Graphic artists Flanders






Raphael Coxie was a Flemish Renaissance painter mainly known for his portrait and history paintings. Details about the life and career of the artist are sketchy. He was only rediscovered as a distinctive artist in the 19th century. He was a pupil of his father and became master in the Mechelen Guild of Saint Luke in 1562. Raphael was a passionate gardener and friend of the Flemish botanist Carolus Clusius to whom he sent drawings of flowers, which Clusius used in his scientific publications. He was active from 1586 in Brussels where he became a master of the local painter's guild in 1605. In the period 1588-89 he spent time in Ghent on a major commission for a painting of the Last Judgement. While in Ghent Coxie also painted a Resurrection of Christ for the monks of the Abbey of Drongen. He is recorded in 1597 as making, in collaboration with Gilbert van Veen, several portraits commissioned by Philip II of Spain.


Hendrik Frans de Cort was a Flemish landscape painter and draughtsman. In 1770 he became a master in the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke. His early landscapes from the time before he moved to England were often made in collaboration with other Flemish artists. De Cort is known for his topographical views of English and Welsh landscapes. These were painted in an Italianate idiom indebted to the style of Gaspar Dughet. He often painted on specially prepared mahogany panels.


Franz Ertinger (German: Franz Ertinger) was a French painter born in Germany but working in France and Flanders, a member of the Guild of St. Luke in Antwerp.
Ertinger is a versatile artist who has applied his talents in various fields of art. He is known as a painter, illustrator and printer of books, draughtsman, designer and writer, and worked as a royal engraver in Paris.


Philips Galle was a Dutch publisher, best known for publishing old master prints, which he also produced as designer and engraver. He is especially known for his reproductive engravings of paintings.
As a resident of Antwerp, Galle witnessed numerous events of the Eighty Years War, notably the siege and looting of the town in 1576 by the Spaniards, called "The Spanish Fury". This rather personal book, which was translated in several languages soon after its first publication, shows Galle as a peace-loving person who intended to stay far away from the political and military turmoil of his era.


Jan Gossaert was a French-speaking painter from the Low Countries also known as Jan Mabuse (the name he adopted from his birthplace, Maubeuge) or Jennyn van Hennegouwe (Hainaut), as he called himself when he matriculated in the Guild of Saint Luke, at Antwerp, in 1503. He was one of the first painters of Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting to visit Italy and Rome, which he did in 1508–09, and a leader of the style known as Romanism, which brought elements of Italian Renaissance painting to the north, sometimes with a rather awkward effect. He achieved fame across at least northern Europe, and painted religious subjects, including large altarpieces, but also portraits and mythological subjects, including some nudity.


Willem Jacob Herreyns, the Younger, was a Flemish painter of history subjects and portraits. He is regarded as one of the last painters in the tradition of the Flemish Baroque and the last follower of Peter Paul Rubens. Herreyns’ work was very highly regarded in his time. His religious compositions stand in the Rubens tradition. Herreyns is considered a draughtsman with a precise line, but his work shows a certain coldness and lacks originality.
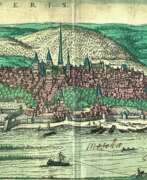

Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He is known for portraits and topographical views as well as historical allegories. He also produced scenes of contemporary historical events. Hogenberg was the author of graphic works, engravings of city views and maps of the first four volumes of the six-volume atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Description and drawings of the most famous cities in the world), published in 1570 by the Flemish geographer Abraham Ortelius. Hogenberg's engravings are an invaluable source of information about urban development in medieval Europe.


Pieter van der Borcht the Elder was a Flemish Renaissance painter, draughtsman and etcher. He is regarded as one of the most gifted botanical painters of the 16th century. Pieter van der Borcht the Elder also introduced new themes such as the 'monkey scene' (also called 'singerie') into Northern art.









