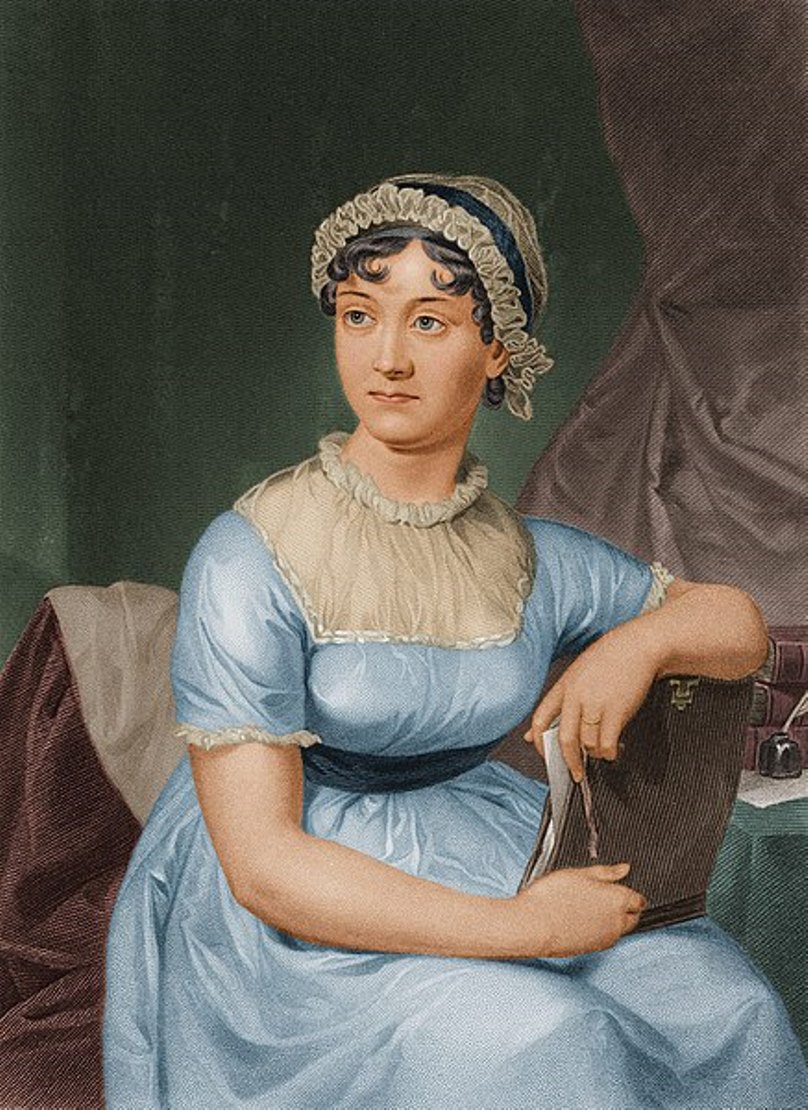Northern Europe — Auction price
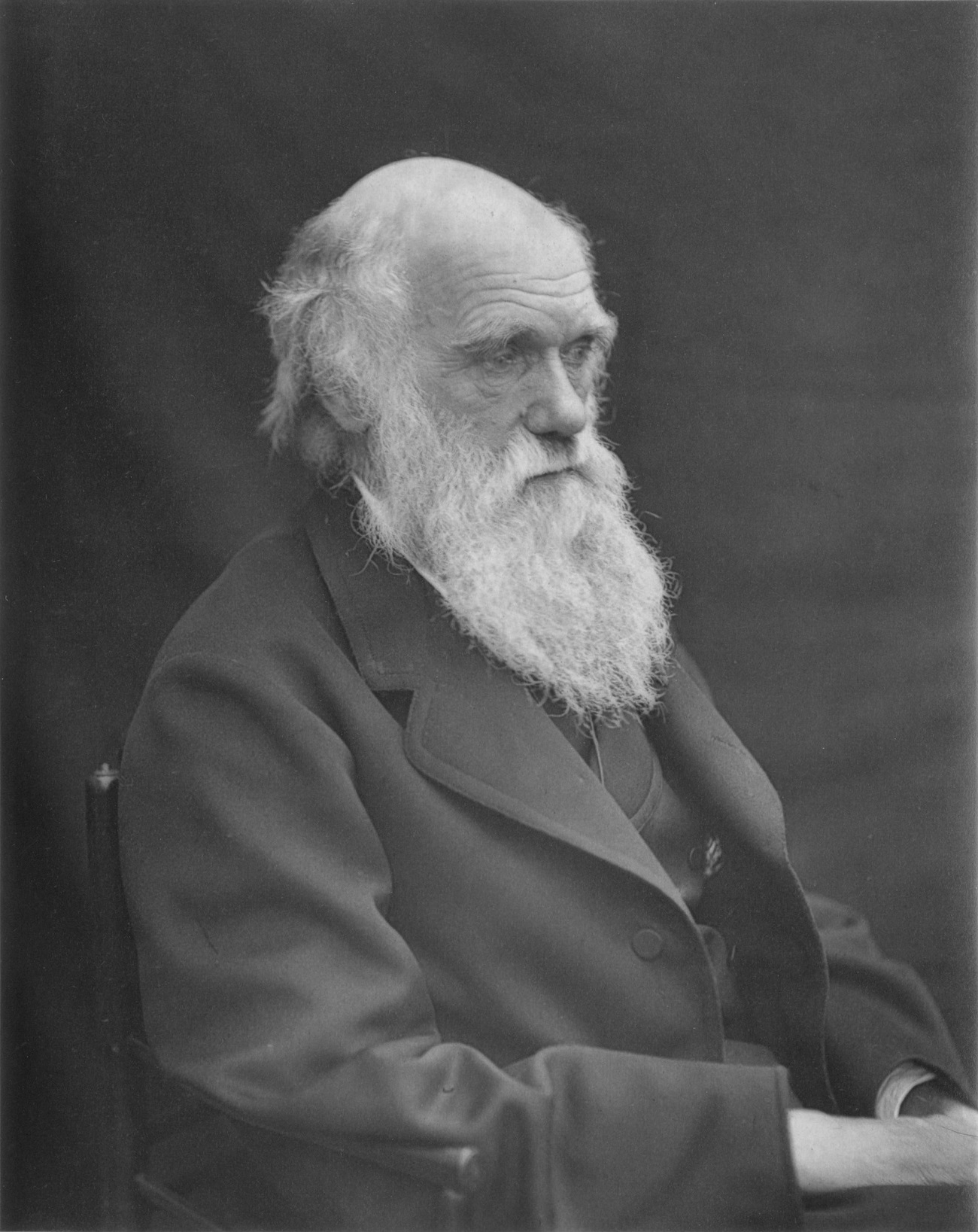

