Judges


Jan (Joan) Willemsz. Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer, publisher and judge.
Jan was born into the family of the cartographer and publisher Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571-1638). He studied in Leiden, where he earned a doctorate in law, and in Padua. He then began to assist his father, who was engaged in the manufacture of globes and maps. After his father's death, Jan, together with his brother Cornelius, continued his work, and succeeded him as cartographer for the Dutch East India Company.
In 1651 Blaeu was elected to the Amsterdam city council and later appointed as a judge. At the same time, he was engaged in his publishing business: he continued to publish volumes of Atlas novus, which contained maps of English counties and, for the first time, an atlas of Scotland, as well as one volume of maps of the Far East.
Blaeu did not have time to complete his most ambitious project, but it made him famous as the author of the famous 11-volume Dutch atlas. Based on his previous maps, Blaeu created the Great Atlas (Atlas Maior) - it contained nearly 600 maps and a total of 3,000 pages of Latin text - and was published in 1662. Blaeu's maps were groundbreaking for their time because they were created in accordance with the heliocentric theories of Nicolaus Copernicus.
In 1672, a great fire in Amsterdam destroyed Blaeu's workshop, and the cartographer died a year later, apparently never recovering from this stroke of fate.


Hugh Henry Brackenridge was an American writer and poet, jurist and Pennsylvania Supreme Court Justice.
Hugh Henry graduated from the College of New Jersey (now Princeton University), learned Latin and Greek, and became a teacher. He later served in George Washington's army and published two verse dramas on revolutionary themes. He worked with the poet Philip Morin Freneau (1752-1832) on satirical and political publications.
Hugh Henry Breckenridge founded the Pittsburgh Academy, now the University of Pittsburgh, and the Pittsburgh Gazette, which is still published today.
Breckenridge is also known as the author of the first novel about frontier life in the United States after the Revolutionary War, Modern Chivalry. Considered one of the earliest American novels, this book was published in installments beginning in 1792 over a period of 23 years. In the latest edition, Captain John Farrago, along with his own Sancho Panza, Teague, leaves his farm in western Pennsylvania and sets out to find adventure in the big world.


Henry of Bracton (also Henry de Bracton, Henricus Bracton, Henry Bretton) was an English medieval jurist, royal judge, and compiler of the English common law. Bracton came from a wealthy family from Devon and studied at Oxford University and held various ecclesiastical offices, finally becoming Chancellor of the Diocese of Exeter. Bracton also received a legal education, and entered first the service of the famous judge William Raleigh, and in 1239 went into the service of King Henry III. In 1244 Bracton became a judge himself, and in 1255-56 he was a member of the King's Council.
Henry Bracton is famous for his two works, De legibus et consuetudinibus Angliae (On the Laws and Customs of England) and Note Book, which together represent one of the most important attempts to streamline and rationalize English medieval common law. The author constructed his works inspired by compilations of Lombard law and Roman civil law. In his first classical treatise, among other things, Bracton introduced the concepts of mens rea (criminal intent) and precedent. Bracton's work, written probably between 1250 and 1260, was cited in court until the eighteenth century.


Henry Fielding was an 18th-century British judge, writer and playwright, and the founder of the English realist novel.
Fielding attended Eton College, where he studied classical writers, and wrote his first play in 1728. In all, he wrote about 25 rather witty and topical plays for the theater. But this activity led to the fact that in 1737, the Act of Theater Censorship was passed, and satire on political topics became virtually forbidden. To find a source of income, Fielding went to study law at Middle Temple and became a lawyer.
In 1741, Fielding wrote his first parody of Samuel Richardson's Pamela: or Rewarded Virtue, he called it "An Apologia of the Life of Mrs. Shamela Andrews." Others followed, and in essence Fielding started a new genre in fiction. And in 1742, he wrote the novel "Joseph Andrews."
In the late 1740s, Fielding was appointed Justice of the Peace of Westminster and then Justice of the Peace of Middlesex. But he did not abandon his creativity and in 1749 he wrote the famous comic "The Story of Tom Jones, the Foundling," a work that is considered one of the greatest early English-language novels. The novel was so warmly received by its first readers that four editions totaling 10,000 copies were published in less than a year.


James Hall was an American lawyer, judge, treasurer, and editor.
Hall studied law, fought in the War of 1812, served as a lawyer and circuit judge, newspaper and magazine editor, Illinois state treasurer, and banker in Cincinnati, Ohio. In addition, he was also a historical and fiction writer. In 1828, Hall compiled the first western literary yearbook, Western Souvenir, and edited the Illinois Monthly Magazine. James Hall wrote a travel book, Letters from the West (1828), a novel, The Head of the Harp (1833), and several volumes of short stories.
Hall also contributed to the three-volume History of the Indian Tribes of North America (1836-1844). This book includes portraits of the chiefs of more than twenty Indian tribes, which were painted by noted artists of the day, with biographical sketches by Superintendent of Indian Affairs Thomas L. McKenney.


