Publishers


Platon Petrovich Beketov (Russian: Платон Петрович Бекетов) was a Russian publisher, book printer, historian and collector.
Platon Beketov was born into an old Russian landowning family, from 1798 he lived in Moscow, where he became interested in collecting and in 1801 opened his own printing house, which was considered one of the best in Moscow. Beketov raised the national printing industry to a worthy level. His books were made with great artistic taste and elegance, more than a hundred beautiful editions in all. A number of editions of Russian authors were printed here, among them Vasily Andreyevich Zhukovsky, Alexander Nikolayevich Radishchev, Mikhail Matveyevich Kheraskov and others. The printing house also printed the magazines "Friend of Enlightenment" (1805) and "Inventory of Books Printed at the Dependence of Platon Beketov's Printing House" (1806).
Beketov was passionate about old manuscripts, especially with portrait miniatures and autographs, and portraits of famous contemporaries. He collected an entire picture gallery, which formed the basis of two of his major projects - the publication "Pantheon of Russian Authors" (1801-1802) and the collection "Collection of Portraits of Russians, famous..." (1821-1824). (1821-1824). The texts for them were written by the publisher's friend and distant relative N.M. Karamzin.
Platon Petrovich Beketov was widely known in the circles of the Russian intellectual elite of the first half of the XIX century. In 1811 he was elected chairman of the Moscow Society of Russian History and Antiquities, a position he held until 1823.


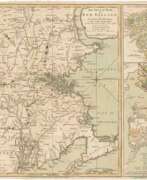
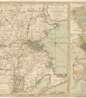
Jan (Joan) Willemsz. Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer, publisher and judge.
Jan was born into the family of the cartographer and publisher Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571-1638). He studied in Leiden, where he earned a doctorate in law, and in Padua. He then began to assist his father, who was engaged in the manufacture of globes and maps. After his father's death, Jan, together with his brother Cornelius, continued his work, and succeeded him as cartographer for the Dutch East India Company.
In 1651 Blaeu was elected to the Amsterdam city council and later appointed as a judge. At the same time, he was engaged in his publishing business: he continued to publish volumes of Atlas novus, which contained maps of English counties and, for the first time, an atlas of Scotland, as well as one volume of maps of the Far East.
Blaeu did not have time to complete his most ambitious project, but it made him famous as the author of the famous 11-volume Dutch atlas. Based on his previous maps, Blaeu created the Great Atlas (Atlas Maior) - it contained nearly 600 maps and a total of 3,000 pages of Latin text - and was published in 1662. Blaeu's maps were groundbreaking for their time because they were created in accordance with the heliocentric theories of Nicolaus Copernicus.
In 1672, a great fire in Amsterdam destroyed Blaeu's workshop, and the cartographer died a year later, apparently never recovering from this stroke of fate.


Willem Janszoon Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer and map publisher.
Willem studied astronomy and cartography under the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe and even discovered the variable star P Swan in 1600. A little later Blaeu settled in Amsterdam, where he began making globes and also began producing land and sea maps, including a 1605 world map. In 1629 he managed to acquire the printing plates of the cartographer Jodok Hondius, with which he published his own atlas.
In 1633, Willem Blaeu was appointed cartographer of the Dutch Republic, as well as the official cartographer of the Dutch East India Company. Blau built up a large collection of maps and conducted an extensive publishing business. After Willem's death, his sons Jan Blaeu (1596-1673) and Cornelius Blaeu successfully continued his work. But in 1672, during a fire in Amsterdam, Blaeu's workshop was destroyed, and the company founded by Willem Blaeu ceased to exist in 1698.