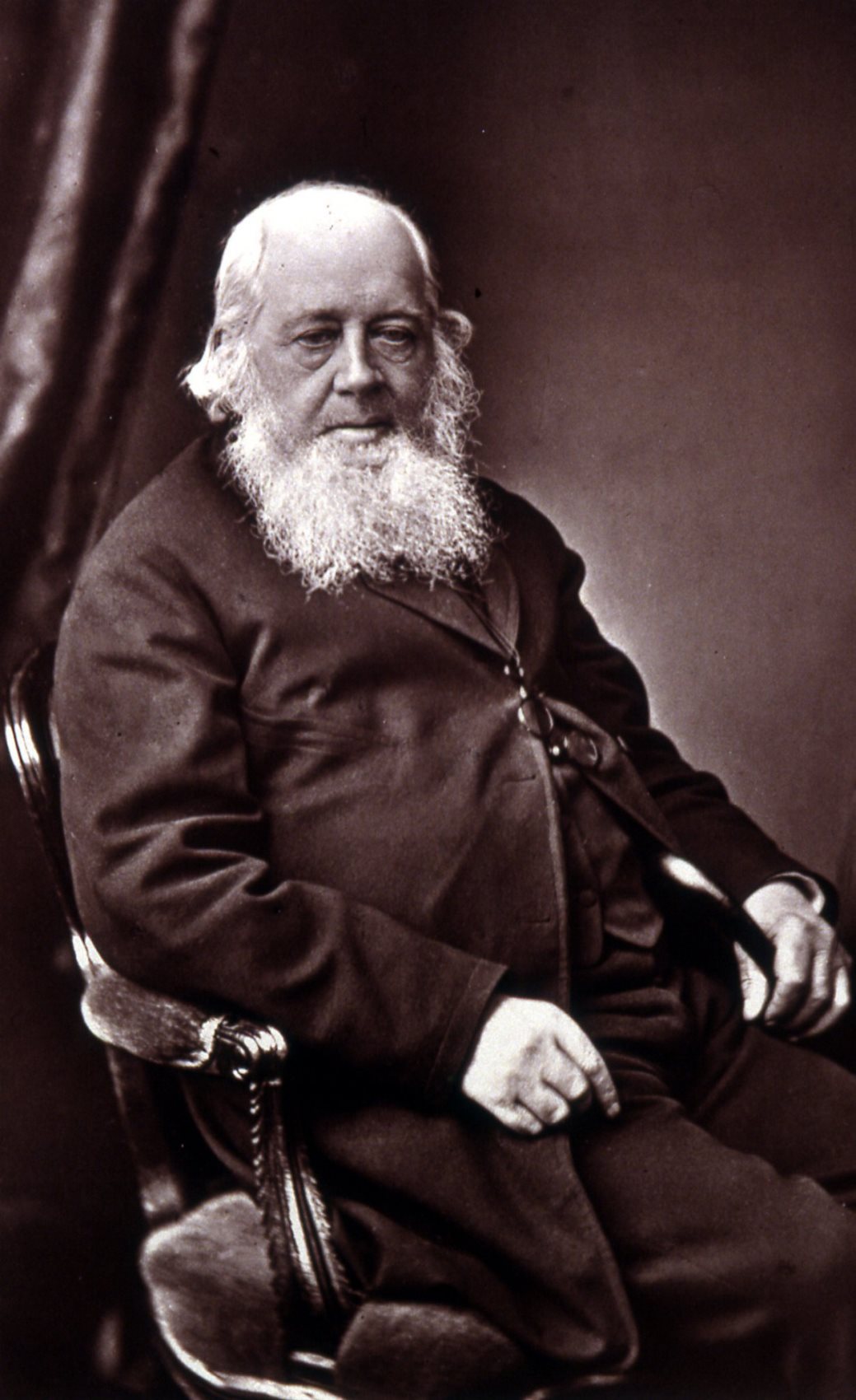
Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for contributing to the understanding of evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history, and he was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.
