was a 19th-century American writer.
Louisa, the daughter of transcendentalist Bronson Alcott, grew up in the company of Ralph Waldo Emerson, Theodore Parker, and Henry David Thoreau. Her education was largely under the guidance of her father, who, however, did not know how to properly provide for the family.
Louisa was forced to begin writing short stories and publishing in The Atlantic Monthly magazine. It could be said that need forced her to write an autobiographical book, Little Women (1868-69), which immediately became so popular that Louisa was finally able to pay off her debts. The book describes the domestic adventures of an optimistic New England family of modest means, tracing the different characters and destinies of four sisters as they grow up and face work, society, and marriage.
Alcott published sequels to the book, Little Men (1871) and Joe's Boys and What Came of Them (1886). There have been numerous films based on Little Women already in the 20th century, including the classic 1933 film starring Katharine Hepburn as Joe and the 2019 Greta Gerwig adaptation.
Alcott wrote other domestic stories based on her early experiences, and her books for younger children remain enduringly popular. Already in the 21st century, the gothic short stories and thrillers published by Alcott under a pseudonym between 1863 and 1869 have been collected and reprinted.
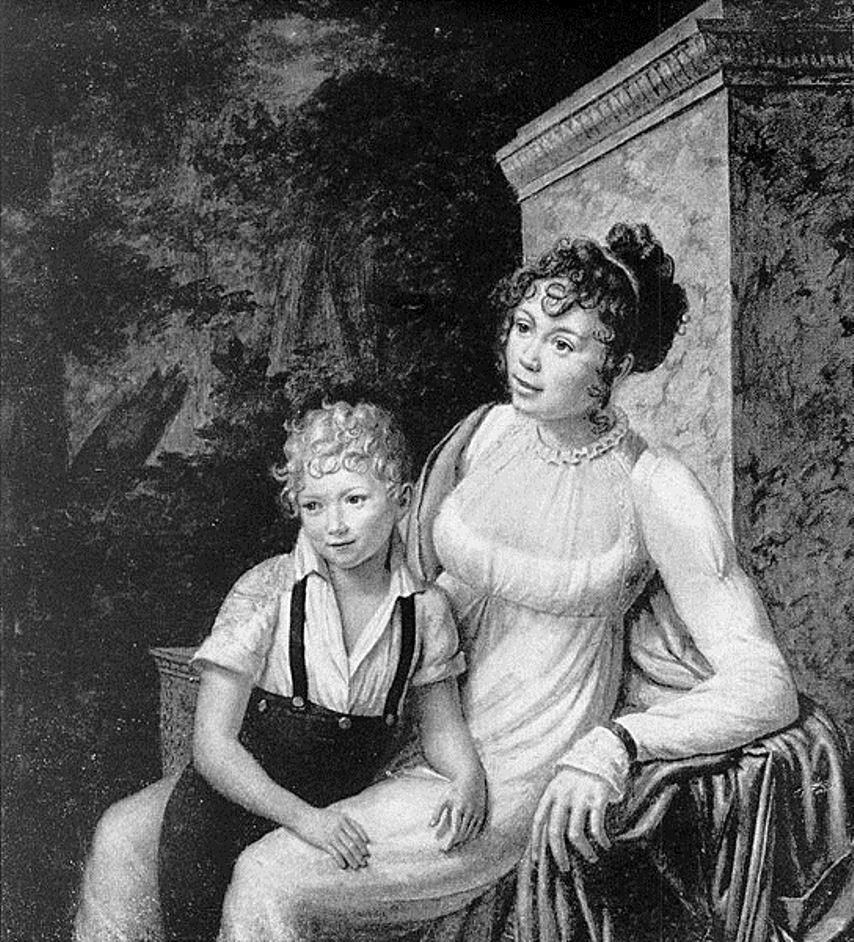


Leonora Sansay, born Honora Davern, is an American author.
Leonora was the author of several adventure novels, including The Secret History and Zelica: Creole, which may be the first American novel with a non-white heroine. Her novels are remarkable in that they document the life and observations of a remarkable woman in a turbulent time.