Johann Ludwig Bleuler, sometimes called Louis Bleuler, was a Swiss landscape painter, engraver and publisher.
He studied painting under his father, the painter Johann Heinrich Bleuler the Elder (1758-1823), and his older brother, the painter Johann Heinrich Bleuler the Younger (1787-1857). He traveled extensively in the picturesque Rhine region, painting landscapes and making sketches, and made study trips to Brussels, Amsterdam, and Paris.
In 1824 Bleuler founded his own publishing company in Schaffhausen and from 1827 he worked on a series of engravings of landscapes of the Rhine from its source in the glaciers of the Alps, eventually publishing a complete set of engravings by about 1843. All of the aquatints were hand-colored using the gouache technique, giving them the appearance of the work of old masters.


Désiré-Magloire Bourneville was a French physician, neurologist, innovator and educator, and statesman.
Born into a modest family, Bourneville began his medical education in 1860 and for about ten years worked as an assistant to Jean-Martin Charcot, where, together with Paul Régnard, he supervised the publication of "Photographic Iconography of Salpetriere". During the Franco-Prussian War, he served as both surgeon and physician's assistant. Appointed physician at Bissetre, Borneville devoted himself to the medical and educational care of "idiots and epileptics" for whom he organized a service, and later directed the Fondation Vallée in Gentilly until his death. He is considered one of the earliest child psychiatrists.
In 1876, Bourneville was elected a municipal councilor of Paris, three years later he became a general councilor of the Seine, and then a deputy. In this capacity, Bourneville carried out several health reforms: he became the rapporteur for the public assistance budget and the budget for psychiatric asylums, achieved the creation of the first special classes for mentally retarded children, and the first municipal nursing school in Salpêtrière.
Bourneville had many very different talents. Very early on he became interested in medical journalism, where he made a name for himself through the vividness of his articles. In 1873, he founded the journal Progrès Médical, which promoted the tenets of avant-garde medicine, open to pioneering scientific developments (Bourneville published Charcot's lessons) and social issues. He fully developed the theoretical and practical foundations of teaching for the nursing profession. Outraged by the lack of practitioners' professional knowledge of obstetrics, he worked to create a new medical specialty, gynecology. But his main purpose in life was to educate and nurture those who were labeled "idiots" and mentally retarded.
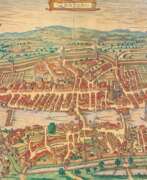

Georg Braun was a German topographical geographer, cartographer and publisher.
Braun was the editor-in-chief of the Civitates orbis terrarum, a groundbreaking atlas of cities, one of the major cartographic achievements of the 16th century. It was the first comprehensive and detailed atlas, with plans of the world's famous cities and bird's-eye views, and became one of the best-selling works of the time.
The book was prepared by Georg Braun in collaboration with the Flemish engraver and cartographer Frans Hoogenberg. Braun, as editor-in-chief, acquired tables, hired artists, and wrote the texts. They drew on existing maps as well as maps based on drawings by the Antwerp artist Joris Hofnagel and his son Jacob. Other authors include Pieter Bruegel the Elder (c. 1525-1569), Jacob van Deventer (c. 1505-1575), and more than a hundred other artists and engravers.


Vincent Brooks, full name Vincent Robert Alfred Brooks, was a British etcher, lithographer and publisher.
Brooks began working for Day & Son, and in 1862 founded his own firm called Vincent Brooks, Day & Sons. He worked for the Arundel Society from 1856 to 1897. Brooks was for many years London's leading lithographer, with many important commissions printed in his publishing house.


William Cullen Bryant is an American poet, journalist, and editor-in-chief of the New York Post.
He began his education at Williams College, then studied law and worked as a lawyer, but a very different fate awaited him. In 1825, he moved to New York City and became co-editor of the New York Review. In 1827 he became editor of the New York Evening Post, and in 1829 he became its editor-in-chief and co-owner.
Bryant remained in this position until his death, for 50 years. He made the Post a voice for free trade, workers' rights, free speech, and abolition of the death penalty, and he was a founding member of the Republican Party.
Bryant wrote poetry from his early youth and announced himself by publishing a book of Poems (1821). His main theme was nature, and his best-known poems are "Thanatopsis" and "To a Waterfowl." In later years he devoted much time to translations and was an active patron of art and literature.