John Hathorne was a merchant and justice of the peace of the colony in Massachusetts, United States.
Hathorne's father, Major William Hathorne, was among the first settlers of the Massachusetts Bay Colony in the 1630s, holding a number of military and political positions over several decades.
John Hathorne himself is known for having participated as a justice of the peace in 1692 in the famous Salem Witch Trials during the witchcraft hysteria. Extant documents prove that Hathorne was the chief prosecutor, convinced of the guilt of the accused. The trial ended with the execution of 20 people, and John Hathorne never repented, although the High Court later acquitted most of the accused. He was appointed a member of the Superior Court in 1702 and sat on it for ten years.
John was the great-great-grandfather of the writer Nathaniel Hawthorne (1804-1864), author of many works, including The Scarlet Letter and The House of the Seven Gables. They are set in Salem and contain allusions to the witch trials in the history of the house. John Hathorne's personality has served as a prototype for the bigoted and demonic characters of many works by other authors. And Nathaniel Hawthorne himself changed the spelling of his surname to distance himself from his ancestor.


John Jay was an American lawyer and diplomat, statesman, and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Jay came from French Huguenots, after graduating from King's College (now Columbia University) he entered law school and was admitted to the bar in 1768. After the outbreak of hostilities in the spring of 1775, Jay continued to serve both in New York and in the Continental Congress, which elected him president in late 1778.
In the fall of 1779 he was appointed minister plenipotentiary to Spain, which had recently entered into an alliance with France against England. In May 1782 he traveled to Paris, where a treaty was concluded that formally ended the war with Great Britain in 1783. Before returning to America in July 1784, Jay was appointed secretary of foreign affairs.
In 1788, Jay actively advocated for the ratification of the U.S. Constitution by the state of New York. Together with future President James Madison and economist Alexander Hamilton, he participated in the creation of the famous book The Federalist (1788). Under the new Constitution, President Washington appointed John Jay Chief Justice of the United States in 1789, and in July 1795 he became Governor of New York. After completing his second term as governor in June 1801. Jay retired to his farm in Bedford, New York.


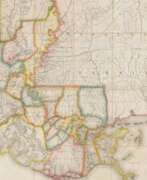
Peter Jefferson was an American cartographer and surveyor, father of the third President of the United States, Thomas Jefferson.
Peter Jefferson was the son of a large landowner in Virginia, and served as sheriff, surveyor, and justice of the peace. He was also a cartographer and surveyor. Along with Colonel and County Surveyor Joshua Fry, he spent several years exploring new lands. In 1750, Lewis Burwell, acting governor of Virginia, commissioned Frye and Jefferson to map the colony, which was done.
This map of early America was based on Frye and Jefferson's meticulous research and accurately delineated the boundaries, roads, settlements, and trails of the original inhabitants. It also included significant new geographic information reported by early wilderness travelers, including George Washington, Christopher Gist, and John Dalrymple. The map was completed in 1751 and engraved and published a few years later. Afterward, Jefferson worked on numerous surveying projects throughout Virginia.


John Marshall was Chief Justice of the United States Supreme Court from 1801 to 1835, Secretary of State, and one of the founders of the American legal system.
During the Revolutionary War, Marshall served first as a lieutenant and after July 1778 as a captain in the Continental Army. In 1781 he left the service, studied law, and began practicing law in Virginia, in Fauquier County, and then in Richmond. He soon became head of the Virginia bar and was a member of the Virginia assembly. In 1788 he took a leading part in the Virginia convention convened to discuss the proposed U.S. Constitution. In 1797-98, along with Charles Cotesworth Pinckney and Elbridge, Gerry Marshall was appointed by John Adams to negotiate with France.
He was Secretary of State under President Adams from June 6, 1800 to March 4, 1801. At the same time he was appointed Chief Justice of the Supreme Court in 1801 and served in that position until 1835.
John Marshall was a personal friend of Washington, he announced his death in 1799, organized his funeral, and delivered his eulogy. Washington's relatives soon asked Marshall to write a biography of the late president. "The Life of George Washington" was published in London in 1804-1807. It includes illustrations, portraits, facsimile letters, and folding maps.


Thomas More was a British lawyer, humanist philosopher, writer and statesman.
As the son of a London judge of the Royal High Court, Thomas studied at Oxford and then in London with the best lawyers. More also studied the works of the ancient classics, improved in Greek and Latin languages, composed his works. In 1497 More met and became friends with Erasmus of Rotterdam, became a member of his humanist circle.
In 1510-1518 Thomas More was deputy sheriff of London, and in 1517 entered the service of the king, becoming one of the most effective and trusted civil servants of Henry VIII. He acted as his secretary, interpreter, speech writer, chief diplomat, counselor, and confidant. He was knighted in 1521, became Speaker of the House of Commons in 1523, and in 1525. - Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster. Around 1515. More wrote The History of Richard III, and in 1516 he published his most significant work, Utopia, in which he described an imaginary ideal state.
Thomas More opposed the divorce of King Henry VIII from Catherine of Aragon and refused to recognize the king as the head of the Church of England, as required by the Act of Supremacy in 1534. For his refusal, he was beheaded in the Tower of London in 1535. 400 years later, in 1935 Thomas More was canonized by the Catholic Church, and in 1980 the Church of England recognized him as a "saint and hero of the Christian Church."


Royall Tyler, real name William Clark Tyler, was an American politician, lawyer and judge, playwright, essayist and educator.
He graduated from Harvard University, was admitted to the bar, and in 1801 was appointed a justice of the Vermont Supreme Court. In 1811, Tyler was appointed professor of jurisprudence at the University of Vermont.
Royall Tyler is best known today as the author of the first American comedy, Contrast, which premiered in 1787 at the John Street Theater. This play is the first to feature a Yankee character, a character native and familiar to local audiences, and the forerunner of many such in later years.