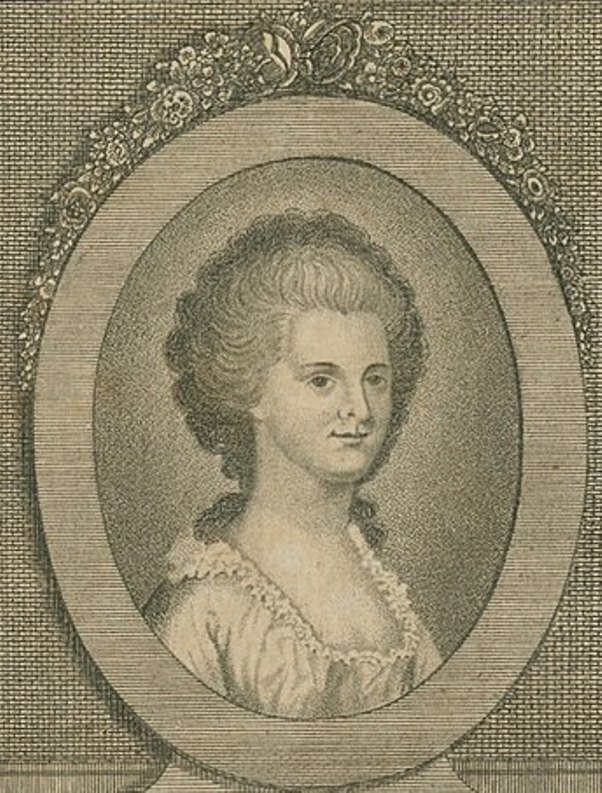


Ann Eliza Bleecker, née Schuyler, is an American poet and writer.
Ann from a young age surprised others with her poetic and literary talent. Married to lawyer John James Bleecker, she continued to write sentimental poems and so-called letters in which she enclosed her compositions. The family idyll was disrupted with the onset of the British offensive during the American Revolution. Ann and her husband had to flee, they experienced much grief and loss. All this greatly affected the character and creativity of Ann Bleecker.
In her most famous fiction narrative "The Story of Maria Kittle", which is addressed to her cousin, Ann describes the hardships of surviving captivity with the cruel Native Americans.
Ann Eliza Bleecker died at the age of 32, leaving behind manuscripts of poetry and prose that she never intended to publish. A few years later, her daughter, the poet Margaret Foger, published a significant portion of Bleeker's work, including twenty-three letters, thirty-six poems, and "The History of Maria Kittle," first in The New-York Magazine in 1790 and 1791, and then in a collection entitled "The Posthumous Works of Anne Eliza Bleecker" in 1793. "The History of Mary Kittle" was reprinted separately in 1797, a testament to the novel's popularity.
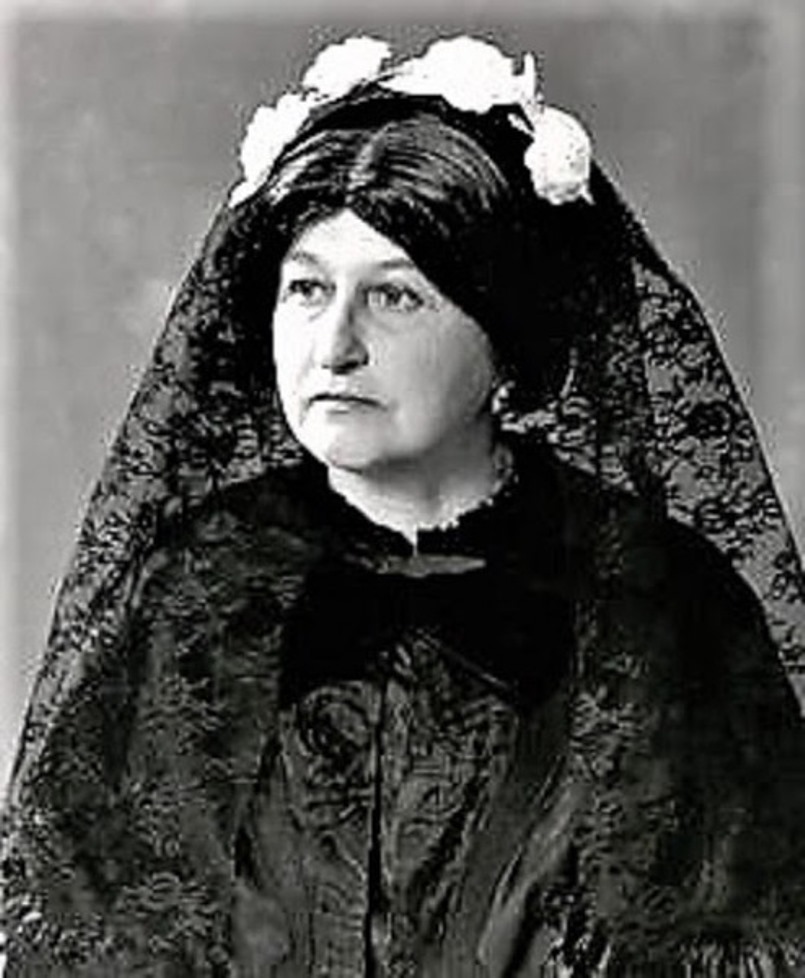


Anne Royall, née Newport, was an American writer, newspaper editor and traveler, one of the first women journalists in the United States.