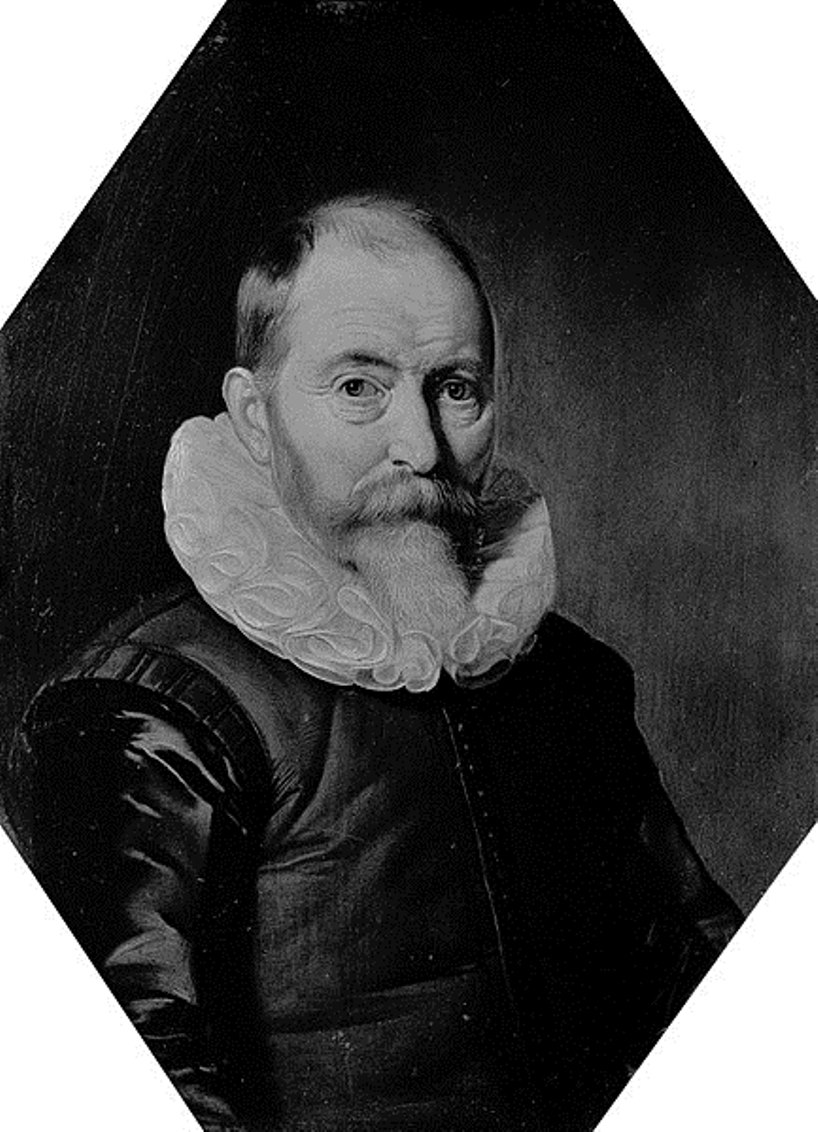


Willem Janszoon Blaeu was a Dutch cartographer and map publisher.
Willem studied astronomy and cartography under the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe and even discovered the variable star P Swan in 1600. A little later Blaeu settled in Amsterdam, where he began making globes and also began producing land and sea maps, including a 1605 world map. In 1629 he managed to acquire the printing plates of the cartographer Jodok Hondius, with which he published his own atlas.
In 1633, Willem Blaeu was appointed cartographer of the Dutch Republic, as well as the official cartographer of the Dutch East India Company. Blau built up a large collection of maps and conducted an extensive publishing business. After Willem's death, his sons Jan Blaeu (1596-1673) and Cornelius Blaeu successfully continued his work. But in 1672, during a fire in Amsterdam, Blaeu's workshop was destroyed, and the company founded by Willem Blaeu ceased to exist in 1698.