After the death of her husband William Royall in 1813, Anne was left destitute, but she did not despair and completely changed her life. She was about 50 years old when she set out to travel the country and describe what she saw. She visited Baltimore, Philadelphia, New York City, Albany, Springfield, Hartford, Worcester, Boston, and New Haven. In each city, she asked respected citizens for interviews and subscriptions to her future books. She made detailed notes on each town's population, industry, physical description, local transportation, regional dialects, fashions, and the character of its inhabitants.
In all, Anne Royall wrote ten volumes of travel books. She was 57 years old when she published under a pseudonym her first book, The Traveler: Sketches of History, Life, and Manners in the United States (1826), which provides a unique look at American life in the early nineteenth century. His first novel, The Tennessean, was published in 1827, followed by several others.
At the age of 62, in her home in Washington, D.C., Royall began publishing her own newspaper, Paul Pry (1831-1836) and then The Huntress (1836-1854). She exposed bribery and corruption and made many powerful enemies. Nevertheless, it is known that the intrepid journalist during her life met and talked with every man who occupied the presidential chair, from George Washington to Abraham Lincoln.
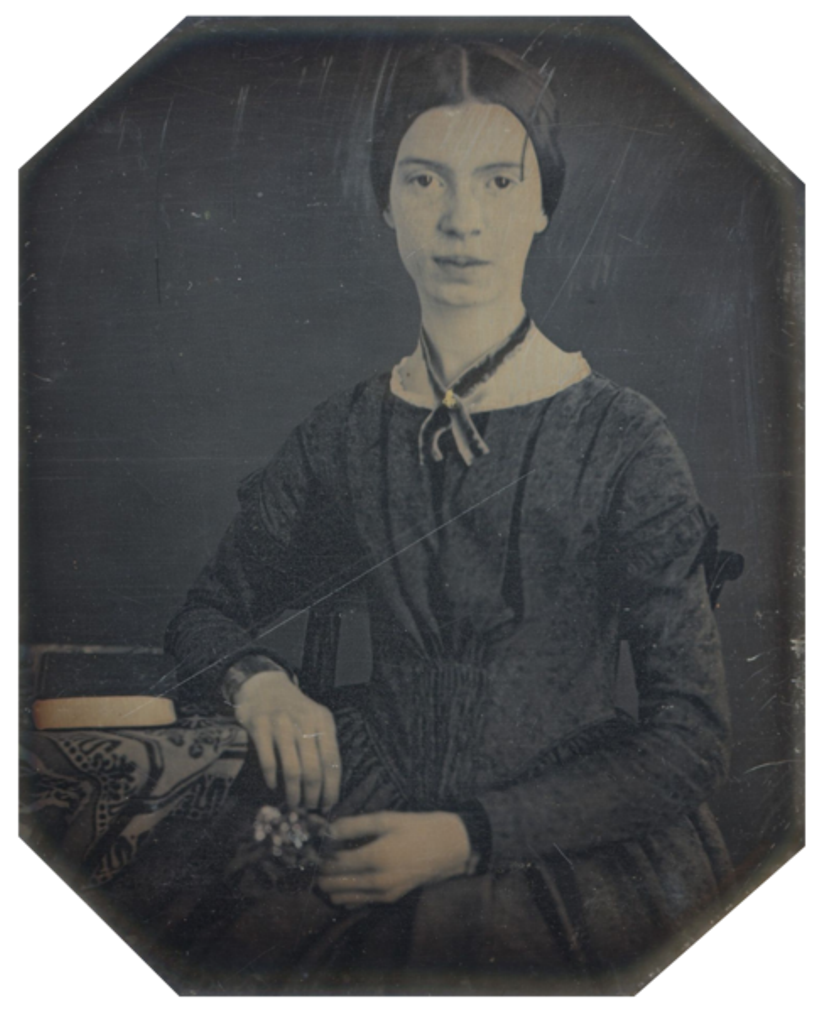


Emily Elizabeth Dickinson was a 19th-century American lyric poet.