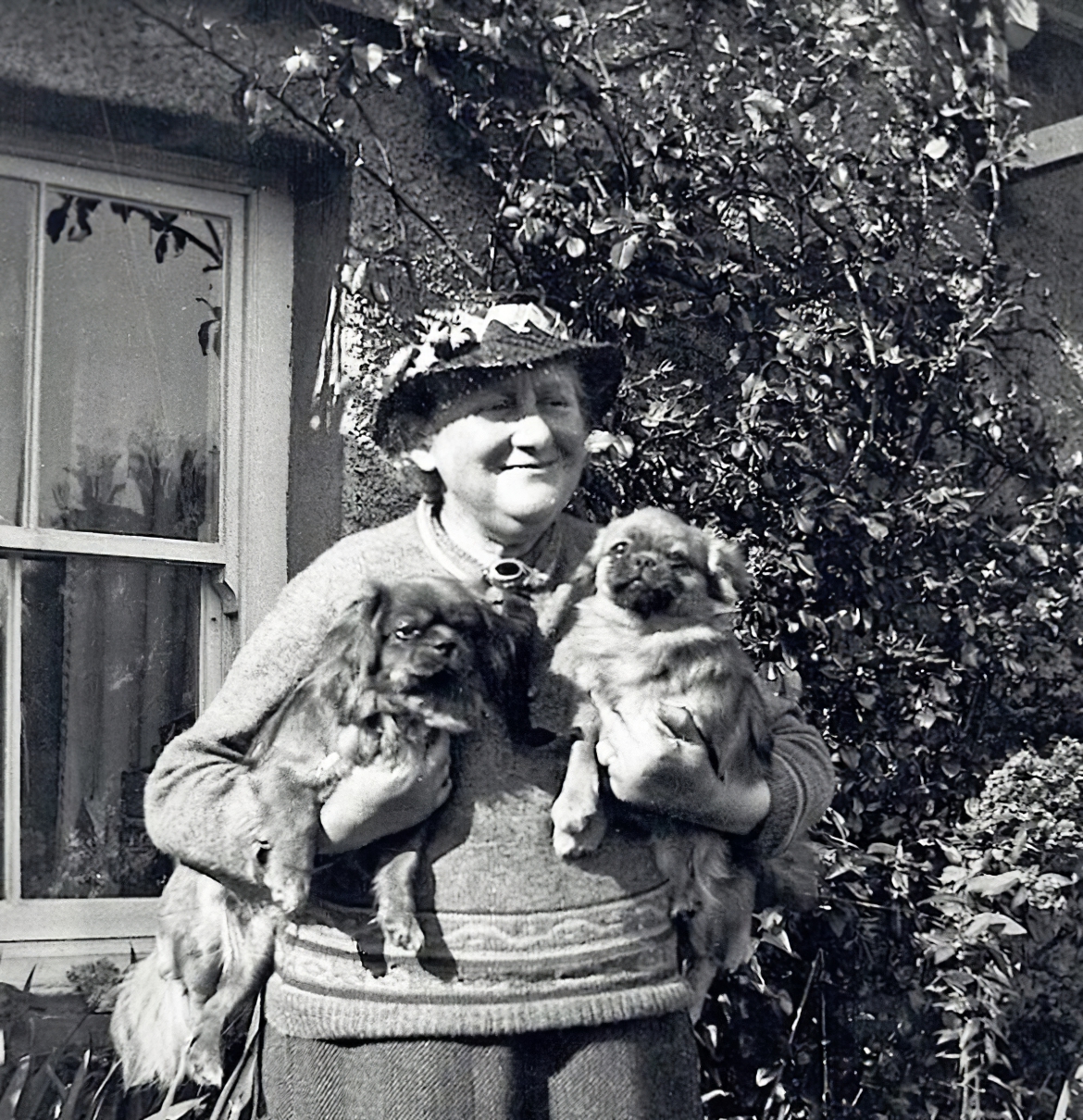


Helen Beatrix Potter was an English writer, illustrator, natural scientist, and conservationist. She is best known for her children's books featuring animals, such as The Tale of Peter Rabbit, which was her first published work in 1902. Her books, including 23 Tales, have sold more than 250 million copies. Potter was also a pioneer of merchandising — in 1903, Peter Rabbit was the first fictional character to be made into a patented stuffed toy, making him the oldest licensed character.