Emily led a secluded and rather unusual lifestyle, preferring active correspondence instead of personal communication. In addition to many brilliant and witty letters to her family and friends, she wrote about two thousand poems during her lifetime, but only about ten were published during her lifetime.
Dickinson possessed an extraordinary brilliance of style and integrity of vision and, along with Walt Whitman, is today considered one of the two leading American poets of the nineteenth century. She easily ignored the usual rules of versification and even grammar, and in the intellectual content of her works showed exceptional courage and originality. It is known that the poetess was particularly impressed by the poetry of Ralph Waldo Emerson, and with Charles Wadsworth she corresponded.
Today, the work of Emily Dickinson is evaluated as a bright forerunner of modernism, it is widely studied in educational institutions in the United States and Europe.


Harriet Beecher Stowe, full name Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe, was an American writer and poet, an activist for the eradication of slavery in the country.
Beecher Stowe is the author of the world-famous novel Uncle Tom's Cabin. Published first in a newspaper and first published as a book in 1852, it aroused widespread anger in the country and galvanized the fight against slavery in the southern United States. This novel was later reprinted many times in all languages of the world and has been screened more than once.
In her youth, Beecher Stowe received an academic education, wrote poetry, notes and essays on social topics. In addition to "The Shack", she wrote several other novels and was engaged in teaching.
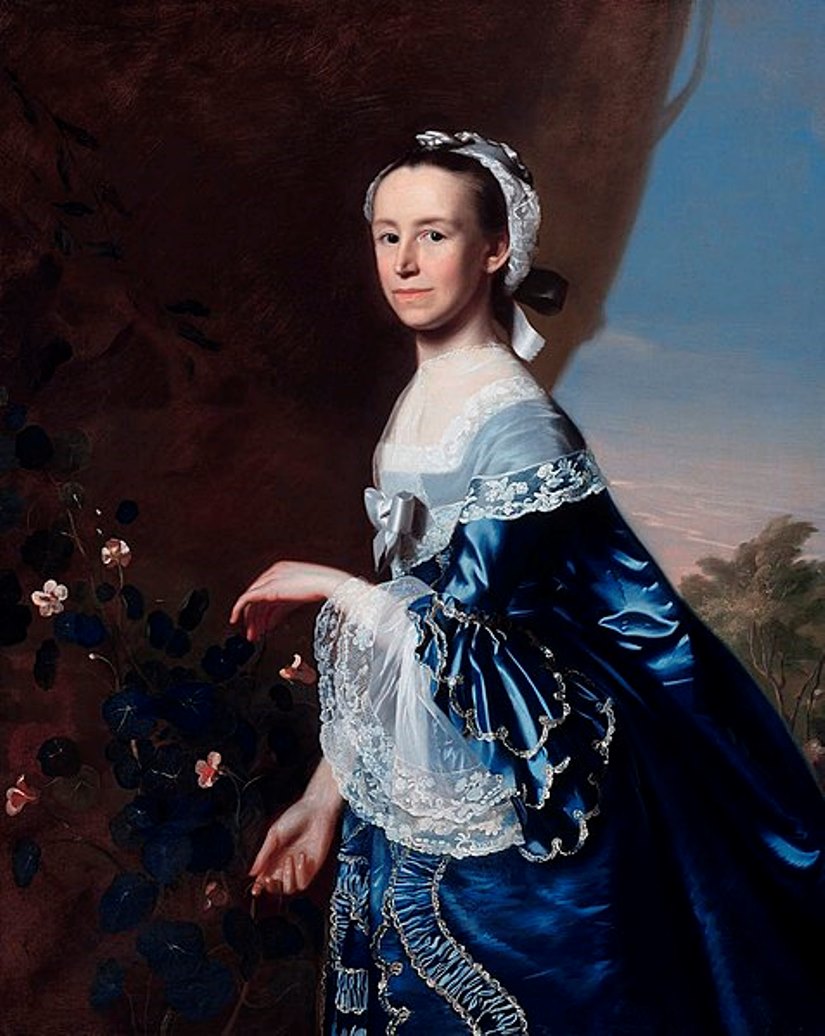


Mercy Otis Warren was an American poet, satirist, playwright, historian, and essayist of the American Revolution.
Mercy Otis was born into a prosperous Cape Cod Island family and was immersed early in the tumultuous political events taking place in the country at the time. One of her brothers was political activist James Otis, who was involved in the American Revolution from the beginning. In 1754, Mercy Otis married farmer James Warren, who later served in the Massachusetts legislature (1766-78). Through her husband's political connections, Warren was personally acquainted with most of the leaders of the Revolution and was constantly at the center of events for more than two decades.
Combining her own convictions with her writing talent, Warren became a poet and historian of the revolutionary era. Her first incisive and polemical pieces in verse were published in a Boston newspaper. This was followed by the prophetic novel Defeat and other works. In 1790 she published a collection of her works, Poems, Dramatic and Miscellaneous, which included two new plays, The Sack of Rome and The Ladies of Castille. For a woman of the time, such publications were very daring, as female writers usually hid under pseudonyms.