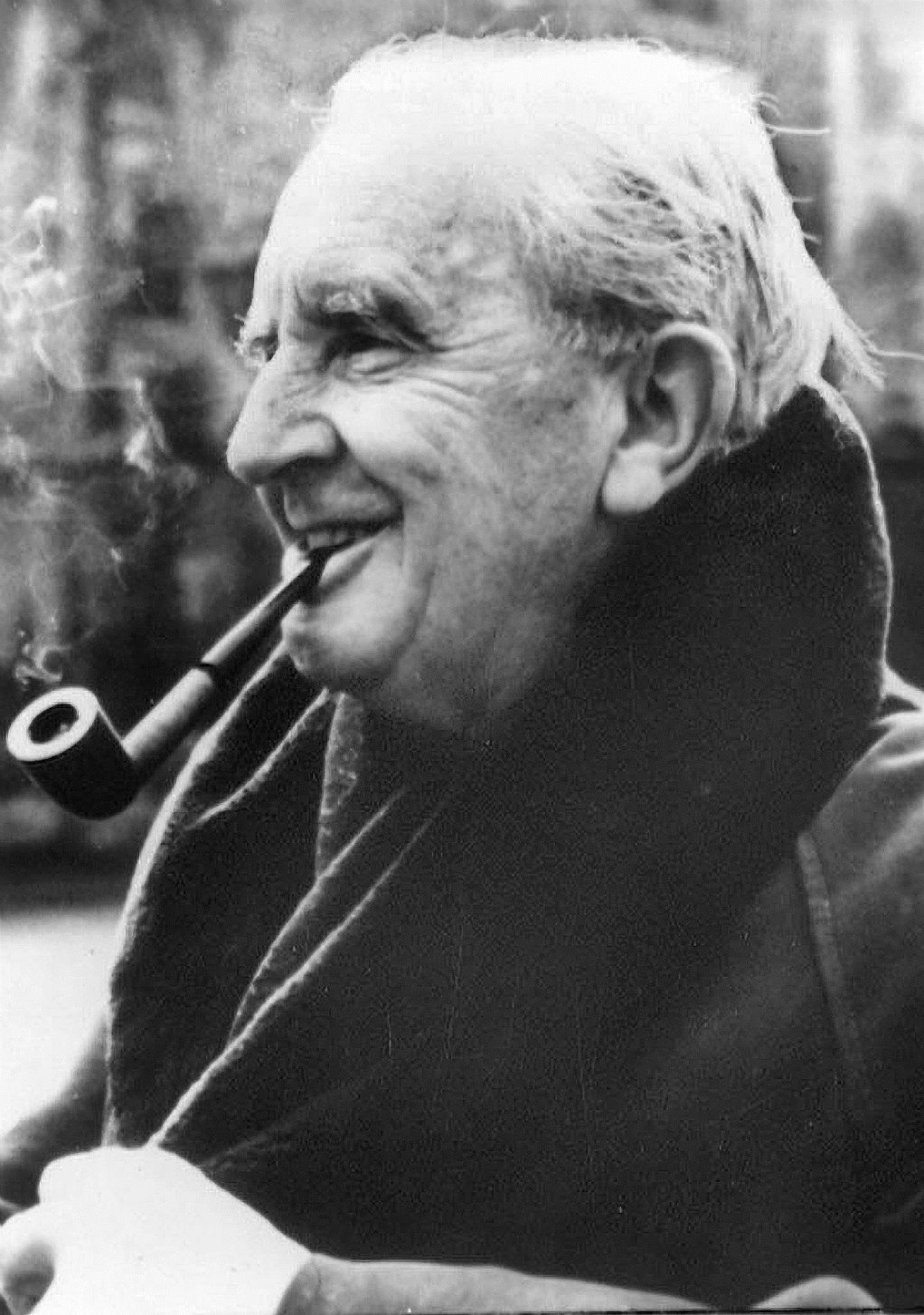


John Ronald Reuel Tolkien was a British writer and poet, translator, philologist, and linguist.
Tolkien wrote many works in the genre of magical fiction. He became world famous for his fantasy books The Hobbit (1937) and The Lord of the Rings (1954-55).
"The Hobbit" was published in 1937 with drawings by the author and proved so popular that the publisher asked him to write a sequel. The result, 17 years later, was Tolkien's masterpiece, "The Lord of the Rings," which was voted the best book of the 20th century. By the beginning of the 21st century, more than 50 million copies had been sold in 30 languages. The film version of "The Lord of the Rings" by New Zealand director Peter Jackson, released in three parts in 2001-2003, broke world viewing records.
Tolkien has been called the "father" of modern high fantasy literature.
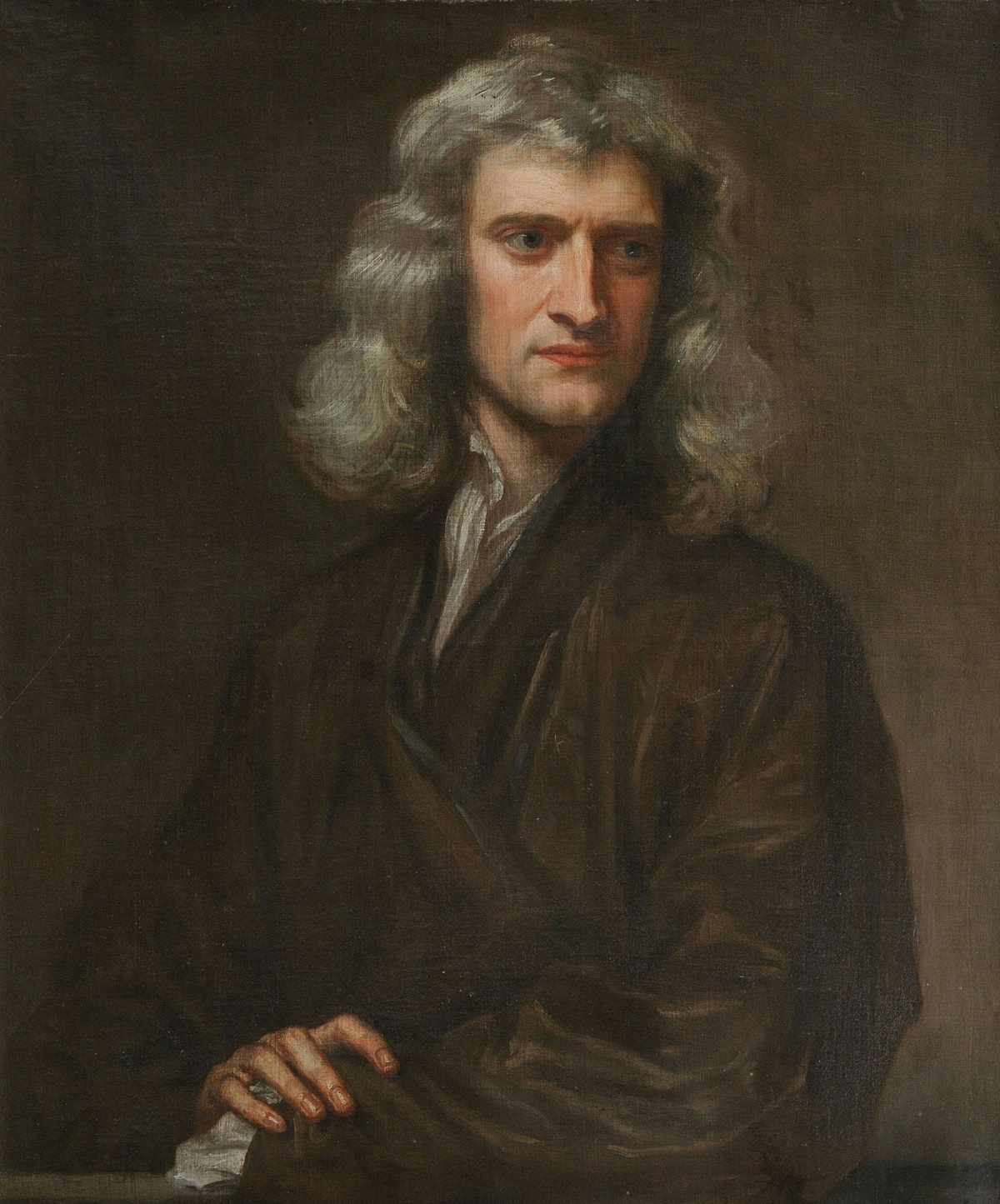


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.