Warren also corresponded extensively with politicians, including George Washington and Thomas Jefferson. In 1805, she completed a three-volume work entitled A History of the Rise, Progress, and Termination of the American Revolution. This book was the earliest work on historical events in the country. Its proximity to political leaders and major national events makes Mercy Warren's writings on the American Revolutionary period especially valuable.


Susanna Rowson, née Haswell, was an American writer and poet, playwright, actress, and educator.
Susanna Haswell was the daughter of an officer in the Royal Navy. She published her first novel, Victoria, in 1786 and soon married businessman William Rowson. Susanna's greatest success was her first American bestseller, the novel Charlotte, A Tale of Truth (1791, in later editions under the title Charlotte Temple). This novel, a conventional sentimental story of seduction and remorse, was immensely popular and went through more than 200 editions.
In 1792 she became an actress and performed with her bankrupt husband in Scotland, as well as in Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Boston. In 1797, after retiring from the stage, Susanna opened the first "female academy" in Boston. Susanna Rowson also wrote many plays and musicals, and in doing so, helped to develop the performing arts in the United States. Later, she also edited the Boston Weekly Magazine, wrote geography and spelling textbooks, and moralizing manuals.


Susanna Rowson, née Haswell, was an American writer and poet, playwright, actress, and educator.
Susanna Haswell was the daughter of an officer in the Royal Navy. She published her first novel, Victoria, in 1786 and soon married businessman William Rowson. Susanna's greatest success was her first American bestseller, the novel Charlotte, A Tale of Truth (1791, in later editions under the title Charlotte Temple). This novel, a conventional sentimental story of seduction and remorse, was immensely popular and went through more than 200 editions.
In 1792 she became an actress and performed with her bankrupt husband in Scotland, as well as in Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Boston. In 1797, after retiring from the stage, Susanna opened the first "female academy" in Boston. Susanna Rowson also wrote many plays and musicals, and in doing so, helped to develop the performing arts in the United States. Later, she also edited the Boston Weekly Magazine, wrote geography and spelling textbooks, and moralizing manuals.


Susanna Rowson, née Haswell, was an American writer and poet, playwright, actress, and educator.
Susanna Haswell was the daughter of an officer in the Royal Navy. She published her first novel, Victoria, in 1786 and soon married businessman William Rowson. Susanna's greatest success was her first American bestseller, the novel Charlotte, A Tale of Truth (1791, in later editions under the title Charlotte Temple). This novel, a conventional sentimental story of seduction and remorse, was immensely popular and went through more than 200 editions.
In 1792 she became an actress and performed with her bankrupt husband in Scotland, as well as in Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Boston. In 1797, after retiring from the stage, Susanna opened the first "female academy" in Boston. Susanna Rowson also wrote many plays and musicals, and in doing so, helped to develop the performing arts in the United States. Later, she also edited the Boston Weekly Magazine, wrote geography and spelling textbooks, and moralizing manuals.
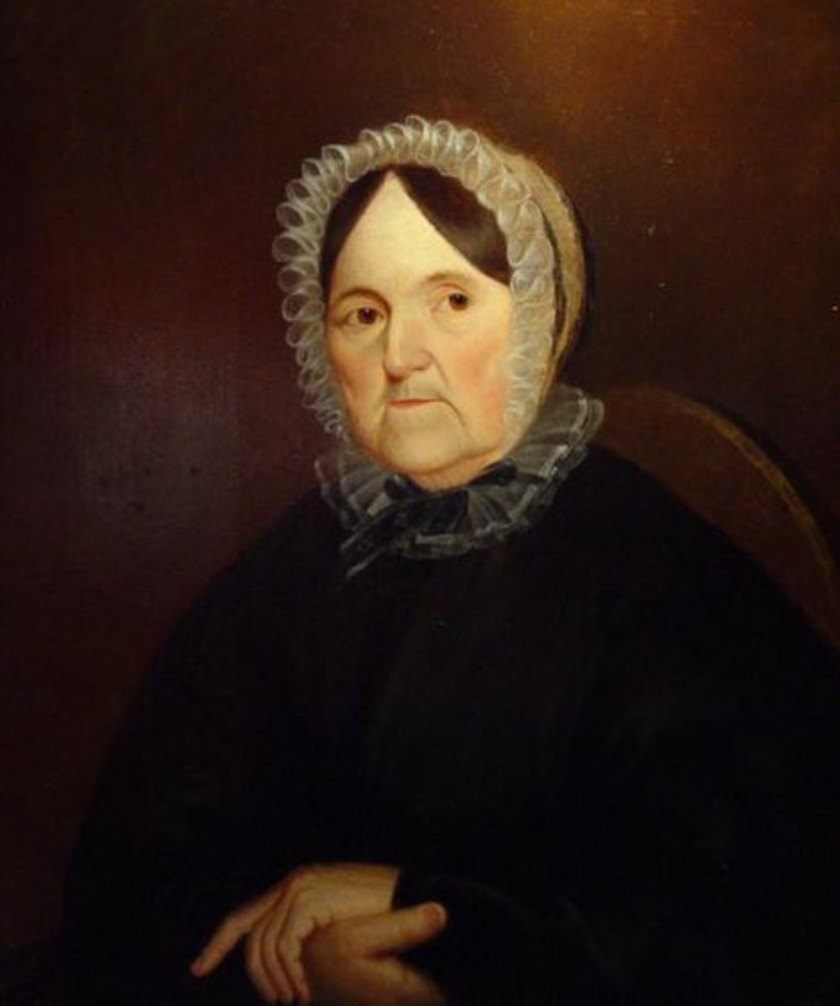


Sally Wood, full name Sarah Sayward Barrell Keating Wood, is an American author.
In her long life, Sally wrote four novels and one collection of fairy tales. She is considered the first American writer of gothic fiction. She signed her novels "The Lady from Massachusetts" or "The Lady from Maine". The first, entitled Julia and the Enlightened Baron, was published in 1800.