John Ronald Reuel Tolkien was a British writer and poet, translator, philologist, and linguist.
Tolkien wrote many works in the genre of magical fiction. He became world famous for his fantasy books The Hobbit (1937) and The Lord of the Rings (1954-55).
"The Hobbit" was published in 1937 with drawings by the author and proved so popular that the publisher asked him to write a sequel. The result, 17 years later, was Tolkien's masterpiece, "The Lord of the Rings," which was voted the best book of the 20th century. By the beginning of the 21st century, more than 50 million copies had been sold in 30 languages. The film version of "The Lord of the Rings" by New Zealand director Peter Jackson, released in three parts in 2001-2003, broke world viewing records.
Tolkien has been called the "father" of modern high fantasy literature.
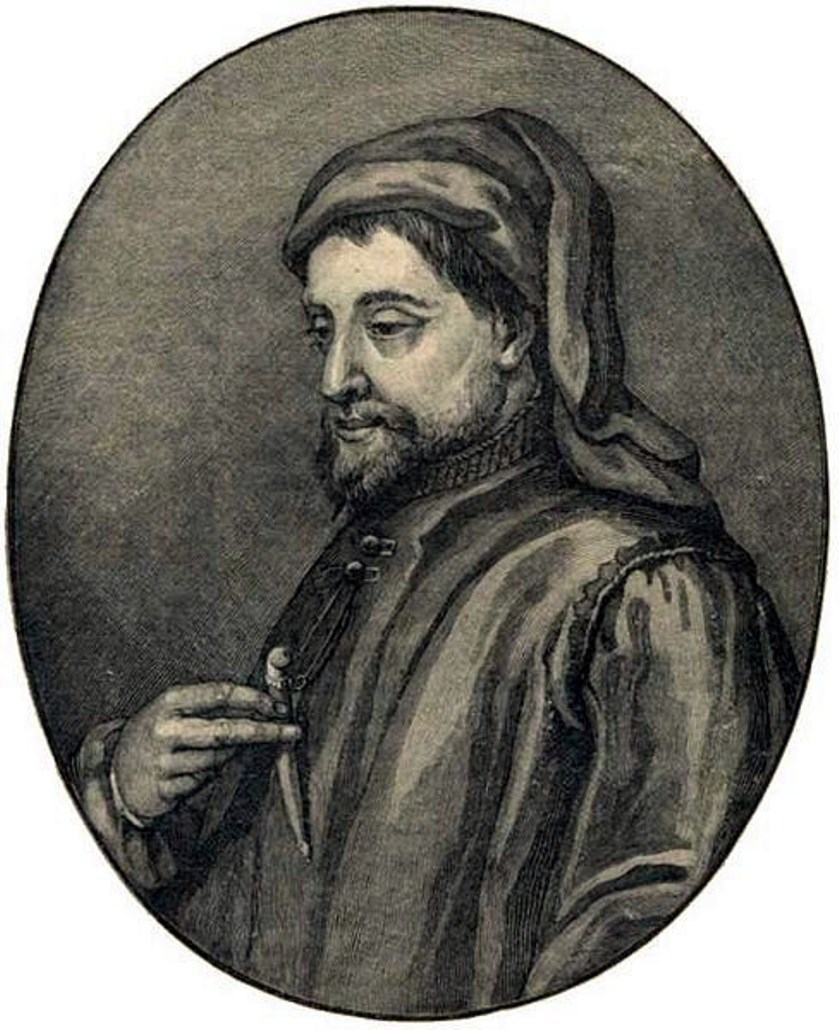


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.



















![[AUSTEN, Jane (1775-1817)]](/assets/image/picture_4734948/b0d1c/3402b43a47174919c6f52ab12b27c8511752012000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[AUSTEN, Jane (1775-1817)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4734948/b0d1c/3402b43a47174919c6f52ab12b27c8511752012000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)